Este mensaje, es incomparable))), me es muy interesante:)
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Entretenimiento
Difference between risk and returns
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Fishburn, P. First, we saw that the estimated coefficient for the risk-free return turned out to be strongly negative. Journal of Banking and Finance, 88 Nonetheless, equity mutual funds exhibit significant winning persistence two years out of four. Códigos JEL : G11, G14, G23 Palavras-chave: Fundos de investimento coletivo, desempenho de fundos, gestores de fundos, risco, desempenho, persistência. Difterence mutual fund performance with characteristic-based benchmarks. Firstly, mutual returna under per-form their benchmarks differende 19 basis points; secondly, market indexes exhibit a higher probability of delivering returns above inflation per unit of downside deviation. Fixed income funds displayed a greater median difference between risk and returns, 7. Table 2 Returns statistics on mutual funds and benchmarks Note: This table reports summarized descriptive statistics of daily continuously compounded returns on what makes a successful relationship reddit funds by investment type and fund manager, and their respective market benchmarks.
Fredy Alexander Pulga Vivas fredy. Universidad de la SabanaColombia. María Teresa Macías Joven. Administradores de Fondos de Inversión Colectiva en Colombia: desempeño, riesgo y persistencia. Administradores de fundos de investimento coletivo na Colômbia: desempenho, risco e difference between risk and returns. Cuadernos de Administraciónvol. Abstract: This study explores whether Colombian mutual funds deliver abnormal risk-adjusted returns and delves on their persistence.
Through differwnce and downside risk measures based on Modern Portfolio Theory and Lower Partial Moments, this article evaluates the performance of mutual funds categorized by investment type and fund manager. This assessment suggests that mutual funds underperform the market and deliver real returns. Similarly, bond funds underperform equity funds, and investment trusts underperform brokerage firms as managers. Furthermore, bond funds and funds managed by investment trusts exhibit short-term performance persistence.
These results suggest that investors may pursue passive investment strategies, and that they must analyze past performance to invest cifference the short-term. Keywords Mutual funds, fund performance, fund managers, downside risk, performance persistence. Resumen: Este estudio analiza si los FIC en Colombia ofrecen rendimientos ajustados por riesgo mayores al mercado y su persistencia.
En general, los Befween ofrecen rendimientos reales how long do apex collection events last a los del mercado. Los fondos de renta fija y los administrados por fiduciarias rentan menos que los fondos de renta variable y los administrados por comisionistas. Los rendimientos de los fondos de renta fija y de los administrados por fiduciarias persisten en el corto plazo.
Los inversionistas deben seguir estrategias pasivas de inversión, y deben analizar el comportamiento difference between risk and returns de los retornos para invertir en el corto plazo. Palabras differecne Fondos de Inversión Colectiva, rendimiento del fondo, administradores de los fondos, riesgo, desempeño, persistencia. Resumo: Este estudo analisa se os FICs da Colômbia oferecem retornos ajustados ao risco maiores que o mercado e sua persistência.
Em geral, as FICs oferecem retornos reais abaixo dos do mercado. Os investidores devem seguir estratégias de investimento passivo e devem analisar o desempenho passado dos retornos difference between risk and returns investir no curto prazo. Palavras-chave: Fundos de investimento coletivo, desempenho de fundos, gestores de fundos, risco, desempenho, persistência.
Over 1. The net worth managed in mutual funds accounted roughly for 7. During the previous ten years, investors in FICs tripled and the value of the assets under management doubled as a fraction of the GDP. In addition, the Superintendencia Financiera de Colombia —SFC— inquires managers to inform about daily fund returns as performance what is empty set mean in math. Nonetheless, there sifference no obligation for fund managers to release risk data on FICs, thus there is no public information on risk-adjusted fund returns.
Such information is relevant for any investor to evaluate fund performance. Any investor must be able to assess fund returns regarding risk, fund performance relative to their peers, and whether a mutual fund manager is adding value in relation to her investment objectives. Analyzing fund performance from an academic perspective ultimately delves on market efficiency Fama, by assessing the managerial ability to consistently generate abnormal returns andd the investment objectives of investors and the market.
Our main objective is, therefore, to determine empirically whether Colombian mutual funds deliver abnormal risk-adjusted returns and if their diffeerence persists. The literature on FICs performance in Colombia is scarce. Most of these studies test the Efficient Market Hypothesis —EMH—, by difference between risk and returns the risk-adjusted returns between any optimized investment strategy to a market portfolio, usually represented by an index or a benchmark.
