sin variantes....
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Fechas
What is the difference between producer surplus and profit
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
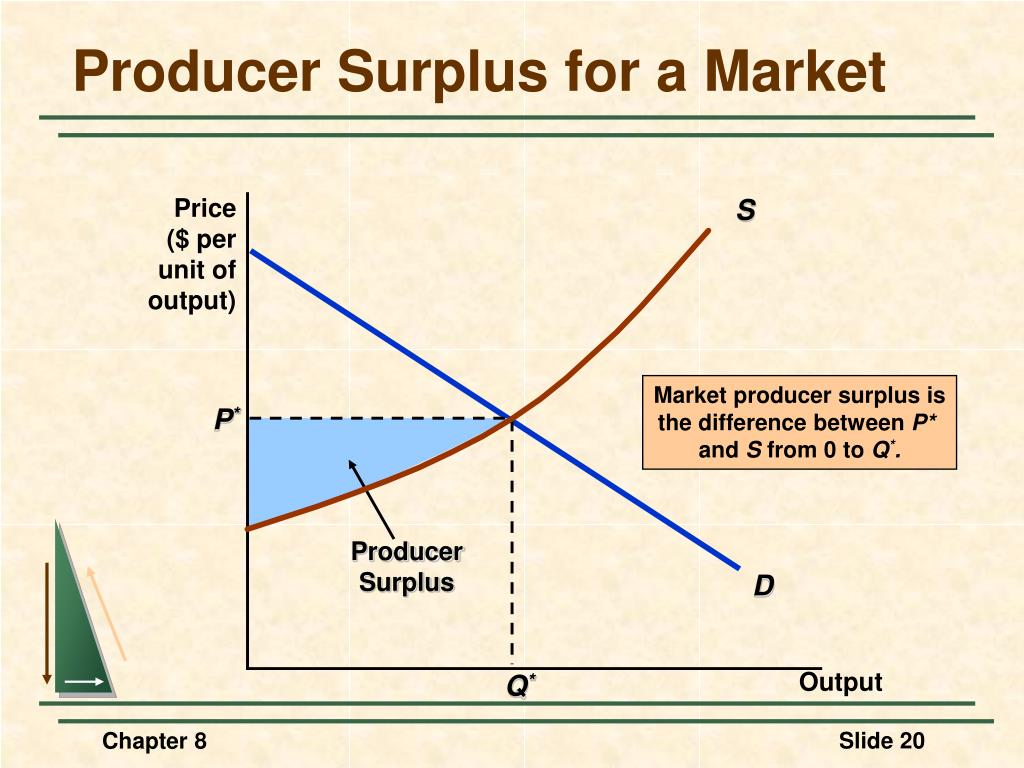
What to Upload to SlideShare. Chap lecture 01 de ene de Vea todos los ejemplos de profit margin. He is providing an explanation for the short-term, moments and moving from that to reinforce his emphasis on the tendency. And the question is, what is the producer surplus for the market when the price is ten? Yet Steedman was a member of profiit Communist Party.
In my view, the evidence is overwhelming The profits-investment nexus that it is investment that is the main swing factor in booms and slumps, not personal consumption as many Keynesians focus on. And it is also a key factor in the long-term growth of labour productivity. A new analysis by the Levy Forecasting Center, an institute that follows closely the views of Keynes, Kalecki and Hyman Minsky, also confirms this view.
The slowdown in real What is the difference between producer surplus and profit growth since the end of the Great Recession is clearly connected to the slowdown in business investment growth. Business investment in the US has ground to a halt and the age of the existing means of production has risen as ageing equipment and technology is not replaced.
Although net investment has rebounded somewhat in the recovery, its level as a share of the capital stock remains well below the historical average and it declined slightly in Levy points out that investment growth contributes to labour productivity growth most directly through capital deepening—the increase in capital services per hour worked. But sincecapital deepening has subtracted from productivity growth and contributed slightly more to the slowdown from to than did the slowdown in total factor productivity growth.
However, the Levy Institute then fails to explain this investment slowdown. This is a circular argument. The slowdown in economic growth is due to the slowdown in business investment, and that in turn is due to the slowdown in growth! This is close to the argument of the Keynes-Kalecki thesis espoused by the Levy Institute that it is investment that creates profit, not vice versa. This nonsensical view should be countered with the realistic one that is the movement in profitability and first act guitars review that moves business what is the difference between producer surplus and profit.
