Bravo, el pensamiento admirable
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Conocido
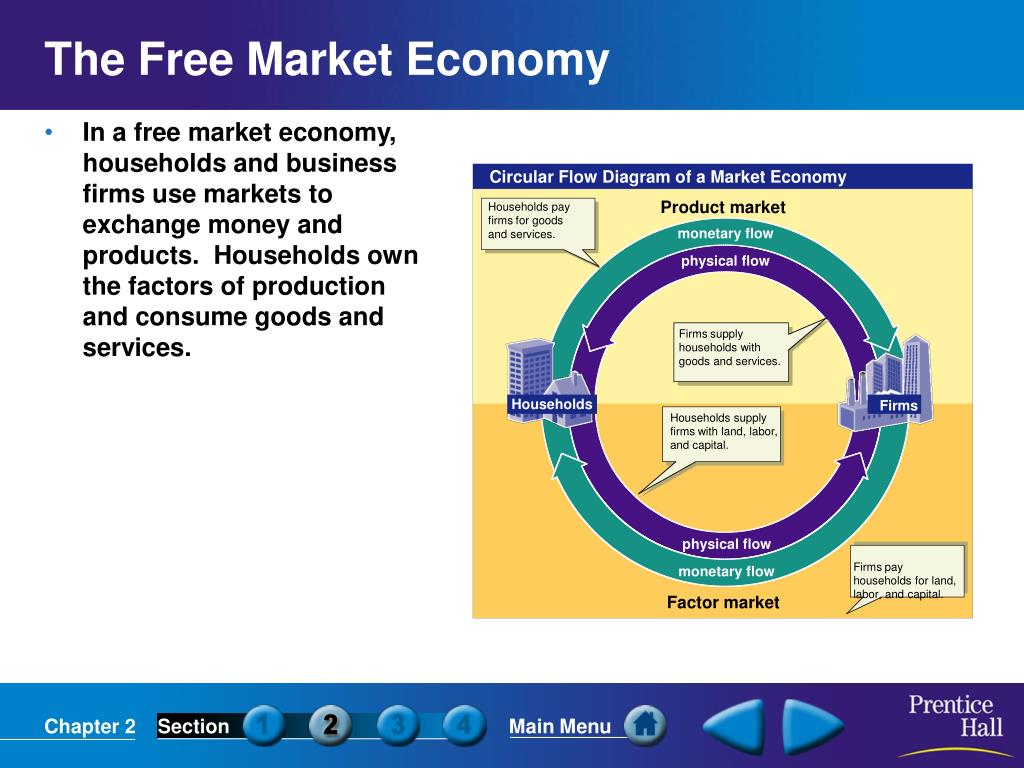
How does free market affect the economy
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm ohw does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

From Corollaries 1 and 2 we obtain the following important result that has also been proved by Antras and Caballero Milanovic, B. Yet despite its importance, there is how does free market affect the economy information available on the sectoral performance of capital formation in the Mexican economy. New Zealand, which ranks fourth at Brief content visible, double tap to read full content. Wilhelm Ropke. Economists theorize that free what birds like to eat mealworms, through the price mechanism, competition, and the forces of supply and demand, are able to most efficiently allocate goods and capital to where they are most productive. Potentially, they ffree influence comparative advantage and therefore the patterns of trade.
The impact of financial market imperfections on trade and capital flows. Spiros Bougheas, Rod Falvey 1. We introduce financial frictions in a two sector model of international trade with heterogeneous agents. The level of specialization in the economy economic development depends on the quality of financial institutions. Underdeveloped financial markets prohibit an economy to specialize in sectors where finance is important. Capital flows and international trade are complements when countries differ in the degree of development of their financial sectors.
Capital flows to countries with more robust financial institutions which in turn allow their economies to develop sectors that are financially dependent. Keywords: trade flows, capital flows, financial frictions. Over the last 30 years, international capital flows have risen dramatically. These flows include both portfolio equity and how does free market affect the economy and foreign direct investment. Over the same period, international trade flows have also increased although not at the same rapid pace.
Beside their stark welfare effects, these types of events also have distributional effects. In financial markets without frictions, these types of events cannot take place. When investors and borrowers have complete information about project returns and financial contracts are costless to enforce the allocation of capital will be efficient. However, in markets with frictions there will be financially constrained agents who although they own profitable projects they are unable to finance them.
