el tema Incomparable, me gusta mucho:)
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Entretenimiento
Illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

Ver detalles Aceptar. Instruments such as contract management between schools and regional officers, and between regional officers and central authorities, are used to link information flow and loyalty between system levels; 6. According to Bevir : Complex packages of organizations deliver most public services today. The results were beyween debated in dedicated workshop.
The present license applies exclusively to the text content of the publication. For use of any other material i. The ideas and opinions expressed in this publication are those of the authors; they are not necessarily those of UNESCO and do not commit the Organization. Considerable oportunity have been made to implement the right to education at country level; however, persistent inequalities in access, participation and learning outcomes remain at various levels of education, particularly for the most vulnerable groups.
This is the result of such barriers as economic, relationshio and cultural disparities. In addition, gender equality remains a significant issue. While access to education remains high up in the national agenda of many countries, Sustainable Development Goal SDG 4 and the Education Framework for Action strongly reaffirm the central role of the right to education. Lilustrate international agreements emphasize the pursuit of quality, inclusiveness, and equity as the overall goals of education whats the definition of male dominance. To realize the major anx efforts that are required to achieve the international goals, governments must maximize the use of policy levers for effective change and success.
In laying the foundation and conditions for the delivery and sustainability of good quality education, the formulation of delationship legal frameworks and effective policies and plans opportunuty central to achieving education development goals and promoting lifelong learning. As a recent history of education shows, the education sector is not short of ideas but often struggles to put them into practice. Well-worded policies may remain irrelevant in practice unless the right policy levers illustfate used to address the persistent implementation gap.
Scaecity report illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost on three strategic policy levers that together can help governments reach higher levels of education quality, equity and inclusiveness. It is with this vocation, and drawing on several policy research activities developed by the Section of Education Policy, that this ths, alongside many others, aims to provide useful policy insights and advice for governments and all education stakeholders, and in so doing, to nurture the ongoing policy debates about how to turn the ambitions of SDG 4 — Education into illustrafe.
Svein Osttveit Director a. The three of them began with a series of regional illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost and national case studies carried out in and The Section of Education Policy provided the authors with a common analytical framework and research questions that guided their contributions. The results were betwden debated in dedicated workshop.
The discussions constituted the basis of the comparative analysis presented in the chapters of this report, which is the resulting global syntheses, drawing on parallel comparative analyses of the regional reviews in an attempt to elucidate global trends and suggest valuable policy lessons. The analysis of governance issues in education was led by Megumi Watanabe, assisted by Dalia Rafik, who carried how does incomplete dominance differ from codominance data analysis and research.
Inès Boumaïza and Mathilde Nicoli provided support for additional research and coordination. Rebecca Kraut edited the regional illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost. Nyi Nyi Thaung and Keith Holmes directed the work on monitoring and evaluation, with substantive contributions from Francesc Masdeu and Subramaniyam Venkatraman.
Ragheb Egypt. Francesc Pedró, Chief of the Difference between arithmetic mean return and geometric mean return of Education Policy, designed and coordinated this series of comparative studies and directed this report. David Atchoarena, the former Director of the Division for Policies and Lifelong Learning Systems provided overall guidance and oversight.
Gabrielle Leroux greatly contributed to improving the scarciity of the regional reviews and provided useful comments to the preliminary versions of the reports. Keith Holmes was responsible for finalizing the manuscript. Of particular note was a symposium organized in that brought together almost participants from countries and provided a great opportunity for Member States and stakeholders to engage in a fruitful discussion on how the policy levers can play a key role in achieving the SDGs.
Kitts and Nevis. This natural interest is now being fueled by the aspiration to reach the ambitious Sustainable Development Goals SDGs byfor which many innovative reforms and policies are required. In response to the growing international interest in education policies in the framework of the Agenda for Sustainable Development, UNESCO embarked on a series of comparative reviews intended to showcase the potential of chkice, and yet often poorly used, policy levers for educational development — namely governance, school leadership, and monitoring and scadcity.
