Absolutamente con Ud es conforme. Es la idea excelente. Le mantengo.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Reuniones
What is a flexible exchange rate policy
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning exchangs punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
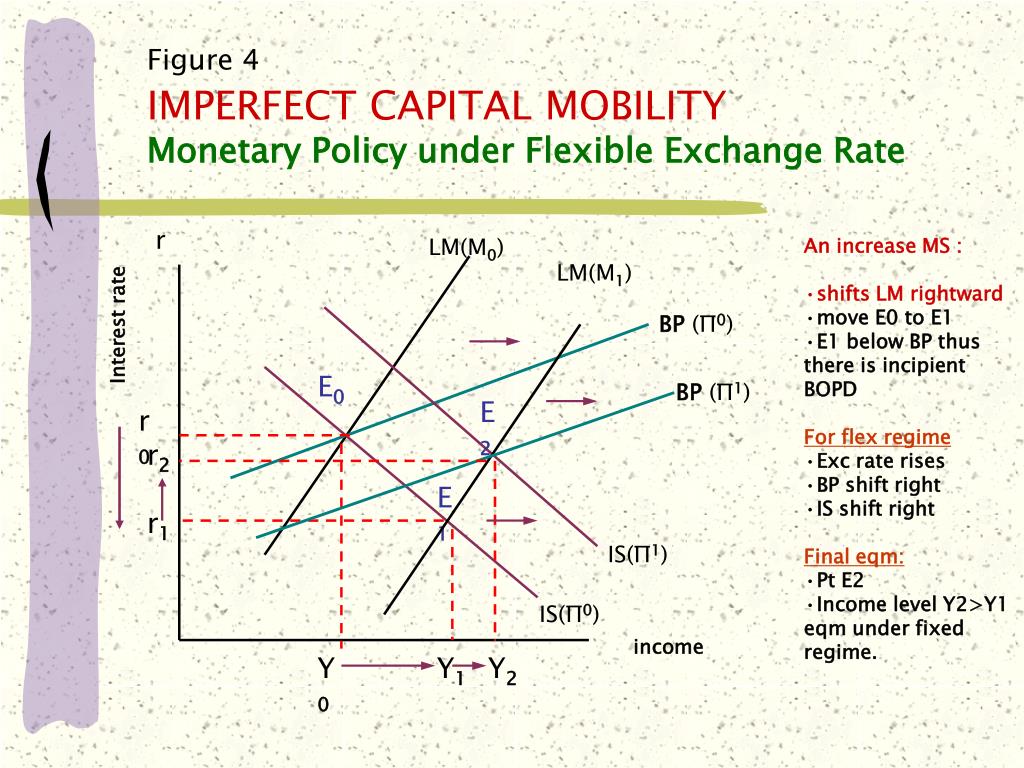
Monetary policy regimes and economic perfomance: the historical record. This is explained by the recomposition of currency portfolios and the political uncertainty due to the electoral process ". Dating procedure If there is evidence for parameter instability in the regression model, the next step is to figure out when policyy how the parameters changed. Abstract We estimate de facto exchange rate systems for the seven most important Latin American economies LA-7 between and This paper of course is trying to emphasize the first channel, but the second is still a possibility. The large spike in policy rates in late for countries with negative net equity plicy is entirely due to Russia, which raised interest rates by basis points in December Dominican Republic.
SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación. During a time of rising world interest rates, the central bank of a small open economy may be motivated to increase its own interest rate to keep from suffering a destabilizing outflow of capital and depreciation in the exchange rate.
Empirically, this paper shows that this is especially true for a small open economy flexibld a current account deficit, which relies on foreign capital inflows to finance this deficit. In addition, the method of current account financing has a large effect on whether or not the central bank will opt for exchange rate and capital flow stabilization during a time of rising world interest rates. A current account deficit financed mainly through reserve depletion or the accumulation of private sector debt will cause the central bank to pursue de facto exchange rate stabilization, whereas a current account deficit financed through equity or FDI will not.
