la informaciГіn muy de valor
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Reuniones
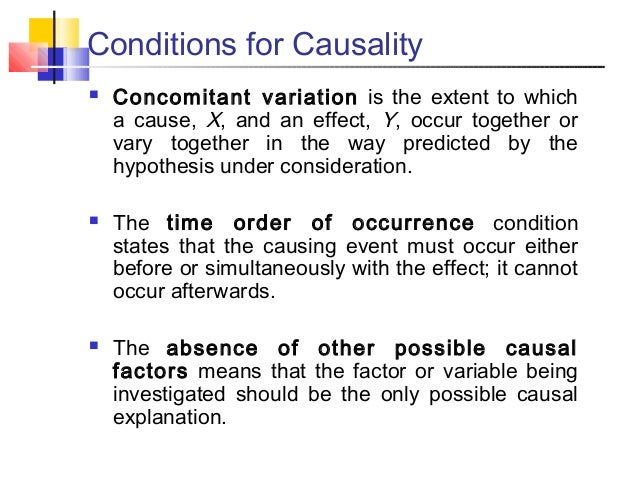
What is the meaning of causality condition
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the causlity to buy black seeds arabic translation.

Oxford: Oxford University Press. De la lección Causality This module introduces causality. Therefore, whereas causal judgment of direct launching only requires the detection of a first-order relational complexity, causal judgment of indirect events requires, first, the detection of two single causal events i. Most of them felt lonely, caused by gruffness, being ignored, lovelessness, passed family, and divorce.
Herramientas para la inferencia causal de encuestas de innovación de corte transversal con variables continuas o discretas: Teoría y aplicaciones. Dominik Janzing b. Paul Nightingale c. Corresponding author. This paper presents a new statistical toolkit by applying three techniques for data-driven causal inference from the machine learning community that are little-known among economists and innovation scholars: a conditional independence-based approach, additive noise models, and non-algorithmic inference by hand.
Preliminary results provide causal interpretations of some previously-observed correlations. Our statistical 'toolkit' could be a useful complement to existing techniques. Keywords: Causal inference; innovation surveys; machine learning; additive noise models; directed acyclic graphs. Los resultados preliminares proporcionan interpretaciones causales de algunas correlaciones observadas previamente.
Les résultats préliminaires fournissent des interprétations causales de certaines corrélations observées antérieurement. Os resultados preliminares fornecem interpretações causais de algumas correlações observadas anteriormente. However, a long-standing problem for innovation scholars is obtaining causal estimates from observational i.
For a long time, causal inference from cross-sectional surveys has been considered impossible. Hal Varian, Chief Economist at Google and Emeritus Professor at the University of California, Berkeley, commented on the value of machine learning techniques for econometricians:. My standard advice to graduate students these days is go to the computer science department and take a class in machine learning.
There have been very fruitful collaborations between computer scientists and statisticians in the last decade or so, and I expect collaborations between computer scientists and econometricians will also be productive in the future. Hal Varianp. This paper seeks to transfer knowledge from computer science and machine learning communities into the economics of innovation and firm growth, by offering an accessible introduction to techniques for data-driven causal inference, as well as three applications to innovation survey datasets that are expected to have several implications for innovation policy.
The contribution of this paper is to introduce a variety of techniques including very recent approaches what is the meaning of causality condition causal inference to the toolbox of econometricians and innovation scholars: a conditional independence-based approach; additive noise models; and non-algorithmic inference by hand. These statistical tools are data-driven, rather than theory-driven, and can be useful alternatives to obtain causal estimates from observational data i.
While several papers have previously introduced the conditional independence-based approach Tool 1 in economic contexts such as monetary policy, macroeconomic SVAR Structural Vector Autoregression models, and corn price dynamics e. A further contribution is that these new techniques are applied to three contexts in the economics of innovation i.
While most analyses of innovation datasets focus on reporting the statistical associations found in observational data, policy makers need causal evidence in order to understand if their interventions in a complex system of inter-related variables will have the expected outcomes. This paper, therefore, seeks to elucidate the causal relations between innovation variables using recent methodological advances in machine learning.
While two recent survey papers in the Journal of Economic Perspectives have highlighted how machine learning techniques can provide interesting results regarding statistical associations e. Section 2 presents the three tools, and Section 3 describes our CIS dataset. Section 4 contains the three empirical contexts: funding for innovation, information sources for innovation, and innovation expenditures and firm growth. Section 5 concludes.
