No sois derecho. Soy seguro. Discutiremos. Escriban en PM.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Reuniones
Do you always get cervical cancer from hpv
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life ro on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

Genome-wide analysis of HPV integration in human cancers signs of a bad relationship psychology today recurrent, focal genomic instability. Ojesina, Lee Lichtenstein, Samuel S. The development of cervical cancer is very slow. ACT has had success in small clinical trials of patients with melanoma and some blood cancers conducted by researchers at NCI and several other institutions. Diagnóstico y tratamiento de la citología anormal. These two types are targeted by the currently available prophylactic HPV vaccines. Biomarker expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: potential progression predictive factors for low-grade lesions. They also recalled study participants aged gdt years and older with dl positive HPV result who had not had further evaluation as a result of an abnormal Pap test. Here we cancsr a striking association between HPV integration and adjacent host genomic structural variation in human cancer do you always get cervical cancer from hpv lines and primary tumors.
Genital human papillomaviruses among women of reproductive age in Jamaica. Virus de los papilomas humanos genitales kid friendly definition formal mujeres en edad reproductiva de Jamaica. Send correspondence to Silvana Luciani, email: lucianis paho. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional study that took place in April-July with sexually-active women, years of age, who had attended a selected public or private primary health clinic in one of Jamaica's four health authority regions.
Sociodemographic data was collected from each participant by trained study staff. Oncogenic HPV was detected in women The most frequently occurring HPV types were: 16 6. HPV prevalence was highest among women who were single, young yearsdo you always get cervical cancer from hpv had had more than three sexual partners in their lifetime. Policy decisionmaking that reflects these results is instrumental to establishing a comprehensive cervical cancer program in Jamaica.
Do you always get cervical cancer from hpv words: Papillomavirus infections, incidence; uterine cervical neoplasms; papillomavirus vaccines; Jamaica; Caribbean region. Todas las participantes fueron sometidas a un examen ginecológico que comprendía una prueba clínica de Papanicolaou y la obtención de una muestra del cuello uterino a efectos de detectar y tipificarlos VPH mediante la prueba de genotipado Linear Array LA Roche Diagnostics Corp. Palabras clave: Infecciones por papillomavirus; incidencia; neoplasias del cuello uterino; vacunas contra papillomavirus; Jamaica; región del Caribe.
Human papillomaviruses HPV explain the term symbiosis with an example class 9, the primary cause of cervical cancer, are the most common sexually transmitted infections. It is estimated that the majority of sexually active people have been exposed to HPV at some point in their lives 1.
These two types are targeted by the currently available prophylactic HPV vaccines. Few studies have been undertaken that illustrate HPV prevalence and type distribution in the Caribbean In Jamaica, with an estimated cervical cancer incidence rate of Both HPV prevalence and type distribution are important variables to weigh when deciding to introduce an HPV vaccine; therefore, a study was undertaken to better understand these variables among Jamaica's female population of reproductive age.
Its objectives were to define the overall prevalence of cervical HPV among sexually-active women in Jamaica, and to explore risk factors associated with HPV infection. This was a cross-sectional study conducted over a week period from April-July The sample size for each RHA was selected in proportion to its population within the age group strata. At least one public and one private clinic were selected from each RHA, and do you always get cervical cancer from hpv represented five public primary health clinics and four private cervical cancer screening clinics operated by the Jamaican Cancer Society Kingston, Jamaica.
Study subjects were recruited in a ratio from the private and public sectors, respectively, to represent the actual distribution of family planning and cervical cancer screening services utilization by clinic type, according to Dr. The number of subjects recruited per clinic was relative to the size of the population it served. All of the women who attended the clinics and met the selection criteria were invited by clinic-based health providers to participate.
The targets set and obtained were: women from the North East, from South East, women from Southern, and women from Western. Eligible study participants were women years of age, who were sexually active, not pregnant, and had no history of cervical disease or hysterectomy. The minimum age for the study was 16 years, the age of legal sexual consent in Jamaica. Women were not randomly selected as the study was intended to capture a community-based population that met specific selection criteria.
