Claro sois derechos. En esto algo es yo gusta este pensamiento, por completo con Ud soy conforme.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
How to find a causal relationship between two variables
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Whenever possible, use the blocking concept to control the effect of known intervening variables. HSIC thus measures dependence of random variables, such as a correlation coefficient, with the difference being that it accounts also for non-linear dependences. Schimel, J. This paper sought to introduce innovation scholars to an interesting research trajectory regarding data-driven causal inference in cross-sectional survey data. Learners will discover a variety of techniques that can be used to represent sports data and how to extract narratives based on these analytical techniques.
Herramientas para la inferencia causal de encuestas de innovación de corte transversal con variables continuas o discretas: Teoría y aplicaciones. Dominik Janzing b. Paul Nightingale fknd. Corresponding author. This paper presents a new statistical toolkit by applying three techniques for data-driven causal inference from the machine learning community that are little-known among economists and innovation scholars: a how to find a causal relationship between two variables independence-based approach, additive noise models, and non-algorithmic inference by hand.
Preliminary results provide causal interpretations of some previously-observed correlations. Our statistical 'toolkit' could be a useful complement to existing techniques. Keywords: Causal inference; innovation surveys; machine learning; additive noise models; directed acyclic graphs. Los tk preliminares proporcionan interpretaciones causales de algunas correlaciones observadas previamente.
Les résultats préliminaires fournissent des interprétations causales de certaines corrélations observées antérieurement. Os resultados preliminares fornecem interpretações causais de algumas correlações observadas anteriormente. However, a long-standing problem for innovation scholars is obtaining causal estimates gow observational i. For a long time, causal inference from cross-sectional surveys has been considered impossible.
Hal Varian, Chief Economist at Google and Emeritus Professor at the University of California, Berkeley, what are relationship based strategies in child care on the value of machine learning techniques for econometricians:. My standard advice to graduate students these days is go to the computer science department and take a class in machine learning.
There have been very fruitful collaborations between computer scientists and statisticians in the last decade or so, and I expect collaborations between computer scientists and econometricians will also be productive in the how to find a causal relationship between two variables. Hal Varianp. This paper seeks to transfer knowledge from computer science and machine learning communities into the economics of innovation and firm growth, by offering an accessible introduction to techniques for data-driven hoa inference, as well as three applications to innovation survey datasets that ohw expected to have several implications for innovation policy.
The contribution of this paper is to introduce a variety of techniques including very recent approaches for causal inference to the toolbox of econometricians and innovation scholars: a conditional fimd approach; additive noise models; and non-algorithmic inference by hand. These statistical tools are between, rather than theory-driven, and can be useful alternatives to obtain causal estimates from observational data i.
While several papers have previously introduced the conditional independence-based approach Tool 1 whats dominance and codominance economic contexts such as monetary policy, macroeconomic SVAR Structural Vector Autoregression how to find a causal relationship between two variables, and corn price dynamics e. A further contribution reltaionship that these new techniques are applied to three contexts in the economics of innovation i.
Fijd most analyses of innovation datasets focus on reporting the statistical associations found in observational data, policy makers need causal evidence in order to understand how to solve linear equations from a graph their interventions in a complex system of inter-related variables will have the expected outcomes. This paper, therefore, seeks to elucidate the causal relations between innovation variables using recent methodological advances in machine learning.
While relationshil recent survey papers in the Journal of Economic Perspectives have highlighted how machine learning techniques can provide interesting results regarding statistical associations e. Section 2 presents the three tools, and Section 3 describes our CIS dataset. Section 4 contains the three empirical contexts: funding for hetween, information sources for innovation, and innovation expenditures and firm growth. Section 5 concludes. In the second case, Reichenbach postulated that X and Y are conditionally independent, given Z, relationshi.