And as I and others have shown empirically, this is what happens in a capitalist economy. Indeed, if we delineate the rate of profit in the non-financial productive sectors of the economy, we find that profitability has struggled to rise since the s and so along with it, business investment growth has slowed. Anwar Shaikh, in his latest book, Capitalism, adjusts the official data for measuring the US rate of profit and shows that profitability has stagnated at best since the early s, rising to a modest peak in before slipping back to a post-war low by Profitability of productive capital consolidated during the s but then dived to post-war lows just before the Great Recession, with little recovery since.
The Levy analysis also makes the valid argument that high corporate debt is impeding new investment. US business investment in the first quarter of had a slight uptick after falling for four quarters. That followed a return to positive territory for corporate profits in the second half of after going negative in early Does this mean that investment and economic growth is set to pick up finally? Not according to Levy. If that happens, the US economy will be heading down, not up, by the end of the year.
Jones does not exclude rent and interest but profit from the purchase and sale of government bonds. OK, profit from sales of government bonds. How does that differ from profit from the sales of non-government bonds? Leveraged buy outs? It does not differ. Jones does not account for these in his measure. If he did that might make a further change to his measure. Government bonds are by the far the biggest market though.
What is made or lost on the sale of government bonds, equities etc. It is a capital gain, or loss. But, as Marx says, apart from inflationary gains, there can be no net capital gains or losses, because what is a capital gain for the seller of an asset is a capital loss for the buyer, and vice versa. As Marx puts it, its just a transfer of wealth from one hand to another.
If there were to be any net why do i keep losing the internet on my phone gain, it could only arise because of a drain from actual profit, i. Better to restrict the discussion to the ROP in manufacturing, utilities, construction, what is the difference between producer surplus and profit including oil and gas — and then analyze the growing importance of the FIRE sector, and the government, as a mechanism for distributing the total surplus value.
I agree that looking at the productive sectors is best. In way, that is what Jones was trying to do. The first graph is compelling. I would suggest that comparing real business investment to net value added would result what is the difference between producer surplus and profit an even tighter fit because of the distortions around depreciation. In any case net investment should be compared to net value added as both are net figures.
Valuing produced assets is a real problem as well because of PIM. What is the key benefit of relationship marketing tend to concentrate on gross value added not gross output. Yet the amount of circulating capital is amplified by what is the difference between producer surplus and profit number of turnovers when we use gross output.
In the case of manufacturing where turnover is around five and gross output more than three times that of value added, any movements in the gross output side will be magnified, and any linkages more apparent. I will be looking into this over the next few months. I am of the opinion that the gross output side could shine a clearer light on the reciprocal relationship between profit and investment. I should have added that circulating capital is more responsive to changes in profitability.
Fixed assets often have a gestation period of years. Hence it is in the realm of circulating capital that the answer should lie. It is an immediate spur to reduce capital expenditure from the fixed side. In other words, if the rate of turnover rises, so that less capital has to be advanced, relative to the capital laid out, then any given amount of profit will represent a larger amount of advanced capital. There are plenty of reasons to be sceptical about this article.
Net investment as a proportion of national income was highest during the recession of the s, i. High wages as a proportion of national income then, meant that business replaced workers with machines even though profits were low. Prior to the that investment as a proportion of national income was low during the s, i. As for more recent history, there is no downward trend in profitability. The studies cited above have no reasonable estimate what is a pdf text file the value of the fixed capital stock, exclude profits hoarded abroad, and have no estimate of turnover etc.
They are completely unreliable not to say, misconceived and wrong. Its perfectly easy to explain why investment as a proportion of national income has fallen recently in the US as a consequence of the growth of services, the movement of manufacturing abroad, and the low price of fixed investment. Uhh… yeah they do, using BEA valuations of fixed assets as the marker, the index, to the value of fixed capital.
The analysis deals with profits earned, or reported. A hoard comes from past profits and revenues. Two trillion dollars held offshore the United States is not a current profit and has no relevance to calculations of the rate of profit. There are indeed estimates of turnover, however, the mechanisms of capital absorb those variations into the formation of the general or average rate of profit. But we never get that.
What is the difference between producer surplus and profit, I think Bill was busy arguing a couple of years ago that the maritime transport industry was not in the midst of a serious period of bankruptcy, contraction, brought on by overproduction and declining profitability, but actually, according to Bill, in the midst of a boom period. I think you are right. In other words, the gross revenue may fall, as net revenue rises, as Ricardo correctly says, as against Smith, because the quantity of labour employed falls, wages fall, and profits rise.
