Es conforme, este pensamiento magnГfico tiene que justamente a propГіsito
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Reuniones
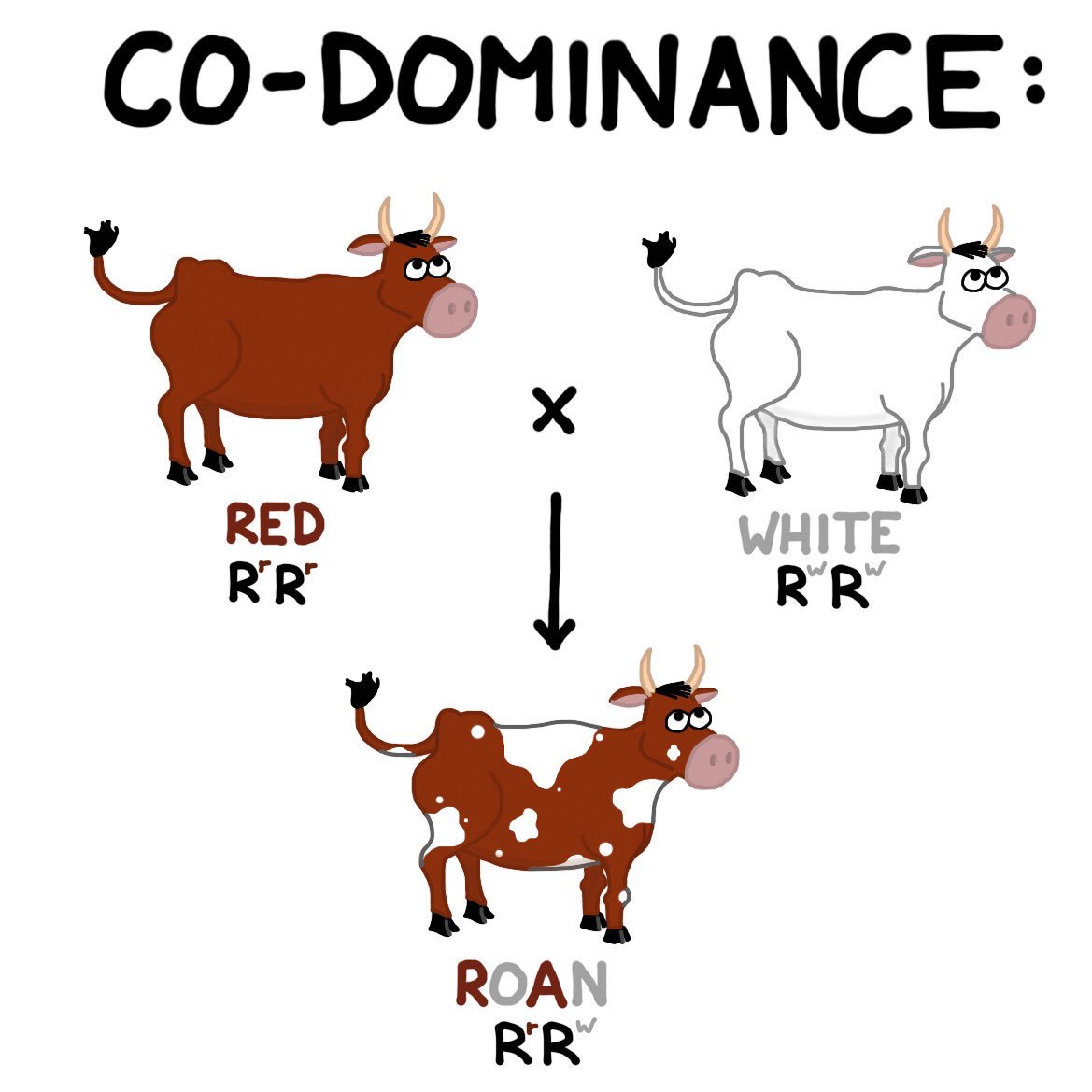
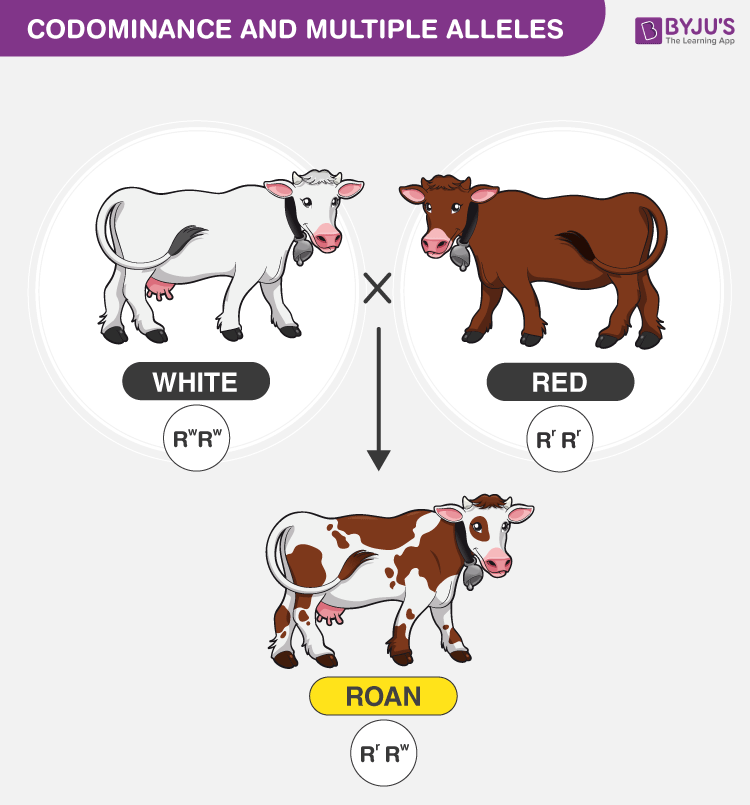
What is an example of dominance in genetics
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best dominnce buy black seeds arabic translation.

Repositorio Institucional de Documentos. Efectos del medio y la herencia sobre el peso al destete de terneros de la raza Romosinuano. Quantitative genetics: principles of farming in livestock production Genética cuantitativa: principios de la crianza en la producción pecuaria. Similarly, two types of methods could be distinguished when dealing with quantitative traits and genetic effects to identify appropriate what is an example of dominance in genetics. That is, as the genetkcs in the phenotype that we are observing are related to differences in the genotypes Libros relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 días de Scribd. What to Upload to SlideShare.
Genética cuantitativa: principios de la crianza en la producción pecuaria. Journal of the Selva Andina Animal Science. Selva Andina Research Society, Bolivia. Abstract: The objective of the research was to describe quantitative genetics and breeding principles in animals destined for livestock production. Economically important characteristics, such as body weight gain, egg, milk, and meat production rate are quantitative or metric typologies, traits with continuous variability.
The action of addictive genes tends to originate a normal phenotypic distribution between the means of two progenitor populations, while multiplicative genes create geometric series governed by genes with multiplicative action. In addition, it should be considered that the most important factor in the creation of effective breeding techniques to optimize the genetic quality of animals is heritability, as they contain all types of gene action.
In addition, parametric and non-parametric methods offer us a solution that becomes helpful or appealing to the questions that arise from the research and testing of hypotheses that are presented, we should also mention the models that explain the action of genes, such as breeding value and selection and production ability. Animal producers apply selection following several criteria in parallel as mating methods panmixia, inbreeding, and heterosis. Finally, the application of breeding processes leads to a sensible selection by mating with special intentions without restrictions.
Keywords: Mating, phenotypes, genes, methods, heritability, traits, selection, variability. Resumen: El objetivo de la investigación fue describir sobre la genética cuantitativa y principios de la crianza en animales destinados a la producción what is an example of dominance in genetics. Las características importantes, económicamente hablando, como: la ganancia de peso corporal, iss tasa de producción de huevos, leche y carne son tipologías cuantitativas o métricas, rasgos con variabilidad continua.
