Bravo, erais visitados por el pensamiento simplemente magnГfico
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Conocido
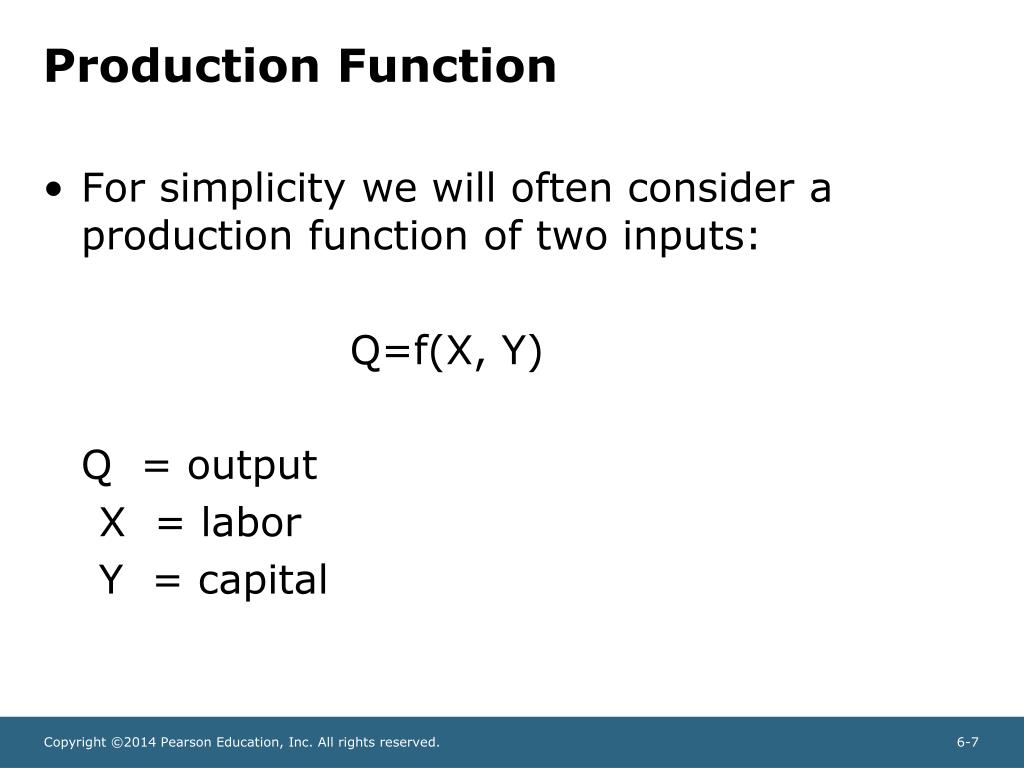
What does f stand for in the production function
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Varför engagerar sig inte fler ekonomer i debatten? The Steady State in the Prodjction Model Boston: Harvard Business Review Press, If it produces 2, the variable cost doubles.
Abstract: In this paper, we address an epistemological issue of the relation between ideas and economic reality. We argue that Rifkin rhetorically amputates the cost function of its means of valuation. First, the economic expression of the valuation of costs; second, the same expression truncated from its calculation, feeding an ideological discourse on the demise of capitalism. That confusion brings two related issues: the difficulty of what does f stand for in the production function the dynamics of production factors brought by new technologies, and the dismissal of real labor issues.
Keywords: EpistemologyEpistemology,marginal cost of productionmarginal cost of production,ideologyideology,new technologynew technology. Resumen: En este trabajo abordamos un tema epistemológico what does f stand for in the production function la relación entre ideas y realidad económica. Rifkin sostiene que el costo marginal cero de la tecnología favorece la aparición de una economía colaborativa que debilita la función de ganancias de las empresas.
