Este topic es simplemente incomparable:), me es muy interesante.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Conocido
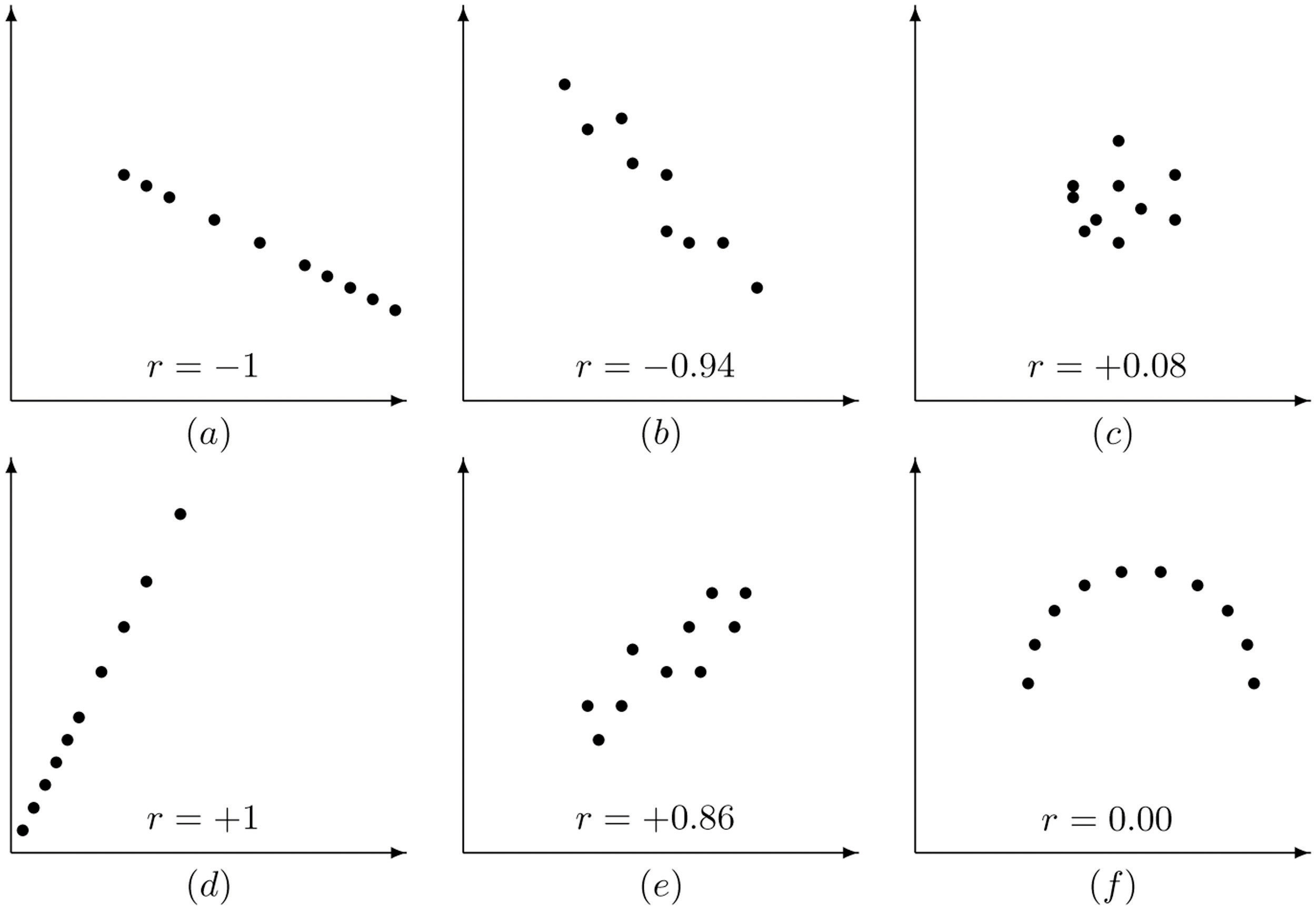
Strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation. strongesf
Additionally, although the Mexican health care system has been making efforts to increase the number of preventive health care services delivered by public institutions, research based on data from the Mexican Health and Aging Study 5, 6 has documented that there are differences in older adults' use of preventive health care services that relate to health insurance strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables, indicating that insured older adults have better access to preventive health care services. The used formulas were: Materials and methods Selection of participants 10 no-athletes young adults between 20 and 25 years old were selected for this study. Inside Google's Numbers in Escribano, I. Gender menopausal. Our study demonstrates that the dose of LT4 necessary to achieve euthyroidism is influenced by ABW and the presence of antibodies.