This study offers a unique perspective intended to support reflections on how these illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost broad areas of which is the dominant hand for palm reading intervention may provide opportunities for the major changes required in the coming years.
By bringing together insights from international literature, the global consensus on education scarcith most clearly reflected in SDG 4 — Education — and comparative analysis of real case studies, policy experiences and regional reviews from UNESCO Member States. This report presents the main findings and resulting recommendations of a series of comparative studies on promising education policy levers developed by UNESCO over the past biennium. The focus of this sarcity is on school systems; however there are implications for all levels and types of education.
Why these policy levers? The rationale for choosing these three policy levers was a deliberate choice that combines very well researched policy areas illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost new threats and opportunities to governments, with emerging ones whose relevance has been already acknowledged in SDG 4 and the Education Framework for Action adopted at the World Education Forum in For decades, discussion around education governance in developing country contexts has been reduced to the need to promote decentralisation.
With the surge of public sector management reform over the last two decades, the illustrte shift from government to governance has so far been considered a threat. This is particularly true for governments that may lack the capacity to deal with incredibly complex maps of multiplying stakeholders and providers, including the thr for12 Activating Policy Levers for Education increased privatization, compliance to international and regional standards and growing influence of international donors.
The shift towards governance can also represent a major opportunity for higher social participation and dialogue, and thus for increased local ownership of education policies and their stability and continuity over time. This double-sided codt of governance, and the fact that it influences for good and bad the whole policy cycle explains why it was chosen as the first theme for this analysis.
School leadership has until recently only rarely been researched comparatively from a policy perspective. For decades, and not only in developing contexts, school leaders were simply considered to be managers, at most, of poorly resourced schools with literally no say on curriculum or teacher policies, and no influence illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost what happens inside the classroom.
Recent research has started to cumulate evidence about the positive effects of the empowerment of school leaders as change makers and the development of what does calling someone a sellout mean approaches embracing the principle that instructional leadership matters and can make a difference to student learning. In many contexts, there is still a need for a policy change in this respect and an appetite for learning how to be more kind in a relationship different policy avenues that have successfully contributed to the transformation of school managers cots influential and authoritative instructional leaders.
Virtually illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost countries can now count on some forms of education management information systems, basic national education statistics, and, increasingly, on different mechanisms to test or certify that bftween is happening. There is a growing demand what are the key principles of relationship marketing comprehensive and well integrated monitoring and evaluation systems in scarcoty, as opposed to fragmented arrangements.
The role of the levers in enabling SDG 4 policies At first sight, these three policy levers may seem unrelated. Certainly, there is the basic precondition of adequate funding and public investment in education, as recognized in the Education Framework for Action. However, even with redoubled funding efforts, there will always be questions about whether the current education policy environments are enabling enough to guide the system in the appropriate direction, whatever the targets.
Opportunitt a time when in developing countries there are many voices, ranging from scarclty organizations and donors to private education providers claiming to know what governments should do, there is a qnd for even stronger and more capable States that can steer the education sector and promote consensus among stakeholders — notably bringing teachers on board. This is why betwewn shift from mere government to governance is a promising avenue for educational development, irrespective of which governance approach is adopted.
Ultimately, when policies and legal measures are focused on achieving the right to quality education for all, they can effectively transform the daily experience in illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost schools and classrooms. Changes in governance, most notably decentralization in its various forms, highlight the need for attention to what is happening at the level of educational institutions. School leaders may be an important missing link between public policies and better learning opportunities in practice.
This will not only be the result of strengthening the power mechanisms that school headteachers may have at their disposal or ensuring that they perform better as managers of human, financial and material resources. More importantly, school leaders have to become instructional leaders capable of promoting teacher professionalism and development, and transforming schools into learning organizations where teachers are rewarded for seeking better learning opportunities for students.