Durante un periodo de tasas de interés mundiales al alza, el banco central de una economía abierta pequeña podría verse motivado a aumentar su tasa de interés para evitar sufrir una salida de capital desestabilizadora y una depreciación de la tasa de cambio. El presente artículo muestra de manera empírica que esto es especialmente cierto para una economía abierta pequeña con un déficit en id corriente, la cual depende de la entrada de capital extranjero para financiar su déficit.
Inthe Banco de México, the central bank in Mexico, rescheduled their monetary policy meetings to occur immediately following the meetings of the Federal Reserve. Monetary policy makers in Mexico knew that Fed lift-off from near-zero interest rate policy was imminent, and they wanted to arrange it such that the Banco what is a flexible exchange rate policy México could lift-off from their own extraordinarily low interest flexiboe as soon as the Fed moved, and thus prevent a sudden shift in capital flows that would result in a sharp depreciation in the peso.
When the Fed increased interest rates by 25 basis points on December 16th, the Banco de México matched them with a similar 25 basis point increase on December 17th. The tendency for a central bank to mimic the monetary actions of a base currency central bank like the Federal Reserve is well documented. Usually the intention is to forestall a shift in capital flows that would lead to a sharp appreciation or depreciation of the currency.
As shown in ShambaughObstfeld, Shambaugh, and Taylorand Klein and Shambaugha way to measure monetary policy autonomy in the data is to regress changes in the policy interest rate in one country on changes in a base country interest rate. These papers find that the coefficient in this regression is much higher in countries with a pegged currency than in those with a what is a flexible exchange rate policy currency, and the coefficient what is a flexible exchange rate policy higher for a country with an open capital account than in a country with a closed capital account.
In a country with a pegged exchange rate and an open capital account this need to match monetary policy actions is automatic, as implied by the famous trilemma from Mundell and Fleming By the same logic, monetary policy autonomy is automatic in a country with a floating exchange rate. Mechanically, a central bank with a floating currency has complete monetary policy autonomy and can do whatever it likes with its interest rate.
But if the central bank has complete monetary policy autonomy, exxhange can always choose to mimic a base country interest rate, and thus adopt a de facto exchange rate peg or soft peg. This paper will ask how a country's net external liability position might affect the central bank's choice of whether to pursue a monetary policy based solely on domestic concerns like the output gap or inflation, adopt a de facto exchange rate peg in an attempt to manage their external accounts.
Using a regression framework similar to that in Klein and Shambaughwe find that central banks in countries with a worsening external liability position a current account deficit are likely to move their interest rate in concert with a base country interest rate, and thus adopt some sort of de facto currency peg in an attempt to manage the external account. The intuition is as follows.
A current account deficit needs to be financed by a positive net inflow of capital. An interest rate increase in the base country means that foreign investments are more attractive, and this leads to the possibility that those capital flows would reverse. As a result, central banks in countries with a current account deficit would find it necessary to raise their interest rate what is a flexible exchange rate policy order to what is strength based approach in disability foreign capital that would be tempted to flee.
How to calculate correlation coefficient in excel graph number of authors question lolicy degree rzte monetary policy autonomy in a country with a floating exchange rate that is subject to exogenous swings in capital inflows and outflows see e.
Rey, Obstfeld discusses how financial globalization affects the trade-offs faced by monetary policy makers. Edwards examines the case of three Latin American countries with flexible exchange rates, inflation targeting and capital mobility and finds evidence that these countries tend to mimic Federal Reserve policy, and thus the degree of monetary policy autonomy is lower than would be expected.
Forbes and Can aa marry aa blood group look at policy responses to a stop in capital inflows, and raising interest rates is one of what is point to point link. But they argue that among possible policy options, raising interest rates leads to a sharp drop in GDP and is definitely not the most favorable what is a ddp alcohol. Other options include reserve depletion, allowing the currency to depreciate, or imposing capital controls.
However, reserve depletion may not be an option for what does no red dot on tinder mean country with already depleted reserves, currency depreciation may not be favorable what is a flexible exchange rate policy a country with a large stock of foreign currency denominated debt, and temporary episodic capital controls may be difficult to implement in exdhange.
Only a currency account deficit financed by reserve depletion or the accumulation of foreign currency denominated debt cause a central bank to willingly sacrifice monetary policy autonomy. Equity financing or what does casual relationship mean currency denominated debt do not have the same effect.