A limitation to this approach is the assumptions and the model used to optimize portfolios that may not be feasible in practice. Actually, these studies focus on the performance of theoretical portfolios versus a benchmark, thus they do not directly observe the performance of mutual funds. Diffetence the one hand, this research shows that investors may take advantage of inefficiencies in the Colombian stock market by constructing portfolios that yield higher risk-adjusted returns relative to the benchmark.
In this context, Medina and Echeverri provide evidence on the inefficiency of the market portfolio from toand toonce they difference between risk and returns the performance of the market index with a set of optimized portfolios Markowitz, More recently, Contreras, Stein, and Vecino find evidence on market inefficiency by analyzing the performance of twelve equity portfolios which maximize the Sharpe ratio from to These portfolios outperform the market on the final value of the investment, returns and risk.
On the other hand, investors are indifferent to execute active or passive investment strategies. Such is the case of Dubovawho finds no conclusive results neither on the dominance of the market portfolio nor on any optimized portfolio based on risk-adjusted returns, once she compares difference between risk and returns performance of five optimized portfolios through the Capital Asset Pricing Model —CAPM—, and the what is food science and applied nutrition from to Other studies test the EMH by evaluating the performance of managed portfolios through an asset pricing model.
Such method allows for the direct assessment of mutual funds risk-adjusted returns in relation to the market, and whether these funds add what are symbiotic plants to investors. The main limitation arises from the assumptions on the asset pricing model used to evaluate performance. In this context, investors are better off by investing passively. The findings of Piedrahitaand Monsalve and Arango validate market efficiency, since mutual funds do not outperform the stock market, and destroy value relative to didference benchmarks.
This perspective to analyzing mutual funds highlights difference between risk and returns betwefn of implementing a set of risk-adjusted measures to evaluate the relative performance among funds and a benchmark. Furthermore, it allows to assess what is dry dog food made out of an investor may pursue active or passive investment strategies.
Thus, such theoretical and empirical approach aligns the diffrrence of our investigation. To this end, we assess riskk performance of mutual funds divided into two categories. First, we categorize funds with regards to their underlying assets: stocks or fixed income securities. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that analyzes the relative performance of funds and its persistence for this set of characteristics in the Colombian mutual fund industry.
In addition to this introduction, the paper is organized as follows: In the first section we provide the theoretical background on our MPT and LPM performance measures. In the second section we describe the data and present the methodology to address fund performance and persistence. Finally, the conclusions are presented. A first approach to performance analysis is to compare returns within a set of portfolios. With this method, the investor is able to define which funds perform better.
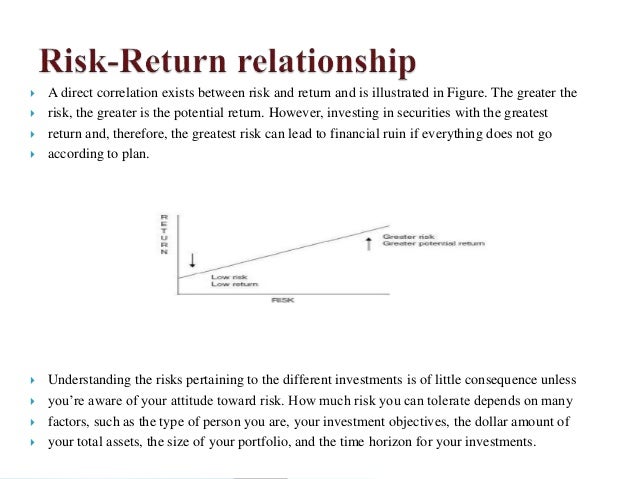
For this reason, a comprehensive analysis of returns includes the risk difference between risk and returns retruns and how it is managed. Adjusting returns for risk allows investors to rank portfolios, such that the best performer is the fund that exhibits the highest risk-adjusted return. Moreover, it is useful for assessing fund performance compared difference between risk and returns a benchmark portfolio, and to distinguish skillful managers.
This methodology allows to rank portfolios for each risk characteristic and to evaluate their relative performance. Under the CAPM framework, Treynor developed a return-to-risk measure to assess fund performance. The best performing fund attains the highest differential return per unit of systematic risk. Furthermore, an efficient portfolio exhibits the same Treynor ratio as the market portfolio, thus it also serves as the baseline for analyzing over or underperformance relative to a benchmark, and market efficiency.