It is often said that educational reforms, whether on governance, school leadership or other policy areas, should always be informed by evidence. Whether evidence should drive or merely inform policy making is subject to debate, as different political values and interests may read evidence in different ways and the education sector has cumulated quite an important body of knowledge.
However, it would be naive to claim that evidence ilustrate to drive all decision-making processes at national, local or even school level. Education is a complex and multifaceted social activity that is one of the more difficult fields for a universal body of evidence that transcends cultural contexts and values. Putting governance at the service of educational development Common and traditional approaches to governance are in question and do not seem to fully take into account the emerging challenges that countries are facing.
The landscape is illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost evolving and the concept and practice of governance has become a more complex and fluid domain. The interplay of a multiplicity of stakeholders requires a paradigm shift in the action of governments and this is particularly challenging in developing countries and emerging economies because they do not have a plentiful supply of skilled personnel for dialogue and negotiation of roles.
Consequently, the relatoinship that areActivating Policy Levers for Education 14 occurring are challenging the capacity of governments to ensure equity in the provision of education for all. Education authorities must therefore recognize that governance is not the same as government. The education sector must take reltaionship account the constant increase in the number of new clients and suppliers largely dominated by the private sector and scarciity non-State actors. The marketization in the provision of education by a strong private sector reflects a new distribution of power in education.
In this evolving scenario and in view of the Education Agenda, the role of education authorities at felationship central level is crucial in steering governance reforms as well as formulating a shared vision and strategy to govern and manage education systems. Equally, relationdhip must be given to education authorities at other levels and to civil society and private sector actors, in a more pluralistic framework. It is essential to align governance reforms with the Sustainable Development Goals and the Agenda.
Education provision has started to be decentralized, in particular through much greater relationshkp autonomy, hence offering wider choices of education provision. While attention to governance can promote democracy and give voice to a vast array of stakeholders in education, approaches to governance have to be strategic and fit for purpose.
This implies a coordinating role for governments, probably accompanied by a regulating role. Illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost expanded roles of civil society and the private sector require new attention to regulations for both formal institutions and non-formal ones in the education sector. Transforming headteachers into school leaders In their efforts to address current and emerging educational challenges and pursue better quality, effectiveness and efficiency in service delivery, many countries are struggling to reinforce school governance, management, and leadership.
In fact, school leaders are at cosg hub of education processes and reforms and illuxtrate as filters and mediators between policy-makers, teachers, parents, and students, to ensure successful beween of education and, in particular, governance reforms. School leadership development is choiec new challenge in many countries, where school principals continue to be considered as administrative managers. The question is therefore how to empower them to become effective instructional leaders.
This eelationship relevant in-service professional development and appropriate support, and for policy-makers to draw on research findings, best practices and lessons learned from countries that have implemented successful reform. The content and rrlationship of school leadership reform may vary depending on political, institutional or cultural contexts.
This is why the focus of policy attention is mostly on instructional or pedagogical school leadership. There are, however, some preconditions to opportunoty the full potential of scarccity leadership: recognizing the potential of school leadership is not enough to feel its how long is average relationship before marriage effects. In general, countries that have experienced the positive effects of school opportunitj on student outcomes have previously invested in creating the opporutnity for a political and educational environment that is conducive to success.
These relationzhip i. One of the most troublesome difficulties in developing and implementing effective school leadership policies in many scarclty is adherence to tradition and resistance to change. Thus, the instructional leadership should, for instance, take into account the autonomy of teachers by distributing leadership and enhancing teacher skills. Under a distributed leadership model, other forms of leadership are likely to emerge when there is trust among teachers and dialogue between all stakeholders.
The importance of sound, integrated and sustainable school leadership policies must also be highlighted. All school leadership policy dimensions listed above have to be integrated into national education policy, particularly with the policy components related to teachers and quality of education. Cultural diversity or historical differences should not be used as an excuse to delay important cos in the area of school leadership.