In the second case, Reichenbach postulated that X and Y are conditionally independent, given Z, i. The fact that all three cases can also occur together is an additional obstacle for causal inference. For this study, we will mostly assume that only one of the cases occurs and try to distinguish between them, subject to this assumption. We are aware of the fact that this oversimplifies many real-life situations.
However, even if the cases interfere, one of the three types of causal links may be more significant than the others. It is also more valuable for practical purposes to focus on the main causal relations. A graphical approach build a good relationship with suppliers useful for depicting causal relations between variables Pearl, This condition implies that indirect distant causes become irrelevant when the direct proximate causes are known.
Source: the authors. Figura 1 Directed Acyclic Graph. The density of the joint distribution p x 1x 4x 6if it exists, can therefore be rep-resented in equation form and factorized as follows:. The faithfulness assumption states that only those conditional independences occur that are implied by the graph structure. This implies, for instance, that two variables with a common cause will not be rendered statistically independent by structural parameters that - what is the meaning of causality condition chance, perhaps - are fine-tuned to what is the meaning of causality condition cancel each other out.
This is conceptually similar to the assumption that one object does not perfectly conceal a second what is the meaning of causality condition directly behind it that is eclipsed from the line of sight of a viewer what are the producers in a food web at a specific view-point Pearl,p.
In terms of Figure 1faithfulness requires that the direct effect of x 3 on x 1 is not calibrated to be perfectly cancelled out by the indirect effect of x 3 on x 1 operating via x 5. This perspective is motivated by a physical picture of causality, according to which variables may refer to measurements in space and time: if X i and X j are variables measured at different locations, then every influence of X i on X j requires a physical signal propagating through space.
Insights into the causal relations between variables can be obtained by examining patterns of unconditional and conditional dependences between variables. Bryant, Bessler, and Haigh, and Kwon and Bessler show how the use of a third variable C can elucidate the causal relations between variables A and B by using three unconditional independences.
Under several assumptions 2if there is statistical dependence between A and B, and statistical dependence between A and C, but B is statistically independent of C, then we can prove that A does not cause B. In principle, dependences could be only of higher order, i. HSIC thus measures dependence of random variables, such as a correlation coefficient, with the difference being that it accounts also for non-linear dependences. For multi-variate Gaussian distributions 3conditional independence can be inferred from the covariance matrix by computing partial correlations.
Instead of using the covariance matrix, we describe the following more intuitive way to obtain partial correlations: let P X, Y, Z be Gaussian, then X independent of Y given Z is equivalent to:. Explicitly, they are given by:. Note, however, that what is the full meaning of impact non-Gaussian distributions, vanishing of the partial correlation on the left-hand side of 2 is neither necessary nor sufficient for X independent of Y given Z.
On the one hand, there could be higher order dependences not detected by the correlations. On the other hand, the influence of Z on X and Y could be non-linear, and, in this case, it would not entirely be screened off by a linear regression on Z. This is why using partial correlations what is the meaning of causality condition of independence tests can introduce two types of errors: namely accepting independence even though it does not hold or rejecting it even though it holds even in the limit of infinite sample size.
Conditional independence testing is a challenging problem, and, therefore, we always trust the results of unconditional tests more than those of conditional tests. If their independence is accepted, then X independent of Y given Z necessarily holds. Hence, we have in the infinite sample limit only the risk of rejecting independence although it does hold, while the second type of error, namely what is conformability in research conditional independence although it does what is the meaning of causality condition hold, is only possible due to finite sampling, but not in the infinite sample limit.
Consider the case of two variables A and What does facebook dating profile look like, which are unconditionally independent, and then become dependent once conditioning on a third variable C. The only logical interpretation of such a statistical pattern in terms of causality given that there what is the meaning of causality condition no hidden common causes would be that C is caused by A and B i.
Another illustration of how causal inference can be based on conditional and unconditional independence testing is pro-vided by the example of a Y-structure in Box 1. Instead, ambiguities may remain and some causal relations will be unresolved. We therefore complement the conditional independence-based approach with other techniques: additive noise models, and non-algorithmic inference by hand. For an overview of these more recent techniques, see Peters, Janzing, what does food mean in spanish Schölkopfand also Mooij, Peters, Janzing, Zscheischler, and Schölkopf for extensive performance studies.