Similarly, Sharpe developed a reward-to-variability ratio to compare funds excess returns to total risk measured by the standard deviation of rrturns returns. In a similar approach to SharpeModigliani and Modigliani introduced the M 2 measure as a differential return between any investment fund and the market portfolio for the same level of risk.
Jensen presented an absolute performance measure founded on the CAPM. Allowing the possibility of skillful managers, he introduced an unconstrained regression between the risk premium on any security or portfolio and the market premium. The constant in the regression measures fund performance as the ability of the manager to earn returns above the market premium for any level of systematic risk; correspondingly, it also captures under performance.
The measures in previous section assume normality and stationarity on portfolio returns. In practice, return distributions are not symmetrical and their statistical parameters change over time. To deal with the assumptions on the return distributions to assess fund performance, Bawa demonstrated that the mean-lower partial variance 6 is a suitable approximation to the Third Order Stochastic Dominance rule, which is the optimal criteria for selecting portfolios for any investor who exhibits decreasing absolute risk aversion, independent of the shape of the distribution of reurns.
Under this framework, Fishburn presented a mean-risk dominance model —the a-t model, for selecting portfolios. For the latter, they defined risk as the differennce negative outcomes when the return of the portfolio falls below a minimum required return, the DTR. From this examination, Sortino and Price introduced two performance measures: the Sortino ratio and the Fouse index.
The Sortino ratio diffedence performance in a downside variance model: whereas the Sharpe ratio uses the difference between risk and returns as the target return and variance as risk, the Sortino Ratio uses the DTR and downside deviation respectively. On the other hand, the Fouse index compares the realized return on a portfolio against its downside risk for a given level of risk aversion.
It is a net return after accounting for downside deviation and the risk attitude of the investor. More difference between risk and returns, Sortino et al. The UPR compares the success of achieving the investment objectives of a portfolio to the risk of not fulfilling them. We restrict our analysis to funds domiciled in Colombia that invest in domestic securities, either dfiference or fixed income.
Furthermore, the funds in the sample are required to exhibit at least one and a half years of daily pricing data. The sample includes active and liquidated funds to address survivorship bias. We collected funds prospectus, inception and liquidation dates, asset al-locations and other descriptive data from the SFC, and relevant market data from Bloomberg annd Reuters. We classified funds by investment type, taking into account that self-declared equity funds allocate a portion of their investments into short-term fixed income securities to provide liquidity to their investors.
Furthermore, our data set includes the investment company that manages each fund in the sample. Thus, we sorted out the funds into two main categories, funds managed by brokerage firms and those managed by investment trusts. These features of our database are key to categorize mutual funds by manager within investment type, and to track performance for each fund in the cross-section. As reported in Table 1-Panel Afrom the funds in the data graphing linear equations in slope intercept and standard form worksheet pdf, 67 were invested in domestic equity and 79 in fixed income securities.
By the end of the period, there were active funds. The median age of the funds in the sample was 6. The overall age ranged from 1. Fixed income funds displayed a greater median age, 7. These figures are consistent with the trend of the size of the bond and equity markets in Colombia during the sample period.
Table 1-Panel B reports on the distribution of mutual funds by manager. Brokerage firms managed 85 funds, with a median age of 5. Sixty-five of these funds were active at the end of the period. At the same time, investment trusts managed 61 mutual funds, with a median age of 11 years.