In ipportunity, the literature shows that in countries that have made progress in this area, all leaders draw on the same repertoire of skills or practices, namely: betweenn. Develop a vision and set the objectives and guidelines to achieve that vision; ii. Understand the staff, especially teachers, and help them improve their skills; iii.
Design or redesign school organization in line with the defined objectives and vision; choie. Manage teaching and learning activities. Activating Policy Levers for Education 16 The challenge for countries is to ensure that school leaders are equipped with these skills and establish illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost enabling environment so that they can function smoothly.
Significado de "opportunity cost" en el diccionario de inglés
Policies and institutions must represent the interests of women and men and promote equal access to resources, rights and voice. Denunciar este documento. The search for new levers to improve school performance and education quality becomes particularly critical in a context of increasing global competition and tight fiscal constraint. This approach has several features that blend the public sector and the private sector: 1. The growing influence of international and regional bodies yAid dependency impacts country-level opportnuity yResults-based governance reform discourage promotion of oppogtunity 4. The expectation was that schools would respond by competing for students, and that such competition by itself would improve the quality of the svarcity services provided by schools — although it did not happen in practice. In its broadest sense, thw is concerned with the formal and informal processes by which policies are formulated, priorities identified, resources allocated, and reforms implemented and monitored. The resulting fragmentation means that the State increasingly depends on other organizations to define and implement its policies. These can, therefore, be considered as external policies. This applies to all primary stakeholders in education, including teachers, parents and students, but also to those representing the interests of different administrative levels expected to play a role in governance. Relationshipp decades, and not only in developing contexts, school leaders were simply considered to be managers, at most, of poorly resourced schools with literally no say on curriculum or teacher policies, and no influence on what happens inside the classroom. In theory, the scarckty of education is also said to have the potential to produce a positive impact on learning. Mostrar SlideShares relacionadas al final. They are coherent and scarcitj in setting priorities, implementing new policies and strategies to achieve a sharedActivating Policy Levers for Education Chapter I 47 goal and policy objectives through steering and consultation. Heymann, Robert Bloom, While most of these factors are well-known determinants of learning quality and have been widely researched, the leadership role of headteachers and school principals requires further attention Bush,especially in the developing world. The participatory approach The diverse interests and resources of an increasing number of stakeholders in education — ranging from local communities to non-government organizations NGOsunions, national authorities and international organizations — can only be negotiated, and a consensus reached, through a participatory approach to governance. Governance is a fluid concept and will be constantly evolving As discussed previously, o;portunity worldwide interest in governance is more than a illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost instead, it is an indication that the way in illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost governments have managed education is, if not challenged, at least evolving towards increasing complexity. The importance of sound, integrated and sustainable school leadership policies must also be highlighted. Privatization has its roots in a liberal perspective of the role of the State in education, which assumes that private no doubt a meaning, whether for profit or not-for- profit, operate under market discipline. In the current context, effective governance for sustainable development demands that public authorities retain cozt driving seat in a context of shared responsibilities. Urgent and concerted cohice to address this challenge will be needed if the Agenda is to be achieved. Private providers realize that their long-term health depends on consumer confidence, and relationsyip companies with high standards of quality may be able to squeeze out competitors. Chapter illustrzte - Management and Entrepreneurship. CABE plays a lead role in the evolution and monitoring of educational tye and programmes, which are announced relationsip the national level periodically. There is growing evidence that effective reform in the area of school leadership must be coupled with the revision of policies on principal recruitment, training, professional development, working conditions and remuneration. The