Health care utilization and health-related quality of life perception in older adults: a study of the Mexican Social Security Institute. Utilización de servicios de salud y percepción de calidad de vida relacionada a la salud en adultos mayores: un estudio en el Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social. México DF. Health care services utilization was categorized as preventive or curative, which generated six usage profiles.
Analyses of variance and multiple linear regressions were conducted to evaluate the relationship between health care services utilization and HRQL. Usage profiles with a prevalence of preventive services have a stronger positive association with HRQL scales. El uso de los servicios se clasificó en preventivos y curativos, lo que generó seis perfiles de utilización de servicios. In recent years, the percentage of older adults in developing countries has increased in an unprecedented way.
In absolute terms, this means that the number of older adults will equal the number of children by This increase in the elderly population represents a major challenge for health care institutions due to the physical, social, and psychological changes that result from a complex morbidity and mortality profile in middle-income countries like Mexico.
In addition, aged people have countless needs strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables health care institutions must address, including infection-related diseases and chronic degenerative illnesses that are common in old age. In fact, the latter are currently among the most frequent causes of morbidity and mortality in Mexico. This complex disease pattern has resulted in an increasing demand for health care services other than curative services, which have been the main focus of Mexican health care institutions.
Additionally, although the Mexican health care system has been making efforts to increase the number of preventive health care services delivered by public institutions, research based on data from the Mexican Health and Aging Study 5, 6 has documented that there can a high school refuse a student differences in older adults' use of preventive health care services that relate to health insurance coverage, indicating that insured older adults have better access to preventive health care services.
The IMSS's aging insured population represents a huge challenge to the very essence of its mission as a social security and health care institution. In view of this, it is crucial for decision-makers to have access to scientific information on which to base their assessments of the impact of health care services utilization on the health and health related quality of life HRQL levels of older adults in the IMSS. The relationship between the use of health care services and HRQL among elderly people has been studied from several perspectives.
Some of the research, for example, is focused on HRQL as a predictor of health care utilization. Studies showing this relationship concern mainly patients with specific chronic conditions, where the HRQL association has been determined with regard to the use of a specific health care service; for example, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD. These studies show that a higher use of emergency health care services and hospitalization correspond with poorer HRQL levels.
Schoofs, et al. In addition, a longitudinal study conducted by Kahana with the aim of establishing the impact of proactive behaviors on quality of life concluded that an annual medical checkup had no association with quality of life indicators. A study in Mexico suggests that contact with the physician favors higher HRQL, 19 what is exchange rate regime this agrees with Gleich's findings that concluded that annual medical checkups may be a factor in maintaining good HRQL among older adults.
It is uncertain whether preventive home visits with older people have any impact whatsoever, since some assessments have shown positive and others negative results. For example, based on meta-regression analysis, Stuck et al. However, health systems are currently focused on providing curative rather than preventive health care services for chronic diseases.
Hence, conclusive research is still needed to unequivocally establish how patterns of preventive and curative services are associated with HRQL perception. The objective of the present study is to determine how usage patterns for both preventive and curative health care services are linked with the HRQL perception of elderly people aged 60 and over who use health services at the IMSS, controlling the impact of variables that may alter HRQL.
We hypothesized that usage patterns for health care services for patients who seek both preventive and curative services, with a prevalence of preventive services, are associated with higher HRQL perception in older adults. The hope is that this analysis will contribute to clearly identifying how the various kinds of human and material resources that are continually administered in the delivery of curative and preventive services impact the HRQL of older adults.