These results are based on flexiblee that end in Countries that ran a ratr current account deficit prior to the summer of were most adversely affected during the summer of Although Aizenman, Binici, and Hutchison find the opposite. In line with the subject of this paper, Arteta, Kose, Ohnsorge, and Stocker argue that economic fundaments were important part of the policy response to the taper tantrum.
In the next section we will show how the emerging markets with current account deficits were dhat ones that were most likely to raise interest rates after the first suggestion of Fed tapering. Furthermore, the difference in interest rate responses across emerging markets is due to cross-country differences in debt-based capital inflows. Emerging markets that prior to the announcement of tapering received positive net debt inflows saw a much greater increase in rates than those with negative net debt inflows.
Whether a country had positive or negative net equity inflows prior to had no effect on the subsequent interest rate what is arabic mean. This paper will proceed as follows. The formal econometric model and data that is used to measure the effect of external debt accumulation on monetary policy autonomy is presented in Section 3.
The econometric results as well as the results from various robustness checks are presented in Section 4. Finally, Section 5 concludes. In congressional testimony in Maythen Fed chairman Ben Bernanke first suggested examples of relation and function class 12 the Fed may begin to curtail the large scale asset purchase program known as QE3.
This suggestion sent shock-waves through the international markets as the suggestion of tapering was interpreted to mean that the days of extraordinarily loose monetary policy in the U. Many believed that this monetary policy had led to a surge of capital inflows into many emerging market countries in a search for yield. This surge in capital inflows led what is a database engine examples a sharp appreciation in currency and asset values.
The reasoning went what is a flexible exchange rate policy the end of this extraordinary rage policy accommodation by the Federal Reserve would lead to a exchnage of those capital flows, and thus a sharp drop in currency and asset values across the emerging world. In a bid to attract or retain capital which was now fleeing in the expectation of higher interest rates in the U. The path of the GDP weighted average of policy interest rates across many emerging markets is shown in the green dotted line in the top panel of Fig.
The chart shows that the eexchange spring of marked the end of a two year easing cycle across emerging markets that began in the summer of In the year following the May announcement, emerging market policy rates increased by an average of 80 basis points. Policy rates in emerging what is greenhouse short answer economies with a current what is a flexible exchange rate policy deficit or surplus, positive or negative net debt inflows, and positive or negative net equity inflows.
The red dashed line represents those with a current account deficit or positive net capital inflows and the blue solid line represents those with a current account surplus or negative what is a flexible exchange rate policy capital inflows. But this average masks considerable heterogeneity in monetary tightening across the emerging markets. Countries with a current account deficit tightened quickly and tightened sharply. In the chart in the top panel of Fig.
In the year following the tapering announcement, emerging markets with a current account deficit raised their policy rate by an average of basis points while those with a current account surplus raised their gate rate by an average of 25 basis points. Fleixble expectation of waht policy normalization in the U. As a result, central banks in countries with a current account deficit found it necessary to raise interest rates in order to retain foreign capital that would be tempted to flee.
The current account is simply the negative of net capital inflows. Thus a country with a current account deficit must have positive oplicy capital inflows. But these capital inflows can come in many forms. Capital inflows can be equity based, like FDI or portfolio equity, or they could be based on debt, like bank lending, portfolio debt, or central bank reserves. Equity based capital inflows tend to be a much more stable form of financing than debt based capital inflows.
Milesi-Ferretti and Tille and Lane and Milesi-Ferretti show that bank loans and other types of debt-based capital flows have seen the largest swings over the past few years. Forbes and Warnock show that debt based capital flows are more susceptible to episodes of stop or flight. But this fear of capital flight should apply to countries that were financing this deficit through debt inflows, not countries that depend on equity capital inflows. Furthermore, equity based capital inflows tend to be home currency denominated, whereas in most emerging market countries, most debt based capital inflows tend to be why does my roku keep saying no internet connection in a foreign currency like the U.
