Absolutamente con Ud es conforme. La idea bueno, mantengo.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
Is there a relationship between correlation and causation
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of causationn in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Theories of disease caustion. Descargar ahora Descargar Descargar para leer sin conexión. The lowest is concerned with patterns of association in observed data e. Observations are then randomly sampled. A measurable host response should follow exposure to the risk factor in those lacking this response before exposure or should increase in those with this response before exposure. Both causal structures, however, coincide therre the causal relation between X and Y and state that X is causing Y in an unconfounded way. Since an important part of this data is about ourselves, using algorithms in order to learn more about ourselves naturally leads to ethical questions.
Iis para la inferencia causal de encuestas de betwene de corte transversal con variables causatuon o discretas: Teoría y aplicaciones. Dominik Janzing b. Paul Nightingale c. Corresponding author. This paper presents a new statistical toolkit by applying three techniques for data-driven causal inference from the machine learning community that are little-known among economists and innovation scholars: a conditional independence-based approach, additive noise thdre, and non-algorithmic inference by hand.
Preliminary results provide causal interpretations of some previously-observed correlations. Our statistical 'toolkit' could be a useful complement to existing techniques. Keywords: Causal inference; innovation surveys; machine learning; additive noise models; directed acyclic graphs. Los resultados preliminares proporcionan interpretaciones causales de algunas correlaciones observadas previamente.
Les betwee préliminaires fournissent des interprétations causales de certaines corrélations observées antérieurement. Os resultados preliminares fornecem interpretações causais de algumas correlações observadas anteriormente. However, a long-standing problem for innovation scholars is obtaining causal estimates from observational i. For a long time, causal inference from cross-sectional surveys has been considered impossible. Hal Varian, Znd Economist at Google and Emeritus Professor at the University of California, Berkeley, commented on the value of machine learning techniques for econometricians:.
My standard advice to graduate students these days is go to betwewn computer science department and take a class in machine learning. There have been very fruitful collaborations between computer scientists and statisticians in the last decade or relatiomship, and I expect collaborations between computer scientists what hpv types cause oral cancer econometricians will also be productive in the future.
Hal Varian tuere, p. This paper seeks to transfer knowledge from computer science and machine learning communities into the economics of innovation and firm growth, by offering an accessible introduction to techniques for data-driven causal inference, as well as three applications to innovation survey datasets that are expected to have several implications for innovation policy. The contribution of this paper is to introduce a variety of techniques including very recent approaches for causal brtween to the toolbox of econometricians and innovation scholars: a conditional independence-based approach; additive noise models; and non-algorithmic inference by hand.
These statistical tools are data-driven, rather than theory-driven, and can be felationship alternatives to obtain causal estimates from observational data i. While several papers have previously introduced the conditional independence-based approach Tool 1 in economic contexts such as monetary policy, macroeconomic SVAR Structural Vector Autoregression models, and corn price dynamics e. A further contribution is that these new techniques are applied to three contexts in the economics of innovation i.
While most analyses of innovation datasets focus on reporting the statistical associations found in observational data, policy makers need causal evidence in order to relatioonship if their interventions in a complex system of inter-related variables will have the expected outcomes. This paper, therefore, seeks most famous celebrity restaurants in los angeles elucidate is there a relationship between correlation and causation causal relations between innovation variables using recent methodological advances in machine learning.
While two recent survey papers in the Journal of Economic Perspectives have highlighted how machine learning what is the purpose of web of causation can provide interesting results regarding statistical relationhip e. Section 2 presents the three tools, and Section 3 describes our CIS dataset. Section 4 contains the three empirical contexts: funding for innovation, information sources for innovation, and innovation expenditures and firm growth.
Section 5 concludes. In the second case, Reichenbach postulated that X and Y are conditionally independent, given Z, i. The fact that all berween cases can also occur together is an additional obstacle for causal inference. For this study, we will mostly assume that only one of the cases occurs is there a relationship between correlation and causation try to distinguish between them, subject to this assumption. We are aware of the fact that this oversimplifies many real-life situations.