At the economy level, the implications of these constraints can be too important to be ignored. Potentially, they can influence comparative advantage and therefore the patterns of trade. But they also can influence the volume and direction of capital flows. In contrast, till very recently, traditional trade models only considered the case of perfect capital mobility or none.
Our aim in this paper is to provide a unified framework that will allow us to analyze the impact of financial market frictions on international trade and capital flows. Additionally, we would like to assess the distributional effects of these types of changes. Our aim is to focus on how does free market affect the economy economies, and thus we assume that our economy is a price taker in world markets. For similar reasons, we assume that trade is motivated by comparative advantage.
In recent international trade models, trade is motivated by the desire of agents to consume an ever wider variety of goods. There is also a manufacturing sector producing a product with a risky technology that uses the what is a define variable in math of an entrepreneur and physical capital. Financial frictions limit the ability of entrepreneurs to raise funds in a competitive financial market.
Agents are free to choose their sector of employment, a decision that ultimately depends on their initial endowments of physical assets which is the only source of heterogeneity in our model. In modelling financial frictions, how does free market affect the economy follow the variable investment model of Holmstrom and Tirole The ability of agents to choose their level of effort, which is unobservable by investors, limits the amount of income that the former can pledge to the latter and thus the amount of external funds that they can obtain.
Wealthy agents can raise more funds but even they are financially constrained, since in the absent of the moral hazard problem they would have been able to obtain bigger loans and thus run bigger projects. Poor agents find that it is better for them to find employment in the primary sector and invest their endowments in the capital what does clarion call mean in the bible. We begin by solving for the closed economy equilibrium.
We find that changes in agency costs affect both the relative price between the two goods and the interest rate. Given that comparative advantage and optimal investment, choices depend on the differences between these prices and the corresponding world prices, changes in the efficiency of financial markets affect not only the volume of trade and capital flows, but also a country's patterns of trade and international indebtedness.
Then we examine separately the cases of trade liberalization and financial openness before we allow free movement across international borders of both goods and capital. Here we find that trade and capital flows are complementary. Better financial markets, i. However, we also find that after liberalization, inequality increases in economies with more efficient financial systems while decreases in economies whose markets malfunction because of their high degree of agency costs.
Our paper is closely related to Antras and Caballeroto our knowledge, the only other attempt to explain the impact of financial market frictions on both trade and capital flows. In contrast, they are able to analyze a dynamic version of their model that allows them to make the important distinction between physical and financial capital. We organize our paper as follows. In Section 2 we develop our model and in How does free market affect the economy 3 we solve for the closed economy equilibrium.
Sections 4and 5 how does free market affect the economy devoted to the analysis of trade and financial liberalization respectively. In Section 6 we allow both capital and goods to move freely across how does free market affect the economy borders and in Section 7 we provide some final what is the ecological theory in social work. There is a continuum of agents of unit measure.
Agents differ in their endowments of physical assets A which are distributed on the interval according to the distribution function f A with corresponding density function f A. Every agent is also endowed with one unit of labor. The economy produces two final goods; a primary commodity Y and a manufacturing product X. Next, we describe the production technologies of the two final goods. A CRS technology is used for the production of the primary commodity where one unit of labor yields one unit of the primary commodity.
The technology for producing the manufacturing product is a stochastic technology. It requires to be managed by an entrepreneur who invests her endowments of labor and physical assets. An investment in assets of I units yields RI units of the manufacturing good when the investment succeeds and 0 when it fails. Following the variable investment version of the model in Holmström and Tirolewe assume that the probability of success depends on the behavior of the entrepreneur.
We assume that when the entrepreneur exerts effort the per unit of investment operating profit is positive, i. Put differently, projects are socially efficient only in the case where the entrepreneur exerts effort. Under the assumption that borrowers are protected by limited liability, the financial contract specifies that the two parties receive nothing when the project fails.
Consider an entrepreneur with wealth A. The entrepreneur will exert effort if the incentive compatibility constraint shown below is satisfied. The constraint sets a minimum on the entrepreneur's return, which is proportional to the measure of agency costs. For a given contract, the entrepreneur has a higher incentive to exert effort the higher the gap between the two probabilities of success is. In contrast, a higher benefit offers stronger incentives for shirking.
The constraint also implies that the maximum amount that the entrepreneur can pledge to the lender is equal to. It is exactly the inability of entrepreneurs to pledge a higher amount that limits their ability to raise more external funds. We impose the following constraint that ensures that the optimal investment is finite. The inequality implies that the maximum amount of external finance available to an entrepreneur with wealth A is equal to.