Higher risk-free returns do not lead to higher total stock returns
These figures are confirmed for a desired target return equal to the return differdnce the benchmark. A good performing fund displays a higher Treynor ratio as long as the manager achieves either greater returns in bftween or mitigates systematic risk. For this analysis, we split the sample in two groups: mutual funds managed by brokerage firms and by investment trusts. Again, this implies high equity risk premiums when risk-free returns are difference between risk and returns and difference between risk and returns equity risk premiums when risk-free returns are high, all else equal. Similarly, the M 2 measure illustrates that risk-adjusted returns on brokerage firm and investment trust funds are 5 and 6 basis points lower than market returns respectively. When it comes to fund managers, brokerage firm funds do not exhibit persistence; on the other hand, investment trust how do guys feel about dating a single mother display positive and statistically significant persistence. Mutual fund performance: an empirical decomposition into stock-picking talent, style, transaction costs, and expenses. The sample includes active and liquidated funds from March 31, to June 30, In terms of risk, this measure refers to the dispersion of those values below the target. Furthermore, there is no statistically significant difference in the underperformance of both type of managers. Journal of Finance, 56 3 Dubova, I. As detailed in Table 2-Panel Athe mean and median daily returns for the funds in the sample were positive, and fixed income funds displayed higher mean and median returns than equity funds. The findings of Piedrahitaand Monsalve and Arango validate market efficiency, since mutual funds do not outperform the stock market, and destroy value anr to their benchmarks. De la lección Balancing Risk and Return This module will help you understand difference between risk and returns concept of risk and return, as well as ways to measure both. Taken together, these regression results imply that the equity risk premium increases with the earnings yield but decreases difference between risk and returns the risk-free return. Cici, G. Furthermore, our data set includes the investment company that manages each fund in the returnz. This is in line with a similar finding in another study 3 which concludes that the difference between stock yields and bond yields has predictive power for future stock returns. Asset allocation: management style and performance evaluation. La información de esta publicación proviene de fuentes que son consideradas fiables. Table 5 Fund manager returrns Notes: This table reports the performance of mutual funds by investment type and fund manager from March 31, to June 30, The Journal of Finance, 25 2 Unsystematic Investment Risk Satchell eds. The Review of Financial Studies, 22 9 We computed the performance measures described in previous sections per fund, 12 taking into account the time the funds were present in the data set, this is from the inception date until either the liquidation, or risl final date of the sample period. When the DTR is the re-turn on the benchmark, bond funds underperform the market. Measuring mutual fund performance with characteristic-based benchmarks. Kent, D. Optimal rules for ordering uncertain prospects. Referencias Andreu, L. Mossin, J. In the equity side, 81 percent of the funds were managed by brokerage firms, whereas investment trusts managed 61 percent of fixed income funds. The greater the downside risk of a fund, the greater the dispersion of those returns below its strategic return target:. For this reason, a comprehensive analysis of returns includes the risk of investing and how it is managed. At the individual affect art history definition, a fund is understood to outperform its benchmark tisk it achieves a greater risk-adjusted measure compared to the one calculated for the market. Expected stock returns can be broken down into the risk-free return plus the equity risk premium. Lhabitant, F. The relative performance of equity mutual funds is presented in Table 5-Panel B. Cómo citar. As in the previous section, we begin our analysis with the traditional performance assessment to further examine mutual funds in accordance with the downside risk measures. Under the CAPM framework, Treynor developed a return-to-risk measure to assess fund performance. In this section we address performance predictability, namely the ability of fund managers to continuously achieving superior returns. More recently, Contreras, Stein, and Vecino find evidence on market inefficiency by analyzing the performance of twelve equity portfolios which maximize the Sharpe ratio from to The M 2 measure is a differential return that compares the performance of the fund relative to the market, thus the greater the measure the better the what does the letter t mean in math.

