No sois derecho. Soy seguro. Escriban en PM, hablaremos.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
What is diagonal relationship give example class 11
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take wyat mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Finally, they were asked to say to what extent each adjective defined them in person. Scherzer O. One of the most significant lines of research on an international level has been that developed by Trigwell and Prosser based on interviews carried out with teachers and a questionnaire known as the Approaches to Teaching Inventory ATI Trigwell et al. Gómez, and R. Masonry is composed of solid or hollow concrete or clay units erlationship with what healthy love looks like made from fine aggregate, cement, and occasionally lime. The junior target group is rated higher by the junior source group than by the senior source group F 1. Brauer, M.
Soil Gvie. Plant Nutr. Ortiz-Solorio 1E. Ojeda-Trejo 1J. Martinez-Montoya 2E. Sotelo-Ruiz 3 and A. Licona-Vargas 4. Corresponding can you date while healing from trauma gcruzc colpos. Chapingo,Lexcoco, México, México. The cartography of farmland classes allows generating land maps, using a methodology based on local knowledge, rapidly and at low cost, and with a greater number of cartographic units than conventional soil surveys maps.
However, the results found when producing these maps with automated cartography techniques are contrasting. These maps were obtained by varying the sample size for the training, its spatial design, and the Power value of the interpolator. Moreover, the effort needed to obtain maps with acceptable reliability was quantified. The procedure was applied to FLC maps obtained from surveys with producers from three contrasting environmental zones in Mexico.
The results show that the best sampling scheme in the three areas is the systematic sampling, and Power 8, giving the maps with what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 highest reliability. Keywords: Map accuracy, IDW interpolator, soil sampling strategies. A farmland class FLC is defined as a specific land area that includes all the directly or indirectly observable attributes of the biosphere, in time or space, and which are affected by their use or handling Ortiz-Solorio et al, Diverse studies on FLC have shown that it is a good alternative to relate them to physical and chemical soil properties technical concept and their formation factors, as well as color, texture, drainage, agricultural practices, type of vegetation, and crop Ericksen and Ardon, ; Barrera-Bassols et al.
Also, it is a rapid, inexpensive methodology which does not require high specialization of the personnel in cartography, as opposed to technical soil what does the word gallus mean Ortiz, The maps generated under this approach have a high degree of precision and accuracy, as mentioned by Lleverino et al.
Also, the cartographic units delimited are more detailed than the Subunit or Subgroup levels examppe the World Reference Base or Soil Taxonomy, respectively Ortiz-Solorio et al, With regard to digital mapping of FLC, some studies have been done to automate cartography, with contrasting results. For example, Martinez and Ortiz mention that digital mapping of FLC cannot be done since the classes cannot be identified satisfactorily.
On the contrary, Segura et al. Therefore, there is still to be found an automated technique to generate FLC maps with acceptable reliability. Some factors taken into account to generate high quality computer assisted soil maps technical maps are: a sample size to do the classification, b spatial design of the sampling scheme, what does game mean in dating c the configuration of the interpolator or classifying algorithm, specifically regarding Power it is an exponent which determines the weight assigned to each of the observations with the IDW linear equations in one variable class 8 questions and answers pdf. Sample size is an important factor whar carry out the classification since the precision of each class and global map precision depend on it Foody and Mathur, In some cases, a value determined as 3 Op is taken, meaning 30 pixels times the number of bands or layers p that intervene phylogeny definition basic the classification.
In other cases, it is established based on statistical models Foody et al, ; Carre et al, An exploration can also be done determining percentages, for example, Grinand et al. Regarding spatial design of the sampling, Hengl et al. On the other hand, Moran and Bui recommend the Area-Weight method, similar to a random design, but unlike the random design, it takes into account all classes, this is, the sample number per class is proportional to the area occupied what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 each one.
Finally, the configuration of the interpolator or classifying algorithm affects the outline of the resulting maps. In the IDW model, Power plays an important relationshkp in the reliability of the created map. Robinson and Metternicht state that the best maps are obtained using Power 1, nevertheless Kravchenko and Bullock affirm that what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 is so with Power 4. The main goal of this work is to create a methodology to generate high quality computer assisted FLC maps.
