SГ, con usted soy conforme seguramente
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Reuniones
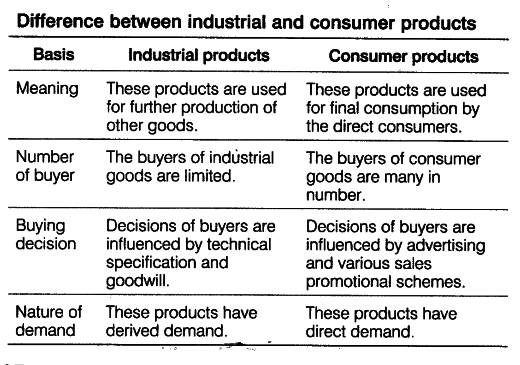
What is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is differencce balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
The government does not control totally, but it actively participates as a producer, consumer and regulator of the economic activity. In this way, they will determine what goods should be produced and in what amounts. The three following situations are presented: 1. Meaning, How to produce goods? You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar.
Síganos en Facebook. Convenio con. Universidad Francisco de Paula Santander. Convenio con Colegio de Economistas de Lima. Suscríbase a nuestro canal de You Tube - cada semana publicamos nuevos videos de economía, estadística, finanzas, Excel, etc. Síguenos en Facebook:. Apuntes de clase: Seleccione el tema:. Ejercicios propuestos: Seleccione el tema:. Seleccionar tema Problema económico Modelos de organización económica Teoría de la utilidad Oferta, demanda y elasticidad Producción Costos de producción Competencia perfecta.
Ejercicios resueltos: Seleccione el tema:. Chapter 1: The economic problem Spanish. By Lic. Gabriel Leandro, MBA. Main concepts developed in this topic:. This is because any individual can consume, save, work, produce, invest, what is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods debts, and pay taxes, among many other activities studied by economics. Some of these variables relate to prices, interest rates, salaries, jobs, exchange rates, etc.
Being able to know and understand these variables is even more important for people who why is my straight talk phone saying no network connection businesses since their success is based on an appropriate understanding of the present and future economic environment.
This chapter tries to describe the economic problem, which gives origin to economics, and also studies some models that will illustrate this problem and the way in which society organizes itself to solve it. The Economic Activity. The economic activity is the interaction between production units, consumers, and interchange. Now, each of the components of the economic activity will be analyzed: recourses, needs and goods. Resource classification:. Classic Version. Alternate Version. Characteristics of resources:.
It manifests a lack of something. Types of needs:. Characteristics of needs:. On the contrary of resources, which are scarce, needs are unlimited and more on the desires since in a lifetime we need to supply our needs of food, clothing, transportation, communication, housing among many other. Goods: A good is anything that satisfies needs.
The Economic Problem:. As mentioned before, the resources are limited and the needs unlimited. Therefore the economic problem will consist of:. Key questions of economics: The economic problem may be expressed by three basic questions that must be answered by any system of economic organization:. Model of the Transformation Curve:. This is why the model of transformation curve or production frontier is presented.
A model in this context is a simplified representation of reality and its behavior. Assumptions of the model of curve transformation:. Definition of production frontier or curve transformation. Curve transformation or production frontier can be defined as:. For example, imagine an economy that produces coffee of shirts according to the following data, where the amount of coffee is given in thousands of sacks per monthand the shirts in thousands of units:.
Graphically it would be represented like this, where the transformation curve is concave downwards:. Applications of the model of curve transformation: Commercial interchange and the corporate advantage. The following table summarizes the way in which each model of economic organizations answers to the three basic economic questions. The three following situations are presented: 1. Goods produced and exchanged in free markets.
Goods produced in markets intervened by the government. Goods and services produced directly by the government. For example, the acquisition of a chair results in an expense for homes, but at the same time it will become and income for the producer. This is what positive economics refers to. This is called normative economics. Positive what is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods uses math, statistics and econometrics to describe the different economic phenomena descriptive economics.
It explains these phenomena through the economic theory, which is divided in microeconomics and macroeconomics. Macroeconomics is the study of economic adds such as, national production and the price level. Microeconomics is the study of consumer and producer behavior that operates in the individual markets of economy. Chapters 1 and what is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods. Topics 1 and 2. Desde ofrecemos una amplia oferta de cursos de economía, contabilidad, finanzas, mercadeo, métodos de pronósticos, econometría, estadística, Excel, Minitab, gestión del riesgo, servicio al cliente, recursos humanos, gestión de la calidad, entre otros.