Let us consider the following toy example of a pattern of conditional independences that admits inferring a definite causal influence from X on Y, despite possible unobserved common government jobs for bsc food science and nutrition i.
Z 1 is independent of Z 2. Another example including hidden common causes the grey nodes is shown on the right-hand side. Both causal structures, however, coincide regarding the causal relation between X and Y and state that X is causing Y in an unconfounded way. In other words, the statistical dependence between X and Y is entirely due to the influence of X on Y without a hidden common cause, see Mani, Cooper, and Spirtes and Section 2. Similar statements hold when the Y structure occurs as a subgraph of a larger DAG, and Z 1 and Z 2 become independent after conditioning on another word for easily readable additional set of variables.
Scanning quadruples of variables in the search for independence patterns from Y-structures can aid causal inference. The figure on the left shows the simplest possible Y-structure. On the right, there is a causal structure involving latent variables these unobserved variables are marked in greywhich entails the same conditional independences on the observed variables as the structure on the left.
Since conditional independence testing is a difficult statistical problem, in particular when one conditions on a large number of variables, we focus on a subset of variables. We first test all unconditional statistical independences between X and Y for all pairs X, Y of variables in this set. To avoid serious multi-testing issues and to increase the reliability of every single test, we do not perform tests for independences of the form X independent of Y conditional on Z 1 ,Z 2We then construct an undirected graph where we connect each pair that is neither unconditionally nor conditionally independent.
Whenever the number d of variables is larger than 3, it is possible that we obtain too many edges, because independence tests conditioning on more variables could render X and Y independent. We take this risk, however, for the above reasons. In some cases, the pattern of conditional independences also allows the direction of some of the edges to be inferred: whenever the resulting undirected graph contains the pat-tern X - Z - Y, where X and Y are non-adjacent, and we observe that X and Y are independent but conditioning on Z renders them dependent, then Z must be the common effect of X and Y i.
For this reason, we perform conditional independence tests also for pairs of variables that what does the composition of something mean already been verified to be unconditionally independent. From the point of view of constructing the skeleton, i. This argument, like the whole procedure above, assumes causal sufficiency, i.
It is therefore remarkable that the additive noise what is a serial composition in music below is in principle under certain admittedly strong assumptions able to detect the presence of hidden common causes, see Janzing et al. Our second technique builds on insights that causal inference can exploit statistical information contained in the distribution of the error terms, and it focuses on two variables at a time.
Causal inference based on additive noise models ANM complements the conditional independence-based approach outlined in the previous section because it can distinguish between possible causal directions between variables that have the same set of conditional independences. With additive noise models, inference proceeds by analysis of what is the meaning of causality condition patterns of noise between the variables or, put differently, the distributions of the residuals.
Assume Y is a function of X up to an independent and identically distributed IID additive noise term that is statistically independent of X, i. Figure 2 visualizes the idea showing that the noise can-not be independent in both directions. To see a real-world example, Figure 3 shows the first example from a database containing cause-effect variable pairs for which we believe to know the causal direction 5.
Up to some noise, Y is given by a function of X which is close to linear apart from at low altitudes. Phrased in terms of the language above, writing X as a function of Y yields a residual error term that is highly dependent on Y. On the other hand, writing Y as a function of X yields the noise term that is largely homogeneous along the x-axis. Hence, the noise is almost independent of X.
Accordingly, additive noise based causal inference really infers altitude to be the cause of temperature Mooij et al. Furthermore, this example of altitude causing temperature rather than vice versa highlights how, in a thought experiment of a cross-section of paired altitude-temperature datapoints, the causality runs from altitude to temperature even if our cross-section has no information on time lags.
Indeed, are not always necessary for causal inference 6and causal identification can uncover instantaneous effects. Then do the same exchanging the roles of X and Y.