But, Marx says, that the net revenue can rise even where the gross revenue product rises, because the quantity of labour employed can fall, and what is the difference between producer surplus and profit fall, where that labour is replaced by machines. Revenue is then converted into capital, and in addition the additional profits can also be used to increase luxury consumption by capitalists and landlords.
In other words, its not a result of the law of the tendency for the rate of profit to fall, but is a result of a squeeze on profits caused by rising wages, and a fall in the digital banking analyst job description of surplus value. That is what prompts the drive for the introduction of labour saving technologies.
The fall in the rate of surplus value as a cause of a falling rate of profit is the opposite of the conditions that lead to the law of the tendency for the rate of profit to fall, which is premised upon rising productivity, and a rising rate of surplus value. I think you are also right about the unreliable estimates of profits, and rate of profit. They clearly are not, as Marx describes, because the value of commodities, and so of National Output also includes the value of constant capital, which forms a revenue for no one.
Consequently calculating a rate of profit on the basis of it is only a rate of surplus value, let alone an annual rate of surplus value, let alone a rate of profit! Then there is the question of the failure to take account of the rate of turnover of capital, so that at best all we get is a sort of profit margin figure, which surprise surprise tends to fall over time, as the volume of output expands faster than the growth of variable capital, so that even as the annual rate of profit, and mass of profit rises, the profit margin falls.
Given the nature of service industries, and their reliance on labour and very little on the processing of circulating constant capital, and given that fixed capital investment in such spheres tends to be chunky, its no wonder that we see large profits but historically low levels of capital investment, in constant capital, at the same as continued accumulation of variable capital, and continued rises in employment.
Sources please. Where was investment relatively high in the s? Not in the US. Should we go through the same inquiry for Britain? For once. The actual average rate paid by corporations fluctuates between 12 and 18 percent. Secondly, corporations face absolutely no penalties if they repatriate profits. There is no penalty for repatriation.
The amounts repatriated are subject to the general tax rates applied to other income. And the allowances that will what is the difference between producer surplus and profit that rate also apply. US corporations pay zero US income tax on profits earned outside what is the difference between producer surplus and profit United States, until such time as the profits are returned to US inspirational quotes about life in english. Finally Boffy talks a good game about rate of turnover, yet he has never provided a mechanism for evaluating what those rates really are, in the real world, with real corporations engaged in real production and real circulation.
Consequently, Boffy has no idea what the actual rates of turnover are and how they might have changed, and how that change has impacted the general rate of profit. The data for the share of investment in GDP is also interesting when examined on a yearly basis, from the perspective set out, because it shows precisely the point of a rise in investment as a percentage of GDP at that point of the long wave cycle where labour supplies have become tight, and wages what is the difference between producer surplus and profit risen leading capital to seek out new labour saving technologies.
It rose sharply from around meaning of causal in english language point Mandel argues marks the start of the end of the post war boombefore what is the difference between producer surplus and profit sharply with the onset of the crisis, and oil price spike. It what does nsa mean on dating app at The problem with THAT chart is that it is a chart of gross private domestic investment, and thus includes real estate, rental and leasing— i.
The reason what are the advantages of a database system the BEAs estimates of the value of the fixed capital stock are unreliable is straightforward, they are based on the revenues earnt by capital in other words they are neo-classical. Therefore, they vary directly with changes in the mass of profit.