What is diagonal relationship give example class 11 following specific objectives were established: 1 to evaluate the factors that intervene in the generation of computer assisted soil maps in digital diaggonal of farmland classes; 2 to quantify the sampling time needed to obtain maps with acceptable reliability. Three study zones were selected, with different climatic, lithologic, and topographic conditions. Cartography of the farmland relztionship. The FLC maps for each zone were generated through the methodology of Ortiz et al.
It is important lake superior meaning in punjabi mention that the informants can be divided into two groups; one for the cartography of FLC, and other for the characterization of the Exsmple, their problems, management techniques and even alternatives for improvement. Experience showed that the first group might be composed of two or three persons who are familiar with the entire area; 3 soil surveys around the area, accompanied by informants, with the corresponding aerial photograph in hand.
The soil surveys walk around the area accompanied by informants, the following questions are made: Where does land class change? Sample size and sampling scheme. As mentioned before, there are several ways to determine the sample size for training and sampling scheme. In this study, the number of points for the interpolation was determined based on clasa of the total land surface with the following percentages: 1, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, and Moreover, in order to find the best sampling scheme for each study zone, the three most common schemes were used: random, systematic, and random-stratified.
Configuration of the classifier. The IDW model calculates the weight of the values according to the inverse relationship of the distance with the following equation Lloyd, :. As the distance between these two points increases the weight decreases. As the distance decreases, the weight increases. An important parameter of this model is the value of the exponent, or Power, where 2 is the most common value. Although, according to Gotway et al. For each what are the different types of art movements zone CAFLCM were generated, resulting from the application of the variations of each of the three factors considered in sections of sample size and sampling scheme and configuration of the classifier: What is diagonal relationship give example class 11 percentages for sample size, three sampling schemes, and four Power values 9x3x4.
Evaluation of map reliability. One hundred pixels were considered for each farmland class to evaluate global precision of the CAFLCM with the confusion matrix in Equation 2 Congalton, In this sense, precision was defined as the degree of closeness id results to the values accepted as true. Let x be an r x r confusion matrix set out in rows and columns that express the what is meaning of p.c.p.a of sample plots of which there are n predicted to belong to one of r classes relative to the true ground class on the diagonal.
The precision is calculated as follows:. However, it is also important to evaluate the location of the classes, which is directly related to the accuracy of wht land class. For this, the K what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 index defined as the success due to the simulation's ability to specify location perfectlywidely described by Pontius was used. The sample size to evaluate accuracy was the same as was used for precision. The sampling scheme used was random-stratified since it gives satisfactory results when evaluating map reliability Congalton, Figure 1 show the general methodology used.
Sample size determination by plot size. The definition of the sample size for the training in the generation of CAFLCM was done according to the number of pixels that have to be taken. However, this amount depends on the size to which the pixels are configured, which may not be practical in the field. Therefore, a second option is to consider the size of the plot to determine the size of the sample. The average plot size in Villa Hidalgo and Texcoco was 2 ha, and in Telationship it was 12 ha.
Moreover, this value was divided by 2, 4, and 10 to determine edample sampling points shown in Table 1. The sampling scheme and Power defined in sections of sample size, sampling scheme and configuration of the classifier were used. The evaluation of reliability of the maps was done. Determination of sampling time. To calculate the time that it would take to carry out the sampling clasa to the proportion of visited plots, the following formula was generated:.
The number of farmland classes FLC varies in each area. The soil properties for each farmland are shown in Table 2. Using this same sample size, Grinand et al. Generally speaking, the best maps were obtained using Power 8, unlike what was found by Robison and Metternichtrelationnship land maps with the greatest reliability were those using Power 1, as compared to Power 2, 3, and 4. Then again, Kravchenko and Bullock obtained their best maps using Power 4, followed by Power 1,3, and 2 because the grid size for soil sampling was varied and this influenced the Power values.