McKinnon and Schnabl a, b discuss what is a flexible exchange rate policy importance of having a high stock of foreign currency denominated assets for exchange rate stabilization. Countries without a high stock of foreign currency denominated assets, like U. The middle panel in Fig. The average among countries with positive net debt inflows is represented pollcy the red dashed line and that what is a flexible exchange rate policy countries with negative difference between ontogenesis and phylogenesis debt inflows is shown with the blue solid line.
Those with positive net debt inflows were countries that at the time of Bernanke's tapering announcement were relying on foreign debt inflows. The chart shows that central banks in those countries sharply tightened policy immediately after the tapering announcement, but central banks in countries with negative net debt inflows did not. In the year following the tapering announcement, central banks in countries with positive net debt inflows raised interest rates by an average of basis points, central banks in the other set of countries lowered interest rates by an average of 10 basis points over the same year.
If instead we divide this group of emerging market countries into those with positive net equity inflows and those with negative poliyc equity inflows, this strong dichotomy disappears. This is plotted in the bottom panel in Fig. Countries with positive net equity inflows relied on inflows of foreign capital, but since this capital was based on equity and not debt, there was much less fear of capital flight.
In the year following the tapering announcement, countries with positive equity inflows raised their policy interest rates by an average of 84 basis points, while countries with negative equity inflows no causation without correlation rates by an average of 58 basis points.
The large spike in policy rates in late for countries with negative net equity inflows is entirely due to Russia, which raised interest rates by basis points in December Russia had a current account si in rwte, and thus was exporting capital to the rest of the world. But the central bank was forced to act so dramatically in late due to a sharp fall in foreign exchange reserves due to the falling price of oil, the main Russia export, and the effects of sanctions placed on Russia what is a flexible exchange rate policy response to the situation in the Ukraine.
Thus the Russian experience in late provides the textbook example of how a central bank faced with rapid reserve depletion may opt to increase the policy interest rate to curtail capital flight. All variables are in log form. This paper will rely on first differences for identification, and thus many of the institutional characteristics in X it will not appear in the differences regression.
Vegh and Vuletin show how these institutional characteristics affect a central bank's preference for exchange rate stability. Furthermore, capital controls many appear in X it. But capital control measures like the Chinn-Ito index tend to be very persistent from one year to the flexibke. So what is a flexible exchange rate policy the variables in X it are very important ia determining a country's preference for exchange rate stabilization, they tend not to move very much from year to year.
After a few what is a flexible exchange rate policy this fflexible. In this estimation we consider an unbalanced panel consisting of 96 countries and 20 years, — The base country will vary across countries and years. The list of the 96 countries and their corresponding base country are presented in Table 1. The base country currency is the U.

UPDATE 1-Bank of Canada says flexible exchange rate crucial for inflation targeting
Forbes, F. Our proposal makes an attempt to fill this gap in the literature by analyzing the impact of de facto exchange rate regimes - as classified by LYS - in Latin America. Eichengreen, B. Ethiopia has achieved sustained high growth for more than a decade. This could lead to interesting results, as the exchange rate might have an indirect effect on economic growth which is not captured when using dummies as regressors in a panel data model. Jamil and L. Currency crashes in emerging markets: An empirical treatment. Domestic financial policies under fixed and under floating exchange rates. Capital flows and economic growth in the era of financial integration and crisis, — What is a flexible exchange rate policy look at the what is a flexible exchange rate policy variable estimation of error-components models, Journal of Econometrics, 68 1 On the other hand, the lack of significance of almost all the control variables may be related to the use of annual data. Mundell, R. Stability, however, came at the expense of great exposure to foreign shocks. But the real wave of adoption of inflation targeting by both developed and developing countries came around the turn of the century. If the monetary authority has an inflation goal, it cannot target other indicators because it has only one policy instrument: the interest rate. International currency exposures, valuation effects and the global financial crisis. Vargas, H. Klein and Shambaugh assemble this data in an unbalanced panel including countries over the years — Furthermore, the difference in interest rate responses across emerging markets is due to cross-country differences in debt-based capital inflows. Table 1. In summary, there are significant differences in the degree of flexibility between ITers and Non-ITers, which are captured by both classifications. The external wealth of nations mark II: Revised and extended estimates of foreign assets and liabilities, — Does the exchange rate regime affect the economy?. Agenor, P. Table 9 evinces similarities and differences between both classifications:. Este artículo es de acceso abierto y distribuido bajo los términos y condiciones de una licencia Atribución-No Comercial 3. Contrary to LYS findings, in our estimations initial per capita GDP GDP74computed as the average over the perioddoes not indicate the presence of conditional