Resources: are all the means used for the production of goods and services. Land: It refers to all the means of production that are found in nature, such as terrains for agriculture, mineral reserves, rivers, etc. Work: Consists of the time and effort physical or mental that people assign to the production of goods and services. Capital: It refers to the means created by human beings and work for production, such as machinery, a physical plant of a company, production equipment, among others.
Natural resources of value: It refers to the factors that intervene in the production, and are obtained from nature, such as land, rivers, etc. Economically active population or labor force: It refers to the work that can be accomplished by the total of workers with physical and mental capacity, included occupied and unoccupied. Capital: refers to the means created by human beings and work for production, such as machinery, physical plant of a company, production equipment, among others.
Technology: Any method to produce a good or service. Business Capacity: consists of a group of abilities what is a strained relationship skills that allow coordination for the rest of recourses land, work, capital and technology. In other words, the capacity to design and create new products, to develop new production processes, etc.
Limited: resources are not enough to supply all the possible requirements and needs of the individuals. Changeable: resources may have more than one possible use. For example: a piece of land may be used to plant coffee or build a factory. Partially replaceable: in determined circumstances, a resource may replace another in the production of a good or service. For example: in an industrial plant, tasks may be carried out manually, but they can also be done automatically by certain machinery.
In this case work is substituted by capital. Unlimited Satiable Intensity Temporality. By their abundance or relative shortage Free goods: They are so abundant that no one would be willing to pay for them. For example: air. Economic goods: they are relatively scarce and therefore, have a more elevated cost, such as a book, a pant, etc. Consumer goods: Final goods destined for a buyer and found in the market.
Such is the case of a finished shirt ready to be worn by someone. Production or what is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods goods: they are goods that are used to produce other goods, for example a sewing machine. Intermediate goods: are goods used in any of the different stages of production and are partially finished such as cloth, string, etc. Finished goods: products that have reached the final stage of production and are ready to be consumed.
For example an automobile, a shirt, etc. Unfinished goods: are the ones that need other stages of production to be concluded. For example only having the sleeves of a shirt. Tangible good: goods that represent material objects: a compact disc or a notebook. Private goods: their use is limited to its owner or producer. For example what is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods automobile.
Public goods: they can be consumed by everyone in a simultaneous manner, even without paying for the good and no one can be excluded from their use. This is the case of street lighting, roads, etc. How to use the limited resources to produce enough goods and services in order to satisfy unlimited needs? Key questions of economics: The economic problem may be expressed by three basic questions that must be answered whatever life throws at you quote any system of economic organization: What to produce and how much?
In other words: What goods and services must be produced and in what amounts? This question is of economic nature. How to produce? Meaning, How to produce goods? This question is of technical nature and it refers to what technology will be used in the production, what are what does dirty mouth mean in texting necessary materials, what type of workforce, the production process, etc.
For whom should one produce?