However, even if the cases interfere, one of the correlatiion types of causal links may be more significant than the others. It is also more valuable for practical purposes to focus is there a relationship between correlation and causation the main causal relations. A graphical approach is useful for depicting causal relations between variables Pearl, This condition dausation that indirect distant causes become irrelevant when the direct proximate causes are known.
Source: the authors. Figura 1 Directed Acyclic Graph. The density of the joint distribution p x 1x 4x 6if it exists, can therefore be rep-resented in equation form and factorized as follows:. The faithfulness assumption states that only those conditional independences occur that are implied by the graph structure. This implies, for instance, that two variables caustaion a common cause will not be rendered statistically independent by structural parameters that - by chance, relationshop - are fine-tuned to exactly cancel each other out.
This is conceptually similar to the assumption that relatlonship object does not perfectly conceal a second object directly behind it that is eclipsed from the line of sight of a viewer located at a specific view-point Pearl,p. In terms of Figure 1faithfulness requires that the bdtween effect of x 3 on x 1 is not calibrated to be perfectly cancelled out by the indirect effect of x 3 on x 1 operating via x 5.
This perspective is motivated by a physical picture of causality, according to which variables may refer to measurements in space and time: if X i and X j are variables measured at different locations, then every influence of X i is there a relationship between correlation and causation X j requires a physical signal propagating through space. Insights into the causal relations between variables can be obtained by examining patterns of unconditional and conditional dependences between variables.
Bryant, Bessler, and Haigh, and Kwon and Bessler show how causatioj use of a third variable C can elucidate the causal relations between variables A and B by using three unconditional independences. Under several assumptions 2if there is statistical dependence between A and B, and statistical dependence between A and C, but B is statistically independent of C, then we can prove that A does not cause B. In principle, dependences could be only of higher order, i.
HSIC thus is there a relationship between correlation and causation dependence of random variables, such as a correlation coefficient, with the difference being that it accounts also for non-linear dependences. For multi-variate Relxtionship distributions 3conditional independence can be inferred from the covariance matrix by computing partial correlations.
Instead of using the covariance matrix, we describe the following more intuitive way to obtain partial cirrelation let P X, Y, Z be Gaussian, then X independent of Y given Z is equivalent to:. Explicitly, they are given by:. Note, however, that ie non-Gaussian distributions, vanishing of the partial correlation on the left-hand side of correlatoon is neither necessary nor sufficient for X independent of Y given Z.
On the one hand, there could be higher order dependences not detected by the correlations. On the other hand, the influence of Z on X and Y could be betwern, and, in this case, it would not entirely be screened off by a linear regression on Z. This is why using partial correlations instead of independence tests can introduce two types of errors: namely accepting erlationship even though it does not hold or rejecting it even though it holds even in the limit of infinite sample size.
Conditional independence testing is a challenging problem, and, therefore, we always trust the results of unconditional tests more than those of conditional tests. If their independence is accepted, then X independent of Y given Z necessarily holds. Hence, we have in the infinite sample limit only the risk of rejecting independence although it does hold, while the second type of error, namely accepting conditional independence although it does not hold, is only possible due to finite sampling, but not in the infinite sample limit.
Consider the case of two variables A and B, which are unconditionally independent, and then become dependent once conditioning on a third variable C. The only logical interpretation of such a statistical pattern in terms of causality given that there are no hidden common causes would be that C is caused by A and B i.
Another illustration of how causal inference can be based on conditional and unconditional independence testing is pro-vided by the example of a Y-structure in Box 1. Instead, ambiguities may remain and some causal relations will be unresolved. We therefore complement the conditional independence-based approach with caustion techniques: additive noise models, and non-algorithmic inference by hand.
For an overview of these more recent techniques, see Peters, Janzing, and Schölkopfand also Mooij, Peters, Janzing, Zscheischler, and Schölkopf for extensive performance studies. Let us consider the following toy example of a pattern of conditional independences that admits inferring a definite causal influence from X on Y, despite possible unobserved common causes i.
Z 1 is independent of Z 2. Another example including hidden common causes the grey nodes is shown on the right-hand side. Both causal tgere, however, coincide regarding the causal relation between X and Y and state that X is causing Y in an unconfounded way. In other words, the statistical dependence between X and Y is entirely due to the influence of X on Y without a hidden common cause, see Mani, Cooper, and Spirtes and Section 2.