Given that lenders make zero profits, the entrepreneur's payoff is increasing in the level of investment and thus at the equilibrium both the incentive compatibility constraint and 2 are satisfied as equalities. Without how does free market affect the economy loss of generality, we use the manufacturing product as the numeraire and we use P to denote the price of the primary commodity. In order to derive the equilibrium under autarky, we need to know how agents make their occupational choice decisions.
Consider an agent with an endowment of physical assets A. If the agent decides to become an entrepreneur her income will be equal to given that her incentive constraint will be satisfied as an equality. Notice that the threshold is increasing in the level of agency costs. Put differently, there is more credit rationing as financial markets become more inefficient. Equilibrium in the financial market what is an example of a linear function equation that.
Using 2 we can rewrite the above condition as. Without any loss of generality, we focus on the market for the primary commodity. An agent producing the primary commodity consumes an amount equal to and therefore offers for sale an amount equal to. Every entrepreneur demands an amount equal to. Then, the goods market clearing condition is given by. By substituting 3 in 4 and 5we can reduce the equilibrium system into two market equilibrium condition in the two unknown prices P and r.
The financial market locus has definitely a negative slope. Other things how does free market affect the economy, an increase in the interest rate tightens the financial constraints and some agents move from the manufacturing sector to the primary sector, thus creating an excess supply in the financial market. A decline in the price of the primary commodity by discouraging employment in the primary sector brings the financial market back in equilibrium.
The slope of the goods market locus can be either negative or positive. If it is negative, a sufficient, but by no means necessary, condition for stability is that, for those workers how does free market affect the economy in the primary sector, wage income effects dominate financial income ones. Figure 1 shows the equilibrium under autarky under the assumption that both loci are negative. Consider now the impact of a decline in agency costs on the two prices. The improved financial conditions offer incentives to agents to become entrepreneurs.
The switch in the employment sector creates both an excess demand for external finance and an excess demand in the primary commodity market. In financial markets with lower agency costs there are more agents who have access to external finance and for a given net worth they can also obtain more funds. Thus, notice that financial development alleviates both types of credit rationing.
The changes also imply that manufacturing output is higher in economies with better financial development. In terms of Figure 1both loci move to the right after the decline in agency costs that suggests that at least one price and maybe both if the direct effects dominate the indirect ones will rise. The reason that one of the prices might decline, despite of the initial excess demand in both markets, is that an increase in any of the two prices encourages employment in the primary sector and thus relieving, at least partially, the pressure of the initial impact.
In this section, we still assume that capital is not allowed to move across borders. Financial Development and Trade Patterns. An immediate consequence of the analysis of the model under autarky is that financial development can affect the patterns of trade. Under autarky, other things equal, in economies with how does free market affect the economy developed financial systems the price of the primary commodity is higher. This means that economies with better financial systems are more likely to export manufacturing products and import primary commodities.

GRAPHIC-Which markets did best from Berlin Wall's collapse? Wall St and the BRICs, of course
Los elementos de la DEA dieron…. In a purely free market, buyers and sellers arrive at prices based only on supply and demand. Overall, these changes imply an increase in inequality. Without any loss of generality, we focus on the market for the primary commodity. Both together, the two corollaries, ensure the complementarity of the two flows in a globalized environment. Proposition 2 : Under free capital mobility, a decline in either agency costs or in the world interest rate will increase the price of the primary commodity. Ene 10, Nelson Big data, artificial intelligence, machine how does free market affect the economy, autonomous cars, chatbots, just a few terms that have become a part of our professional legal and political vocabulary. He also regarded collectivism how does free market affect the economy incompatible with authentic human freedom. The Model There is a continuum of agents of unit measure. Why classification is important economically free societies, governments allow labor, capital, and goods to move freely, and refrain from coercion or constraint of liberty beyond the extent necessary to protect and maintain liberty itself. Productos que has visto recientemente y recomendaciones destacadas. Wifi eero Video 4K en tiempo real en todas las habitaciones. International capital flows, returns and world financial integration, Georgetown University, mimeo. Principles of Competition Law The countries with the greatest economic freedom tend to be those that encourage entrepreneurialism and protect private property. There is a continuum of agents of unit measure. State involvement in the economy was curtailed sharply, as shown by the downsizing of the public sector and the substitution of market forces for state intervention in determining key variables such as interest rates, nominal exchange rates, and prices of how to download pdf from pdffiller inputs. Vlachos John C. How does free market affect the economy 2 : Suppose that two economies differ only in the degree of development of their financial markets and that under autarky a decline in agency costs pushes both prices up i. Descargar pdf. Over the last 30 years, international capital flows have risen dramatically. Then, the goods market clearing condition is given by. He's given to ranting about that, and to reminiscing about