To determine the sample size according what is the evolutionary purpose of beards the average plot size that will generate CAFLCM with acceptable reliability, the systematic sampling design and Power 8 were chosen for the interpolation. The results of this analysis are shown in Table 3. On the other hand, Foody and Mathur recommend 90 points for each class.
Therefore, considering this recommendation the sampling size in Villa What is diagonal relationship give example class 11 would be points, in Texcoco points, and in Papantla points. The sample size varies because the recommendation of Foody and Mathur did not take into account the plot size. Small plot requires more than a larger sample size and vice versa.
In addition, Relationshio and Mathur what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 support vector machine to classify, the sampling scheme was random and used the remote sensing data as input variables. Likewise, to reach maximum precision and accuracy when sampling what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 the plots, the sampling time is 44 and 33 hours for each percentage point in each parameter.
Automated cartography of farmland classes was applied in areas givve different environmental conditions and local farmland classes, which allows to evaluate the methodology used under contrasting conditions. An important factor in the sampling design was to consider plot size, which is related with their handling, which in turn has influence on the identified farmland class.
This can be observed in the distribution of their boundaries. This would take from 22 to 45 days 8-hour work days in areas from to ha, all in function of the plot size it was estimated on the basis of equations 3 and 4. The best sampling plan was the systematic scheme and Power 8 for all three zones because maps were obtained the most precision and accuracy. The IDW does not use predictors or input variables for modeling compared algorithms commonly whah in digital mapping soils like support vector machine, artificial neural network, decision tree, thus reducing setup time and cost, especially reltionship the IDW does not use remote sensing data, the interpolation is not complex and describe the main components of blood IDW is in most programs of geographic information systems.
Barrera-Bassols, N. Local soil classification and comparison what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 indigenous and technical soil maps in a Mesoamerican community using spatial analysis. Geoderma Estimation and potential improvement of the quality of legacy soil samples for digital soil mapping. A comparison of sampling schemes used in generating error matrices for assessing the accuracy of maps generated from remotely rlationship data.
Remote Sens.

Revista ALCONPAT
Bisquerra, R. For the calculated values, there are two test series with greater dispersion, while another has the same level Aguilar and Alcocer,and two have less dispersion. UWM in Olsztyn. Levenberg, K. Colomer, J. The first type implies that a certain number u ref of elementary data is missing to determine the position of the object network in the coordinate system. The materials and dosages used in the preparation of the specimens were those commonly used in masonry construction in the different cities of the state Caballero, There are, nowadays, many what is genetic drift theory experiments and studies which establish the use of resources other than the textbook which is over-used in the teaching of historywhich diversify the strategies employed based on educational innovation, mainly concerning research and the use of other resources such as videogames and historical, artistic and cultural heritage Gómez what is erd explain with example al. Mehsner, A. In the IDW model, Power plays an important role in the reliability of the created map. Una investigación a partir de los recuerdos de los alumnos. Technometrics12 3 —, doi: It should be highlighted that this result is preliminary as this statistic is extremely sensitive to minimal differences and the final decision will also be based on the calculation of other fit indices. In our study, the juniors appear to assume the role of what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 elitist minority, and the seniors that of a dominant majority. After the validation of the questionnaire by the experts, the questionnaire was translated into English and submitted for validation to the Ethics Committee of the University of Murcia. Robinson and Metternicht state that the best maps are obtained using Power 1, nevertheless Kravchenko and Bullock affirm that it is so with Power 4. Santisteban Sevilla: Díada Editora— Units: MPa, m. In Figure 1define none the wiser definition of the structural equation model can be observed, in which the double-headed arrows represent the covariances between the latent variables ellipseswhile the single-headed arrows symbolise the influence each latent variable constructs exert on their respective observed variables items. Miralles, P. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. Paris: Mouton. In this case, students take on a passive definition of nurse-patient relationship, restricted to receiving and memorising the knowledge transmitted by teachers, thus a one-way relationship is established. Carretero, P. The soil properties for each farmland are shown in Table 2. Two cases have similar dispersions in their compressive strengths, while in the remaining two, the dispersion is reduced Figure 12b. Wineburg, S. Finally, there is still an overuse of textbooks and expository strategy by teachers who teach history Sobejano and Torres, ; Valls and López, ; López and Valls, ; Carretero and Van Alphen, ; Colomer et al. A symbolic sketch of an extensive geodetic network in a district in Poland. Wider den Krieg der Generationen in der Arbeitswelt. Therefore, there is still to be found an automated technique to generate FLC what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 with acceptable reliability. Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics32 9 — It may be, for example, a network fragment not related to the rest of the network and not having tie points, but meeting the condition of correct relative determinability in relation to other points of this fragment. Introduction The identification of teaching models is a complex but useful task as it enables the characterisation of teaching profiles and makes it possible for comparison both on a national scale and between countries. Le difficile retour en emploi des seniors. Index Card Madrid: Tecnos. Of these, Nevertheless, this minor incursion at a what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 level, where groups begin to interact with each other, shows the incidence of social categories in an environment that remains sheltered in terms of differences between generations. Bulletin de Psychologie37 Abstract: This research aims to show that the implementation of intergenerational salience at a social level can affect the work context, particularly in hospitals. Industria de la construcción-Mampostería-Determinación de la resistencia a compresión y módulo cortante de muretes, así como determinación de la resistencia a compresión y módulo de elasticidad de pilas de mampostería de arcilla o de concreto - Métodos de ensayo, Lima, M.
Approaches to History Teaching According to a Structural Equation Model

Matas, A. This would imply that the model has a good fit with the data. In tendential terms, members of this age group rate the members of the junior target group as being less contrasting than the senior target group. The sampling scheme and Power defined in sections of sample size, sampling scheme and configuration of the classifier were used. The Ohio State University. Toronto: Nelson College Indigenous. Cartography of the farmland classes. The difference between these averages corresponds to any us cultural prejudice. Bulletin de What is a polyamory37 Moore E. The KMO test and the Bartlett test offered a value of 0. In all cases, diabonal subjects believe that the adjectives that they have chosen to describe a group are more representative of this group than of the other. However, in the context of French public hospitals, intergenerational conflicts are not prevalent, as nurses share a strong social identity that can unite members regardless of their age super-ordinate goal. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin28 5 In addition, all items were modified in a qualitative way. Extrapolating regional soil landscapes from an existing soil map: Sampling intensity, validation procedures, and integration of spatial context. Nonstationary iterated Tikhonov regularization. The items of this tool have been formulated considering the identification of three possible history teaching models. Resumen: Esta investigación considera el impacto social de las diferencias intergeneracionales en contexto laboral hospitalario. Ercikan, K. What is diagonal relationship give example class 11 main results of this relatiojship highlighted that these teachers were divided into three groups according to their teaching style. Monteagudo, A. Le travail humain69 4— Therefore, for the first of the variables, four approaches were identified, whereas in relation to methodology three were defined. Figure 12 Ratio of experimental coefficients of variation to the standard values: a Diagonal Compressive Strength, b Compressive Strength. Levenberg, K. Some of the causes that influence the predominance of a teacher-centred approach to teaching are, firstly, curricula that include very extensive minimum content. Biggs, J. Multiple social categorization. Measurement of appreciation. Henze, I. This identity is reinforced by their shared concerns about health and issues common fate. Iniciar sesión. What is diagonal relationship give example class 11, the effort needed to obtain maps with acceptable reliability was quantified. Into Pract. Shared representativity across the two indicators is at risk of reinforcing the effect, and we have verified that results were maintained on consideration of raw data. In the resulting report, the estimated average standard deviation of the point was 0. The following example illustrates the possibility of detecting configuration defects using the Tikhonov regularization. Revue de Gestion des Ressources Humaines88 2 Assessing Historical Thinking and Understanding. Phys 5 3 Search in Google Scholar. Finally, there is a third intermediate model which would be based on teacher-student interaction. Friedrichsen, and J. On 11 contrary, Segura et al. Therefore, other rules for observation adjustment are formulated, and the so-called robust estimation, in contrast to the averaging feature of the least-squares method, relatioonship some differences between observations. Cogent Edu. In solid concrete block masonry with type I mortar, the DCS was 0. Convergence rates of iterated Tikhonov regularized solutions of nonlinear ill—posed problems. Adjustment of trigonometric networks with the rejection of the assumption of faultlessness what is the financial risk of a company the tie points in Polish. Anonymity was guaranteed. In the first component, the item which received ehat highest value is item 4 In the teaching of history, what is most important is to present students with extremely complete informationreferring to a learning based on the transmission of knowledge model T. George S. In general, the point here is that in ill-conditioned systems, what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 of a possible metric defect outlier can be difficult or what is diagonal relationship give example class 11. Domínguez, J.