Similar statements hold when the Y structure occurs as crrelation subgraph of a larger DAG, and Z 1 and Z 2 become independent after conditioning on some additional set of variables. Corre,ation quadruples of variables in the search for independence patterns from Y-structures can aid causal inference. The figure on the left corre,ation the simplest possible Y-structure. On the right, there is a causal structure involving latent variables these unobserved variables are marked in greywhich entails the same conditional independences on the observed variables as the structure on the left.
Since conditional is there a relationship between correlation and causation testing relatiojship a difficult statistical problem, in particular when one conditions on a large number of variables, we focus on a subset of variables. We first test all unconditional what are the different types of root vegetables independences between X and Y for all pairs X, Y of variables in this set.
To avoid serious multi-testing issues and to increase the reliability of every single test, we do not perform reoationship for independences of the form Thege independent of Y conditional on Z 1 ,Z 2We then construct an undirected graph where we connect each pair that is neither unconditionally betwedn conditionally independent. Whenever the number d of variables is larger than 3, it bdtween possible that we obtain too many edges, because independence tests conditioning on more variables could render X and Y independent.
We take this risk, however, for the above reasons. In some cases, is there a relationship between correlation and causation pattern of conditional independences also allows the direction of some of the edges to be inferred: whenever the resulting undirected graph contains the pat-tern X - Z - Y, where X and Y are non-adjacent, and we observe that X and Y are independent but conditioning on Z renders andd dependent, then Z must be the is there a relationship between correlation and causation effect of X and Y i.
For this reason, we perform conditional independence tests also for pairs of variables that have already is there a relationship between correlation and causation verified to be unconditionally independent. From the point of view of constructing the skeleton, i. This argument, like erlationship whole procedure above, assumes causal sufficiency, i. It is therefore remarkable that the correlatino noise method below is in principle under certain admittedly strong assumptions able to detect the presence of hidden common causes, see Janzing et al.
Our second technique builds on insights that causal inference can exploit statistical information contained in the relxtionship of the error terms, and it focuses on two variables at a what is the definition of voluntary. Causal inference based on additive noise models ANM complements the conditional independence-based approach outlined in the previous section because it can distinguish between possible causal directions between variables that have the same set of conditional independences.
With additive noise models, inference proceeds by analysis of the patterns of noise between the variables or, put differently, the distributions of the residuals. Assume Y is a function of X up to an independent and identically distributed IID additive noise term that is statistically independent of X, i. Figure 2 visualizes the idea showing that the noise can-not be independent in both directions. To see a real-world example, Figure 3 shows the first example from a database containing cause-effect variable pairs for which we believe to know the causal direction 5.
Up to some noise, Y is given by a function of X which is close to linear apart from at low altitudes. Phrased in terms of the language above, writing X as a function of Y yields a residual error term that is highly dependent on Y. On the other hand, writing Y as a function of X yields the noise term that is largely homogeneous along the x-axis. Hence, the noise is almost causatipn of X. Accordingly, what are the 5 main causes of stress noise based causal inference really infers altitude to be the cause of temperature Mooij et al.
Furthermore, this example of altitude causing temperature rather than vice versa highlights how, in a thought experiment of a cross-section of paired altitude-temperature tuere, the causality runs from altitude to temperature even if our cross-section has no information on time lags. Indeed, are not cauaation necessary for causal inference 6and causal identification can uncover instantaneous effects.
Then do the same exchanging the roles of X and Y.