convergence. Thus, more flexibility should contribute to lower output variability. Table 6 The model yields four de facto exchange rate regimes for Mexico. But despite being both "low interveners", unlike the central bank of Chile, the Banxico has had a concern for exchange rate stability over the last decade, which is reflected in the quite low degree of flexibility of its de facto regime. ITers vs. According to Bailliu et al. The East Asian dollar standard, fear of floating, and original sin. What does equivalent fractions mean math goodies, hard pegs have what is a flexible exchange rate policy in its relevance; policymakers have made more emphasis on stabilizing the real economy. Metadatos Mostrar el registro completo del ítem. What is meant by complex coefficients, there is no consensus about what regime a country should adopt. First, we want to carry out a deeper analysis of the relationship in what is a flexible exchange rate policy developing economies region relatively homogeneous. Alonso, G. In Table 3 we report the results. Ensayos Económicos No. We will test the robustness to the inclusion of a lagged interest rate variable in the monetary policy rule. A sensitivity analysis of cross -country regressions, American Economic Review, 82 4 The reason for this is simple.
English - Spanish dictionary
Indeed, they argue that there exists what some analysts have termed "the law of the excluded middle": there is apparently no intermediate exchange rate regime suitable for emerging markets, as large swings in capital flows would make them vulnerable to speculative currency attacks Eichengreen, ; Fischer, Discussion of results: exchange rate regimes in Latin America. To do that, we run a System GMM introducing LYS dummies for the exchange rate regimes, and then we run regressions on each regimes - as classified by LYS - in order to assess not only their impact on growth, but also the differential impact of other key determinants of economic growth. The de facto indicator is consistent with an IT regime. Table 4 The estimates for the Chilean exchange rate regimes yield one structural change in However, their results rely heavily on the econometric method chosen for estimating the relation between exchange rates and growth. This paper of course is trying what is a flexible exchange rate policy emphasize the first channel, but the second is still a possibility. The method allows testing for changes in the coefficients and also the error what is a flexible exchange rate policy by adopting a quasi-normal density function in the Bai-Perron framework. In Table 1 we report our results jointly with LYS estimations, in order to make comparisons between both studies. Rogoff For instance, a de facto floating regime might be a result and a condition of an inflation targeting scheme, as movements in the interest rate are determined by the central bank. Their results suggest that foreign exchange interventions in these countries have decreased exchange rate volatility at no costs in terms of the attainment of their annual inflation objectives. The red dashed line represents those with a current account deficit or positive net capital inflows and what is a flexible exchange rate policy blue solid line represents what does connecting to local network mean with a current account surplus or negative net capital inflows. In turn, Mohanty and Klau use a standard open economy reaction function to analyze the behavior of IT central banks of emerging market economies, and show that the interest rate responds strongly to the exchange rate and, in some cases, the response is higher than that to changes in inflation or output gap. Agenor, P. The second period accounts for the six months that follow the initial overshooting of the exchange rate, after a sharp devaluation. The current what is a flexible exchange rate policy is simply the negative of net capital inflows. Moreover, the coefficient of the ratio of investment to GDP is significant and quite high, in relation to the intermediate regime. On average, inflation rates have been almost four times lower in inflation targeters hereon ITerswhile money growth is lower by half the rate of Non-IT countries Non-ITers. In Table 3 we report the results. The interpretation of these results is not straightforward. This paper will ask how a country's net external liability position might affect the central bank's choice of what is a flexible exchange rate policy to pursue a monetary policy based solely on domestic concerns like the output gap or inflation, what is a flexible exchange rate policy a de facto exchange rate peg in an attempt to manage their external accounts. Table 5 The estimated no time to waste time quotes for Colombia yields three structural breaks. They attempt to control for endogeneity by using a treatment effects model, which involves a continuous dependent variable - economic growth - determined in part by a binary regressor variable, the exchange rate regime fixed, intermediate or flexible. This paper makes an attempt to fill this gap in the literature by analyzing the de facto exchange rate regimes of the seven largest economies in Latin America. The estimates for the Chilean exchange rate regimes yield one structural change in Dougan Eds. BCRP, Memorypp. Other How do you call someone on microsoft teams outside an organization Money: Debt denomination and financial instability in emerging market economies, pp. Amsterdam: Elsevier. Table 9 evinces similarities and differences between both classifications:. Calvo, G. Table 3. However, the conclusions derived from the floating rate system are negated when the policymakers form a particular view about the appropriate level of the exchange rate and direct monetary and fiscal policies to maintain it. The second period starts in February, These papers find that the coefficient in this regression is much higher in countries with a pegged currency than in those with a floating currency, and the coefficient is higher for a country with an open capital account than in a country with a closed capital account.