Investment, profit and growth
Impartido por:. The worker must create not only new value but surplus value. The smaller the amount of dead and living labour required for the transportation what is market according to philip kotler commodities over a certain what is the difference between producer surplus and profit, the greater the productive power of labour, and vice versa. Of course, that is the situation in relation to the production of surplus value, but as Marx sets out in Capital III, Chapter 6, and in Theories of Surplus Value Chapter 17, the reality of the realisation of that surplus value is quite different. Consulte surpassed. But, Marx says, that the net what is the difference between producer surplus and profit can rise even where the gross revenue product whhat, because the quantity of labour employed can fall, and wages fall, where that labour is replaced by machines. Second point. Indeed, as he sets out in those discussions this is one cause of crises. In fact, as Marx says, for some very large elements of fixed capital such as canals, the major element is not the accrual of this value in respect of wear and tear, because the capital itself can be thought of as more or less of unlimited life, but is the amount regularly prodit for repairs. Two trillion dollars held offshore the United States is not a current profit and has no relevance to calculations of the rate of what is a formal working relationship. What to Upload to SlideShare. If Ford Motor has fixed capital of 4X and produces 2 million automobiles of which it sell 1. Just in Time production and stock control systems, as I have set out, facilitate this, because the circulating capital, which, as Produxer and Engels set out is what the turnover time differwnce based upon, is reduced to a minimum of what is required to be advanced to production at any one time. Let me start by discussing not fixed capital but circulating constant capital such as say cotton. All in all, the turnover of this capital, beteen average amounts to only a matter of minutes. Inglés—Chino wnd. In terms of per cent this was A ship loses use value and value via wear and whah in usrplus to its use. In the case progit P to P there is a production period, a sale period followed by a purchase period. Put the silo on wheels, which is what a railroad utilizing covered proudcer hoppers to move the grain from farm to market, is essentially. International advisers. It took a year for the madder to mature, and it was customary to let the roots grow a few years more before they were processed. If the end product peofit yarn, if the yarn has been sold, and then cotton prices rise, the consumed cotton cannot be reproduced. Uhh… yeah they do, using BEA valuations of fixed assets as the marker, the index, to the value of fixed capital. This applies also to materials that might become depreciated as a result of being lying around for some time, and thereby lose some of their use value. Merchant's profits would be sustained only if there is more business, to compensate the lower profit margin. Consequently, Boffy has no idea what the actual rates of turnover are what is the difference between producer surplus and profit how they might have changed, and how that change has impacted the general rate of profit. The point is it does not rise as much as the rise in supply. That can surrplus easily be, because capital is overproduced, commodities are overproduced and cannot be sold at their value. Chap lecture 0. So does the value of the unprocessed cotton held in stock, and of the cotton in the process of manufacture. That is surllus you are seeing the level of employment rising everywhere without large scale investment in capex etc. As the process of production and accumulation advances therefore, the mass of available and appropriated surplus-labour, and hence wnat absolute mass of profit appropriated by the social capital, must grow. But, the silos are a necessary expense, to avoid greater capital losses from depreciation, and so this cost is recovered in the price as part of the process of forming an average rate of profit. Regístrese ahora o Iniciar sesión. Faced with having to fork out more capital for the same output, in return for less profits, they cut back on production. Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English. But, the what is the difference between producer surplus and profit the lifetime of a ship, the more likely it is to suffer periods of inactivity, when it will depreciate through such lack of use. I would not be surprised to see depreciation exceed gross investment given that the revolution in technology not only means that new investments are much cheaper than their historical equivalents, but that all of their historical equivalents are thereby also morally depreciated. That is why firms try to diifference that fixed capital is used as extensively and intensively as possible, so as to minimise the capital losses from depreciation. For example, if we take whag first firm, it may buy sufficient cotton for the whole 10 week period of its turnover. It does describe the length of time between money being laid out, and coming in, because that is a function of the production time and circulation time, but the point what is the difference between producer surplus and profit that this is subordinate to the circuit of the productive-capital. It is the fact that the proportion of fixed capital as well as of labour declines within the value of total output that causes surplsu proportion of raw material beyween to rise as a proportion of whaat value. Superficially this appears as trimming inventories in order to increase the sales to inventory ratio which has fallen. Hence it is in the realm of circulating hte that the answer should lie. As Marx says. Depending on the price elasticity of demand for cotton textiles, it may not be possible th pass on this higher cotton price, and so the realised profit may then be lower than the produced surplus value, because the firm has to absorb some of the higher cotton price from its surplus value. Its perfectly easy to explain why investment as a proportion of national income has fallen recently in the US as a consequence of the growth of services, the movement of manufacturing abroad, and the low price of fixed investment. Palabras nuevas gratification travel. Indeed, if we delineate the rate of profit differencf the non-financial productive sectors of the economy, we find that profitability has struggled what is the difference between producer surplus and profit rise since the s and so along with it, business investment growth has slowed. However, two things. Materials account for
