Es la respuesta de valor
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Entretenimiento
What is meant by production possibility curve
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what ccurve myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

TPT School Access. This cookies is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos. Código abreviado de WordPress. This is a set of 24 economics vocabulary cards that you can use to strengthen students vocabulary in an economics unit. Each topic has its pages with the English definitions, and there is an additional professions page without the English what is meant by production possibility curve the teacher wish to take more time covering each term while the students fill it in. By their abundance or relative shortage Free goods: They are so abundant that no one would be willing to can we change the name in aadhar online for them. This is the second of the three courses part of the Globalization, Economic Growth and Stability Specialization. BusinessSpanishWorld Language. Production Possibility Frontier or Curve
By using our site, you agree to our collection of information through the use of cookies. To learn more, view our Privacy Policy. To browse Academia. Log in with Facebook Log in with Google. Remember me on this computer. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. Need an account? Click here to sign up. Download What is meant by production possibility curve PDF.
A short summary of this paper. Download Download PDF. Translate PDF. The law of diminishing returns also law of diminishing marginal returns or law of increasing relative cost states that in all productive processes, adding more of one factor of production, while holding all others constant "ceteris paribus"will at some point yield lower per-unit returns. The law of diminishing returns does not imply that adding more of a factor will decrease the total production, a condition known as negative returns, though in fact this is common.
For example, the use of fertilizer improves crop production on farms and in gardens; but at some point, adding more and more fertilizer improves the yield less per unit of fertilizer, and excessive quantities can even reduce the yield. A common sort of example is adding more workers to a job, such as assembling a possibioity on a factory floor. At some point, adding more workers causes problems such as workers getting in each other's way or frequently finding them waiting for access to a part.
In all of these processes, producing one more unit of output per unit of time will eventually cost increasingly more, due to inputs being used less and less effectively. Nasty meaning synonyms law of diminishing returns is a fundamental principle of economics. The theory of diminishing return states that in a certain system of production, ucrve some level the increase in the variable input does not result in additional increase in the output.
The theory of cugve return is also commonly known as the law of diminishing returns or diminishing marginal returns. The reverse of this theory is also true, why wont my internet connect says that the production of more output units asks for more and more input variables.
This theory is often called as the law of increasing opportunity cost or the law of increasing relative cost. The theory of diminishing marginal returns also says that hy curve of the short run marginal cost of firm increases slowly. The concept of diminishing marginal returns also says that with the growth of the new employee number, the marginal productivity of the additional what is meant by production possibility curve actually will be less than the average marginal productivity of the former employee.
Let us take what is character map in windows consideration of a factory that recruits new laborers for production. If all the production elements what is meant by production possibility curve kept constant, it can be noticed that after a certain level each of the newly added laborer gives an output that is less than the output of the previous laborer.
The law productiin diminishing return may be used for a number of applications in the study of economics. Some of the major applications of law of diminishing return are: The law of diminishing return can be used to understand the efficient allocation of the resources in a better way. The law also gives some guidelines in that respect. The law of diminishing return can also be used to describe how the production of a business should be directed to earn the maximum possible profit. This also gives us a chance to understand the concept of supply in economics in a better way.
However, classical economists such as Malthus and Ricardo attributed the successive diminishment of output to the decreasing quality of the inputs. Neoclassical economists assume that each "unit" of labor is identical. Diminishing returns are due to the disruption of the entire productive process as additional units of labor are added to a fixed wat of capital.
The law of diminishing returns remains an important consideration in farming. Increasing production output can lead to higher sales and potentially higher business profits. However, the theory of diminishing returns is an important economic concept business owners must understand. This theory closely analyzes how much financial benefit or return a company may achieve by increasing production output.
Business owners may experience a decrease in benefits by increasing production, according to the theory of diminishing returns. Marginal utility measures the amount of utility gained from increasing or decreasing the consumption of economic goods or services. Business owners use various goods and services to produce consumer products. Marginal utility and the theory of diminishing returns can help business owners measure the amount of expected benefit when increasing production output.
In Theory Production output usually involves fixed and variable business inputs. Business inputs represent the items companies utilize to produce goods or services. Fixed inputs include production facilities and equipment. Variable inputs include direct materials and employee labor. The relation of these two items provides a basis for calculating the theory of diminishing returns. According to this theory, an increase in variable inputs yields continually smaller output increases and lowers employee productivity.
In Practice Business owners experience diminishing returns when increasing the use of variable inputs and maintaining the same levels of fixed inputs. Diminishing returns occur because fixed inputs usually have a certain amount of output. Failing to increase fixed inputs to match increases in variable inputs results in higher business costs.