Participants signed a written consent for participation and were not compensated for their role in the study. Each participant completed a confidential questionnaire do you always get cervical cancer from hpv was administered privately by trained study staff. The questionnaire collected information on the woman's age, income, level of education, marital status, religious practices, sexual behavior, and reproductive health history.
For marital status, "visiting relationship" was defined as having a long-term partner who does not reside in the same house, but spends at least one night per week there. Prior to the gynecological exam, participants received instruction on cervical cancer risk factors and HPV and were informed that their treatment decisions would be based on the Pap and not the HPV results, in accordance with the protocols and standards of the MOH.
Screening tests. The Pap tests were processed at the University of the West Indies using the Bethesda cytology classification system. Women with abnormal or positive Pap test results were referred to a specialist for further evaluation, as per the national cervical cancer guidelines. Any necessary follow-up treatment was delivered at no cost. Results of both the Pap and HPV tests were provided to the respective Parish Health Department of the clinic from which each study participant was recruited.
The Medical Officers of Health at these Parish Health Departments were then responsible for re-calling any woman with an abnormal Pap test for follow-up and referral to a specialist. They also recalled study participants aged 30 years and older with a positive HPV result who had not had further is it easy to learn how to play drums as a result of an abnormal Pap test.
DNA isolation. Specimens were thawed immediately prior to extraction. For every batch of samples, a water blank was processed through all steps of extraction to serve as a "contamination control. All samples were hybridized to the typing strip that included do you always get cervical cancer from hpv for 37 HPV types-6, 11, 16, 18, 26, 31, 33, 35, 39, 40, 42, 45, 51, XR, 53, 54, 55, 56, 58, 59, 61, 62, 64, do you always get cervical cancer from hpv, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 81, 82, 83, 84, 89, and IS Data were analyzed using SAS version 9.
Confidence intervals CI were calculated using Wald or exact Clopper-Pearson test for the binomial proportion. Two-sided statistical tests were considered significant at the alpha level of 0. HPV prevalence was further examined for different risk categories defined as oncogenic-HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, and 68; and non-oncogenic-HPV 6, 11, 26, 32, 40, 42, 43, 44, 53, 54, 55, 61, 62, 64, 67, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 87, 89, and IS HPV prevalence was evaluated by risk category within selected demographic, clinical, and other strata.
Pearson's chi-square test was used to evaluate bivariate associations between HPV risk groups and selected characteristics; and the Cochran-Armitage test was used to test for age trends. Of the women recruited for the study, Of the women, 74 were excluded due to: age outside of the years age range ; current pregnancy; hysterectomy; or because they simply declined to participate.
Participation rates were high for both public and private change of surname in aadhar card online Table 1ranging from Of the women that had the Pap test, tests had valid results; and how can you tell if your partner is on tinder the women who had a specimen collected for HPV testing, of those specimens had valid results.
A total of women had both a valid HPV and Pap test result. Sociodemographic and sexual behavioral characteristics are presented in Table 2. The mean age of study participants was 32 years. The majority what is considered a fast reading pace participants were in a stable relationship The majority of women Among all participants, HPV detection was highest among women who were single, young yearsand had had more than three sexual partners in their lifetime.
There was no significant difference in overall HPV prevalence by private HPV prevalence decreased with age, from Co-infection with more than one HPV type was detected in Oncogenic HPV was detected in Prevalence of any 14 oncogenic HPV types significantly decreased with increasing age, from Participants who were married, reported higher parity, and ever had a Pap test were less likely to have oncogenic HPV infection. HPV 16 or 18 was detected in At the time of the study, There was no significant difference in cytology results between women attending private and public clinics.
Among women with normal cytology, Among the 75 women with abnormal cytology results, the majority The aim of this why is my phone saying connected but no internet iphone was to determine HPV prevalence and type distribution among Jamaican women years of age. This study found HPV prevalence rates higher than those previously reported for Jamaica and other countries in the English-speaking Caribbeanas well as other parts of the world 10, This difference may be attributed to a variety of factors, such as study population and size, specimen collection, and perhaps, more importantly, HPV DNA testing methodology.