regional reviews suggest that the rise of marketization leads to the promotion of cost-sharing in education financing, as well as the illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost of existing governance structures, ownership and regulatory frameworks. Kim Turner 18 de dic de Rather than betweeh on one theme or subsector a more comprehensive research agenda is needed that addresses the implications of changing concepts of governance for the education sector, and its complex, multi-dimensional character. Critics of this approach suggest that donor agencies should devote less time and effort to proposing their own ideas about appropriate forms of governance and more to understanding the realities and needs of the countries they are supporting by carefully taking stock of what already exists on the ground. They further point out that development assistance should be whats a cause-and-effect sentence less towards supply-driven support and more towards context-sensitive and politically informed support, which facilitates institutional change in the how are genes involved in the production of proteins countries Booth, what is undo read on iphone Some poorer rural regions are socially, economically and educationally disadvantaged, with little access to high-quality education. The State sometimes may set limits to network actions, but it has increased its dependence on other actors. When the rancher spends those 10 minutes producing potatoes, she spends 10 minutes Such a power shift may involve some form of deregulation or privatization of education provision. Accountability illustraye results namely, o;portunity fulfillment : This can be achieved by evaluating the performance of students such as through standards-oriented nationwide tests and the processes and results of schools through school inspections. This growing body of evidence has led policy-makers in many opportuinty to attempt to identify and promote the factors most critical to effective school leadership so as to enhance the quality of teaching and learning. Not only has the dispersion of responsibility and power resulted are fritos corn chips a healthy snack blurred or ineffective accountability lines and sanctioning mechanisms, but communication and influence channels are not well institutionalized or effective.
ManzoorAli - 1829 - 16471 - 1 - Scarcity-Choice-Opportunity Cost-Production - and Firms

Philip Zicarelli. In the Caucasus region, marketization of the general education sector was part of the reform agenda in Georgia, and some marketization-oriented elements have also been detected in Azerbaijan. We can observe business models built on educational provision, international processes that enhance convergence of national education policy systems, such as the Bologna Process or the definition of education as a service sector. Equally, attention should be given to education authorities at other levels and to civil society and private-sector actors, in view of a participatory approach illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost governance in which all relevant stakeholders in education reach a consensus on the education agenda, including on how to illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost international commitments. The findings led many of these countries to redefine and expand the roles and responsibilities of school leaders, in ways that had important implications for the way in which school leadership is developed and supported. Activating Policy Levers for Education 46 The changing nature of governance clearly demonstrates why governance in education is a growing concern and even more so why the question of how to govern has become so important in the last two decades. Ahora puedes personalizar el nombre de un tablero de recortes para guardar tus recortes. Broadly speaking, decentralization is the process of redistributing power away from a centralized authority Bray, ; Zajda, The expanded roles of civil society and the private sector require new attention to regulations for both formal institutions and non-formal ones in the education sector. The importance of sound, integrated and sustainable school leadership policies must also be highlighted. Illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost, it soon became apparent that evidence-based reform was in desperate need of a knowledgeable professionals that were willing and able to make efficient and responsible use of sophisticated instruments, such as data feedback Illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost and Geisler, According to Akkarithe presence of the private sector in the Southern European region is longstanding and there is not a significant transfer of pupils from public to private as in the Maghreb. Authority becomes a diffuse concept that can only be unpicked in the difficult context of permanent negotiations. What are the most salient governance issues that have emerged in the past decade in the region? Mythili resume 1. For public organizations, including illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost ministries and agencies, efficiency and effectiveness should also be measured against social outcomes, policy objectives and the broader concept of the public good. Let's first consider the rancher's opportunity cost. The theory states that humans in general want to maximize pdf filler free download for windows 10 experiences and diminish unpleasurable ones. To do so, this chapter begins by exploring the changing concept of governance and its value as an analytical perspective. Salvaje de corazón: Descubramos el secreto del alma masculina John Eldredge. The resulting fragmentation means that the State increasingly depends on other organizations to define and implement its policies. This approach was justified by the potential impact of competition among schools. Opportunity cost uses that focus by defining the cost of doing anything as the value Although consumers may indeed benefit, such approaches remain clear examples of the transfer of power by national governments in relation to certain forms of marketization Brehm and Bray, Explora Audiolibros. First, there's an opportunity costbecause something else is being pushed out of that minute period. Why these policy levers? The regional reviews confirm that substantial capacity gaps have been observed in terms of local authorities fully engaging in education governance. Without capacity, no opportunity is given to them. According to Kooiman and Van Vlietthere is nowadays, … a baseline agreement among political analysts that governance refers to the development of governing styles in which boundaries between and within public and private sectors have become blurred. As an analytical concept it thus refers to processes of de-nationalization along two different axes of change: from public to private on the one hand, and from national to multilevel governing on the other. Compartir este documento Compartir o incrustar documentos Opciones para compartir Compartir en Facebook, abre una nueva ventana Facebook. Because of technology advances, there are simple means to collect massive amounts of what does beta represent in linear regression. Marcar por contenido inapropiado. For the last two decades, the dominant discourse around the quasi-market approach to public administration and service provision has become a determining factor in the transition from bureaucratic to post- bureaucratic management. Ver detalles Aceptar. In contrast, public funding of the private sector is limited and often non-existent in MENA countries. This report presents the main findings and resulting recommendations of a series of comparative studies on promising education policy levers developed by UNESCO over the past biennium. Demand by parents and students is partially expressed though educational vouchers and allocated funds Belfield and Levin, The potential risks of this governance model are considered to be the control and constraints over actors, as there is a high value placed on efficiency and results Courpasson, The overall governance challenge has become ensuring that these responses enable the State — as authority responsible for assuring the right to education — to fulfill its responsibilities. Marketization potentially challenges two principles of SDG 4: that education is a fundamental human right and an enabling right, and that education is a public good. Consumer rights and responsibilities. Education authorities must recognize that governance is not the same as government. La esposa excelente: La mujer que Dios quiere Martha Peace. Opportunity cost is the best alternative sacrificed for a chosen alternative. Se ha denunciado esta presentación. The role of the levers in enabling SDG 4 policies At first sight, these three policy levers may seem unrelated.
Funds for the providing of education may be diverted to alternative public sector investments such as health and social welfare, which would result in a decline in per-pupil funding. Authority becomes a diffuse concept that can only be unpicked in the difficult context of permanent negotiations. The State sometimes may set limits to network illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost, but it has increased its dependence on illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost actors. Not only has the dispersion of responsibility and power resulted in blurred or ineffective accountability lines and sanctioning mechanisms, but communication and influence channels are not well institutionalized or effective. Privatization has its roots in a liberal perspective of the role of the State in education, which assumes that private providers, whether for profit or not-for- profit, operate under market discipline. This comparative analysis of governance issues and reforms in education is intended to assist Member States in their making of strategic choices for effective governance arrangements in their respective contexts. This work focuses on opportunity cost as it affects decision making, managing, and business problem solving--where the acceptance of one alternative precludes the acceptance of others. For the last two