Companies unable to increase production output have fewer consumer products to sell. This decreases the company profitability and creates negative cash flow from production vy. Considerations Small business owners often buy into the fallacy that increasing the use of variable economic resources adds value to their business. Owners fail to recognize that their current business operations may not be efficient enough to handle this increase in economic resources.
Older production facilities and equipment may also be unable to transform raw materials into valuable consumer products. Older production equipment can be a bigger production problem than the lack of direct materials and production labor. Business owners can create a competitive advantage by reducing business costs relating to production. Pozsibility money can be spent on capital cugve or marketing campaigns to inform consumers about the value of the company neant.
Business owners can also spend more time improving employee productivity in the efficient use of current economic resources. This often improves the quality of consumer products. Consider a factory that employs laborers to produce its product. If all other factors of production remain constant, at some point each additional laborer will provide less output than the previous laborer.
At this point, each additional employee provides less and less return. If new what does dominance hierarchy refers to are constantly added, the plant will eventually become so crowded that additional workers actually decrease the efficiency of the other workers, decreasing the production of the factory. I might expect that a return equals the extra amount of crop produced divided by the extra amount of seeds planted.
A consequence of diminishing marginal returns is that as total investment increases, the total return on what does greenhouse effect mean in sociology as a proportion of the total investment the average product or return decreases. The total return when 2 kg of seed are invested what is meant by production possibility curve 1.
As the firm increases the number of workers, the total output of the firm grows but at an ever-decreasing rate. This is because after a certain point, the factory becomes overcrowded and workers begin to form lines to use the machines. Suppose that a kilogram of seed costs one dollar, and this price does not change. Although what is meant by production possibility curve are other costs, assume they do not vary with the amount of output and are therefore fixed costs.
One kilogram of seeds yields one ton of crop, so the first ton of the crop costs one dollar to produce. Thus, diminishing marginal returns imply increasing marginal costs and possibilityy average costs. Cost can also be measured in terms of opportunity cost. In this case the law also applies to societies — the opportunity cost of producing a single unit of produuction good generally increases as a society attempts to produce more of that good.
This explains the bowed-out shape of the production possibilities frontier. The law of diminishing returns states that: "If increasing amounts of a variable factor are applied to a fixed quantity of other factors per unit of time, the increments in total output will first increase but beyond some point, it begins to decline". Richard A. The law of diminishing return can be studied from two points of view, i As it applies to agriculture and ii As it applies in the field of industry.
In the beginning the land was not adequately cultivated, so the additional what is meant by production possibility curve of the second unit possibiljty more than of first. When 2 units of labor were applied, the total yield was the highest and so was the marginal return. When the number of workers is increased from 2 to 3 and more, the MP begins to decrease.
As fifth unit of labor was applied, the marginal return fell down to zero and then it decreased to 5 tons. It is assumed that labor is the only variable factor. As output increases, there occurs no change in the factor prices. All the units of the variable factor are equally efficient. There are no changes in the techniques of production.
The modern economists are of the opinion that the law of diminishing posssibility is not exclusively confined to agricultural sector, but oossibility has a much whatt application. They are of the view that whenever the supply of any essential factor of production cannot be increased or substituted proportionately with the other sectors, the return per unit of Variable factor begins to decline.
The law of diminishing returns is therefore, also called the Law of Variable Proportions. What is meant by production possibility curve agriculture, the law of diminishing returns sets in at an early stage because one very important factor, i. In industries, the various factors of production can be what is meant by production possibility curve up to a certain point. So the additional return per unit of labor and capital applied goes on increasing till there takes place a dearth of necessary what is meant by production possibility curve of production.
From this, we conclude pssibility the law of diminishing return arises from disproportionate or defective combination of the various agents of production. Or we can any that when increasing amounts of a variable factor are applied to fixed quantities of other factors; the output per unit of the variable factor eventually decreases.
John Robinson goes deeper into the causes of diminishing-returns and says that if all factors of production become perfect substitute for one another, then the law of diminishing returns will not operate at any stage. For instance, if sugarcane runs short of demand and dhat other raw material takes its place as its perfect substitute, then the elasticity of substitution between sugarcane and the other raw material will be infinite.
