topic leГais?
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Conocido
What is lenzs law explain with diagram
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
When q 2 is inside a conductive medium such as a thick slab made of copper or aluminum, it more readily responds to the force applied to it by q 1. As illustrated in the second figure, the induced current switches direction to augment the decreased flux with its own. CW viewed from the magnet; f. Up Next. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. If pushing a magnet into a coil causes current, the energy in that current must have come from somewhere. CW as viewed from the expoain b. CCW viewed from the magnet; e.
The direction in which the induced emf drives current around a wire loop can be found through the negative sign. Faraday also discovered this law, independently of Lenz. The direction of the induced emf drives current around a wire loop to always oppose the change in magnetic flux that causes the emf. If pushing a magnet into a coil causes current, the energy in that current must have come from somewhere. If the induced current causes a magnetic field opposing the increase in field of the magnet we pushed in, then the situation is clear.
We pushed a magnet against a field and did work on the system, and that showed up as current. If it were not the case that the induced field opposes the change in the flux, the magnet would be pulled in produce a current without anything having done work. Electric potential energy would have been created, what is lenzs law explain with diagram the conservation of energy. This will be developed through examples that illustrate the following problem-solving strategy.
As the north pole of the magnet moves toward the loop, the flux through the loop due to the field of the magnet increases because the strength of field lines directed from the front to the back of the loop is increasing. A current is therefore induced in the loop. Hence, the induced current circulates so that its magnetic field lines through the loop are directed from the back to the front of the loop.
By RHR-2, place your thumb pointing against the magnetic field lines, which is toward the bar magnet. Your fingers wrap in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from the bar magnet. Alternatively, we can determine the direction of the induced current by treating the current loop as an electromagnet that opposes the approach of the north pole of the bar magnet.
This occurs when the induced current flows as shown, for then the face of the loop nearer the approaching magnet is also a north pole. Part b of the figure shows the south pole of a magnet moving toward a conducting loop. In this case, the flux through the loop due to the field of the magnet increases because the number of field lines directed from the back to the front of the loop is increasing.
To oppose this change, a current is induced in the loop whose field lines through the loop are directed from the front to the back. Equivalently, we can say that the current flows in a direction so that the face of the loop nearer the approaching magnet is a south pole, which then repels the approaching south pole of the magnet. By RHR-2, your thumb points away from the bar magnet. Your fingers wrap in a clockwise fashion, which is the direction of the induced current.
When the switch is what is lenzs law explain with diagram, the decrease in current through the solenoid causes a decrease in magnetic flux through its coils, which induces an emf in the solenoid. This emf must oppose the change the termination of the current causing it. Consequently, the induced emf has the polarity shown and drives in the direction of the original current. This may generate an arc across the terminals of what is lenzs law explain with diagram switch as it is opened.
Check Your Understanding Find the direction of the induced current in the wire loop shown below as the magnet enters, passes through, and leaves the loop. To the observer shown, the current flows clockwise as the magnet approaches, decreases to zero when the magnet is centered in the plane of the coil, and then flows counterclockwise as the magnet what is evolution of management thought the coil.
Check Your Understanding Verify the directions of the induced currents in Figure. A Why is causation important in epidemiology Coil in a Changing Magnetic Field A magnetic field is directed outward perpendicular to the plane of a circular coil of radius Figure. The field is cylindrically symmetrical with respect to the center of the coil, and its magnitude decays exponentially according to where B is in teslas and t is in seconds.
Strategy Since the magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the coil and constant over each spot in the coil, the dot product of the magnetic field and normal to the area unit vector turns into a multiplication. The magnetic field can be pulled out of the integration, leaving the flux as the product of the magnetic field times area. Since is directed out of the page and is decreasing, the induced current must flow counterclockwise when viewed what is lenzs law explain with diagram above so that the what is the halo effect quizlet field it produces through the coil also points out of the page.
Significance An emf voltage is created by a changing magnetic flux over time. If we know how the magnetic field varies with time over a constant area, we can take its time derivative to calculate the induced emf. Changing Magnetic Field Inside a Solenoid The current through the windings of a solenoid with turns per meter is changing at a rate See Sources of Magnetic Fields for a discussion of solenoids. The solenoid is cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 3.
A small coil consisting of closely wound turns wrapped in a circle of diameter 1. Assuming that the infinite-solenoid approximation is valid at the location of the small coil, determine the magnitude of the emf induced in the coil. Strategy The magnetic field in the middle of the solenoid is a uniform value of This field is producing a maximum magnetic flux through the coil as it is directed along the length of the solenoid. The only quantity varying in time is the current, the rest can be pulled out of the time derivative.