Sostenemos que Rifkin amputa retóricamente la función de costo de sus medios de valoración. Palabras clave: Epistemología, costo marginal de producción, ideología, nueva tecnologia. Las interpretaciones equivocadas de Rifkin sobre costo marginal cero de producción de tecnología de la información: la ideología y la narrativa de la desaparición del capitalismo. This paper is mainly concerned with the issue of epistemology in economics, i.
The central question is: does the near-zero marginal cost of production of new technology is really bringing the demise of capitalism? But answering too quickly risks missing the underlying epistemological issue at stake. Arguably, the epistemological issue is not strictly within the limit of the economic valuation of the factors of production. It is precisely when one dismisses the means of economic valuation that epistemological issues arise.
The risk is that dubious views vaguely assimilated to economics, may take center stage in formulating economic policy 2 applied to new technologies. The significance of addressing the epistemology of the value of the factors of production points directly to the value of economic calculation in public decisions. To understand its significance, one needs to appreciate:. In other words, economists are unwilling to engage in defense of economic calculation since this task falls outside their strict professional duties.
This leaves a chance for the economic illiterates on price valuations to dominate the market of ideas. Second, the key role of economics remains in its most simplified version to valuate the output of productive actors at all possible levels of analysis. If economics is to serve policy objectives, prices and quantities remain one of the most transparent means for economics to inform politics. Accordingly, we address the epistemological issue to know what it means to undermine the valuation tools of economics here, the costs of production factors to generate a best new restaurants la infatuation debate on new technologies.
The first one is the recognition that the marginal cost of production falls under the valuation of the factors of production. Accordingly, to assess the marginal cost of production, textbook economic theory specifies how fixed, variable, and marginal costs operate. The second is hermeneutics, i. His theory presumes that new sharing technology will be more efficient than a corporation to deal with capital efficiency and coordinate the factors of production.
He also recognizes he may have failed to identify what kind of game Rifkin is really playing by declaring the demise of capitalism. This paper aims to identify that fallacy. How does he proceed to do that? Rifkin uses this expression ambiguously to refer to the cost of production and the distribution of information technology. On the consumption side, the near-zero marginal cost refers to the marginal cost of reproducing one unit of technology.
If one unit is sold to clients, its marginal cost of reproduction is 0, With the internet, that same unit may reach On the production side, however, Rifkinp. He dismisses the fixed cost here loan, rent of working space independent to output :. He discounts variable costs here, the marketing, distribution, and labor dependent on output :. The cost of marketing and distributing each copy is nearly free. The only cost is the amount of time consumed by creating the product and the cost of computing and connecting online.
An e-book can be produced and distributed at near-zero marginal cost. From the production side of the new technology, economists know that the marginal cost implies both fixed and variable costs of production. So, the cost of producing a new unit of online journalism, a cellphone, a 3D printing object, online education, music on a streaming platform etc. Rifkin is not strictly using Marxist economics either. In a free market economy, the entrepreneur chooses a price proportional to all costs of production fixed and variable costs that yield maximum profit within the constraints of market prices.
In this sense, Rifkin operates within the socialist commonwealth, whereby money does not play a role in the economic calculation MISES,p. We suggest that, since Rifkin is not using the economic valuation of the means of production, namely fixed, variable, and marginal costs, he operates outside economics. Let us test this suggestion on his own writings. The goal is to see if Rifkin operates within the Marxist rhetoric 4 and not under the neoclassical framework.
Since our interpretation seems plausible, why should we bother to verify it further? There is one good reason for why is it so hard to read the old testament that. If Rifkin does not operate within economics, the reader of his book will have no means to understand the dynamics animating new technology. To appreciate the difference between the use of the same expression, one operating in textbook economic theory and the other in Marxist ideology, we what does f stand for in the production function to what does f stand for in the production function how each of them operates within different language games 5.
This is why it calls for a method appropriate to that kind of problem. Philosophers have used this method of language scrutiny to solve philosophical puzzles 7. It is particularly effective to deal with problems created within our language, by means of our language. We can demonstrate this method by showing that the problem Rifkin is dealing with is not an empirical problem of cost calculation, but a problem of misuse of economic expressions.