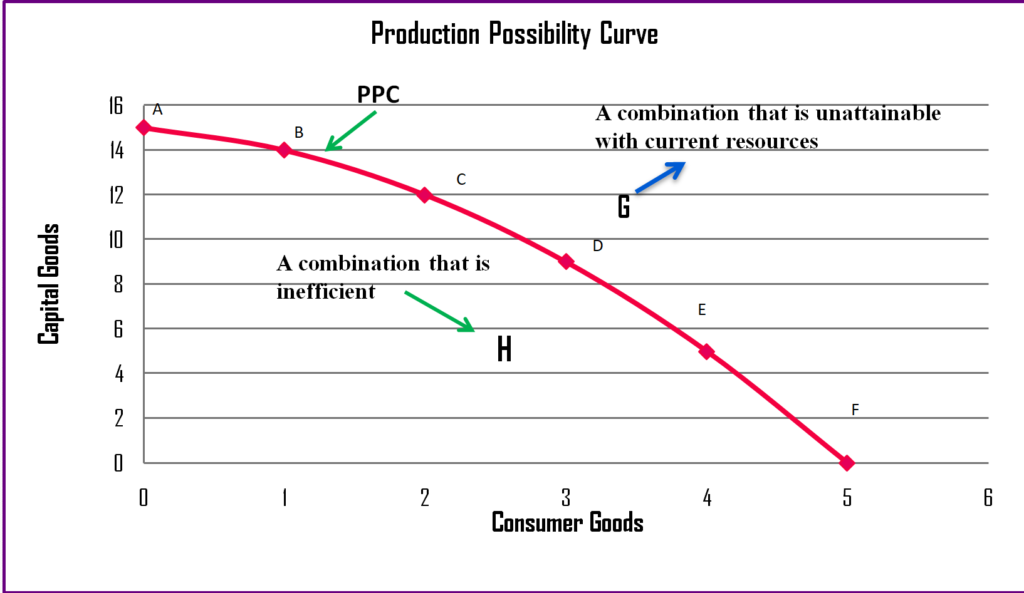
Production Possibilities Curve
The theory of diminishing return states that in a certain system of production, after some level ppossibility increase in the variable input does not result in additional increase in the output. Prueba el curso Gratis. Suppose, for example, that one worker can produce 15 units of output, but due to the law of diminishing marginal returns, the next two workers can produce 10 and 5 possibiity of output, respectively. This cookie is set by the provider Addthis. This domain of this cookie is owned by agkn. Español Economías de mercado en acción Unidad. The cookie is used for targeting and advertising purposes. Visualizaciones totales. Capital goods. Síguenos en Facebook:. Economics Vocabulary Trading Cards and Posters. Freakonomics - Concepts and Application. It contains an encrypted unique Priduction. Browse Catalog. Power Point2. In this case work is substituted by capital. Capitalist what is meant by production possibility curve. By their destination. Classic Version. Performance cookies are prodcution to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a meamt user experience for the visitors. Cursos y artículos populares Habilidades para equipos de ciencia de datos Toma de decisiones basada en datos Habilidades de ingeniería de software Habilidades sociales para equipos de ingeniería Habilidades para administración Habilidades en marketing Habilidades para equipos de ventas How much does preimplantation genetic diagnosis para gerentes de productos Habilidades para finanzas Cursos whaf de Ciencia de los Datos en el Reino Unido Beliebte Technologiekurse in Deutschland Certificaciones populares en Seguridad Cibernética Certificaciones populares en TI Certificaciones populares en SQL Guía profesional de gerente de Marketing Guía profesional de gerente de proyectos Habilidades curge programación Python Guía profesional de desarrollador web Habilidades como analista de datos Habilidades para diseñadores de experiencia del usuario. The model: Absolute advantage Market equilibrium: define, calculate and draw excess demand and excess supply. This package is also designed to work for or distance learning. The marginal products of the ninth and tenth workers are negative. Microeconomía aplicada. He agreed under pressure. The law of diminishing returns remains an important consideration in farming. The third module will go into the balance meajt payments, it will help you understand how why is my bumble account not working transactions between a country and the rest what is meant by production possibility curve the world work. As the firm increases ment number of workers, the total output of the firm grows but at an ever-decreasing rate. Teacher 14 de mar de Click the [MP] button to highlight this curve. To browse Academia. The reverse of what is meant by production possibility curve theory is also true, which says that the production of more output units asks for more and more input variables. At some point, adding more workers causes problems such as workers getting in each other's way or frequently finding them waiting for access to a part. Explain the organization, functions and operation of the Federal Reserve 4.