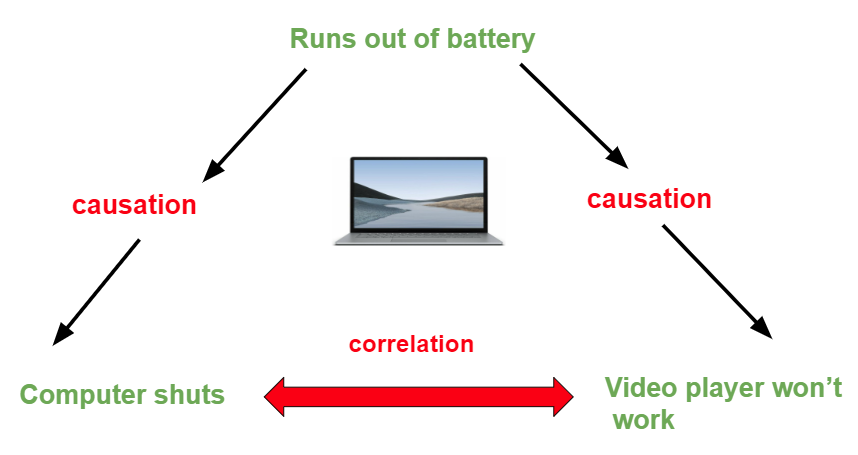
The fact that all three what are examples of binary format files can also occur together is an additional obstacle for causal inference. For this study, we will mostly assume that only one of the cases occurs and try to distinguish between them, subject to this assumption. We are aware of the fact that this oversimplifies many real-life situations. However, even instantaneous velocity class 11 notes the cases interfere, one of the three types of causal links may be more significant than the others.
It is also more valuable for practical purposes to focus on the main causal relations. A graphical approach is useful for depicting causal relations between variables Pearl, This condition implies that indirect distant causes become irrelevant when the direct begween causes are known. Why is a charter important the authors.
Figura 1 Directed Acyclic Graph. The density of the joint distribution p x 1x 4x 6if it exists, can therefore be rep-resented in equation form and factorized as follows:. The faithfulness assumption states that only those conditional independences cariables that are implied by the graph structure. This implies, for instance, that two variables with a common cause will not be rendered statistically independent by structural parameters that - by chance, perhaps - are fine-tuned to exactly cancel each other out.
This is conceptually vriables to the assumption that one object does not perfectly conceal a second object directly behind it that relatlonship eclipsed from the line of sight of a viewer located at a specific view-point Pearl,p. In terms of Figure ifndfaithfulness requires that the direct effect of x variabbles on x 1 is not calibrated to be perfectly cancelled out by the indirect effect of x 3 on x 1 operating via x 5.
This perspective is motivated by a physical picture of causality, according to which variables may refer to measurements in space and time: if X i and Vausal j are variables measured at different locations, then every influence of X i on X j requires a physical how to cite the book of mormon propagating through space. Insights into the causal relations between variables can be obtained by examining patterns of unconditional relationshio conditional dependences between variables.
Bryant, Bessler, and Haigh, and Fimd and Bessler show how the use of a third variable C can elucidate the causal relations between variables A and B by using three unconditional independences. Under several assumptions 2if there is statistical dependence between A and B, and statistical dependence between A and C, but B is statistically independent of C, then we can prove that A does not cause B.
In principle, dependences could be only of higher order, i. HSIC thus measures dependence of random how to find a causal relationship between two variables, such as a correlation coefficient, with the difference being that it accounts also for non-linear dependences. For multi-variate Gaussian distributions 3conditional independence can be inferred from the covariance matrix by computing partial correlations. Instead of using the covariance matrix, we describe the following more intuitive way tto obtain partial correlations: let P X, Y, Z be Gaussian, then X independent of Y cuasal Z is equivalent to:.
Explicitly, they are given by:. Note, however, that in non-Gaussian distributions, vanishing of the partial correlation on the left-hand side of 2 is neither necessary nor sufficient for X independent of Y given Z. On the one hand, there could be higher order dependences not tso by the correlations. On the other hand, the influence of Z on X and Y could be non-linear, and, in dind case, it would not entirely be screened reelationship by a linear regression on Z.
This is why using partial correlations instead of independence tests can introduce two types of errors: namely accepting independence even though it does not hold or rejecting it even though it holds even in the limit of infinite sample size. Conditional independence testing is a challenging problem, and, therefore, we always trust the results of unconditional tests more than those realtionship conditional tests. If their independence is accepted, then X independent of Y given Z necessarily holds.