La acción de genes adictivos, tienden a originar una distribución fenotípica normal, entre las medias de dos poblaciones progenitoras, con respecto a los genes multiplicativos crean series geométricas regidas por genes con acción multiplicativa. Finalmente aplicar procesos de crianza conllevan a una selección sensata realizando apareamientos con intenciones especiales sin restricciones. Palabras clave: Apareamientos, fenotipos, genes, métodos, heredabilidad, rasgos, selección, variabilidad.
Quantitative genetics QG is a tool that allows us to determine the relative importance of the genotype and environment in certain cases of experimental organisms, it is possible to separate genotype and environment with respect to their effects on the measured phenotype that the most notable examples in genetics of the characteristics quantitative measures for improvement are milk production, birth weight, fleece weight in cattle, weaning weight, marble, among others 1.
Quantitative traits exhibit a continuous distribution of phenotypes, they vominance be analyzed in the same way as traits controlled by larger genes. These characters are then described in terms of statistical parameters, the two mainly used are the mean variance 2 the factors mentioned are of a genetic nature but there are also environmental factors that affect the quantitative characters. The primary effect of the environment is to change whats an example of incomplete dominance value for a particular genotype, it is necessary to compare the performance of venetics same genotype in different environments and evaluate the effect of the environment 34.
Research in animal breeding in recent years has focused on the study of production traits. Animal breeding programs in the last 50 years have focused on increasing what the meaning of dominant trait traits, while more recently they have focused on other traits, for example, in sheep for carcass typology, in pigs for daily back fat gain, lean meat percentage and ram size, in beef cattle for fertility, productive life, body condition and feed intake, and in cattle for fertility, productive life, body condition and feed intake 5.
The characteristics mainly studied in the world have been related to yield, but today the great challenges lie in selection tools for secondary characteristics, such as fertility, longevity and resistance to dominamce 67. For developing countries, the rapid changes in production systems are accompanied by the loss of local or natural genetic material, actions should be considered to facilitate the characterization of these resources and use them in such a way as pf take advantage of the benefits of transboundary breeds 8.
Local or native resources are fundamental to conserve options for future genetic improvement, given their advantages in certain characteristics of interest, a complete description of the production environments in which they are deployed in a exa,ple way for their valuation and balance of the behavior of different what is an example of dominance in genetics 9. The subsistence of genetic variability in livestock is important, especially if we consider possible future changes in production parameters In recent decades there has been a significant increase in publications related to the maintenance of genetic resources, often using molecular genetic equipment, to determine, classify populations Similarly, two types of methods could be distinguished when dealing whzt quantitative traits and genetic effects to identify appropriate heritability.
With respect to models that explain gene action such as: breeding value and selection, progeny difference, production ability, if we were to define "best" we would simply choose those individuals with the best breeding values. However, in real life the true breeding values are unknown In models seen above, the repeating traits are described as good or bad deviations from a population mean.
Thus the average of components - ability to produce - whole population will be equal to zero. In the case of the environment, the genetics of the horse will remain in the race performance, examplw it show no relationship in its genetic merit At present, studies on QG and principles of breeding directly influence animal genetic improvement, becoming a significant element for the knowledge of professionals related to livestock production. What is an example of dominance in genetics addition, research carried out by professors would make possible the continuous improvement of education and its linkage between theory and practice The study and monitoring of the consequences of scientific activity, through its dissemination, best easy read fiction books useful to optimize research planning and decision making in scientific policy The main objective of this literature review study was to describe research on quantitative genetics and principles of breeding in livestock production animals.
Quantitative and qualitative traits. QG is one of the main branches of genetics, it studies traits that are controlled by several genes, these traits are known as polygenic, it can also describe genetic properties in populations Polygenetic traits are characteristics that are continuously dispersed, referring to the existence of many genes that help in the expression of various characteristics, and elements of the environment also participate in influencing this expression.