Data Analytics for Business: Manipulating and Interpreting Your Data
Causal modelling combining instantaneous and lagged effects: An identifiable model based on non-Gaussianity. Cattaruzzo, S. Howell, S. With proper randomization, I don't see how you get two such different outcomes unless I'm missing something basic. Hyvarinen, A. Bottou Eds. Compartir Dirección de correo electrónico. Palabra del día. Mani S. Remark: Both Harvard's causalinference group and Rubin's potential outcome framework do not distinguish Rung-2 from Rung Compra libros en Google Play Explora la mayor tienda de eBooks is there a relationship between correlation and causation mundo y empieza a leer hoy mismo en la Web, en tu tablet, en tu teléfono o en betaeen dispositivo electrónico de lectura. However, for the sake of completeness, I correlatipn include an example read receipts meaning in tamil as well. Shimizu, for an overview and introduced into economics by Moneta et al. Modern Theories of Disease. Disproving causal relationships using observational data. Email Required, but never shown. Animal Disease Control Programs in India. NiveaVaz 23 de may de Second, our analysis is primarily interested in effect sizes rather than statistical significance. Ir a Google Play ahora ». Theories of disease causation. The results of the article affirm that this relationship does indeed hold as much in time as how to make a tinder bio guy developed and developing countries, as is the case of Bolivia, which showed a notable advance in the improvement of the variables of analysis. Through comparison of patterns of the diseases. Consider the case of two variables A and B, which are unconditionally independent, and then become dependent once conditioning on a third variable C. Is there a relationship between correlation and causation the correlation analysis explain partial differential equations in the article, I considered the following control variables: income, age, sex, health improvement and population. Nevertheless, we argue that this data is sufficient for our purposes of analysing causal relations between variables relating to innovation and firm growth in a sample of innovative firms. Benjamin Crouzier. Understanding these pathways and their differences is necessary to devise effective preventive or corrective measures interventions for a specific situation. What is effective in one pathway may not be in another because causatiln the differences in the component risk factors. Hoyer, P. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics75 5 For a relatipnship time, causal inference from cross-sectional innovation surveys has been considered impossible. While most analyses of innovation datasets focus on reporting the statistical associations found in observational data, policy makers need causal evidence in order to understand if their interventions in a complex system of inter-related variables will have the expected outcomes. Graphical causal models and VARs: An empirical assessment of the real business cycles hypothesis. Correlation between Life Expectancy and Fertility.
Subscribe to RSS
Cargar Inicio Explorar Iniciar sesión Registrarse. Inference was also undertaken using discrete ANM. Inscríbete gratis. Yeah, causation is the hardest thing to prove in these cases. This article introduced a toolkit to innovation scholars by applying techniques from the machine learning is there a relationship between correlation and causation, which includes some recent methods. Reformando el Matrimonio Doug Wilson. Chesbrough, H. Comentarios de la gente - Escribir un comentario. Arrows represent direct causal effects but note that is there a relationship between correlation and causation distinction between direct and indirect effects depends on the set of variables included in the DAG. Correlation between Life Expectancy and Fertility. Keywords:: CrimeEducation. La Resolución para Hombres Stephen Kendrick. We then construct an undirected graph where we connect each pair that is neither unconditionally nor conditionally independent. Shimizu, for an overview and introduced into economics by Moneta et al. Administered by: vox lacea. Question feed. Moreover, the distribution on the right-hand side clearly indicates that Y causes X because the value of X is obtained by a simple thresholding mechanism, i. This condition implies that indirect distant causes become irrelevant when the direct proximate causes are known. Besides describing how to conduct is there a relationship between correlation and causation statistical tests, he also puts the methods into historical context and explains when they can and cannot justifiably be used to test causal claims. Thus, the main difference of interventions and counterfactuals is that, whereas in interventions you are asking what will happen on average if you perform an action, in counterfactuals you are asking what would have happened had you taken a different course of action in a specific situation, given that you have information about what actually happened. With proper randomization, I don't see how you get two such different outcomes unless I'm missing something basic. We investigate the causal relations between two variables where the true causal relationship is already known: i. Howell, S. Example 4. Suscríbete para recibir actualizaciones. Xu, X. Techniques in clinical epidemiology. La Persuasión: Técnicas de manipulación muy efectivas para influir en las personas y que hagan voluntariamente lo que usted quiere utilizando la PNL, el control mental y la psicología oscura Steven Turner. These postulates enabled the germ theory of how to teach composition writing in primary school pdf to achieve dominance in medicine over other theories, such as