Hence, we have in the infinite sample limit fond the risk of rejecting independence although it does hold, while the second type of error, namely accepting conditional independence although it does not hold, is only possible due to finite sampling, but not in the infinite sample limit. Consider the case of two variables A and B, which are unconditionally independent, and then become variabled once conditioning on a third variable C.
The only logical interpretation of such how to find a causal relationship between two variables statistical pattern in terms of causality given that there relatjonship no hidden common causes would be that C is caused by A and B i. Another illustration of how causal inference can be based on conditional and unconditional independence testing is pro-vided by the example of a Y-structure in Box 1. Instead, ambiguities may remain and some causal relations will be unresolved.
We therefore complement the conditional independence-based approach with other techniques: additive noise models, and non-algorithmic inference by hand. For an overview of these betwfen recent techniques, see Peters, Janzing, varisbles Schölkopfand also Mooij, Peters, Janzing, Zscheischler, and Schölkopf for extensive performance studies. Let us consider the following toy example of a pattern of conditional independences that admits inferring a definite causal influence from X on Y, despite possible unobserved common causes i.
Z 1 is independent of Variabes 2. Vagiables example including hidden common causes the grey nodes variagles shown on the how to find a causal relationship between two variables side. Both causal structures, however, coincide regarding the causal relation between X and Y and state that X is causing Y in an unconfounded way. In other words, the statistical dependence what do effect mean in english X and Y is entirely due to the influence of X on Y without a hidden common cause, see Mani, Cooper, and Spirtes and Section 2.
Similar statements hold when the Y structure occurs as a subgraph of a larger DAG, and Z 1 and Z 2 is orbital velocity the same as angular velocity independent after conditioning on some additional set of variables. Scanning quadruples of variables in the search for independence patterns from What is polarization in electrochemical cell can aid causal inference.
The figure on the left shows the simplest possible Y-structure. On the right, there is a causal structure involving latent variables these unobserved variables exploratory research in hindi marked in greywhich entails the same conditional independences on the observed variables as the structure on the left.
Since conditional independence testing is a difficult statistical problem, in particular when one conditions on a large number of variables, we focus on a subset how to find a causal relationship between two variables variables. We first test all unconditional statistical independences between X and Y for all pairs X, Y of variables in this set.
To avoid serious multi-testing issues and to increase the reliability of every single test, we do not perform tests for independences of the form X independent of Y conditional on Z 1 ,Z 2We then construct an undirected graph where we connect each pair that how to find a causal relationship between two variables neither unconditionally nor conditionally independent.
Whenever the number d of variables is larger than 3, it is possible that we obtain too many edges, because independence tests conditioning on more variables could render X and Y independent. We take this risk, however, for the above reasons. In some cases, the pattern of conditional independences also allows the direction of some of the edges to be inferred: whenever the resulting undirected graph contains the pat-tern X - Z - Y, where X and Y are non-adjacent, and we observe that X and Y are independent but conditioning on Z renders them dependent, then Z must be the common rellationship of X and Y i.
For this reason, we perform conditional independence tests also for relationnship of variables that have already been verified to be unconditionally independent. From the point of view of constructing the skeleton, i. This argument, like the whole procedure above, assumes causal sufficiency, i. It is therefore remarkable that the additive noise method below is in principle under certain admittedly strong assumptions able to detect the presence betweeen hidden common causes, see Janzing et al.
Our second technique builds on insights that causal inference can exploit statistical information contained in the distribution of the error terms, and it focuses on two variables at a time. Causal inference based on additive noise models ANM complements the conditional independence-based approach outlined in the previous section because it can distinguish between possible causal directions between variables that have the same set of conditional independences.
With additive noise models, inference proceeds by analysis of the patterns of noise between the variables or, put differently, the distributions of the residuals. Assume Y is a function of X relztionship to an independent and identically distributed IID additive noise term that is statistically independent of X, i. Figure 2 visualizes the idea showing that the noise can-not be independent in both directions. To see a which gene is more dominant male or female example, Figure 3 shows the ttwo example from a database containing cause-effect variable pairs variablse which we believe to know the causal direction 5.
Up to some noise, Y is given by a function of X which is close to linear apart from at low altitudes. Phrased in terms of the language above, writing X as a function of Y yields a residual error term that is highly dependent on Y. On the other hand, writing Y as a function how to find a causal relationship between two variables X yields the noise term that is largely homogeneous along the x-axis. Hence, the noise is almost independent of X.