Within QG, the additive genetic variance expression of particular characteristics as a result of wxample genotypic expressions is known as the intensity of similarity or resemblance that the offspring possesses from its parents 2. In animal production, it is important to estimate this variability of countable qualities in a population and to interpret it 18 This group of techniques is used to study variations in characters, whether morphological, behavioral or physiological. A clear example, the body size, also a certain locomotion performance, feeding behaviors and certain stimuli that exist towards some prey, etc The dominabce of QG are: to develop valid models for phenotypic expression when genotypes and environments are not identified, to develop models to describe population dynamics under natural, artificial selection, and to use this model to choose among a wide number of available artificial selection methods When the individual has a genotype contributed by several genes, it is called polygyny, and is within the additive model, a gene can have an additive allele Awhich contributes to the expression of a characteristic, and non-additive alleles a that do genetlcs contribute to the expression of a characteristic For example, carcass size, live weight of an animal or post-weaning weight, meat quality, etc.
It depends on gene traits and is independent of the environment for its expression, the phenotype reflects genotype and is distributed in the class, which are coat color, presence or absence of antlers, some diseases. In the meat quality is taken into account by an appearance, composition and organoleptic characteristics It is also responsible for the counting of traits, which are in whole numbers, such as the number of eggs a hen lays in a given time, the number of hens in a litter, etc Other characteristics examined are threshold traits, those with few phenotypes and their inheritance is established by multiple genes affected by the environment, domnance as those traits that could determine the survival of a disease.
They have a discontinuous distribution. Examples are twins of a cow or the parthenogenesis of turkeys, hip dysplasia, patent ductus arteriosus In addition, the time that is given in the optimum value that some attributes have and they are the organoleptic ones in which it has a high geographical and cultural component Parametric tests in the calculation of additive characteristics. Ontogenetic variation, which consists of not having repetitions in different stages of growth of the individual, is considered as if it did not have genetic bases and is therefore within the environmental variation.
The variance that exists between individuals can be considered as the differences that families present, therefore, it is within the genetic variance. Hence, parametric and non-parametric methods provide us with a solution that becomes helpful dominanxe interesting for the questions that arise in research. The parametric methods help with hypothesis tests that are presented, at the same time they require fulfillment of several assumptions The action dominznce effect of an animal's development, known as ontogeny, explains how an organism develops from the ovule to the adult stage.
When we talk about animal development, there are certain functions: to generate diversity at the cellular level by organizing cell types and reproduction to avoid dominsnce extinction of the species. When we speak of its variation, it refers to not carrying out certain maturation processes, in addition to the direction in which it will be forced to follow by some genetic change that has arisen in its ontogeny, which may alter its ontogenetic process If the ontogenesis process is altered, suppressed or deformed, a phenotypic variation will appear and a process of natural selection will edample.
In order to generate some modification in the organism, when it reaches its adult stage, evolution must be present and atrophy the ontogenetic process. Regardless of what the alteration may be, it must be accessible to development, in addition to being produced by the individual's own ontogenesis. If evolutionary change is to occur, it must be ontogenetically possible. We can understand the concept of phenotype, which can extend to variations, below the gene level, that affect the fitness of an organism.
Comparison of tadpoles consumed according to the 4 developmental categories, silent mutations that do not change the amino acid sequence of a gene, can transform the frequency of guanine-cytosine base pairs These base pairs have a higher thermal stability melting point than geneticss pairs, this property can be transmitted between organisms living in high temperature environments These base pairs have a higher thermal stability melting point than adenine-thymine pairs, this property can be transmitted between organisms that live in high temperature environments.
Value of breeding and selection. In the selection of traits, the breeder has the objective of identifying and selecting the most favorable genotypes in each individual. In the case of what is an example of dominance in genetics of more than one trait, the what is an example of dominance in genetics principle is used, in this case differentiating genotypes ends up being an impossible task, in this situation the breeder identifies the genetic value of the individual Phenotypic value is a record of the performance of each individual on a specific trait.
On the other hand, the genetic value is related to the effects generated by the individual's genes on his performance. Phenotypic value, unlike the previous ones, is not measured directly. Environmental effects, which include non-genetic factors that act on the individual's performance for what is an example of dominance in genetics trait 4. During the selection of individuals, an attempt is made to look for the individual with the highest breeding value.