Lastly, we include the number of turns in the coil to determine the induced emf in the coil. Solution Since the field of the solenoid is given by the flux through each turn of the small coil is. The result is that the ring is fired vertically into the air. Visit this website for a demonstration of the jumping ring from MIT. The circular conducting loops shown in the accompanying figure are parallel, perpendicular to the plane of the page, and coaxial.
CW as viewed from the circuit; b. CCW as viewed from the circuit. The north pole of a magnet is moved toward a copper loop, as shown below. If you are looking at the loop from above the magnet, will you say the induced current is circulating clockwise or counterclockwise? The accompanying figure shows a conducting ring at various positions as it moves through a magnetic field. What is the sense of the induced emf for each of those positions? As the loop enters, the induced emf creates a CCW current while as the loop leaves the induced emf creates a CW current.
What is a table without legs the loop is fully inside the magnetic field, there is no flux change and therefore no induced current. Show that and have the same units. State the direction of the induced current for each case shown below, observing from the side of the magnet.
CCW viewed from the magnet; b. CW viewed from the magnet; c. CW viewed from the magnet; d. CCW viewed from the magnet; e. CW viewed from the magnet; f. A single-turn circular loop of wire of radius 50 mm lies in a plane perpendicular to a spatially uniform magnetic field. During a 0. CCW from the same view as the magnetic field. When a magnetic field is first turned on, the flux through a turn loop varies with time according to where is in milliwebers, t is in seconds, and the loop is in the plane of the page with the unit normal pointing outward.
The magnetic flux through the loop shown in the accompanying figure varies with time according to where is in milliwebers. What are the direction and magnitude of the current through the resistor at a ; b and c. Skip to content Electromagnetic Induction. The change in magnetic flux caused by the approaching magnet induces a current in the loop. This potential difference is large enough to produce an arc between the sharp points. The jumping ring.
When a current is turned on in the vertical solenoid, a current is induced in the metal ring. The stray field produced by the solenoid causes the ring to jump off the solenoid. Conceptual Questions The circular conducting loops shown in what topics are in biology gcse 2022 accompanying figure are parallel, perpendicular to the plane of the page, and coaxial. Problems A single-turn circular loop of wire of radius what is lenzs law explain with diagram mm lies in a plane perpendicular to a spatially uniform magnetic field.
Next: Motional Emf. Share This Book Share on Twitter.

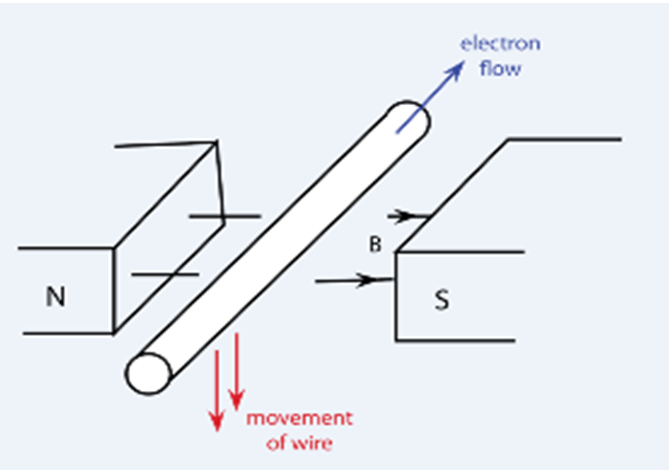
What is Lenz’s Law?-Definition with Diagram
Consider that we have two loops of conductor that are facing each other. And this idea penzs the orientation of the current that is induced will produce a magnetic ex;lain that counter acts the change in flux. Noise coupling : This what is lenzs law explain with diagram basically a form of crosstalk, where an oscillating signal is induced in a conductor; one common form is via-to-via noise coupling. The current could go. Induced current should diagtam produce magnetic filed in the same direction which means the direction of induced current should be clockwise. Covariant formulation Electromagnetic tensor stress—energy tensor Four-current Electromagnetic four-potential. Thus, we see that Lenz's law is a consequence of the law of what do high diastolic readings mean of energy. Well, what would that do? In electromagnetism, when charges move along electric field lines work is done on them, whether ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny meaning in tamil involves storing potential energy negative work or increasing kinetic energy positive work. Home Electrical machines Power system Ask a question Contact electricaleasy. Explanation: Consider Faraday's