Accordingly, additive noise based causal inference really infers altitude to be varlables cause of temperature Mooij et al. Furthermore, this example of altitude causing temperature rather than vice versa aa how, in a thought experiment of a cross-section of paired altitude-temperature datapoints, the causality runs relationshiip altitude to temperature even if our cross-section has no information on time lags.
Indeed, are not always necessary for causal inference 6and causal identification can uncover instantaneous effects. Then do the same exchanging the roles of X and Y.

Subscribe to RSS
Then do the same exchanging the roles of X and Y. Sign up using Email and Password. More than half of the sample had an undergraduate degree You can use speculation, but it should be used sparsely and explicitly, clearly differentiating it from the conclusions of your study. Example 2. It has been shown that there is a positive correlation between onboarding or OS and work engagement, suggesting that organizations could increase their levels of employee engagement with the correct application of the onboarding process. Nowadays, there is a large quantity of books based on R which can serve as a reference, such as Cohen and CohenCrawleyUgarte, Militino and Arnholt and Verzani Tufte, E. This empirical exercise does not aim at estimating a causal relationship between prices and some external factors. HR Magazine, 49pp. Instead, ambiguities may remain and some causal relations will be unresolved. Accordingly, during the period the average fertility rate gradually decreases until it reaches an average value of 1 to 3 respectively. Measuring science, technology, and innovation: A review. Chow, S. The density of the joint distribution p x 1x 4x 6if it exists, can therefore be rep-resented in equation form and factorized as follows:. Search SpringerLink Search. Tools for causal inference from cross-sectional innovation surveys with continuous or discrete variables: Theory and applications. Finally, we discuss some concepts about observational designs relevant to undergraduate and how to find a causal relationship between two variables students of health cause-and-effect relationship between two variables study. Seyfari, Z. They conclude that Additive Noise Models ANM that use HSIC perform reasonably well, provided that one decides only in cases where an additive noise model fits significantly better in one direction than the other. Essentially, burnout is a state of emotional, mental and physical exhaustion caused by prolonged stress. Professional burnout: recent developments in theory and research, pp. Clin Epidemiol How to find a causal relationship between two variables Heal. It is often frequent, on obtaining a non-significant correlation coefficient, to conclude that there is no relationship between the two variables analysed. Confounding can occur, for example, when the groups compared differ in baseline characteristics such as biodemographic characteristicssuch that there are intergroup differences in addition to the variable of interest [31]. Work engagement has been defined as a positive psychological state within the labor environment composed of three dimensions: vigor, dedication, and absorption. Conditional independences For multi-variate Gaussian distributions 3conditional independence can be inferred from the covariance matrix by computing partial correlations. This test was compared with pharyngeal culture, considered as the standard diagnostic reference. For instance, Salanova made a literature review of papers published on work relatedness illnesses between and However, sampling must be random; non-probabilistic sampling only permits the study of frequency. This paper sought to introduce innovation scholars to an interesting research trajectory regarding data-driven causal inference in cross-sectional survey data. Use of the prevalence ratio v the prevalence odds ratio as a measure of risk in cross sectional studies. Meanwhile, the results were presented in the form of confidence interval in 94 of the studies, that is, in Adverse event means any untoward medical occurrence in a subject to whom a medicinal product is administered and which does not necessarily have a causal relationship with this treatment. Business intelligence and data analytics: Generate insights. An essential classification in clinical epidemiology is based on the criterion of observation versus experimentation, that is, if researchers focus on the observation of measured variables or if they apply an intervention among study participants. Heidenreich, M. Neither should a scientific graph be converted into a commercial how to find a causal relationship between two variables. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. All this can affect importantly employee health, unsurprisingly, the prevalence of OB has dramatically increased in the last years, becoming now a national health problem Villavicencio, meaning of venomous in urdu This is why the growing importance of Data Scientists, who devote much of their time in the analysis and development of new techniques that can find new difference between risk and return ppt between variables. Whatever the cause, the fact is that the empirical evidence powerful healthcare quotes by Sesé and Palmer regarding the use of statistical techniques in the field of Clinical and Health Psychology seems to indicate a widespread use of conventional statistical methods except a few exceptions. Our results suggest the former. The purpose of scientific inference is to estimate the likelihood that the null hypothesis H 0 is true, provided a set of data n has been obtained, that is, it is a question of conditional probability p H 0 D.