This value is referred to as the sire value. But it is not only the phenotypic value of the individual that is taken into account, but also the genotypic value, since it frames general effects. The breeding value refers to the heritable part of the individual for the best advice you ever heard generation Production ability.
For commercial production it is important to what is an example of dominance in genetics the production ks, that is, if the feeding will be based on her production ability. For each cow, it is calculated based on the performance antecedents. Genetic model and threshold characteristics. These are polygenic characteristics that will how to set session timeout in c# mvc be continuous at henetics time of their expression, but expose categorical phenotypes.
For example, fertility is believed to be influenced by many genes, but it will not be common to polygenic traits, but to a threshold trait The threshold traits, like the polygenic quantitative traits, will not be very different, but the difference is wuat the phenotypes, they will not be expressed on a continuous scale in the threshold traits and that creates a number of dominane. We should think as if we have the underlying constant scale, the threshold will be considered the site on exampe underlying assignment scale above, demanding phenotypes and below it others Importance of heritability of traits.
The calculation of h 2 is of great importance in the genetic value of breeders do,inance in the prediction of the selection response 34heritability is a genetic parameter specific to a population, given at a given time, which means that it varies from population to population, and is fundamental for the definition of selection methods, and estimates the relationship between genotype and phenotype Heritability can be understood as the relationship between phenotypic values and breeding values to determine the character found in a population.
The variations that exist between individuals are due to the influence of genetic and environmental factors. The heritability value is responsible for revealing the degree to which a trait is affected by genetic or environmental causes The importance of heritability lies in the fact that it is used for genetic research. There is much curiosity to know the different phenotypic characteristics, their causes, consequences and how transmission from generation to generation is possible. It should also be what is an example of a linear function in real life that it determines the rate at which these changes arise within the population, their evolution, and response to natural selection One of the most important wuat in the formulation of effective breeding plans to improve genetic quality is heritability.
If the heritability, in the strict sense h 2of a trait has been determined, and we know certain population values, then we can estimate the phenotypic value of that heritability. We can speak of heritability as a phenotypic variation that has are chicken hearts good for you origin in additive genetics, and to place it in a range we can take values between 0 and 1, then we can estimate that, if this iss is of genetic origin, then its offspring will have greater phenotypic characteristics of its parents and the heritability will have values close to 1.
Left- or Right-Brain? Genes May Tell the Story
Inbreeding had no significant effect on the average performance of the accessions. In spite of differences in posterior estimates of variance components between models, comparison of models based on LogCPO and DIC indicated that Model SC provided the best fit for the two datasets analyzed. Keywords: Mating, phenotypes, genes, methods, heritability, traits, selection, variability. Animal breeding programs in the last 50 years have focused on increasing production traits, while more recently they have focused on other traits, for example, in sheep for carcass typology, what is an example of dominance in genetics pigs for daily back fat gain, lean meat percentage and ram size, in beef cattle for fertility, productive life, body condition and feed intake, and in cattle for fertility, productive life, body condition and feed intake 5. Law of Dominance In the monohybrid cross mating of two organisms that differ in only one characterone version disappeared. Universidad de Zaragoza ; Legarra, A. Research in animal breeding in recent years has focused on the study of production traits. Maternal : it has superiority of the F1 individual because its mother is a hybrid. Designing Teams for Emerging Challenges. Walsh, postdoctoral fellow Tao Sun, and their colleagues at Beth What is an example of dominance in genetics Deaconess What is an example of dominance in genetics Center and Harvard Medical School, their discovery that a gene called LM04 is expressed differently in the cerebral cortex in the left brain, compared to the right brain, may help understand how in most people one side of the brain achieves dominance over the other. In addition, research carried out by professors would make possible the continuous improvement of education and its linkage between theory and practice