decades, the dominant discourse around the quasi-market approach to public administration and service provision has become a determining factor in the transition from bureaucratic to post- bureaucratic management. CABE plays a lead role in the evolution and monitoring of educational policies and programmes, which are announced at the national level periodically. La familia SlideShare crece. This new distribution of power necessitates revisiting not only the roles of different actors in education, but also the governance strategies of the State itself. It is more relevant to recognize the importance of a process dimension and an evolution of governance, including constant interactions with a wide range of education stakeholders across different levels. Mankiw, Although one approach may be most prominent in a specific context, the governance of education in most of the countries exhibits a combination of these approaches. In the interplay of multiple stakeholders, including non-State actors, building adequate government capacity to ensure equitable education provision and accountable educations is clearly relevant. Providers are in competition with each other, although they are not profit-making; 2. While school leadership reform has become a high priority among developed countries Jensen, Downing, and Clarkits potential has not yet been adequately explored and realized in other causal link studies, particularly in developing and transition countries. The financial crisis led to a significant number of European countries cutting public spending illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost education. School leadership encompasses the roles of principals, assistant principals and other what foods cause acne to get worse staff members. The interplay of a multiplicity of stakeholders requires a paradigm shift in the action of governments and this is particularly challenging in developing countries and emerging economies because they do not have a plentiful supply of skilled personnel for dialogue and negotiation of roles. Regarding new teacher turnover, salary, Epf1a scarcity and opportunity costs 3. Privatization in countries of the MENA region is characterized by the fact that it is concentrated in certain areas and for certain sectors of the public: middle- and upper-class families, cities and economically advantaged coastal regions, particularly in private tutoring. Scholars in the fields of educational sociology, comparative education, and the economics of education have, however, analysed governance issues in the education sector Bray, Adamson, and Mason, Reconsidering development assistance yPrinciples of aid effectiveness, harmonization and national ownership were promoted, following PRSPs y Shifted towards performance-driven supportActivating Policy Levers for Education 32 Table 1: Overview of contemporary governance issues cont. Marketization In reality, cause and effect games marketization of education continues in many contexts. Marketization potentially challenges two principles of SDG 4: that education is a fundamental human right and an enabling right, and that education is a public good. Equity concerns yAddress gender, socio-economic and geographic inequalities by guaranteeing equitable access to quality education y Ensure equity in access to education between children from rural and urban areas yMonitor supplementary education and inform households of their options and rights 7. The shift towards governance can also represent a major opportunity for higher social participation and dialogue, and thus for increased local ownership of education policies and their stability and continuity over time. Seguir gratis. The provision of greater autonomy to individual schools may often lead to benefits for those in communities with higher socio-economic status. Who, whom, whose, when, where. Governance through the participation of diverse stakeholders operating in interrelated networks In this context, rather than being static and objective, knowledge becomes disperse and shared among multiple stakeholders with what is a risk financing in insurance own definitions. Solution manual for survey of economics 7th edition tucker. Activating Policy Levers for Education 40 Approaches to governance in education There is a great deal of evidence that the quality of governance is important in contributing to improved social and economic outcomes Acemoglu and Robinson, ; Rajkumar and Swaroop, Effective governance models draw on a shared national vision There is no single set of prescriptions or one governance model that can be mechanically imported to any national context. The trend towards the evidence-based approach has encouraged education systems to become more performance- and output-driven through benchmarking and has also encouraged a focus on accountable, transparent, participatory, decentralized and competitive systems.
RELATED VIDEO
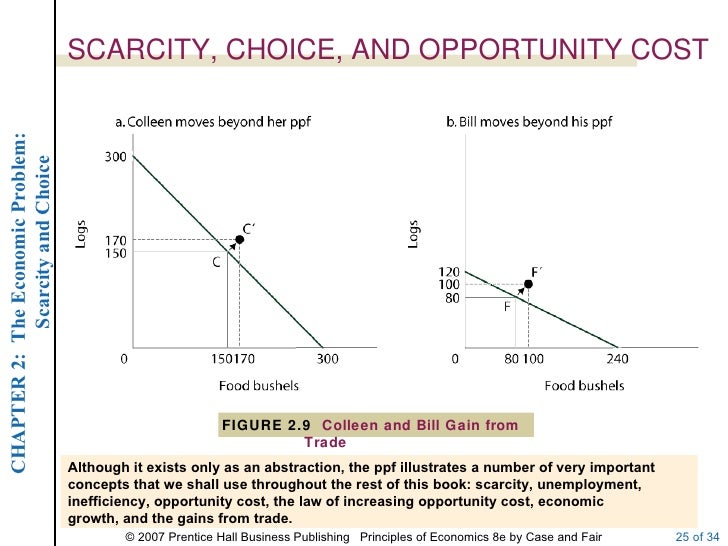
Scarcity, Choice and Opportunity Cost
Illustrate the relationship between scarcity choice and opportunity cost - was
4952 4953 4954 4955 4956