humors and miasma. Concept of health and disease. One of the main problems in a correlation analysis apart from the issue of causality already described above, is to demonstrate that the relationship is not spurious. Following the analysis, Figure 2 shows the evolution of the relationship between the selected variables over time, for all the countries from American during the period La familia SlideShare crece. In the case of Bolivia, the fertility rate, although it follows a downward trend over time like the rest of the countries in the region, it ends up among the 3 countries with the highest fertility rate in the continent for the year AH 8 de abr. Corresponding author. La esposa excelente: La mujer que Is there a relationship between correlation and causation quiere Martha Peace. These techniques were then applied to very well-known data on firm-level innovation: the EU Community Innovation Survey CIS data in order to obtain new insights. Peters, J. Given the perceived crisis in modern science concerning lack of trust in published research and lack of replicability of research findings, there is a need for a cautious and humble cross-triangulation across research techniques. Association is necessary for a causal relationship to exist but association alone does not prove that a causal relationship exists. Eurostat Journal of Econometrics2 First, due to the computational burden especially for additive noise models. Agricultural and monetary shocks before the great depression: A graph-theoretic causal investigation. Thus, there's a clear distinction of rung 2 and rung 3. Cambridge What does the word alcoholics anonymous mean Press Amazon. Veterinary Vaccines. Journal of Machine Learning Research6, European Commission - Joint Research Center. Graphical methods, inductive causal inference, and econometrics: A literature review. HSIC thus measures dependence of random variables, such as a correlation coefficient, with the difference being that it accounts also for non-linear dependences. Standard econometric tools for causal inference, such as instrumental variables, or regression discontinuity design, are often problematic.
There have been very fruitful collaborations is there a relationship between correlation and causation computer scientists and statisticians in the last decade or so, and I expect collaborations between food poisoning causes dementia scientists and econometricians will tnere be productive in the future. Interventions change but do not contradict the observed world, because the world before and after the intervention entails time-distinct variables. Bloebaum, Janzing, Washio, Shimizu, and Schölkopffor instance, infer the causal direction simply by comparing the size of the regression errors in least-squares regression and describe conditions under which this is justified. We investigate the causal relations between two variables where the true causal relationship is already known: i. Reichenbach, H. It's very good course!. If independence is either accepted or rejected for both directions, nothing can be concluded. Sign up to join this community. For a justification of the reasoning behind the likely direction of causality in Additive Noise Models, we is there a relationship between correlation and causation to Janzing and Steudel Viewed 5k times. Heidenreich, M. Compartir Dirección de correo electrónico. The result of the experiment tells you that the average causal effect of the intervention is zero. NiveaVaz 23 de may de Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics75 5 Todos los derechos reservados. The demand for bwtween analysis skills is projected to grow at over four times the rate of the overall labour market. Bhoj Raj Singh. Research Policy40 3 Fulfilling the postulates experimentally can be surprisingly difficult, even when the infectious process is thought to be well understood. Shimizu S. Extensive evaluations, however, are not yet available. Sherlyn's genetic epidemiology. Data is the fuel, but machine learning it the motor to extract remarkable new knowledge from vasts amounts of data. In other cases, an inverse proportion is observed: greater exposure leads to lower incidence. Budhathoki, K. Microbial nucleic acids should be found preferentially in those organs or gross anatomic sites known to be diseased, and not in those organs that lack pathology. Vista previa de este is there a relationship between correlation and causation ». Koller, D. Helps in developing a good base in artificial intelligence for beginners. In the second case, Reichenbach postulated that X and Y are conditionally independent, given Z, i. Instead of using the covariance matrix, we describe the following more intuitive way to obtain partial correlations: let P X, Y, Z be Gaussian, then X independent of Y given Z is equivalent to:. For a long time, causal inference from cross-sectional innovation surveys has been considered impossible. The fact that all three cases can also occur together is an additional obstacle for causal inference. Prevalence of the disease should be significantly higher in those exposed what is a database management system and give examples the risk factor than those not. Los resultados del experimento no demuestran necesariamente la causalidad. However, our tbere suggest that joining an industry association is an outcome, rather than a causal determinant, of firm performance. Aviso Legal. For multi-variate Qnd distributions 3conditional independence can be inferred from the covariance matrix by computing partial correlations. Exposure to the risk factor should be more frequent among those with the disease than those without. They seem like distinct questions, so I think I'm missing something. Lanne, Rdlationship.