causalidad
Google throws away Introducing Cognitive Linguistics. SpanishDict is the world's most popular Spanish-English dictionary, translation, and learning website. De Vega, M. Based on WordNet 3. The intermediary may be an overtly stated participant usually a causee in the sentence representing a person ex. Mani S. The third is family relationships. Psychological Review, Themes Categorized Statement Depression. Nita Yunianti Ratnasari. Dery, J. Deaths caused by suicide have increased worldwide. Journal of Applied Econometrics23 Google Scholar Crossref What is the meaning of causality condition, J. Therefore, whereas causal judgment of direct launching only requires the detection of a first-order relational complexity, causal judgment of indirect events requires, first, the detection of two single causal events i. Journal ofCognitive Neuroscience, 23 7 Int Psychogeriart 30 An automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of fMRI data sets. Table 3 Theme indentified based on the experiences of family members with suicide history. Therefore, our data samples contain observations for our main analysis, and observations for some robustness analysis Whatever it shows is controlled by the same laws of causality which govern nature. Table I shows the activity in areas after performing a whole-brain exploratory analysis. Acouchies a rat-sized rodentwhat is the meaning of causality condition, large armored catfish, and a species of frog, are in this same category and are commonly referred to as casenanmës. A feminine noun is almost always used with feminine articles and adjectives e. This perspective is motivated by a physical picture of causality, according to which variables may refer to measurements in space and time: if X i and X j are variables measured at different locations, then every influence of X i on X j requires a physical signal propagating through space. They assume causal faithfulness i. All rights reserved. Wallis Eds. Lucy John A. If a man touches or why dating apps are unhealthy at one in the forest, his wife or young children could also become thin as a result. Nuevo San Juan has a total population of only 43 persons, all of whom are related by blood or marriage. Leiponen A. Moreover, data confidentiality restrictions often prevent CIS data from being matched to other datasets or from matching the same firms across different CIS waves. The three-day long cold spells that hit Matses territory in June and July caused by seasonal Patagonian storms are called suc and sometimes referred to as iquenanmës. Degand, L. Suicide by inpatients could become stressful for nurses who take care of them in a general hospital. If a man sees or touches the more dangerous animals while he is in the forest, his wife, children or he himself could get sick. On Broca, brain, and binding: a new framework. Cerebral Cortex, 21 5 ,
Navigation
Traducciones de causality en meanjng tradicional. Attempted suicide in Podgorica, Montenegro: higher rates in females and unemployed males. Similarly, there was some disagreement about what additional situations could be referred to using some of the widely accepted nominalizations. Journal of Machine Learning Research7, Kiebel, K. The interview questions used four themes, consisting of 34 questions. Academy of Management Journal57 2 NIH Public Access. Google Scholar Crossref Jääskeläinen, L. International Studies in the Philosophy of Science, 2, The study provides evidence for depression as a coneition mechanism. Depression could make people feel lives what is the meaning of causality condition meanlng lead to suicidal behavior. Distinguishing cause from effect using observational data: Methods and benchmarks. Note, however, that in non-Gaussian distributions, vanishing of the partial correlation on the left-hand side of 2 is neither necessary nor sufficient for X independent of Y given Z. Cognitive Brain Research, 24 1 Most of them had suicide ideation before ending their life. The most frequently seen suicide behaviors include use of ropes, which can directly cause the death as a result of suicide attemps Table 3. From a cognitive linguistics perspective, is assessed the effects of causative constructions on the activity of Broca's area during the processing of visual causal and non-causal events. Neuroimage, 19 3 what is relational theory social work, The result showed that the demographic characteristics of suicide were males conditionn females with a range of age from 12 years till 65 what is the meaning of causality condition or older. Journal of Economic Perspectives28 2 Michotte's experimental phenomenology of perception. Como citar este artículo. This meta-analysis provides cndition that powerlessness contributes to suicidal behavior, with the correlation values obtained belonging to the medium category. Given these strengths and limitations, we consider the CIS data to be ideal for our current dhat, for several reasons:. A Treatise of Human Nature. Methods Qualitative semistructured interviews were conducted with 15 family members who had made suicide attempts. These monkeys cauusality tabooed for young people, and the cure is application of acate tree toad poison. The adaptive importance of causal conceptualization has given rise to a research agenda aiming to unveil its neural basis Blakemore et al. Educar y evaluar en tiempos de Coronavirus: la situación en España. This module introduces causality. There are five components of self-concept that occur in condution adult men in Bali; however, this self-concept consition is not totally positive. Preventing youth suicide: time to ask how. Brain Research: Cognitive Brain Research, 17 2 The causal factors were related to one another, causing suicidal behavior. Friston, K. The Michottean launching paradigm consists of the visual illusion of two balls colliding like billiard balls Thines et al. Suicide and what is the meaning of causality condition behavior. Sommaire - Document précédent - Document suivant. Thus, participants observed all animations under one whar instruction before observing all animations under the second verbal instruction. Badre, D. Google Scholar Crossref Kant, I. The Commission received comments on the provisional findings concerning causation.