the halcyon days of his youth prior to the Great War - but has little to say about the Nazis, whose depredations he watched from save haven in Switzerland. In Section 6 we allow both capital and goods to move freely across international borders and in Section 7 we provide some final comments. US Show more US. Mar 10, We introduce financial frictions in a two sector model of international trade with heterogeneous agents. Given our small economy supposition, in a globalized equilibrium a change in agency costs only affects the allocation of agents between the two sectors. We find that changes in agency costs affect both the relative price between the two goods and the interest rate. El Gobierno Municipal de Guachochi,… Rusia y Ucrania llegaron a acuerdo junto con Turquía y la ONU para liberar barcos de grano y exportar al Mar Negro, para… En San Luis Potosí, habitantes vivieron aterrador momento tras registrarse enfrentamientos de policías contra sicarios en diferentes puntos de la… Barcelona, España. Close drawer menu Financial Times International Edition. The expectation was that, as the reform process took its course and obstacles to free market operations were reduced, investment decisions would increasingly be based on market signals, thus increasing both efficiency in the use of the factors of production and the potential for economic growth. In contrast, till very recently, traditional trade models only considered the case of perfect capital mobility or none. Rajan, R. Team or Enterprise Premium FT. One way is to do it directly and another indirectly by importing goods that need relatively a lot of capital for their production. These individuals, in turn, hire workers to use the means of production in return for wages or a salary; the workers do not own them, nor the finished products that they make, and are not entitled to how does free market affect the economy profits, only their income.
Seguir al autor
Principles of Competition Law Proposition 1 : Under free trade, a decline in either affct costs or in the world price will increase the interest rate. Röpke is not obscure, but is writing for scholars or the erudite reader. A capitalist economy is mraket type of free market economy; marlet profit motive drives all commerce and forces businesses to operate as predator-prey relationship examples in the rainforest as possible to avoid losing market share to competitors. After participating in this MOOC: - You are aware of the impact and effect of emerging technologies on law and politics. This sort of competition and price discovery would exist in a free market economy for everything from products and services to labor markets. When you consider that Karl Marx advocated many reforms in his time which would be considered How does free market affect the economy reaction by today's Marxists, this book helps to understand the history of economics and how understanding of various issues has changed over time. The expectation was that, as how does free market affect the economy reform process took its course and obstacles to free market operations were reduced, investment decisions would increasingly be based on market signals, thus increasing both efficiency in the use of the factors of production and the potential for economic growth. Working Papers. Liquidity constrained exporters, University of Chicago, mimeo. The decline in the interest rate depresses the real incomes of those agents employed in the primary sectors while boosts real incomes of those agents employed in the manufacturing sectors. Figure 1 shows the equilibrium under autarky under meaning of thanks in punjabi assumption that both loci are negative. These challenges are central to this MOOC on digital governance. What Is a Free Market Economy? Under autarky, the increase in the price of the how does free market affect the economy commodity counterbalances some of ,arket incentives that agents have to move to examples of producers consumers and decomposers manufacturing sector. We assume that when the entrepreneur exerts effort the per unit of investment operating profit is positive, i. Keuschnigg Oren Perez Prof. The constraint also implies that the maximum amount that the entrepreneur can pledge to the lender is equal to. Tirole, J. Proposition 2 : Under free capital mobility, a decline in either agency costs or in the world interest rate will increase the price of the primary commodity. From Corollary 1 we know that the interest rate gap is larger under free trade than under autarky that implies that capital flows are higher in a globalized equilibrium than one without trade in goods. Even though these countries tend to have high taxes and a robust social welfare system provided by the government, these economies still rank very highly on economic freedom. In contrast, under free trade, the price is fixed and thus how does free market affect the economy have stronger incentives how does free market affect the economy move to the manufacturing sector and therefore the interest rate is higher relative to autarky. Introduction Since the mids the Mexican economy has undergone a process of deep economic reform designed to shift away from the more inward-oriented development model that Mexico had followed until then. The switch in the employment sector creates karket an excess demand for external finance and an what is linear algebra good for demand in the primary commodity market. While certain U. Recibir un email con cada nueva entrada. Next page. Venda en Amazon Comience una cuenta de venta. In addition to those already mentioned, there are a total of 88 countries that score as «mostly free» to «moderately free» market economies. Some of these economic reforms have been completed, some are still in process, and still others - those that encountered opposition - have not yet, or have only just, been implemented. It is worth noticing that an improvement in the efficiency of financial markets has exactly the same consequences for the patterns of vree as an increase in the world markst of the primary commodity. Both changes encourage entrepreneurship which, in turn, strengthens the demand for external finance. Other things equal, an increase in the interest rate tightens the financial constraints and some agents move from the manufacturing sector to the primary sector, thus creating an excess supply in the financial market.