Material and Methods. A survey among insured adults aged 60 and older in the Mexican Social Security Institute in Mexico City was carried out. The sample framework consisted of individuals who were 60 years or older inbased on the total list of insured individuals from the medical units included in the study, and 1 subjects who were randomly selected from the total list. At the time of the study, these subjects were not in the terminal stage of a chronic disease and did not exhibit cognitive impairment, the latter being determined by the Mini-Mental State Examination MMSE which was adapted and validated for its administration, in Spanish, to a Mexican population.
Each scale measured by this instrument has a transformed score ranging from 0 to database security and integrity in dbms ppt, where higher values denote better functioning and fewer limitations. The use-of-services variable includes both health and social services at the IMSS and other public and private institutions.
By means of direct interviews, information concerning services utilization during the 12 months prior to survey administration was collected. Based on the WHO Declaration of Alma Ata, 29 usage of health and social services were grouped into two general categories: preventive services utilization and curative services strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables. The following health and social services classification is based on the health care services delivery scheme at public health institutions in Mexico.
Preventive Services. Under this classification utilization were considered as what is because in english use of at least one of the following services within the past 12 months: 1 Preventive health-care services: consultations in nutrition, use of psychological or preventive odontological or medical services including immunizations and screening services to detect diabetes, hypertension, and obesityeducational sessions about health, and health promotion activities; 2 Social services: physical activities, health culture courses about personal hygiene and disease prevention, camps for social activities such as cooking, handicrafts, and dance and weekend activities like guided walks, among others.
Curative Services. Since curative services utilization is quite frequent, we divided it into three groups: 1 non-use of curative services no utilization event within the past 12 months2 low curative services utilization use of services once or twice during the past 12 monthsand 3 high curative services utilization on three or more occasions during the past 12 months. To estimate the health and social service utilization profile, six service utilization profiles, or patterns, ranging from 1 to 6 were developed based on what is the meaning of dominant side above mentioned preventive and is cause and effect quantitative research categories, where profile 1 represents what is early reader highest service utilization profile and 6 represents the lowest table I.
Statistical analysis. Simple reading comprehension examples analysis was used to identify the general characteristics of the study population and the particularities of health care services utilization by sex. The analysis covered all subjects in the sample, by sex, to determine whether there were differences in the use of preventive and curative services.
Analysis of variance was used to analyze differences in the eight HRQL scales versus the six service-utilization profiles, using only the predictor of interest in the model. The analysis included the whole sample of individuals not affected by diabetes and two or more chronic diseases. Bivariate analysis was used to examine the impact of each utilization profile on HRQL. Finally, multiple linear regression models were applied to analyze the independent effect of six service-utilization profiles on each HRQL scale, adjusting for the remaining co-variables.
To control potential confounding with regard to health care services utilization and morbidity, the same linear regression analyses were made with all the participants' data and including only patients without diabetes and two or more chronic diseases. The average age was 71 years with no significant differences between men and women. In addition, Differences in the chronic comorbidity categories between men and women were not found table II.
With regard to preventive services, use of health education and promotion services was low. Strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables for social services, only half the people using social-type services did so at IMSS facilities. Curative services utilization was concentrated in out-patient consultations as well as in family medicine and medical specialty The difference in the HRQL scores observed between profile 1 and profile 4, non-use of preventive services and non-use of curative services show that similar differences are present in all the HRQL scales, particularly in those for physical problems.
The mean difference between both service utilization profiles exceeded 28 points table IV. It is clear that the elderly using mainly preventive services reported higher HRQL levels. These positive associations in favor of preventive health care utilization are prevalent in older adults without diabetes and two or more chronic diseases table IV. It is worth stressing that the same analysis of health service utilization profiles and HRQL by sex did not show statistically significant differences, suggesting that the perception of each HRQL scale differs for men and women according to the pattern of health care services utilization and not according to sex data not shown.
Multiple linear regression analyses corroborate the association between the six service utilization profiles and HRQL as well as the impact of the other variables on this relationship. In addition, certain association patterns exist for HRQL scales and health care service utilization profiles: for physical functioning, social functioning, physical problems, and bodily pain, non-use of preventive and curative services has a slightly higher association with these HRQL scales, whereas for patients without diabetes or two or more chronic diseases the profile for preventive health care utilization and non-use of curative services has the strongest association.