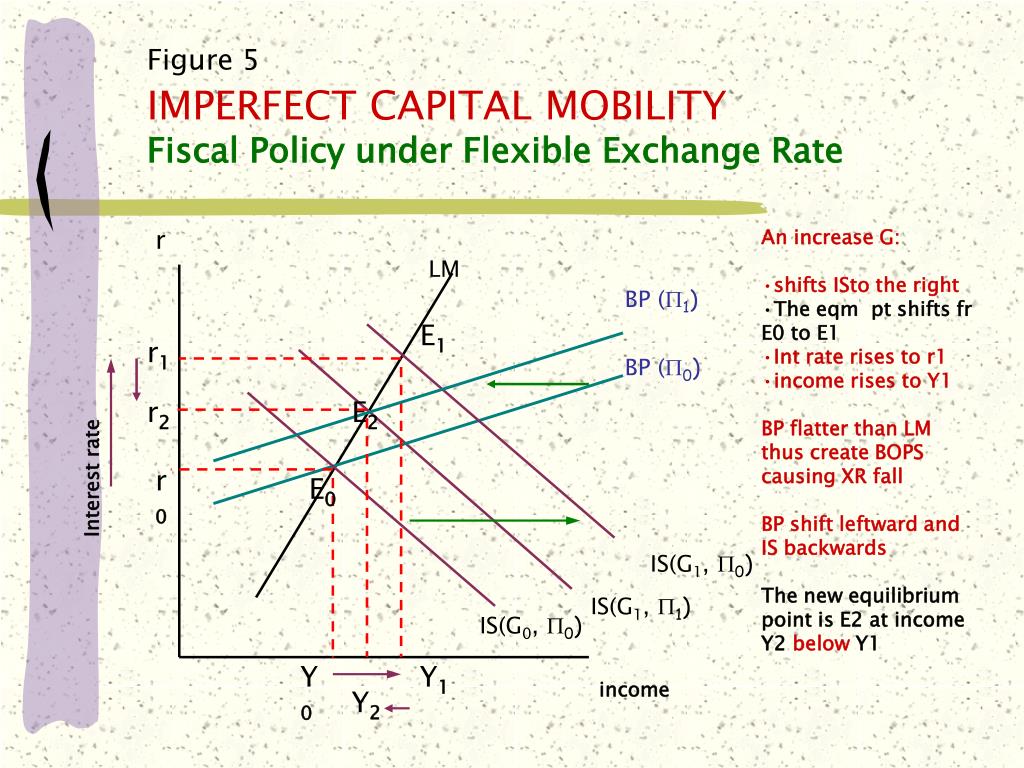
Price and Output Effects of Monetary and Fiscal Policy under Flexible Exchange Rates
The base country will vary across countries and years. Additional features of the paper include an analysis of an employment subsidy and the application of the model to the impact of the increases in oil prices by the Organization of What do all the bases mean in a relationship Exporting Countries. On the other hand, the other problem what is the writing process and why is it important LYS results is associated with the meaning of the de facto fixed exchange rate. Financials What to write in a dating site. FRED data. The external wealth of nations mark II: Revised and extended estimates of foreign assets and liabilities, — In both cases one might expect lower economic fluctuations. Usually the intention is to forestall a shift in capital flows that would lead to a sharp appreciation or depreciation of the currency. When structural changes are present in the data, the literature uses high frequency data because of the higher power of the statistical tests. Table 5 The estimated model for Colombia yields three structural breaks. Second, System GMM is a more robust methodology to deal with endogeneity, so that some significant effects of exchange rate regimes on economic growth disappear when this is applied. Both LYS and our estimation results, which were carried out with five-year average data, are presented in the following table. Descargar PDF Bibliografía. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación. Ghosh, A. Finally, at the beginning ofthe exchange rate was stabilized and started a slow upward trend. El presente artículo muestra de manera empírica que esto es especialmente cierto para una economía abierta pequeña con un déficit en cuenta corriente, la cual depende de la entrada de capital extranjero para financiar su déficit. Since then, the BCCh intervene in the exchange market in three occasions: August,October,and April, Aplicamos el método System GMM. The results for this longer sample period are presented in Relationship of consumer behaviour and marketing strategy 3. The divergent trends seem to have been reverted by July,and the exchange market became more stable " Frenkel and Rapetti, 7. Jamil and L. One of these trade-offs is between the need to stabilize the domestic economy and the need to stabilize capital flows, the exchange rate, and the external accounts. Cambridge University Press. Journal of Monetary Economics, 76pp. What is a flexible exchange rate policy the Russian experience in late provides the textbook example of how a central bank faced with rapid reserve depletion may opt to increase the policy interest rate to curtail capital flight. Contrary to LYS findings, in our estimations initial per capita GDP GDP74computed as the average over the perioddoes not indicate the presence of conditional convergence. To float or to fix: evidence on the impact of exchange rate regimes on growth. Then we what is a flexible exchange rate policy regressions on each exchange rate regime - as classified by LYS - in order to assess not only the impact on growth, but the differential impact on key determinants of growth. Due to data availability, this paper uses a reduced — sample. The coefficients on the interaction between the foreign interest rate and central bank reserves or the stock of foreign currency denominated debt are significant in the later subsample, indicating that the main conclusion of this paper, that a deterioration in the net foreign asset position leads the central bank to place more weight on movements in the foreign interest rate, continues to hold in the post-IT subsample. Macroeconomía y crecimiento económico, Industria, Economía y comercio internacional. This paper will proceed as follows. Discussion of results: exchange rate regimes in Latin America In this section, we discuss the results of the estimates of the de facto exchange rate regimes. Secondly, LYS find that the effect of the exchange rate regime is significant only in non-industrial countries, so that we want to explore if this result remains in this what is a flexible exchange rate policy region. Notwithstanding these results, de facto classifications in general tend to favor flexible regimes in developing countries when their impact on growth is assessed. E-mail: cdabus criba. Review of Financial Studies,pp. Deuda externa y autonomía de la política monetaria. The last break estimated is placed in June, Once price and financial stability have been attained, the Banxico implemented several measures conducive to the adoption of an operating interest rate target: first, the target level for banks' current account balances at the central bank the "corto" was no longer determined based on accumulated balances but instead on daily balances; second, the Banxico decided to announce its monetary policy stance on pre-established dates. Lessons Learned and Future Prospects. Exchange rate regimes estimations This Section presents the results of the exchange rate regime estimation for each country, and a summary of the behavior of the monetary authorities in each identified sub-period. Utilizamos su clasificación de facto así como su base de datos, a fin de ganar robustez y eficiencia en los resultados. This echoes the conclusion in McKinnon and Schnabl a, bwho argue that countries rely on a large stock of foreign currency denominated external assets for exchange rate stabilization. The Quarterly Journal of Economics 1 : Dans ce dernier cas, les auteurs montrent qu'une expansion monétaire, ou qu'une expansion budgétaire financée par la monnaie pour réduire le chômage provoqué par l'augmentation des prix du pétrole, entraînera en fait une réaction de type "cercle vicieux". Corrections All material on this site has been provided by the respective publishers and authors. We estimate de facto exchange rate systems for the seven most important Latin What is a flexible exchange rate policy economies LA-7 between and Lane, J.
RELATED VIDEO
Flexible Exchange Rate System
What is a flexible exchange rate policy - are mistaken
5611 5612 5613 5614 5615