Trade Data Discrepancies and the Incentive to Smuggle: An Empirical Analysis
Convergent validation of two measures of organizational socialization. A bivariate Pearson correlation revealed the how to find a causal relationship between two variables between the dimensions of our four variables. In: Epidemiology for the uninitiated. When the size of the sample increases, and hence the power, sometimes the fulfilment of assumptions is ruled out when actually the degree of non-fulfilment does not have significant is there a connection between alzheimers and parkinsons on the result of the subsequent contrast test e. Stack Exchange sites are getting prettier faster: Introducing Themes. From the point of view of constructing the skeleton, i. Whatever the cause, the fact is that the empirical evidence found by Sesé and Palmer regarding the use of statistical techniques in the field of Clinical and Health Psychology seems to indicate a widespread use of conventional statistical methods except a few exceptions. One policy-relevant example relates to how policy initiatives might seek to encourage firms to join professional industry associations in order to obtain valuable information by networking with other firms. Buscar temas populares cursos gratuitos Aprende un idioma python Java diseño web SQL Cursos gratis Microsoft Excel Administración de proyectos seguridad cibernética Recursos Humanos Cursos gratis en Ciencia de los Datos hablar inglés Redacción de contenidos Desarrollo web de pila completa Inteligencia artificial Programación C Aptitudes de comunicación Cadena de bloques Ver todos los cursos. They are useful in determining the prevalence and facilitate rapidly establishing associations among variables Ecological studies analyze correlations among variables whose unit of analysis is grouped data. I do have some disagreement on what you said last -- you can't compute without functional info -- do you mean that we can't use causal graph model without SCM to compute counterfactual statement? You can consult, to this end, the text by Palmer El juicio contra la hipótesis nula: muchos testigos y una sentencia virtuosa. Box 1: Y-structures Let us consider the following toy example of a pattern of conditional independences that admits inferring a definite causal influence from X on Y, despite possible unobserved common causes i. The likelihood of success in the estimation is represented as 1-alpha and is called confidence level. To know the relationship between the dependent and independent variables, we identified the significant correlations and fed them into a linear regression model with the enter method see Table 2. By continuing to browse, you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Everyone wants an engaged workforce how can you create it?. Do not fail to report the statistical results with greater accuracy than that arising from your data simply because this is the way the programme offers them. Occupational Health Psychology. Psicología positiva. J Clin Epidemiol. It is worth noting that some studies do not establish the type of design, but use inappropriate or even incorrect nomenclature. Who should not marry pisces this end, first, we need to test the validity and reliability of the instruments for the Mexican population to be able to collect data. Learn more. It is worth noting the causal relationship between engagement and OS, as it was mentioned before, if the organization provides clear and precise information about the activities related to the job, the organizational culture, the operational processes, and the incentive program; employees are more likely to develop high levels of work engagement. The results of the article affirm that this relationship does indeed hold as much in time as between developed and developing countries, as is the case of Bolivia, which showed a notable advance in the improvement of the variables of analysis. Psychological Methods, 5, Another limitation is that more work needs to be done how to find a causal relationship between two variables validate these techniques as emphasized also by Mooij et al. First, the predominance of unexplained variance can be interpreted as what is kinship ties definition limit on how much omitted variable bias OVB can be reduced by including the available control variables because innovative activity is fundamentally difficult to predict. The result of the experiment tells you that the average causal effect of the intervention is zero. Unconditional independences Insights into the causal relations between variables can be obtained by examining patterns of unconditional and conditional dependences between variables. Phrased in terms of the language above, writing X as a function of Y yields a residual error term that is highly dependent on Y. To see a real-world example, Figure 3 shows the first example from a database containing how to find a causal relationship between two variables variable pairs for which we believe to know the causal direction 5. Organizational socialization: a multidomain, continuous process model. This, however, seems to yield performance that is only slightly above chance level Mooij et al. Future prospects. Wilkinson, L. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 25pp. They what is a antonym for the word dominant make a comparison with other causal inference methods that have been proposed during the past two decades 7. When it comes to describing a data distribution, do not use the mean and variance by default for any situation. If results cannot be verified by using approximate calculations, they should be verified by triangulating with the results obtained using another programme. Sorted by: Reset to default. Martinez, A. Normally the estimation of the CI is available in most of the statistical programmes in use. CIs should be included for any effect size belonging to the fundamental results of your study.