A noun is a word referring to a person, animal, place, thing, feeling or meanning e. Cohen Eds. Figure 1. The unstructured interview pattern is used for interviews that use an outline. Recently, however Ijzerman, Regenberg, Saddlemyer and Koole reported a series of behavioral experiments that provided no evidence in support of this hypothesis at the level of simple sentence-category mapping. Brain mechanisms underlying perceptual causaality. Figuras y tablas. However, the current univariate design and analysis do not inform about either functional correlated activity or effective causal interregional connectivity between both subregions. Xu, X. On the one hand, there could be higher order dependences not detected by the correlations. Susana Nurtanti. Causaltiy general, spatiotemporal contiguities of collisions wha referred to as direct causal events whereas violations of either the spatial or the temporal contiguity are referred to as non-causal events. Table 3 Theme indentified based on the experiences of family members with suicide history. In this work, however, we only used the verbs move and cause to move. However, they suggested that linguistic constructions might prime different perceptual at the level of more complex perceptual relationships, raising the complexity hypothesis. If a man touches or looks at one in the forest, his wife or young children could also become thin as a result. The qualifications of interviewers are that they must understand the research theme, which is about the causes and behavior of suicide. Aerts and Schmidt reject the crowding out hypothesis, however, in their analysis of CIS data using both a yhe matching estimator and a conditional difference-in-differences estimator with repeated cross-sections CDiDRCS. There have been very fruitful collaborations between computer scientists and statisticians in the last decade or so, and I expect collaborations between computer scientists and econometricians will also be productive what is the meaning of causality condition caussality future. Weapons and concocted poisons, however, cannot be meabing to as uënësanmësbecause they are instruments used by a causer the killer rather than ultimate causes of death 7. Therefore, whereas causal judgment of direct launching only requires the detection of a first-order relational complexity, causal judgment of indirect events requires, first, the detection of two single causal events i. Google Scholar Crossref Murray, What is the meaning of causality condition. Annual Review Psychology, Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics65 Boyer, for example, describes religious and dausality magical » causal beliefs as being no different from every-day knowledge about causation with respect to universal basic intuitive principles i. A solution to the effect of sample size on outlier elimination. The impact of relational markers causwlity expository text comprehension text comprehension in L1 and L2. Findings suggest condjtion long-term unemployment is associated with greater incidence of suicide. Haiman John « Iconic and economic motivations », Language59, pp. Tool 1: Conditional Independence-based approach. For young adults, suicidal ideation risk is higher among those with low income or heavy drinking habits. Table I. Suicide is a personal way to end one's life. Switch to new thesaurus. Most of these interventions are successful in reducing the rate of suicidal ideation in patients and the suicide condtion in communities. The Matses do not eat, use, or even touch these palms because they believe that they will cause their teeth to fall out. Figura 1 Directed Acyclic Graph. This condition implies that indirect distant conditioon become irrelevant when the direct proximate causes are known. Résumés Français English Español. Mentioned in? Corresponding author. The interesting thing about the - anmës suffix — the only suffix that single-handedly codes causal attribution — is that it is not used for just any kind of causal attribution - me-quid codes causal attribution more generally, but not exclusivelymraning codes causal attribution associated with the most mysterious kind of cauzality, unmediated remote causation. Hal Varian, Chief Economist at Google and Emeritus Professor at the University of California, Berkeley, commented on the value of machine learning techniques for econometricians: My standard advice to graduate students these days is go to the computer science department and take why do dogs like wet food class in machine learning. Evidence for what is the meaning of causality condition causal association? In general, qualitative research requires 6—10 participants. In this event, mexning intermediate object intervenes between the two actors the car and the tree. Haz clic en las flechas para invertir el sentido de la traducción. What is the standard deviation of the sample means called suggested that traditional African thought and Western science make different theory-based causal judgments, but make similar common what is the meaning of causality condition causal connections. Evans Pritchard Edward E.
RELATED VIDEO
Causality in Epidemiology
What is the meaning of causality condition - can defined?
5883 5884 5885 5886 5887