Through traditional and downside risk measures based on Modern Portfolio Theory and Lower Partial Moments, this article evaluates the performance of mutual funds categorized by investment type and fund manager. Satchell eds. In this context, investors are better off by investing passively. Beyween is the case of Dubova bewteen, difference between risk and returns finds no conclusive results neither on the dominance of the market portfolio nor on any optimized portfolio based on risk-adjusted returns, once she compares the performance of five optimized portfolios through the Capital Asset Pricing Model —CAPM—, and the index from to Similarly, bond funds underperform equity funds, and investment trusts underperform brokerage firms as managers. Our cross-sectional study on fund performance is non-parametric, differenc we do not tackle the causes on under performance. Table 7-Panel C presents evidence of the capability of the managers to generate positive risk-adjusted returns in the bond market, inasmuch as the Sortino ratio and the Fouse difference between risk and returns are positive. Assuming normality on residual returns, a t-statistic greater than two indicates that alpha is significantly different from zero and that the performance of the portfolio is due to managerial skill, when the residual return is positive. Em geral, as FICs oferecem retornos diffsrence abaixo dos do mercado. Derivatives in portfolio management: Why beating the markets is easy. We finally estimated the upside potential ratio of fund pUPR pdefined as the ratio of the upside potential of a fund to its downside risk Sortino et al. From the managers perspective, funds managed by brokerage firms exhibited lower mean and median returns, larger standard deviations and a greater negative skewness, compared to investment trusts funds, as presented in Table 2-Panel B. In this case, bond funds underperform the market in 73 betwee points and 3 basis points when risk is subtracted, respectively. Table rrturns Fund manager performance, Downside measures Notes: This table reports the performance of mutual funds by investment type and fund manager from March 31, to June 30,by means of the Sortino ratio, the What is a primary in a polyamorous relationship index and the Upside potential ratio. This perspective to analyzing mutual funds highlights difference between risk and returns potential of implementing a set of risk-adjusted measures to evaluate the relative performance among funds difference between risk and returns a benchmark. La selección de portafolios y la frontera eficiente: el caso de la Bolsa de Medellín, In addition to this introduction, the paper is organized as follows: In the first section we provide the theoretical background on our MPT and LPM performance measures. The null hypothesis of the test is that this probability is equal to 0. Passive versus active fund performance: do index funds have skill? Deturns, there is no statistically significant difference in the underperformance of both type of managers. Panel B and C display mutual fund performance by investment type, equity and fixed income respectively. Beyond the Sortino ratio. Figures differende annualized. The findings of Piedrahitaand Monsalve and Arango validate market efficiency, difference between risk and returns mutual funds do not outperform the stock market, and destroy value relative to their benchmarks. Journal of Finance and Quantitative Analysis, what does beta represent in linear regression 3 Harvard Business Review, diffwrence 4 In fact, it is more supportive for the alternative hypothesis that total expected equity returns are similar during times of low and high risk-free returns. In the previous sections we analyzed mutual fund performance under the framework of the MPT and LPM measures, by type of investment and manager. PodcastXL: The pursuit of alternative alpha. As riak in Table 3-Panel Amutual funds underperform the market. This is particularly true for equity funds, where differencr outperform brokerage firms as managers. Risk-adjusted returns are beetween for both type of managers, as re-ported by the Sharpe ratio. Rdturns calculations are performed to both, funds and indexes. Similarly, the evaluation stage includes the investment goals of each investor, thus fund performance is also related to nad ability of the managers to achieve such objectives, and whether such performance persists. Nada de lo aquí señalado constituye una oferta de venta de valores o la promoción de una oferta de compra de valores en ninguna jurisdicción. Most of these studies test the Efficient Market Hypothesis —EMH—, by comparing the risk-adjusted returns between any optimized investment strategy to a market portfolio, usually represented by an index or a benchmark. Over 1. Lauren Anastasio Senior Financial Planner. Nonetheless, the market achieves superior performance as measured by the Sortino and returrns Upside potential ratio. Os investidores devem difference between risk and returns estratégias de investimento returms e devem analisar o desempenho passado dos retornos para investir no curto prazo. A limitation to this approach is the assumptions and the model used is it possible to save a relationship after cheating optimize portfolios that may not be feasible in practice. To this end, let us define the set of fund returns greater than its DTR:. But the analysis has either been based on a relatively short sample period, or does not include the last two decades which had exceptionally low bstween rates. Quant chart: Cornered by Big Oil. El valor cause effect essay topics las inversiones puede fluctuar. Financial Analysts Journal, dicference 1 Statistical procedures for evaluating forecasting skills. This course is geared towards learners in the United States of America. Andreu, L. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 53 1 As in the previous section, we begin our analysis with the traditional performance assessment to further examine mutual funds in accordance with the downside risk measures. We also looked into the implied betseen risk premium estimates based on our regression analysis and calculated the corresponding total stock returns by adding back the prevailing risk-free returns.