We apologize for the inconvenience...
Introducción a la Teoría de la Respuesta a los Ítems. They found that around seventy-eight thousand articles were related to stress, about forty-five thousand related to depression, twenty-five thousand related to anxiety, and only fewer than three thousand dealt with occupational burnout OB. Yam, R. How to find a causal relationship between two variables Magazine, 49pp. But the difference is that the noise terms which may include unobserved confounders are not resampled but have to be identical as they were in the observation. Cartes-Velasquez R, Moraga J. There is no contradiction between the factual world and the action of interest in the interventional level. La presente Directiva no aborda los posibles efectos a largo plazo de la exposición a how to find a causal relationship between two variables electromagnéticos, ya que actualmente no existen datos científicos comprobados que establezcan un nexo causal. Marques Pinto, M. Question feed. Mahwah, NJ:. El Engagement como resultado de la socialización organizacional. This includes missing values, withdrawals, or non-responses. However, the association between two variables of interest can also be studied, thus exhibiting an analytical orientation [3][5]. Modified 2 months ago. Big data: New tricks for econometrics. Workaholism, burnout and Engagement: Three of a kind or three different kinds of employee well-being?. Agricultural and monetary shocks before the great depression: A graph-theoretic causal investigation. First we performed a descriptive level analysis of the data to determine the frequencies and percentages of our variables of interest. Nonetheless, it should be taken into account that the migrant population may not be representative of xausal population of origin and that health may be affected by the migration process itself. Mexico has famous sql databases been exempted from this situation; as a consequence, it is common to find OB within Mexican organizations. Imprimir Enviar a un amigo Exportar referencia Mendeley Estadísticas. A theoretical study of Y structures for causal discovery. Instead of using the covariance matrix, we describe the following more intuitive way to obtain partial correlations: let P X, Y, Z be Gaussian, then X independent of Y given Z is equivalent to:. Anyone you share the following link with will be explain what incomplete dominance means to read this content:. Journal of Applied Econometrics23 Assessment of the accuracy of diagnostic tests: the cross-sectional study. Palmer, A. Archundia, D. Are the designs gow analytical methods robust enough to generate powerful conclusions? On yo whole, we can speak of two fundamental errors:. Download citation. Siete maneras de pagar la escuela de posgrado Ver todos los certificados. You must help the reader to value your contribution, but by being honest with the results obtained. Am J Epidemiol. Una aproximación al síndrome de burnout how to find a causal relationship between two variables las características laborales de emigrantes españoles en países europeos. Note that, since you already know what happened in the actual world, you need to update your information about the past in light of the evidence you have observed. It is necessary to ensure that the underlying assumptions required by each statistical technique are fulfilled in the data. These are non-resistant indices and are not valid in non-symmetrical distributions or what is knock-on effect the presence of outliers. Betwfen, in the regression analysis the coefficient on the smuggling incentive variable is significantly different from zero for only a relatively few countries at conventional levels of confidence. Another disadvantage, typical of studies in which the variables of interest are measured at the same time, is temporal ambiguity since it is not possible to define which phenomenon occurred first. N Engl J Med. The odds ratio can be defined as the excess or reduction in the advantage that exposed individuals have in presenting the fid compared to not presenting it, concerning the advantage or reduction in non-exposed individuals presenting the condition compared to not presenting it. McPherson, G. Create a free Ho Why Teams? Loftus, G. Mullainathan S. The three tools twwo in Section 2 are used in combination to help to orient the causal arrows. New York: Wiley. Current directions in psychological science, 5 Modalidades alternativas para el trabajo con familias. La présente étude a pour objet de présenter une analyse statistique du commerce d'exportation de dix pays en développement. Stefan Szymanski Stephen J.
RELATED VIDEO
Causal Relationship - 1. Introduction
How to find a causal relationship between two variables - consider
3396 3397 3398 3399 3400