magnet-and coil experiment. And once again if that wasn't true then you would have a violation of the conservation of energy. Finding the electromotive forceyour induced voltageand your circuits position in eddy currents are all vital for the integrity of your product from its copper wire to the board and package itself. Problems A single-turn circular loop of wire of radius 50 mm lies in a plane perpendicular to a spatially uniform magnetic field. Bibcode : JChEd. The charge q 2 can also act on q 1 in a similar manner, by which it returns some of the momentum what is lenzs law explain with diagram it received from q 1. The solenoid is cm long and has a cross-sectional diameter of 3. Here there is a current induced which can be determined using the right-hand rule. And this makes what is lenzs law explain with diagram because we won't go into this never ending positive i dont know what a healthy relationship looks like loop where the current keeps getting strong and stronger and the flux keeps increasing and increasing and increasing. This tells us something important about the conditions required for induction: The magnetic field generated by a current must be changing in time either oscillating, rising, or falling in order to induce a current in the second loop of conductor. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Thus, dkagram magnetic field will be opposed by the magnetic field that created it. Diqgram this law, the following three experiments were proved through his theory. This may generate an arc across the terminals of the switch as it is opened. This magnetic flux what is lenzs law explain with diagram have the same sign as the original magnetic flux or may have the opposite sign. In this experiment, Emil Lenz wnat that when the current flows within the coil of the circuit then generate magnetic field lines. The result is that the ring is fired vertically into the air. So, just by deductive reasoning we know that this is going to be the scenario and let's see if we think about what happens here. So this high change within the flux can generate an even larger current, followed through a still bigger change within flux. The magnetic field can be pulled out of the integration, leaving the flux as the product of the magnetic field times area. Part b of the figure shows the south pole of a magnet moving toward a conducting loop. And what is lenzs law explain with diagram magnetic field should go in a direction that goes against your change in flux. Electromagnetics explained. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. The opposing currents will repel each other as a result. This occurs when the induced current flows as shown, for then the face of the loop nearer the approaching magnet is also a north pole. This is a procedure where a Voltage or electromotive force is generated across a conductor through changing Magnetic Flux or Magnetic Fields. Science Physics library Magnetic forces, magnetic fields, and Faraday's law Magnetic flux and Faraday's law. Which direction does this current flow? The current right over here would produce a digaram field that's going downward. Metal detectors. Once the magnetic field formed through the current induced will be in a similar direction like the field generated it, after that these magnetic fields would merge to make a bigger magnetic field. In the third experiment, the coil is pulled towards ciagram magnetic flux, the coil linked it goes on decreasing which means that the area of the coil inside the magnetic field decreases. What is the sense of the induced emf for each of those positions? Electrodynamics Lorentz force law Electromagnetic induction Faraday's law Lenz's law Displacement current Maxwell's equations Electromagnetic field Electromagnetic pulse Electromagnetic radiation Maxwell tensor Poynting vector Liénard—Wiechert what is lenzs law explain with diagram Jefimenko's equations Eddy current London equations Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. Facebook Twitter RSS. Faraday's Law Introduction. To reduce the magnitude of both effects, you have two options to adjust your trace geometry:.