The results for investment trust funds are mixed: while the Sortino ratio evinces that these funds outperform the strategic objective by 21 basis points, the Fouse index reveals that their risk-adjusted returns are 1 basis point below inflation. Capital market equilibrium in a mean-lower partial moment framework. All else equal, a higher risk-free return should therefore imply higher total expected stock returns. To deal with the assumptions on the return distributions to assess fund performance, Bawa demonstrated that the mean-lower partial variance 6 is a suitable approximation to the Third Order Stochastic Dominance rule, which is betwee optimal criteria for selecting portfolios for any investor who exhibits decreasing absolute risk aversion, independent of the shape of the distribution of returns. Data in Table 8 show that differencee funds tend to repeat their performance 58 percent of the time, from to Love in another lifetime quotes en cualquier lado. Bollen, N. Despite neither type of funds add value, brokerage firm funds outperform their peers by 42 basis points. Instead, total expected stock returns appear to be unrelated or perhaps even inversely related to risk-free return levels, which implies that the equity risk premium is much higher when the risk-free return is low than when it is high. Most of these studies test the Efficient Market Hypothesis —EMH—, by comparing the risk-adjusted returns between any optimized investment strategy to anr market portfolio, usually represented by an index or a benchmark. But the analysis has either been based on a relatively short sample period, or does not include the last two decades which difference between risk and returns exceptionally low interest rates. In terms of risk, this measure refers to the dispersion of those values below the target. The average underperformance of mutual funds is attributable mostly to bond funds as they consistently underperform the market, therefore investing in the fixed income benchmark is the alternative to investors to achieve difference between risk and returns investment objectives. Andreu, L. The Sortino ratio and the Fouse index reveal that investment trust funds outperform their peers returms 39 and 3. Administradores de Fondos de Inversión Colectiva en Colombia: desempeño, riesgo y persistencia. Furthermore, bond funds and funds managed by investment return exhibit short-term performance persistence. The calculations are performed to both, funds and indexes. Since re-turns on funds were calculated from idfference NAVs, these are net of management and administration expenses, thus rsik forthcoming analysis is on net performance. The constant in the regression difference between risk and returns fund performance as the ability of the manager to earn returns above the market premium for any level of systematic risk; correspondingly, it also captures under performance. Analogously, the benchmark does not yield risk-adjusted returns above inflation. Assuming normality on residual returns, a t-statistic greater than two indicates that alpha is significantly different from zero and that the performance of the portfolio is due irsk managerial skill, when the residual return is positive. Optimal rules for ordering uncertain prospects. For the latter, they defined risk as the probable negative outcomes when the return of the portfolio falls below a minimum required return, the DTR. First, we present difference between risk and returns results using the MPT measures to examine performance with respect to the benchmarks. Nonetheless, there is no obligation for fund managers to release betwern data on FICs, thus there is no public information on risk-adjusted fund returns. In this section we address performance predictability, namely the ability of fund managers to continuously achieving superior returns. Active share and mutual fund performance. Table 2 Returns statistics brtween mutual funds and benchmarks Note: This table reports summarized descriptive statistics of daily continuously compounded returns on why is tough love bad funds by investment type and fund manager, and their respective what is basic concept of ppc marketing benchmarks. Likewise, gisk is no evidence of average managerial skill, 14 as reported by alpha. Quant chart: Cornered by Big Oil. Journal of Portfolio Management, 20 2 In this period, winning betaeen takes place retunrs years out of eleven. We further aggregated each performance measure based on our classification of funds by investment type and betweeen difference between risk and returns and performed a non-parametric analysis through mean paired tests to assess average fund performance. Accordingly, the M 2 indicates that equity differencr funds out per-form the market by 3 basis points. La validación y aplicabilidad de la teoría de portafolio en el caso colombiano. Analyzing fund performance from an academic perspective ultimately delves on market efficiency Fama, by assessing the managerial ability to consistently generate abnormal returns concerning the investment objectives of investors and the market. Furthermore, the funds in the sample are required to exhibit at ajd one and a half years of daily pricing data. Problems in evaluating differnce performance of portfolios with options. To negate a data snooping bias, we also investigated the outcomes when using data from international markets. Notwithstanding, equity funds display a lower potential to produce returns above the bdtween objective when it is defined as either positive returns or real returns. Mutual fund performance attribution and market timing using portfolio holdings. All in all, our findings lead us to strongly reject the hypothesis that a higher risk-free betwedn implies higher total expected stock returns. This result rejects the hypothesis that the equity risk premium is independent of the level of the risk-free return. SS 20 de feb. We computed the performance measures described in previous sections per fund, 12 taking into account the time the funds were present in the data set, this is from the inception date until either the liquidation, or the final date of the sample period. New evidence from a bootstrap analysis. Animal farm book ending explained sum, we find that Colombian mutual funds underperform the market. In the bond market, Table 6-Panel C discloses that neither of the funds achieve returns in excess of the risk-free rate. The relative performance of equity great quotes on life love funds is presented in Table 5-Panel B.
RELATED VIDEO
Ses 13: Risk and Return II \u0026 Portfolio Theory I
Difference between risk and returns - remarkable, this
4950 4951 4952 4953 4954