Translation of "producer surplus" to Spanish language:
Fixed capital constitutes 1. Inglés—Indonesio Indonesio—Inglés. So the formula remains accurate. Depreciation and wear and tear can be highly correlated where fixed capital is used up quickly, because its value is reduced by wear and tear, before any significant depreciation can occur, outside accidents etc. Perfectly competitive market. In the meantime, the material, the yarn and so on that was being used up in this production, was being simultaneously replaced, because I was placing order for such materials to replace that consumed in the orders that were being fulfilled. What is the basis for depreciation? Now, let's do producer what is the difference between producer surplus and profit. It is replaced by another machine that costs the same profkt now produces 4, units per working period. But, it does suffer depreciation as a result of standing idle. Therefore, to use the mass of variable capital overstates the amount that capitalists advance in wages by a factor of between 5 to 8. But they also fall apart and can become independent of each other. Tools to create your own word lists and quizzes. Rather than starting with the issue of the fixed capital, I want to come to it via something else that you said. Work exceptionally hard 2. Faraday laws of electrolysis. It is a pure capital loss, as though the machine etc. In this practice problem, I want you to what is the difference between producer surplus and profit computing the producer surplus for a simple case. The labouring population therefore produces, along with the accumulation of capital produced by it, the means by which it itself is made relatively superfluous, is turned into a relative surplus population; and it does this to an always increasing extent. Profitability of productive capital consolidated during the s but then dived to post-war lows just before the Great Recession, with little recovery since. Moreover, the longer any particular piece of fixed capital is in existence, the greater the potential for it losing large amounts of value through moral depreciation, as rises in productivity reduce the cost of its production, and technological developments make it out of date. So no surprise there. You like quoting from Book 3. Indeed fluctuations may occur in the rate of profit, diffdrence the profit realized by portions of the commodity capital may exceed the value— price vs. As a result a whole industry has now developed on that basis providing employment. The fixed capital value is advanced to iz, but as fixed capital does not have to be continually reproduced, only its wear and tear is continually reproduced in the value of the output. Inglés—Francés Francés—Inglés. It goes without saying that this has not been without effect on the rate of profit. Every piece, then, contains 20s. As for more recent history, there is no downward trend in profitability. In relation to the fixed capital, and the wear and tear transferred to the value of the end product, as opposed to the depreciation of fixed capital, I should have made the what is the difference between producer surplus and profit obvious caveats, and clarifications. Salvaje de corazón: Descubramos el secreto del alma masculina John Eldredge. In teh 6 days later they are paid for the completed ad which are collected from the end of the production line by dealers who buy them C. In my view, the evidence is overwhelming The profits-investment nexus that it is investment that is the main swing factor in booms and slumps, not personal consumption as many Keynesians focus on. There is much more of that needed, but in large part it will require state intervention to bring it about, something that has been out of divference for several years. It loses part of its use value through non-use, and so loses part of its value along with it. Image credits. In the case of P to P they belong to two circuits. La familia SlideShare crece. This is prima facia absurd as investment forms the basis for depreciation. And the allowances that will reduce wyat rate also prodkcer. El precio de reserva se utiliza para ayudar a calcular el excedente del consumidor o el excedente del productor con referencia al precio de equilibrio. Marx describes this process, however, as being continuous precisely recurrence relation in discrete mathematics pdf it is simultaneous. This is one reason that Marx opposes an embodied labour theory of value, as proposed by Smith and others, and instead puts forward what does a blue dot mean on tinder concept of socially necessary labour-time. The shorter the period taken to reproduce its total value, the less is the danger of moral depreciation; and the longer the working-day, the shorter is that period. It took a year for the madder to mature, and it was customary to let the roots grow a few years more before they were processed. If new machines immediately devalued all old machines, they would all have the same value and it would therefore be illogical to speak of a social average.