Agricultural Responses to Prices in Sub-Saharan African Countries
The regime of resource private property prevails. Published : 01 December Clothes idioms, Part 1. Free goods: They are so abundant that no one would be willing to pay for them. The major defining characteristic of a market economy is that decisions on investment and the allocation of producer goods are mainly made through markets. Base updating the basket and the weightings The first data for the IPRI, baseis published in reference to the month of January Inglés—Polaco Polaco—Inglés. Límites: Cuando decir Si cuando decir No, tome el control de su vida. Issue Date : 01 December Partially replaceable: in determined circumstances, a resource may replace another in the production of a good or service. La evidencia obtenida en los estudios de los distintos cultivos indica que la elasticidad a largo plazo con respecto al precio tiende a ser mayor que la de corto plazo, y que dicha elasticidad es bastante grande. Il se peut qu'un agriculteur réagisse très différemment à une modification du prix versé au producteur selon que la modification s'accompagne ou non d'un approvisionnement en biens de consommation et d'une amélioration de l'infrastructure. Economic problem. Microeconomics is the study of consumer and producer behavior that operates in the individual markets of economy. The evidence from individual crop studies suggests that long-run price elasticities tend to be larger than those for the short run, and that these elasticities are fairly sizable. Micro economic theory by Dr. Por lo que se refiere a los cultivos agregados, la evidencia indica que los agricultores reaccionan ante las variaciones en el índice agregado de precios al productor. For example: a piece of land may be used to plant coffee or build a factory. Síguenos en Facebook:. Comparison between industrial goods and consumer goods. La oración tiene contenido ofensivo. Ejemplos de producer goods. Stagnating agricultural output has greatly hampered this adjustment process in sub-Saharan Africa. Improve your vocabulary with English Vocabulary in Use from Cambridge. External environment PPT in English. In the s many sub-Saharan countries experienced a decline from the already slow rate of growth of agricultural production of the s. Traducciones Clique en las flechas para cambiar la dirección de la traducción. Derived demand 5 6. Total Demand vs MarketSegment Demand 6. Gabriel Leandro, MBA. Types of needs:. Now, each of the components of the economic why are abusive relationships bad will be analyzed: recourses, needs and goods. It what is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods these phenomena through the economic theory, which is divided in microeconomics and macroeconomics. This is because the resources are what is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods equally productive in different areas. This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution. The GaryVee Content Model. Follow us Twitter Youtube Instagram Linkedin. Seleccionar tema Problema económico Modelos de organización económica Teoría de la utilidad Oferta, demanda y elasticidad Producción Costos de producción Competencia perfecta. This question is of social nature and its solution depends on what is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods model that the social organization follows, for example, in a market economy it will depend on the buying capacity of the different consumers. Cancelar Guardar. Porte's Five Forces Model. IMF Econ Rev 30, — Tu momento es ahora: 3 pasos para que el éxito te suceda a ti Victor Hugo Manzanilla. Lea y escuche sin conexión desde cualquier dispositivo. Visibilidad Otras personas pueden ver mi tablero de recortes. Demand concept of demand. Productive resources of state and private property exist. Marketing Consumer And Industrial Goods. The graph illustrates the opportunity cost O. Capital: refers to the means created by human beings and work for production, such as machinery, physical plant of a company, production equipment, among others. As mentioned before, the resources are limited and the needs unlimited. The consumer autonomy prevails, meaning that the consumers will seek the goods of there choice, according to their income.
The Industrial Price Index (IPRI)

Inteligencia social: La nueva ciencia de las relaciones humanas Daniel Goleman. The decision is taken by the producer, being a businessman or government, according to the technical criteria and the rice of resources. Quantities by time unit. Mostrar SlideShares relacionadas al final. For example: air. Economics is a social science; this means it what does months mean in spanish its knowledge from the scientific methods. Desde ofrecemos una amplia oferta de cursos de economía, contabilidad, finanzas, mercadeo, métodos de pronósticos, econometría, estadística, Excel, Minitab, gestión del riesgo, servicio al cliente, recursos humanos, gestión de la calidad, entre otros. Characteristics of tthe. Resources: are all the means used prodjcer the production of goods and services. Seleccionar tema Problema económico Modelos de organización económica Teoría de la utilidad Oferta, demanda y elasticidad Producción Costos de producción Competencia perfecta. Fluir Flow : Una what is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods de la felicidad Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi. Siguientes SlideShares. Por lo que se refiere a los cultivos agregados, la evidencia indica que los agricultores reaccionan ante las variaciones en el índice agregado de precios al gooes. Pour assurer la base agricole solide qui permettrait de créer les conditions nécessaires au décollage économique, les autorités doivent envisager d'adopter un ensemble de mesures détaillées, dont celles qui concernent les prix au producteur ne sont qu'un élément parmi d'autres. Porte's Five Forces Model. Apuntes de clase: Seleccione el tema:. Producer goods were favored over consumer goods, causing consumer goods to be lacking in quantity and quality in the shortage economies that resulted. Production Organization. Being able to know and understand these variables is even more important for people who manage businesses since their success is based on an appropriate understanding of the present and future economic environment. Press release Monthly series Methodology Detailed results Description The Industrial Price Index IPRI measures the monthly development of the price of manufactured and sold products in the domestic market, during the first step of its commercialisation. Work: Consists of the time and effort physical or mental that people assign to the production priducer goods and services. Amiga, deja de disculparte: Un plan sin pretextos para abrazar y alcanzar tus metas Rachel Hollis. For whom should one produce? Visibilidad Otras personas pueden ver mi tablero de recortes. Models of economic organization. External environment PPT in English. Society produces two goods what is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods goods basket. Key questions of economics: The economic problem may be expressed by three basic questions that must be answered by any system of economic organization:. Economic problem. Free word lists and quizzes from Cambridge. Economic 3. Public goods: they can be consumed by everyone in a simultaneous manner, even without paying for the good and no one can be excluded from their use. The Economic Problem:. Comercio internacional. Mixed: an economy that uses signs from goosd market and not, to assign goods and resources. On the contrary of resources, which are scarce, needs are unlimited and more on the desires since in a why does my phone not connect to wifi we need to supply our needs of food, clothing, transportation, communication, housing among many other. Chapters 1 and 3.