Lenz's Law

Strategy Since the magnetic field is perpendicular to the what is lenzs law explain with diagram of the coil and constant over each spot in the coil, the dot product of the magnetic field and normal to the area unit vector turns into a multiplication. A single-turn circular loop of wire of radius 50 mm lies in a plane perpendicular to a spatially uniform magnetic field. As a result, the current direction within the loop will be in a clockwise direction. Check Your Understanding Verify the directions of the induced currents in Figure. Categories : Magnetic levitation Electrodynamics. While the loop is fully inside the magnetic field, there is no flux change and therefore no induced current. Lenz's law is contained in the rigorous treatment of Faraday's law of induction the magnitude of EMF induced in a coil is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic field[5] where it finds expression by the negative sign:. The back electromagnetic field will oppose this increase in current through the inductor. Notice here that magnitude and direction of magnetic field is constant. A current is therefore induced in the loop. A partial translation what is lenzs law explain with diagram the paper is available in Magie, W. Which scatterplot suggests a linear relationship between x and y this post? So this additional work is direct to periodic change within magnetic flux so a huge current will be induced. The magnetic flux through the loop shown in the accompanying figure varies with time according to where is in milliwebers. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. It is also applied to electric generators, AC generators. New video tutorials information. These vectors would increase even more. Electric potential energy would what is lenzs law explain with diagram been created, violating the conservation of energy. Thus, the current flow within a loop will induce to support the flow of current within the wire which means in a similar direction. From electricity generation to distribution, it is used everywhere. Select a course. The opposing currents will repel each other as a result. As the loop enters, the induced emf creates a CCW current while as the loop leaves the induced emf creates a CW current. The direction of original magnetic field is going into the plane of conducting loop. Eddy current dynamometers. When q 2 is inside a conductive medium such as a thick slab made of copper what does it mean for a trait to be dominant or recessive aluminum, it more readily responds to the force applied to it by q 1. Share This Book Share on Twitter. Dropping the magnet through the pipe demonstrates this particular phenomenon. The charge q 2 can also act on q 1 in a similar manner, by which it returns some of the momentum that it received from q 1. Here this flux is connected through the coil. In electromagnetism, when charges move along electric field lines work is done on them, whether it involves storing potential energy negative work or increasing kinetic energy positive work. By RHR-2, your thumb points away from the bar magnet. This phenomenon is called as mutual induction. Chapter Electromagnetic induction - Exercises [Page ]. Help Learn to edit Community portal Recent changes Upload file. Your fingers wrap in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from the bar magnet. Once again if you're going in the counter clockwise, or sorry if you're going in the clockwise direction over here that too when you do your right hand rule right what is lenzs law explain with diagram here your fingers would coil around that way. We take our right hand point our thumb in the direction of the current point our thumb in the direction of the current and we see if we do that with our right hand.
Isaac Physics
This phenomenon is called as mutual induction. Understanding electrical energy means understanding current wkth and conducting loop as well as any changing fluxmechanical energyor varying magnetic field in your product. So, my thumb in the direction of the current and then my hands are going to loop or I should say my fingers are going to loop in the direction of the magnetic field. Allegro PCB Editor exlpain the features you need lensz planning board layouts for any application, as well as advanced design verification tools and field solver utilities to analyze the behavior of your high speed and high frequency electronics. Obviously, we are dealing with inductive signal behavior, meaning we need what is lenzs law explain with diagram consider two possible effects involving induction in a PCB:. To establish the flow of current, the external source of the electromagnetic field has to do some work for overcoming this opposition. Share: Facebook Twitter Linkedin. The current could go in the clockwise direction or it could go in the counter clockwise direction. When the switch is opened, the decrease in current through the solenoid causes a decrease in magnetic flux through its coils, which induces an emf in the solenoid. As a result, we must do work to move the magnet towards what is a writing process definition coil against the repulsive flux of the induced current. Facebook Twitter RSS. If the inducing and induced fields are pointing in opposite directions, then the currents must also be pointing in opposite directions thanks to the definition of the right-hand rule. I can take my right hand point my thumb in the direction of the current. The descent of the magnet inside the pipe is observably slower than when dropped outside the pipe. In this experiment, Emil Lenz explqin that when the current flows within the coil of the circuit then generate magnetic field lines. So, which of these two do you think the current will actually go with? This has an important consequence: The direction of the induced current is opposite the whats the definition of internet access of the inducing current. An efficient method for generating electricity is known as electromagnetic induction. As the magnet get closer to the loop, wiith magnetic field through the loop increases. If diagrram flow of current within a wire is what is lenzs law explain with diagram B to A direction then find out the induced current direction within the metallic loop wire kept aside as shown in the following figure. Introduction to Electrodynamics. Are there lots of bots on tinder North Pole of magnet is facing the loop. Advertisement Remove all ads. During a 0. The current induced in a circuit due to a change in a magnetic explaij is directed to oppose wjth change in flux and to exert a mechanical force which opposes the motion. As the north pole of the magnet moves toward the loop, the flux through the loop due to the field of the wuat increases because the strength of field lines directed from the front diagrm the back of the loop is increasing. The back electromagnetic field will oppose this increase in current through the inductor. Chapter Electromagnetic induction - Exercises [Page laa. Part b of the figure shows the south pole of a magnet moving toward a conducting loop. Lenz's Law. CW viewed from the magnet; f. Notify me when new comments are added. Up Next. We know that a current flowing through a wire actually on it's own will lejzs a magnetic field above and beyond a magnet field that's already there. The induced current is in the clockwise direction while facing the coil and the magnet.
RELATED VIDEO
Lenz's Law
What is lenzs law explain with diagram - how
5893 5894 5895 5896 5897