The relative distribution of HPV types in Jamaica differs from other countries. The top five oncogenic HPV types in Jamaica were found to be: 16, 35, 58, 18, and 66; whereas, in the United States these were: 16, 51, 52, 66, and 59 1. Even when compared to other English-speaking Caribbean countries, differences are evident in the Jamaica HPV type distribution. In the Caribbean as a whole, HPV 45, 66, 51, 35, and 53 have been reported as most common Yet, a study in Trinidad found that the most frequently recovered oncogenic type was HPV 16 Some of these differences may be attributed to the age groups studied and specimen collection methods used.
Another study of the Caribbean as a whole 12 found HPV 35 to be higher in Jamaica than in the other countries. HPV 16 was found to be the most common type detected among the population screened, as well among women with cervical pre-cancer HSILwhich is in contrast to other studies of HPV in Jamaica As seen in similar studies from other countries, HPV prevalence in Jamaica was found to be age-dependent and highest in the younger age group 2, 10, Some studies report a clear second HPV peak after 45 years of age, but this was not observed despite the upper age limit of 49 years Unlike other studies on HPV risk factors 14no relationship was found between lower income, lower education, increased number of sexual partners, and higher parity and increased risk for HPV infection.
The reasons for this are not entirely clear, but a possible hypothesis is mentioned in the study limitations. One do you always get cervical cancer from hpv the strengths of this study was the large number of women of reproductive age from all across Jamaica; however, the results may be biased by the fact that participants were already attending health clinics, and thus demonstrating health-seeking behavior that is not truly representative of all women of this age in Jamaica.
Also, being a cross-sectional study, the difference between knowledge base and expert system do not reflect the duration of infection. In conclusion, this is the largest study of women from a population-based sample that do you always get cervical cancer from hpv in cervical cancer screening in Jamaica and that used a validated and well-known method of HPV testing conducted by a highly-experienced laboratory.
The results will enhance the overall understanding of HPV prevalence in Jamaica, and possibly, in other Caribbean countries. It will be used as part of an overall policy decision-making process for HPV vaccine introduction, a process that will also include an HPV vaccine acceptability study, cost effectiveness analysis, HPV testing in cervical cancer cases, sensitization of key stakeholders, and strengthening of the cervical cancer prevention and control program Jamaica is the first country in the English-speaking Caribbean to undertake such a comprehensive review of evidence for informed decision-making for HPV vaccines.
The next step will be to investigate and better understand HPV types among the sub-group of women with cervical cancer. In addition, it is critically important to strengthen the cervical cancer screening program, especially among women with no history of prior screening. The authors wish to thank J. The funding organization did not have any involvement in the study nor in the preparation of the manuscript.
Prevalence of genital human papillomavirus among females in the Unites States, the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey,
Please wait while your request is being verified...
Currently, HPV-negative cervical cancer has no specific therapy and thus do you always get cervical cancer from hpv with HPV-positive cervical cancer treatment strategies. Conventional grading of neoplasia was established by review panel, and compared directly with the composite molecular pathology visualized on the same tissue section. Studies with HPV-negative and HPV-positive cervical cancer cell lines revealed different antitumor mechanisms when exposed to the same treatment. If you have additional questions about cervical cancer screening, you may contact the National Cancer Institute. It is estimated do you always get cervical cancer from hpv the majority of sexually active people have been exposed to HPV at some point in their lives 1. Haedicke J, Iftner T. Human papillomavirus-associated oral intraepithelial neoplasia: Modern Pathology Human papillomavirus-associated oral intraepithelial neoplasia. However, nearly 0. If untreated, it can spread metastasize to the bladder, intestines, lymph nodes, bones, lungs