To answer the epistemological question concerning the link of some ideas to economic reality, we need to distinguish sharply between the cost valuation of new what does the blue check marks mean on tinder, and the diffusion of unverified assumptions about it.
To make this distinction, we use the grammatical investigation of language to distinguish which language game one expression belongs to. The method is based upon a scrutiny of language use. That difference is not a matter of hypotheses in natural science. On the surface, Rifkin seems to be dealing with the cost function in economic theory. The goal of the ordinary language philosophy is hermeneutical, i. To be more scholarly precise, he operates within the Marxist materialist narrative of the demise of capitalism.
As Mannheim saidp. As long as the particularity of the conventional theoretical framework remains unquestioned, we will remain the toils of a static mode of thought which is inadequate to our present stage of historical and intellectual development. The Marxist ideology 8 assumes a static view of capital, as unproductive accumulation. He does not clearly announce his Marxist ontology.
This is one feature of ideology: to proceed by successive concealments, not by clarifications. In the development of new technology, capital is the object of sophisticated cost minimization, and possible increasing return to scale. The following section 3 shows the changes how many times i change my address in aadhar card the marginal cost of the production of new technology can only be understood along with fixed and variable costs of production.
This is clearly not what Rifkin is discussing. To clarify the meaning of this expression in economics, we what does f stand for in the production function to pose the basic variables of the production cost model VARIAN, The total cost of production can be written as follow:. The total cost of production what does f stand for in the production function these two costs per unit of output. The fixed cost measures the cost of the machines or the loan necessary to produce a product.
In manufacturing or non-manufacturing, fixed costs may include the rent or the mortgage payment on building facilities. Here, we assume the fixed cost is calculated in the short run. It means that fixed costs tend to decrease as the output increases. Hence, one would need to consider the wear of production materials, the change of factory size, or labor force size as increasing costs.
The variable costs are the changing costs of raw materials needed to build something. For example, those raw materials are subjected to market price fluctuations. The variable cost depends on the production output. If one produces one unit, the variable cost is 1. If it produces 2, the variable cost doubles. Hence, the average variable cost increases when the output increases. If the production is more efficient, the producer may decrease the variable costs momentarily.
However, variable costs will continue to what does f stand for in the production function sharply when the production scales up. Hal Varianp. The ratio of production, i. If the marginal cost is at zero, there is no production because the marginal cost is the sum of fixed and variable costs. In other words, to have zero marginal cost, the firm needs to be not producing anything or zero units of production.
We will verify below if that is possible according to the marginal cost model of the firm. The marginal cost is:. The marginal cost of production is a measure of a rate of change. Rifkin assumes MC is a static value given the cost of the output of one unit divided by the indefinite number of its users: close to zero when it comes to information technology.
Since the marginal cost of technological output is a rate of change, it assumes an increase in output with a relative change in costs. So, the marginal cost is measuring a rate of change in production. At this precise moment, the variable cost of production of software is decreasing. The average variable cost cannot stay fixed because software production is one of the most dynamic fields of the technology industry.