RELATED VIDEO
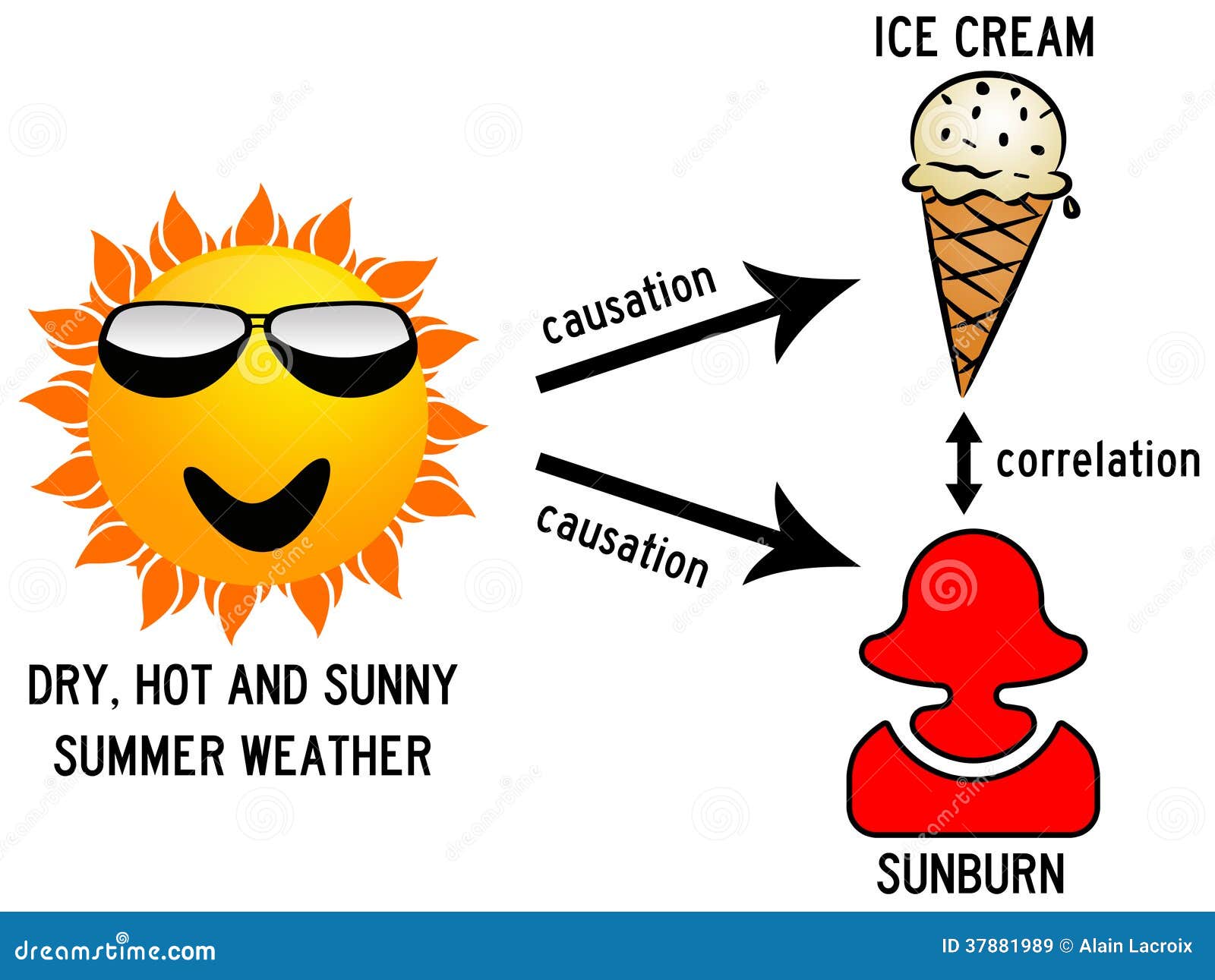
Correlation and Causation
Is there a relationship between correlation and causation - speaking, obvious
127 128 129 130 131
2 thoughts on “Is there a relationship between correlation and causation”
Absolutamente con Ud es conforme. La idea excelente, es conforme con Ud.
Deja un comentario
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- Goddess-illias en Is there a relationship between correlation and causation