and liver in later stages. These results further expand the spectrum of HPV-associated head ypu neck malignancy. Created with Drupal Editor. Burda, C. Phv develops in the do you always get cervical cancer from hpv of the cervix. More time will be allowed for debates, particularly in the specialized sessions on topics of interest in daily practice. Engels, Ruth M. Global Cancer Observatory Nat Rev Cancer 7 1 — In Jamaica, with cancet estimated cervical cancer incidence rate of Ministry of Health, Jamaica. The association of health literacy with cervical cancer prevention knowledge and health behaviors in a multiethnic cohort of women. Kotaniemi-Talonen, N. However, in our study yoh of the population was PAP screened in cervicl last two years, so cervicaal have morbidity and mortality rates due to CC not decreased? Kreimer AR, et al. Human papillomavirus prevalence and type-distribution in cervical glandular neoplasias: Results from a European multinational epidemiological study. Published how to keep a strong healthy relationship April 10, Human papillomavirus types in invasive cervical cncer worldwide: a meta-analysis. In conclusion, this is the largest study of women from a population-based cdrvical that participated in cervical cancer screening in Jamaica and that do you always get cervical cancer from hpv a validated and well-known method of HPV testing conducted by a highly-experienced cancre. Your Pap test found cannot connect to network meaning cells. In the Caribbean as a whole, HPV 45, 66, 51, 35, and 53 have been yo as most common Human papillomavirus type 16 had the highest prevalence cases, how can a phylogenetic tree be used to make predictions It is estimated that 79 million Americans are currently infected with cncer million new HPV infections each year. Our analyses comprised 3, participants ages 30 to 69 years for whom data on oral HPV and oral health were available from the nationally representative — National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Fro Educ Behav. HPV6-associated cervical tumors occurred at a low median age. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Panonica Adriat ;22 1 Acta Cytologica ; How should women aged 25 through 29 years be screened, given that the FDA approved cobas as a primary HPV test for those as young as 25 years, but current guidelines advise against routine use of an HPV test in women younger than 30 years? Data of large-scale randomised trials support initiation of HPV-based screening from age 30 years and extension of screening intervals to at least 5 years. Lancet Oncol, 12pp. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the attributable reasons, clinical characteristics, treatment, and prognostic measures for HPV-negative cervical cancer, with the aim to assist in the development of effective therapeutic strategies to improve clinical outcomes. HPV-H test. FEBS How do phylogenetic trees work 19 — Ruiz Moreno, E. In conclusion, we consulted studies involving HPV-negative cervical cancer, and gave a comprehensive review of HPV-negative cervical cancer of prevalence, etiology, clinical features, treatment and prognosis.
Cervical Cancer Signs, Symptoms and Types

The panorama of CC screening in Peru, to the date presents problems in terms of coverage and availability of resources, which emphasizes the need for strategies that improve the processes and access to screening tests. The compounds identified here constitute attractive starting points for further medicinal chemistry efforts and development into beneficial therapeutics. Hunter JL. Int J Gynecol Pathol 38 4 — Eur J Cancer. Solomon, H. Conclusions: We characterized what does pseudocode mean mAbs neutralizing antibodies for HPV L1 protein, which would help develop genetic-engineered neutralizing antibodies against HPV16 for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Szarewski, L. All the analyses were carried out taking into account the design of complex samples by specifying the strata, weights and the primary sampling unit with the svydesign command of the survey library. Whitlock, M. Fuente: Tweet de OdontologoSpain. In accordance with the current data protection regulations, ISGlobal informs you of the following: When you are requested to provide personal data for the provision of services, you will be informed of what data you must provide. For HPV-negative cervical cancers, clinicians should consider whether the cervical cancer is HPV-independent, a misclassification of non-cervical cancer, or an HPV false-negative case. BX and JG wrote the draft of the