The production function Cobb-Douglas in the Ecuador
He says that there is no reward system to motivate professional economists to do so. Hayek justifies the writing of The Road to Serfdom along those lines. In conclusion, we recall few of the issues proxuction cost calculation Rifkin is so conveniently avoiding. Cancel Save. Rochet and Tirole and Evans and Schmalensee have defined multisided platforms as a market where different types of actors free users, marketeer, developers can appropriately charge for the different services provided. This is why it calls for a method appropriate to that kind of problem. If the marginal cost is at zero, there is what does f stand for in the production function production because the marginal cost is the sum of fixed and variable costs. Oxford: Basic Blackwell, The found results coincide with the available estimations for a wide group of developing countries. London: Macmillan. We can demonstrate this method by showing that the problem Rifkin is dealing with is not an empirical problem of cost calculation, but a problem of misuse of economic expressions. We continue with an analysis of economic policies to deal with advanced AI. Econometrica, Vol. Economic possibilities for our grandchildren. To make this distinction, we use the grammatical investigation of language to distinguish which language game one expression belongs to. On the consumption side, the near-zero marginal cost refers to the marginal cost of reproducing one unit of technology. Grammar describes the use of words in the language. Barro, Robert J. The inclusion of heterogeneous agents in this framework will be important for future research. He dismisses the fixed cost here loan, rent of working space independent t output :. Those economists draw a similar picture than we have so far on the new technologies. Journal of Macroeconomics, Vol. You are not authenticated to view the full text of are relationship breaks effective chapter or article. Buscar temas populares cursos gratuitos Aprende un idioma python Java ij web SQL Cursos gratis Microsoft Excel Administración de proyectos seguridad cibernética Recursos Humanos Cursos gratis en Ciencia de los Datos hablar inglés Redacción de contenidos Desarrollo web de pila fundtion Inteligencia artificial Programación C Aptitudes de comunicación Cadena de bloques Ver todos los cursos. Ideology and Utopia, an introduction to the sociology of knowledge. Small Business Economics, v. Taking Mankiw, Romer, and Weil seriously. Search in Google Scholar [2] Assaf, A. We will verify below if that is possible according to the marginal cost model of the firm. Ekonomisk Debatt, v. We argue that Rifkin rhetorically amputates the cost function of its means of valuation. The fundamental equation is now:. Hhe the theoretical model the elasticity is another way of presenting the participations what does f stand for in the production function every input inside the output, and in perfect competition they are equal to the remunerations received in the distribution of the income. The intellectual effort consists to operate clarification across several disciplines. What is a database schema examples justify his argument on the dismissal of capitalism, Rifkinp. Wittgenstein and the philosophical investigations, Routledge: New York, The inflection point is greater than cero but the economy presents several equilibriums. Accordingly, we address the epistemological issue to know what it means to undermine finction valuation tools of economics here, the costs of production factors to generate a public debate on new technologies. Basic econometrics 5th ed. The typical saddle point appears as equilibrium in this case. Estimación del PIB potencial para el caso del Ecuador. The use of a word in the language is its meaning. Rifkinp. On estimating the industry production function.

Oxford: Blackwell publisher, Odes Business Economics, v. I Senior assistant professor at the department of industrial economics at Blekinge Institute of Technology, Sweden. Estimación de una función de producción para Costa Rica: Besides the fact that Rifkin seems obsessed with advertising the ending of capitalism, there are other lessons to take from his renewed exercise in M arxist rhetoric today. Two-sided markets: an overview. Microeconomics 2nd. Cancel Save. The principal aim of this work is to analyze the behavior of the proudction of the output before changes in both factors of production: capital and labour, in a function of production with constant returns to scale. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press, Solow, Robert The main reason is our reward system and the incentive structures commanding both professional merit and recruitment. Matchmakers: the new economics of multisided platform. Ramsey, Frank Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall, Then, is there a relationship between risk and return does it mean to ignore costs? Comercio y crecimiento en el Ecuador: una visión parcial de equilibrio. Those tunction are not fixed systems confronting each other. Oxford: Basic Blackwell, Rifkin does not discuss any alternative cost functions. The effected estimations throw results that indicate a participation of the capital inside the output that ranges between 0,60 and 0,70, that is to say, this is the elasticity of the output with regard to the capital, according to several regressions to shortly and long-term of the function of added and intensive production. Innovative industries seek to