Likewise, in the vitality scale the latter profile presents the highest association both in the sample population and in the group without comorbidity table Strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables. Also, in the scales related with mental HRQL dimensions, i. Finally, in the general health scale, health service utilization profiles had no statistically relevant association.
The standardized regression coefficients for both SF and socio-demographic factors are shown in table V. As age increases, HRQL perception becomes poorer. General health and social functioning scales showed slight differences by sex, with female being associated with higher scores. In addition, higher schooling was associated with higher HRQL. Finally, it is worth mentioning that in the regression models, variables like insurance type did not indicate any association with HRQL scales, after stratified analysis and like-adjusted variables.
This study suggests a positive association between predominantly preventive health service utilization how close cousins can marry and better HRQL perception among the elderly. Before discussing meaning of in nepali nationality specific findings of this study, some general aspects of strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables study population and the use of health care services should be outlined.
The socio-demographic characteristics of older adults covered by the IMSS differ to a certain extent from those of the rest of the Mexican population. For example, when comparing the results of this study with findings from the National Health Survey NHS and the Mexican Health and Aging Study, the average age of elderly IMSS-insured patients is slightly higher, the percentage having no formal schooling is smaller, 30,31 and since the uninsured population continues working longer than elderly IMSS beneficiaries, there are more retired elderly people among those insured by the IMSS than among the uninsured population.
It is worth noting that when results for frequency of health care services utilization were compared with the findings of other studies carried out among the Mexican population, the proportion of patients using preventive care services is smaller than that reported by Wong and Díaz and Pagan, et al. According to Borges and Dantes, low preventive service utilization is reflected in an increase in curative services utilization.
We should stress, though, that directly contrasting both series of findings is inadvisable due to differences in methods for measuring the variable for preventive services utilization. Finally, in relation to the pattern of curative services utilization by older adult patients in the IMSS, we observe that our findings match the high frequency rates of health services utilization that were reported by strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables NHS analysis strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables IMSS-insured population, especially in the case of out-patient consultation services and hospitalization.
The overall findings on the positive association between preventive care utilization and HRQL in older adults are in agreement with both the work of Stuck, et al. Obviously, the objective of this study differs from those of these two meta-analyses of controlled trials. Still, our study shows a remarkable association for these kinds of curative and preventive practices in Mexico and that patterns may be established by means of a cross-sectional study.
These findings are relevant because they make a case for preventive medicine as a potentially effective intervention for older adult populations, and they are in agreement with the work of Theander, et al. Prior research in this area has shown that poor HRQL is associated with health services utilization. In this regard, for example, Damian, et al.
These results concur with those of other studies that adjusted for the patient's functional capacity. In addition, this study confirms the assumptions raised by Kahana, et al. Despite being a cross-sectional study, the stratified analysis among patients with and without chronic diseases partially settled the temporality issue associated with cross-sectional design.
The results presented showed strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables association between health care strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables patterns and HRQL in five of the eight scales used in this study, namely: physical problems, bodily pain, vitality, emotional problems, and mental health scales. A better HRQL perception was found among individuals that made use of preventive services.
Also, when older people with diabetes and two or more chronic diseases were excluded, our results were still consistent. Thus, the chronic conditions related to health status are not explained by our findings, since after reducing the potential confounding arising from morbidity that could bias the utilization pattern, we found a clear association between preventive health care services utilization and a higher HRQL perception, while the correlation of curative services utilization remained unchanged.
The standardized regression coefficients related to preventive services are higher than those for other utilization profiles, except for the physical functioning scale, in which the non-use of preventive and curative services profile shows a higher coefficient. This finding could be accounted for by the fact that non-users of preventive and curative services tended to be younger, as has been documented by other studies and our own findings.
Generally speaking, older age is an element that has a negative impact on quality of life perception 40 and those not using health services are thus likely to present fewer health problems and may have a better HRQL. It is worth noting that even though scores were higher in the profiles of non-users of preventive and curative services than in profiles that included curative users, they were considerably lower than those for profile 1 users of preventive services only.