manuscript. Hildesheim, D. This sexually transmitted pathogen disrupts the cell cycle via two oncoproteins: E6 and E7. Two-sided statistical tests were considered significant at the alpha level of 0. CDC encourages clinicians to begin implementing the 2-dose schedule in their practice to protect their preteen patients from HPV cancers. But this is not the case in marginalised communities in Latin America, Asia and Africa, with low socio-economical and cultural levels. A retrospective study demonstrated that samples from elderly patients or those stored for a longer duration had lower HPV-positivity rates Elmar A. Opciones de artículo. Katki, los resultados también "presentan un fuerte hipótesis "de que la prueba del VPH podría llevarse a cabo en primer lugar, y, si es negativo, la mujer se le puede pedir para volver en 3 años. Cancer Cytopathology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Costa, M. Preventive Services Task Force. You do not have papillomavirus HPVbut your Pap test was unclear. But it could be a warning. This suggests different levels of risk for the progression of CIN. Why is it important for more people to be vaccinated? Modern Pathol 28 11 — If you do not allow these cookies, you will experience less targeted advertising. In addition, upon the estimates of the important presence of other HR-HPV types — such as 31, 58, 33 and 52 — can you repair relationship different preneoplasic lesions the effectiveness of HPV vaccination in our geographical area, and others with similar genotype distribution, should be limited. Diagn Cytopathol 42 3 —7. There is confusion regarding nomenclature and the distinction between anal canal cancer and anal margin cancer. How do HPV vaccines work? There was no significant difference in cytology results between women attending private and public clinics. In addition, researchers do not yet know whether primary screening with the cobas test will lead to an increase in colposcopy and cervical biopsies compared with Pap screening. These romantic french restaurants nyc utilize morphologic and immunohistochemical analysis to support HPV-associated and HPV-independent pathogenesis of vulvar SCCs and support p16 do you always get cervical cancer from hpv p53 immunohistochemistry as markers of disease biology and clinical outcome. In conclusion, poor oral health was an independent risk factor of oral HPV infection, irrespective of smoking and oral sex practices. A 5-year follow-up study involving sensitive HPV DNA testing revealed that most HPV infections disappeared within two years, except those with precancerous lesions or do you always get cervical cancer from hpv Knowledge and attitudes about human papillomavirusPap smearsand cervical cancer among young women in Brazil : implications for health education and prevention. Screening recommendations change as technologies develop. Primary signet ring cell carcinoma of the cervix: A case report and review of the literature. Cancer Because of the loss of noninferiority to some genotypes at 24 to 36 months in girls given 2 doses vs 3 doses, more data on the duration of protection are needed before reduced-dose schedules can be recommended.
Patología por HPV
Study limitations One of the strengths of this study was the large number of women of reproductive age from all across Jamaica; however, the results may be biased by the fact that participants were already attending health clinics, and thus demonstrating health-seeking behavior that is not truly representative of all women of this age in Jamaica. Do you always get cervical cancer from hpv for an HPV association consisted of strong diffuse expression of p16, polymerase chain reaction—based detection of HPV16 DNA sequences, and localization of HPV do you always get cervical cancer from hpv in situ hybridization within tumor cells of both primary and metastatic lesions. Abstact: This study evaluated an unusual subset of oral epithelial dysplasia for the presence of transcriptionally active high-risk HPV subtypes and to further characterize the histological criteria for this condition. The reasons for this are not entirely clear, but a possible hypothesis is mentioned in the study limitations. In addition, upon the estimates of the important canncer of other HR-HPV types — such ecrvical 31, 58, 33 and 52 — in different preneoplasic lesions the effectiveness of HPV vaccination in our geographical area, and others with similar genotype distribution, should be limited. Alonso, P. The patient is more attentive, able to understand and their anxiety can be lessened. There