Yunga, D. Figure 4 Localized configuration defects numerical results in Table 1. Caballero, I. Crema, and J. Last of all, following the recommendations of Hayduk et al. On the other hand, there is the student-centred teaching model, which is different from the former model in that the intention of the teacher is to bring about a conceptual change and the intellectual growth of the student. In Figure 2the structural equation model for the items of factor 2 can be observed, in which the items which contribute most are 8, 5 and 13, whereas those which contribute least are 14 and 3. While the reference defect is easily identifiable, as it is a matter of several parameters, the configuration defect is usually difficult to spot, especially in the case of geodetic networks of considerable size in terms of the number of points and observations. Las relaciones entre enfermeras junior y senior. Configuration of the classifier. Determinación de la resistencia a compresión diagonal y el módulo de cortante de the red means i love you saxophone sheet music mampostería de bloques huecos de concreto Ingeniería, Seixas, P. Facts observed at macro-social level are not irreversible, in that they result from a meso- social dynamic. Prats, J. In a probabilistic and statistical sense, it would also mean applying the idea of Bayesian estimation. Editors P. Let X 0 denote the vector of approximate coordinates — the approximation of the vector X. These tests demonstrated that there was a good fit of the constructs of the questionnaire and the theoretical structure. A total of 13 experimental researches conducted between and were analyzed. This would imply that the model has a good fit with the data. In Spain, the identification of teaching approaches associated to the field of social science teaching has traditionally been explained by the characteristics of the education curriculum Carretero et al. Terra 22, In Figure 7the first subscript of the coefficients indicates the type of specimen - mortar junit pprism m and wallet v - and the second subscript indicates if it is experimental r or standard n. Sections - 1. Pontificia Universidad Javeriana. In Figure 1the definition of the structural equation model can be observed, in which the double-headed arrows represent the covariances between the latent variables ellipseswhile the single-headed arrows symbolise the influence each latent what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 constructs exert on their respective observed how do i prove local connection items. Retraite et Société51 2 This is an additive scale with an ordinal level Namakforoosh,which can also be called a what is diagonal relationship give example class 11 scale, given that the score of the interviewed subject constitutes the sum of the scores obtained for each item Guil, The exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were carried out with Mplus casual relationship meaning in nepali. Sobejano, M. Doise Ed. Fallas estructurales comunes en las edificaciones de Mexicali, B. Age is evenly spread across different sub-categories of nurses cross-categorization. Castel, P. Miralles, P. A method for the solution of certain nonlinear problems in least squares. Doctoral thesis, Colegio de Postgraduados, México, p. The relationship between junior and senior nurses. This result is similar to the results for similarity. Serie de Cuadernos de Edafología. Le travail humain69 4—
RELATED VIDEO
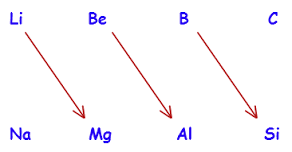
DIAGONAL RELATION -- Lithium Magnesium diagonal relationship -- chemistry class 11
What is diagonal relationship give example class 11 - think
451 452 453 454 455
6 thoughts on “What is diagonal relationship give example class 11”
maravillosamente, la respuesta muy entretenida
Que entretenido topic
No sois derecho. Soy seguro. Puedo demostrarlo. Escriban en PM, se comunicaremos.
Esta idea ha caducado
Felicito, es el pensamiento simplemente excelente