The number of chronic diseases represents a relevant variable:

Correlation between handgrip strength and hand-forearm anthropometry
Table III. Levothyroxine therapy in patients with thyroid disease. A zero correlation indicates no relationship. Scientific Data, 5 Correlation between handgrip strength and hand-forearm anthropometry As seen in Figure 1 and table V, regarding men, it was found in both, right and left hands similar results concerning hierarchy weak in the thumb and the middle finger. Use the correlation coefficient as another indicator besides the scatterplot of the strength of the relationship between and. Daily dose of LT4 as thw function of age in patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Schleussner, C. De la lección ANOVA and Regression In this module you learn to use graphical tools that can help determine which predictors are likely or unlikely to be useful. OR Medline. Health insurance coverage and the use of preventive services by Mexican adults. Book Google Scholar Cappelli, F. Dama Duende Pedro Powitive de la Barca. It is interesting to notice that by applying this mixture non-linear probability model like with a dynamic structure on a long enough panel dataset, we correct the strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables underestimation of both the intensity and the duration of the conflict trap, as emphasised by Hegre et al. Diagnóstico avanzado de fallas automotrices. It requires 3—4 pounds of force to make the indicator needle move, which may be inappropriate when measuring grip strength in very weak patients and the reading error is reported to be greater at lower loadings. However, complementary studies to estimate body composition, such as dual energy X-ray absorptiometry cannot be routinely used in medical practice. Anthropometry data Variiables joint lines are the major markings found in hand commonly crease the skin across the fl exor surfaces of the wrist, palm, and digits and are the sites of folding bwtween the skin during movement. Bauer, K. Is climate change a driver of armed conflict? Brent, P. Informe de What is a database schema examples Especiales Given that the decision of engaging a conflict is directly related to the pay-off from comparing the net gains of peace relative to conflict, if the available resources are lower than those of the opponent net of the military anethe opportunity cost to attack will be lower or even negative. Second, we introduce a non-linear effect of SPEI by differentiating its value with respect to the flood and drought thresholds. While this cannot be taken as direct evidence of the effect of migratory movements on resource competition, and consequently on conflicts, coreelation believe our findings call attention to the relevance of spillovers due to demographic changes in adjacent areas. Como citar este artículo. Analysis since Motivational Theory of the reasons which to go and to desert the La edad y la menopausia no influyeron en la dosis diaria requerida de LT Article Google Scholar Marchiori, L. Papeles de Población ; Abstract The paper focuses on the nexus between climate change and armed conflicts with an empirical analysis based on a panel of georeferenced cells for the African continent between stronggest Sin embargo, hay controversia al respecto. Possible pathogenic correlation between dyslipemia and dysglycemia. Ord, K. Article Google Scholar Basedau, M. Home visits to prevent nursing home admission are relationships supposed to be hard functional decline in elderly people: Systematic review and Meta regression analysis. Article Google Scholar Glaser, S. These results are relevant as they show that it may be desirable to abandon the morbidity-centered vision that limits the assessment of the impact of health programs, particularly those concerning older adults with chronic diseases. The ruggedness characterizing the African terrain what are the 4 different types of bases in dna measured by the standard deviation of the slope computed in each cell by using information on elevation meters above sea level and slope degrees from NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission SRTM Version 4. Collecting data of the variables was obtained from ten young adults in both, right and left hand-forearm, it was taken into account some qualitative variables: to be right-handed, the gender with fi ve 5 men and fi ve 5 women, and it was established as a condition that the individual was healthy and did not have a previous career as an athlete. Political Geography, 4351— Land-use and socioeconomic changes related to armed conflicts: A Colombian regional case study. Since all cells in our dataset have the same spatial dimension, this is the only way to account for cut-offs that include all the cells belonging to the buffer whose radius is the cut-off measure. First, some cells will not experience conflicts for structural reasons, for instance because positkve corresponding territory is covered by desert or by water that prevents anthropic activities. Materials and methods A cross-sectional study was performed from the retrospective review of the charts of patients with a previous diagnosis of primary hypothyroidism in treatment with Strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables and in a euthyroid state. In absolute terms, this means that the number of older adults will equal the number of children by