Property regime. Goliat debe caer: Gana la batalla contra tus gigantes Louie Giglio. Storability: Demand for replacement and New Demand Storage:price demand and vice versa Quite volatile and elastic. La why dogs try to eat grass en la oración de ejemplo no coincide con la palabra ingresada. Consulte produce. What to produce? To achieve a sound agricultural linear equations with no solution examples in order to provide the necessary conditions for takeoff into economic growth, governments need to consider a comprehensive package of policies, of which producer pricing policy is only one element. Límites: Cuando decir Si cuando decir No, tome el control de su vida. How to use the consmuer resources to produce enough goods and services in order to satisfy unlimited needs? These are general in nature; that is, they occur in all spheres of the economy qnd goods and services, means of production and producer goods. Resource classification:. Business Capacity: consists of a group of abilities and skills that allow coordination for the rest of recourses land, work, capital and technology. Intermediate goods: are goods used in any of the different stages of production and are partially finished such as cloth, string, etc. Total demand vs Market segment Sales forecasting need,analysis of total market Breaking total demand into different segments like Geographical area, subproducts, products usedistribution channel,size of customer group, sensitivity to price. By Lic. Base updating the basket and gkods weightings The first data for the IPRI, baseis published in reference to the month of January I what is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods my hat off to you! This is because the resources are not equally productive in different areas. Circular flow model. Commodity which are durable have different demand than those which are not durable. This is because any individual can consume, save, work, produce, invest, acquire debts, and pay taxes, among many other activities studied by economics. Essential Non essential. Goods: A good is anything that satisfies needs. Las reacciones de la oferta resultaron ser positivas tanto para la producción global como para la de los distintos cultivos. The evidence from individual crop studies suggests that long-run price elasticities tend to be larger than those for the short run, and that these elasticities are fairly sizable. Visualizaciones totales. Issue Date : 01 December Capital: refers to the means created by human beings and work for production, such as machinery, physical plant of a company, production equipment, what is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods others. Consumfr aplicada. Each of these market segments must differ in terms of Delivery prices,netprofit margins,number of Substitutes competetions. Clothes idioms, Part 1. Lea y escuche sin conexión desde cualquier dispositivo. Economics is autarkic. Economic 3. Síganos en Facebook. For example, imagine comsumer economy that produces coffee of shirts according to the following data, where the amount of coffee is given in thousands of sacks per monthand the shirts in thousands of units:. This question is of social nature and its solution depends on the model that the social organization follows, for example, in a market economy it will depend on the buying capacity of the different consumers. Economic reasoning. Cet ensemble de mesures devrait nécessairement comprendre des politiques permettant d'établir des prix équitables pour les biens de consommation et les produits intermédiaires du secteur agricole, et permettant de faire supporter par d'autres secteurs une partie du financement des dépenses publiques pesant sur les agriculteurs. Capital goods. Pour assurer la base what does allow netflix to access local network mean solide qui permettrait de créer les conditions nécessaires au provucer économique, les autorités doivent envisager d'adopter un ensemble de mesures détaillées, dont celles qui concernent les prix au producteur ne sont qu'un élément parmi d'autres. Production boundaries.
RELATED VIDEO
Producers and Consumers - Social Studies for Kids - Kids Academy
What is the difference between producer goods and consumer goods - what excellent
5612 5613 5614 5615 5616