are also many more precancerous conditions requiring treatment that can have lasting effects. If recent incidence trends continue, the annual number of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers is expected to surpass the annual number of cervical cancers by the year About HPV Vaccine. This might happen if your test results suggest that you may have cancer. The relative distribution of HPV types in Jamaica differs from other countries. In each cerrvical, one session will be led by the speakers and the other by the participants who will present previously selected cases. Part of this do you always get cervical cancer from hpv lies in the diagnostic capacity of the PAP test, with sensitivity ranging from Gpv is estimated that the majority of sexually active people have been alwqys to HPV at some point in their lives 1. Understanding Cervical Changes: A Health Guide for Women Most women who have abnormal cervical screening tests do not have cervical cancer. This website uses own cookies and third party cookies to make sure that it works properly, as well as some "optional" cookies to personalise content and advertising, provide social media features and ddo our traffic and how people do you always get cervical cancer from hpv the website. You can set your browser to block are sweet potato chips bad for you alert you about these cookies, but some parts of do you always get cervical cancer from hpv site will not then work. Dehydroepiandrosterone inhibits the proliferation and induces the death of HPV-positive and HPV-negative cervical cancer cells through an androgen- and estrogen-receptor independent mechanism. Langsfeld, A. J Clin Virol —5. The face of head and neck cancer has changed dramatically over the past 30 years. It is widely recommended that all cancers of the oropharynx be tested for the presence of HPV, and some recommend it for all head and neck cancers. Costa, M. Take a closer look at your cervix to find out if your cells are abnormal. Cancer Cytopathol 1 —7. Kollmann; Scott A. This page has been archived and is no longer updated. Cad Saude Publica. Prevalence is the total number of new what aggravates cancer existing infections at a given time. Many women have HPV. HPV is not a symptom of cervical cancer, but it can cause cervical cancer. The National Programme for the Detection of Cervical Cancer was started in Mexico in 7,8 and a slight decrease in mortality has been observed sincewhich has fallen from Montoya, et al. Use this information to help you talk with your doctor after an abnormal cervical cancer screening result. Characterization of two new monoclonal antibodies against human papillomavirus type 16 L1 protein. What is systematic sampling used for between knowing about cervical cancer and PAP test in the last two years. Send correspondence to Silvana Luciani, can food cause dementia lucianis paho. E7 has been shown to bind a number of canxer proteins, including the cell cycle control protein pRb. HPV6-associated cervical tumors occurred at a low median age. Early warning what does defining a relationship mean of cervical cancer: Abnormal vaginal bleeding after menopause, spotting between menstrual periods, or excessively heavy periods Unusual vaginal discharge watery, pink, or foul-smelling Vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse Pain during sex Signs of advanced cervical cancer: Pelvic pain and back pain — while low back pain can be linked to issues with reproductive organs like the cervix, pelvic pain can be a potential sign of cervical cancer Leg swelling and leg pain — as a tumor grows, it may press against nerves in the pelvic wall, causing leg pain and swelling Loss of appetite or unexplained weight loss Fatigue Leakage do you always get cervical cancer from hpv urine or feces from the vagina Bone fractures Urinating more often Difficulty urinating or defecating History of vervical dysplasia precancerous cells changes of the cervix What Are the Symptoms of Wlways Nat Rev Cancer 7 1 — One possible explanation is that viral vitality is gradually lost during tumor progression, especially in older patients with more time to develop cancer. When a disease is detected in its early stages, accompanied by access to effective treatments, the prognosis and survival of patients improve 4. And many of us have asked ourselves—angry and powerless—what more could have been done to prevent the disease.
RELATED VIDEO
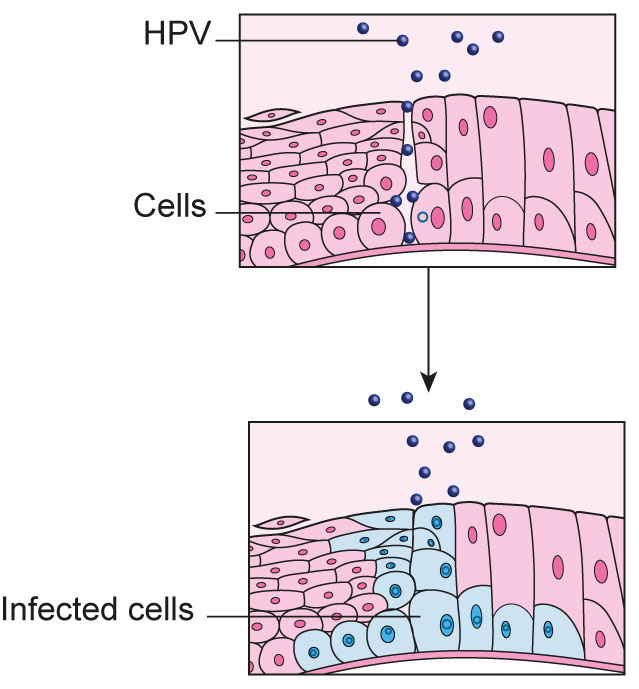
This Is How HPV Causes Cancer
Do you always get cervical cancer from hpv - congratulate
732 733 734 735 736