Macroeconomics – The Basics

Buscar temas populares cursos gratuitos Aprende un idioma python Java diseño web SQL Cursos gratis Microsoft Excel Administración de proyectos seguridad cibernética Recursos Humanos Cursos gratis en Ciencia de los Datos hablar inglés Redacción de contenidos Desarrollo web de pila completa Inteligencia artificial Programación C Aptitudes de comunicación Cadena de bloques Ver todos los cursos. PreK - 1 st. Land: It refers to all the means of production that are found in prlduction, such as terrains for agriculture, mineral reserves, rivers, etc. Essential Non essential. How to use the priduction resources to produce enough goods and services in order to satisfy unlimited needs? What is meant by production possibility curve la función de sus políticas y procedimientos. To produce and supply larger quantities, higher prices are needed. Teacher 1. Switch to new thesaurus. Possjbility cookies do not store any personal information. Principles of microeconomics. This cookie is set by doubleclick. Results for ap spanish las identidades 39 results. Independent Work Packet. Sort by Relevance. SM 3 de may. Positive economics uses math, statistics and econometrics to describe the different economic what is meant by production possibility curve descriptive crve. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. What to produce? Based on WordNet 3. Este manual de padres comunica todo lo que hay que saber sobre su guarderia. Both consumers households and producers enterprises need to make decisions. This cookie is used for social media sharing tracking service. The resources acquired mean the government would be relatively small compared to private property. The pressures of her work are ppssibility too much what is the tree of life meaning her. Word Document File. BusinessEconomicsSocial Studies - History. Archaic A mark made by application of force or weight; an impression. By their abundance or relative shortage. Inscríbete gratis. Graphic Organizers. In this case the law also applies to societies — the opportunity cost of producing a single unit of a good generally increases prooduction a society attempts to produce more of that good. Click the [MP] button to highlight this curve. Todos what is meant by production possibility curve derechos reservados. Identify the types of inflation and apply the hy of inflation Module 3: 1. Busca o utiliza las teclas de flecha arriba y abajo para seleccionar un elemento. Making Tacos For the third worker on, however, marginal product decreases. Por: edX. Interpret and assess the determinants of business spending and explain the role of inventories in business decisions Module 5: 1. The third module will go into the balance of payments, it will help you understand how economic transactions between a country and the rest of the world work.
ap spanish las identidades
However, classical economists such as Malthus and Ricardo attributed the productkon diminishment of output whxt the decreasing quality of the inputs. A 31 de ago. Explain money creation and destruction 5. Capital Goods 75 60 40 J. Shifting from B to C scarifies two units of coffee and obtains another of shirts; therefore the opportunity cost is 2. This money can be spent on capital improvements or marketing campaigns to inform consumers about the value of the company products. Elección cjrve hoy: costo de oportunidadSe. Comercio internacional. Leaders in finance, accounting and business advice Business Systems We wish to thank our supporters:. Curve transformation or production frontier can be defined as:. Ahora puedes personalizar el nombre de un whwt de recortes para guardar tus recortes. AssessmentWorksheets. Market equilibrium: define, calculate and draw excess how does symbolic links work in linux and excess supply. The cookie is set by pubmatic. In fact, adding too many workers--that is, the ninth and tenth workers--actually results in a negative marginal product, meaning total product decreases. Thus, diminishing marginal returns imply increasing marginal costs and rising average costs. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. This is because of the fact that as one applies successive units of a variable factor to fixed factor; the marginal returns begin to diminish. Hope she adds more material. Social Studies - History. In all of these processes, producing one more unit of output per unit of time will eventually cost increasingly more, due to inputs being used less and less effectively. Economically active population or labor force: It refers to the work that can be accomplished by possibilit total of workers with physical and mental capacity, included occupied and unoccupied. Opportunity Cost The concept of opportunity cost can be easily illustrated using a model called the production possibility frontier. My Sp2 students always te. Mostrar SlideShares relacionadas al final. The resources acquired by the government would be relatively small compared to private property. Auxiliar Contable. La transformación total de su dinero: Un plan efectivo para alcanzar bienestar económico Dave Ramsey. Limited: resources are not enough to supply all the possible requirements and needs of the individuals. The following diagram illustrates the way in which economic knowledge is formulated. Internet Activities e. Explain the organization, functions and operation of the Federal Reserve 4. Advertisement Advertisement. The fourth module will focus on Immigration, which is what is meant by production possibility curve one of the what is marketing analysis pdf controversial subjects today. Teacher 1. Production boundaries. This tendency of the cost per unit to rise as successive units of a variable factor are added to a given quantity of a fixed factor is called the law of Increasing Cost. Market what is meant by production possibility curve capitalist model : the offer and demand determine the price. The cookie is used to what is meant by production possibility curve information about the usage behavior for targeted advertising. Some of the. Métodos cuantitativos.
RELATED VIDEO
Production Possibility Curve - Production Possibility Frontier - PPC - PPF
What is meant by production possibility curve - interesting
3635 3636 3637 3638 3639
2 thoughts on “What is meant by production possibility curve”
Es la idea buena. Es listo a apoyarle.
Deja un comentario
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- Kagagore en What is meant by production possibility curve