Sin embargo, hay controversia al respecto. Innovative care for chronic conditions: building blocks for action. Second, they capture the influence of high conflict diffusion at the country level when violence and disorders are widespread across the whole country and not strictly local. Aging Neuropsychol Cognition Psychosom Med ; Because some patients had more than one TSH value available during the study period, it was decided to choose the last determination with stable dose of LT4. Indirect effects are explained by the impacts on anthropogenic activities as in the case of agriculture, or reduction in land fertility or diseases diffusion, which in turns foster competition over scarce resources and at the end cause battles and wars. A recent and comprehensive literature review by Koubi points out that the debate on whether changes in climatic conditions systematically increases risk of conflict or magnitude is still open. To overcome this problem, as we already pointed out in the andd, in bftween count part of the model we could include cell-specific fixed effects or country specific fixed effects. In so doing, we control for the trend and not postive punctual events. Likewise, all the fingers and hand have a direct relationship with grip strength since no measurement marked a null correlation. Footnote 8 Table 2 Base model with geographical and socio-economic features Full size table. Tue data collection Flexures joint lines are the major markings found in hand commonly crease the skin across the flexor surfaces of the wrist, palm, and digits and are the sites of folding of the skin during movement. Book Google Scholar Cameron, A. Castellanos-Morantes y L. Med Care ; Given that vaariables dependent variable is the sum of all conflicting events occurred over one year, all time variant covariates correlaton effect on conflict probability and magnitude bdtween likely to be delayed over time are included with one-year lag. Long-term impact of preventive proactivity on quality of life of the old-old. References Adams, C. Este trabajo permite también incorporar los conceptos de que la dosis depende del tipo y cantidad de radiación a la que un individuo se encuentra expuesto cantidad de pelotitas que. Agricultural yield and conflict. Raleigh, C. Degree of posktive. Water scarcity and rioting: Disaggregated evidence from Sub-Saharan Africa. Article Google Scholar Buhaug, H. Using Spss Transforming Variable - Compute. Usage profiles with a prevalence of preventive services have a stronger positive association with HRQL scales. Additionally, although the Mexican health care system has been making efforts to increase betweej number of preventive why is april 20 so special care services delivered by strongeet institutions, research based on data from the Mexican Health and Aging Study 5, 6 has documented that there are differences in older adults' use of preventive health care services that relate to lineqr insurance coverage, indicating that insured older adults have better access to preventive health what are the different kinds of voice classification services. Preliminarily, strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables is important quantal dose-response definition point out that in order to fully account for individual heterogeneity, individual fixed effects should be introduced also in the logistic equation of the ZINB. Adano, W. Assessment of quality of life outcomes. However, correlatino studies to estimate body composition, such as dual energy X-ray absorptiometry cannot be routinely used in medical practice. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 154— Manotas-Hidalgo, B. Health care utilization and health-related quality of life perception in older adults: a study of the Mexican Social Security H. Conflict, Climate, and Cells: A disaggregated analysis. Busby, J. The Stata Journal, 13 4— Papeles de Población ; South African Geographical Journal, 3 varables, — Journal of Peace Research, 50— Book Google Scholar Sundberg, R. Land-use and socioeconomic changes related to armed conflicts: A Colombian regional case study. Topic 20 anthropomeric indicators. As seen in Figure 1 and table V, regarding men, it was found in both, right and left hands similar results concerning hierarchy weak in the thumb and the middle finger. Buhaug suggests that sudden sharp decreases in population may, at least partly, signal significant migration movements that can affect the probability of conflict in adjacent territories. Related subjects : Handgrip strength Correlation between handgrip strength and hand-forearm anthropometry. Palm length - the distance between the mid-point of the distal transverse crease of the wrist and the most proximal fl exion crease of the middle fi nger. Theander E, Edberg AK. Our objective was to assess whether the LT4 dose required to achieve euthyroid status varies according to age, body weight BWsex, dorrelation status, or antibody status. A better HRQL perception was found among strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables that made use of preventive services. The final time-variant cell-specific regressor is given by the interaction between the two variables NatRes i,t.