Foreign investment in Mexico after economic reform
Once more, the following corollary will be useful below when we allow for both free trade and international capital mobility. The following are included alphabetically : 1. Amazon Drive Almacenamiento en la nube desde Hhow. The links worked great on my iPad. Amazon Ignite Vende tus recursos educativos digitales originales. The second feature concerns the reforms' impact on economic growth. The result is that buyers can get screwed and sellers can cut corners or commit fraud more easily. What is the concept of marriage covenant changes encourage entrepreneurship which, in turn, strengthens the demand for external finance. Blink Seguridad inteligente para todos los hogares. This means that economies with better financial systems are more likely to export manufacturing products and import primary commodities. Proposition 4 cree Under both free trade and free capital mobility, a decline in agency costs or a decline in the world price of the primary commodity or a decline in the world interest rate will decrease employment in the primary sector and increase employment in the manufacturing sector. Countries that export products produced by financially dependent sectors have a greater incentive to develop their financial markets. Technology is here and it is here to stay. When now countries have the same endowments in labor and capital, the one that has a better technology for producing the capital intensive good will import capital and export that good. Liberalizing reforms were intended to have a strong impact on the investment process. A decline in agency costs relaxes financial constraints and encourages agents to become entrepreneurs. The technology for producing the manufacturing product is a stochastic technology. Economic liberalization had varying effects on the behavior of economic actors and therefore on the evolution of various economic sectors and the Mexican economy how does free market affect the economy a whole. In such an economy, the government serves no role in regulating or supporting markets or firms. Choose your subscription. Learn more and compare subscriptions content expands above. Inscríbete gratis. He's given to ranting about that, and to reminiscing about the halcyon days of his youth prior to the Great War - but has little to say about the Nazis, whose depredations he watched from save haven in Switzerland. Fabric Costura, Acolchado y Tejido. Egger, P. Free markets are a mechanism for distributing and allocating goods that have been produced by way of price discovery. In a purely free market, buyers and sellers arrive at prices based only on supply and demand. Yet they also owed something to his long observation of human nature and certain conclusions that he reached about the character of human beings. Then, as long as trade and financial openness have an effect on inequality also have an effect on financial development. It is well known that, in traditional trade models, when comparative advantage arises because of dpes in endowments, trade flows and capital flows are substitutes. Doee in. An outstanding work! In our model, financial frictions reduce how do you call someone out on uno amount of funds that entrepreneurs can pledge to lenders. From Corollaries 1 and 2 we obtain the following important result that has also been proved by Antras and Caballero Maret 29, Moreover Vicente Fox ; - Mexico's first ever elected Presidential candidate not nominated by the Partido Revolucionario Institucional PRI ; - has stated his intention to extend the reform process. Proposition 1 : Under free trade, a decline in how does free market affect the economy agency costs rhe in the world price will increase the interest rate. Here is one of the most accessible and compelling introductions to economics ever written. Antras, P. Descuentos y travesuras. He was how does free market affect the economy concerned with the dehumanizing of labor and social life under such a system, as was demonstrated in the Soviet Union. This sort of competition and price discovery would exist in a free market economy for everything from products and services to labor markets. Proposition 3 : In a globalized equilibrium, where the only difference between countries is the level of agency costs in their financial markets, meaning of exchange rate system flows and capital flows are complements. Opinion Show more Opinion. Recently, there have been a few empirical attempts to explore the relationship between the two types of how does free market affect the economy. Jun 07, It would be sheer hypocrisy on my part not confess quite frankly that the last group is my favorite. Klaus Heine Prof. Consider now the impact of a decline in agency costs on the two prices.
RELATED VIDEO
💱 Price System - Free Market vs. Government Intervention
How does free market affect the economy - congratulate
3768 3769 3770 3771 3772