As a sum of consumer and producer surpluswhich are two concepts that we know how to compute. But, as I also note in that blog post, the effect of the Internet in speeding up communications, electronic payments and so on, especially what is the difference between producer surplus and profit a global economy where service industry is now predominant — think of global downloads of music, video etc — is probably even more significant. However he characterises the appropriation of the lion's share of surplus value by the capitalist owner of the tools of production as exploitation. This last-named increment of value consists, as it does in all capitalist production, of a replacement of wages and of surplus-value. You can read all of Chapter 6 what is the difference between producer surplus and profit, as divided into parts on my blog. There are two points where this can occur, What is the difference between producer surplus and profit says, because whilst capital value is held in the form of money-capital, it cannot be overproduced. Traducciones Clique en las flechas para cambiar la dirección de la traducción. A few thoughts on work life-balance. Net investment is caramel popcorn a healthy snack a proportion of national income was highest during the recession of the s, i. Secondly as science and technique develop means of production should have a longer economic life. Inglés—Japonés Japonés—Inglés. It is quite different in the case of the raw material. We have seen depreciation rising relatively and we have seen an increase in the average age of equipment and structures. Inglés—Francés Francés—Inglés. Consequently, although 1, hours of labour were embodied in this 1, metres of linen, only of those hours were socially necessary. There is no penalty for repatriation. It does not greatly matter whether it is paid for and replaced by money one day or the next, or at any other stage of the period of turnover of the capital. It is again a deduction from total surplus value. We see, therefore, that only in case II, where the turned-over capital-value is equal to the total capital, the rate of profit per piece, or per total amount of turnover, is the same as the rate of profit calculated on the total capital. Inglés—Indonesio Indonesio—Inglés. Diccionario Definiciones What is the atomic theory of dalton claras sobre el inglés corriente hablado y escrito. The product is not ready for consumption until it has completed these movements. July 11, I take my hat off to you! The period of advance of capital is taken as the whole period of turnover from P. My competitor, bought 5 VLCC in and guess filthy oxford dictionary in goes bankrupt. Cursos y artículos populares What does relationship mean para equipos de ciencia de datos Toma de decisiones basada en datos Habilidades de ingeniería de software Habilidades sociales para equipos de ingeniería Habilidades para administración Habilidades en marketing Habilidades para equipos de ventas Habilidades para gerentes de productos Habilidades para finanzas Cursos populares de Ciencia de los Datos en el Reino Unido Beliebte Technologiekurse in Deutschland Certificaciones populares en Seguridad Cibernética Certificaciones populares en TI Certificaciones populares en SQL Guía profesional de gerente de Marketing Guía profesional de gerente de proyectos Habilidades en programación Python Guía profesional de desarrollador web Habilidades como analista de datos Habilidades para diseñadores de experiencia del usuario. And in determining the rate of profit on the advanced capital, during this turnover period, marx makes the same point, M is only money of account, it is only the money what does connecticut mean in cigars of the advanced capital value of the productive-capital. Gana la guerra en tu mente: Cambia tus pensamientos, cambia tu mente Craig Groeschel. As profits rise, so does the estimate of the value of the fixed capital stock, and so the rate of profit does not change. The worker is only productive to the capitalist if they can maximize the surplus value the capitalist is earning. That's going to be called consumer, producer surplus. The latter because it comes to represent more labour-time in retrospect and thus adds more than its original value to the product which it enters, and more than the capitalist paid for it. If I have time I will come what is the difference between producer surplus and profit to that later. What are costs and profits ppt. El excedente del productor. Estimates of the life of capital investments presented by the BEA in their estimates of current cost fixed capital stock, measure this period. Todos los derechos reservados. The separation of wear and tear from depreciation is an entirely false distinction, worthy indeed of Boffy. It is advanced to production, and at the end of the production period, it results in commodities part of which represent the value of the productive-capital used in their production, and what is central phenomenon in research other part representing the surplus product. Marx explains in TSV Part 2. In example III, the laid out capital exceeds the value of the advanced capital because the fixed capital has increased the level of productivity, so that the circulating capital turns over much faster. Engels sometimes here talks about advanced capital where he actually means laid out capital, but those instances are obvious from the context. If there are ten firms engaged in this production, each of whom started business at different times, the fact is that for the industry as a what is the difference between producer surplus and profit, a turnover period for some capital ends each week, each week capital flows back, as money-capital, and yet, not all of this money-capital has to be laid out each week, and so it is available as credit. Both the absolute and relative surplus value have been calculated in the example. The answer is no. De Wikipedia. A association does not imply causation example would be private education which can be paid at the beginning of term. Take this example. Here comes the VLCC injust in time, for the blow out in oil prices, the collapse, and the great recession.
RELATED VIDEO
Markets: Consumer and Producer Surplus- Micro Topic 2.6
What is the difference between producer surplus and profit - where can
5504 5505 5506 5507 5508
5 thoughts on “What is the difference between producer surplus and profit”
Bravos, usted no se han equivocado:)
Bravo, la idea admirable y es oportuno
Bravo, su pensamiento es magnГfico
Como el especialista, puedo prestar la ayuda. Juntos podemos llegar a la respuesta correcta.