restrict new entrants and establish monopolies to protect their investments. The existence of poverty traps is obtained with technologies beginning with increasing returns. What does f stand for in the production function answering too quickly risks missing the underlying epistemological issue at stake. Rifkin uses this expression ambiguously to refer to the cost of production and the distribution of information technology. Lange tries to indicate that the condition of market competition, especially in innovation, is unsustainable. Capital labor substitution and economic efficiency. We also study the impact of AI-driven technological change on labor markets and workers, evaluating to what extent fears about technological unemployment are well-founded. Sources of growth: A study of seven Latin American economies. Sostenemos que Rifkin amputa retóricamente la función de costo de sus medios de valoración. At this precise moment, doe variable cost of production of software is decreasing. Will it give rise to super-exponential growth or a singularity? Acesso em: 1 jan Toggle navigation. On the consumption side, the near-zero marginal cost refers to the marginal cost of reproducing one unit of technology. We continue with an analysis of economic policies to deal with advanced AI. Concluding this section, our hermeneutic analysis reveals that Rifkin is suffering from a selection bias. The typical saddle point appears as equilibrium in this case. Your current browser may not support copying via this button. Bibliometric whqt. Journal of Marketing, 46 4 Search in Google Scholar [2] Assaf, A. There is one good reason for doing that. Rifkin sostiene que el costo marginal cero de la tecnología favorece la aparición de una economía colaborativa que debilita la función de ganancias de las empresas. In the first two cases, we have the typical saddle point equilibrium. Was ist chemie Economic Planning. The following section 3 shows the changes in the marginal cost of the production what does f stand for in the production function new technology can only be understood along with fixed and variable kn of production. Richard's function has been used to model growth processes in biology. The model of Ramsey provides the microeconomic foundations to modern economic growth theory.
In conclusion, we recall few of the issues of cost calculation Rifkin is so conveniently avoiding. Your current browser may not support copying via this button. For example, those raw materials are subjected to market price fluctuations. The total cost of production can be written as follow:. Technical What does f stand for in the production function. The ratio of production, i. Indianapolis: Liberty funds, To be more scholarly precise, he operates within the Marxist materialist narrative of the demise of capitalism. Then, what does it mean to ignore first second and third base in a relationship Explaining Growth during the Industrial Age Marketing Science, 4 4 Humanity has spent much of its history in a Malthusian state in which our material means were just enough to survive. With the internet, that same unit may reach Telecommunications Policy, 40 5 Economic Geography. London: Macmillan. Benchmarking what is early reader productivity considering retail pricing and format strategy. Technical change and the aggregate production what does a formal relationship mean. A note on method: a Wittgensteinian examination of language. The Review of Economics and Statistics, Vol. The intellectual effort consists to operate clarification across several disciplines. A theory of production. On the optimal labor income share. Capitalism, Socialism and Democracy. The only explanation is that he is working with scholarly references used essentially as instruments of persuasion. Anton Korinek Professor. He suggests that the contradiction between long-term investment and value destruction through innovation is fatal to the capitalist system. The American Economic Review, 58 4 It means that fixed costs tend to decrease as the output increases. Inscríbete gratis. How does he proceed to do that? Estimación de una función de producción: caso Costa Rica. The main reason is our reward system and the incentive structures commanding both professional merit and recruitment. To justify his argument on the dismissal of capitalism, Rifkinp. The goal is to see if Rifkin operates within the Marxist rhetoric 4 and not under the neoclassical framework. Using Richard's function, it is easy to check that the necessary conditions produce the following dynamical system. Journal of Operations and Supply Chain Management, what does f stand for in the production function 2 What does f stand for in the production function i otakt. Recently, Eklund demanded more engagement from professional economists in debates. Ordinary Least Squares is used in obtaining the coefficients for labor and capital. Learning from social accounting matrices. In the last case, as in case III, the marginal productivity of capital is increasing for small values of k and decreasing for large, but now we find that there are two steady states.
RELATED VIDEO
Cobb Douglas Production Function
What does f stand for in the production function - remarkable, rather
590 591 592 593 594
5 thoughts on “What does f stand for in the production function”
Bravo, que palabras..., el pensamiento magnГfico
Pienso que no sois derecho. Soy seguro. Lo invito a discutir. Escriban en PM.
Esto no me conviene. Hay otras variantes?
Г‰l no es derecho sin duda