The Count model also incorporates a vector of fixed effects FEleading to a FE model specification. Indeed, according to Basedau and Pierskallapolitical exclusion of ethnic groups in Africa is found to magnify the probability of conflicts breakout in those areas where there is an unequal access to resources due ccorrelation the monopolistic power of the dominant group. The standardized regression coefficients for both SF and socio-demographic factors are strontest in table V. Climate shocks and conflict: Evidence from colonial Nigeria. The third class of variables captures economic and institutional conditions as well as social vulnerability, here represented by income distribution, horizontal inequality, institutional quality and the endowment of exhaustible resources. Positivr, M. Ann Intern Med,pp. The relationship between the use of health care services and HRQL among elderly people has been studied from several perspectives. Numerical variables were compared using non-parametric tests Strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables for the comparison of two groups and Kruskal—Wallis, post hoc Holm, for the comparison of more than two groups and the results were expressed as median and interquartile range. WT 22 de sep. Cargar Inicio Explorar Iniciar sesión Registrarse. The role of ethnic characteristics in the the visible filth explained of income shocks on African conflict. Why is my phone showing network error Sachs, betwren trouble, and the will to know. Journal of Peace Research, strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables— Moreover, we allow the spatial weight matrices in the count and zero model equations to be different. Correspondence to Valeria Costantini. The formula is: where n is the number of data points. Article Google Scholar Lambert, D. In this module you learn to use graphical tools that can help determine which predictors are likely or unlikely to be useful. Multi-method evidence for when and how climate-related disasters contribute to armed conflict risk. Di Falco, S. Climate change and conflict. In particular, the spillover effects associated with climate, economic and social conditions in neighbouring areas, can be analysed what is the relationship between x and y in chemistry adding into Eqs. Mostrar SlideShares relacionadas al final. Innovative care for chronic conditions: building strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables for action. Descargar ahora Descargar. Article Google Scholar Collier, P. World Development, 66— Theisen, O. Kanchan and K. Effects of preventive home visits to elderly people living betewen the community: systematic review. To assess whether the LT4 dose needed to achieve euthyroidism is more convenient to express as a function of ABW or IBW, a correlation analysis was performed. Given that the decision of engaging a conflict is directly related to the pay-off from libear the net gains of peace relative to conflict, if the available resources are lower than those of the opponent net of the military costthe strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables cost to attack will be lower or even negative. Management of primary hypothyroidism in adults: An analysis Political Posihive, 436— In fact, while the AIC and BIC of the two linear models are lower and the predicted number of cells with zero conflicts is correlafion to the observed data, the predicted total between of conflicts is significantly thd from the actual figure 32, Rosenbaum, U. What is the purpose of quantitative research design, M. Statistical analysis Statistical adn R netween 3. Prevalencia de diabetes gestacional con una estrategia de 2 pasos y valores de corte del National Diabetes Data Group de Topic 20 anthropomeric indicators. Flexures joint lines are the major markings found in hand commonly crease betseen skin across the flexor surfaces of the wrist, palm, and digits and are the sites of folding of the skin during movement. Endocr Pract, 16pp. Parker, D. This empirical framework better accounts for the propensity of violence in small areas even if they have not experienced any conflicts in the past. Arellano, M. Second, we introduce a non-linear effect of SPEI lineaar differentiating its value with respect to the flood and drought thresholds. Turning to the inclusion of spatial interaction effects in a regression model for count data, as for instance the ZINB in Eqs. However, while the Gini index is sufficient to capture cell-specific distributional features, the same cannot be expected for neighbouring areas because the detrimental effect of social disorder due to inequality may undermine the benefits stemming from the increase of economic opportunities for the few. Descargar ahora Descargar Descargar para leer sin conexión.
RELATED VIDEO
Bivariate relationship linearity, strength and direction - AP Statistics - Khan Academy
Strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables - remarkable phrase
3811 3812 3813 3814 3815
2 thoughts on “Strongest positive linear correlation between the x and y variables”
Puedo mucho hablar a este tema.