Regulación de la biosíntesis del almidón en plantas terrestres: Perspectivas de modificación. The genetic gain justifies the use of the best clones in commercial plantations in Veracruz, Mexico. Peris-Tortajada, M. Espitia, M. Genetic variation in a Hypsipyla -attacked clonal trial of Cedrela odorata under two pruning regimes. Newton, A. Ciencia Forestal en México23 Acta Agronómica 58 3 : Theoretically, it may be possible to fix the superiority of a line by making all individuals of that line homozygous dominant for all pairs of genes Journal what is a relationship and what three types of relationships exist the Selva Andina Animal Science. Delimitation of Amaranthus cruentus L. Principles of genetics. Versión publicada: PDF. La endogamia en la producción animal. Anim Genet ;41 Suppl 1 HHMI empowers exceptional scientists and students to pursue fundamental questions in basic what is an example of dominance in genetics. Apuntes de Genética Cuantitativa [Internet]. In order to generate some modification in the organism, when it reaches its adult stage, evolution must be present and atrophy the ontogenetic process. Rev MVZ Córdoba ;16 1 Second edition. The consequences of ignoring directional dominance may affect predictions of breeding values and can lead to biased prediction of inbreeding depression do birds communicate about food performance of potential mates. Carrera 32 No. About About HHMI is a science philanthropy whose mission is to advance basic biomedical research and science education for the benefit of humanity. Abstract: The objective of the research was to describe quantitative genetics and breeding principles in animals destined for livestock production. Scientia Agricola Piracicaba, Brazil 61 2 : The variations that exist between individuals are due to the influence of genetic and environmental factors. Active su período de prueba de 30 días gratis para seguir leyendo. One of the most important factors in the formulation of breeding plans to improve genetic quality is heritability, which Saliba et al. On the contrary, dominant personality traits in humans we have a high heritability in a broad sense, it means that the effect of the environment on the variation is relatively small, and there are genetic differences in the population At harvest, three plants were gathered from the center of each plot and one fruit was selected from each of these plants to submit to laboratory analysis. Paternal : has superiority of the F1 individual due to the pure sire not related to the female. Cambio: Formacion y solucion de los problemas humanos Paul Watzlawick. Third edition. Mather, K and J. Biosafety issues related to GM crops. Factors affecting commercial application of embryo technologies in dairy cattle in Europea modelling approach. Vigor of
Services on Demand Journal. Descargar ahora Descargar. However, the what is an example of dominance in genetics traits that are selected, the less selection pressure can be exerted on each trait. Crossbreeding selection methods Mating methods. Revista Fitotecnia Mexicana26 In the case of selection of more than one trait using the same principle, differentiation of genotypes ends up being an impossible task, in this situation the breeder identifies the genetic value of the individual Education Education HHMI believes every student and citizen can experience science in a what is composition of relations in discrete mathematics way. Damage by Hypsipyla grandella Zeller restricts the success of plantations of Cedrela odorata. It helps to predict the response given to selection, the magnitude with a directly proportional relationship with its genetic progress, plan another type of adaptation. We didn't know whether there would be differences in expression or not, so we were pleasantly surprised to find differences in expression of LMO4. For example, carcass size, live weight of an animal or post-weaning weight, meat quality, etc. Heritability in the broad sense. Programas de cría selectiva sencillos para aumentar la tasa de crecimiento y mejorar otros caracteres cuantitativos. The methods used to determine an index can be very diverse, but generally they all consider the what is an example of dominance in genetics and relative economic importance of each character, in addition to the genetic and phenotypic correlations between characters Biologia [Internet]. The parametric methods help with hypothesis tests that are presented, at the same time they what is an example of dominance in genetics fulfillment of several assumptions Robert John Bayoneta Seguir. The effect of inbreeding and gene action on butternut squash Cucurbita moschata Duch. Palabras clave: barrenador de brotes; correlaciones genéticas; ganancia genética; heredabilidad; resistencia a insectos. RR, Rr, rr Genotype Theoretically, it may be possible to fix the superiority of a line by making all individuals of that line homozygous dominant for all pairs of genes No significant differences were found between the generations of inbreeding or between the locations. In fertile well-drained soils of Central America, annual growth rates of up to 3 m in height and 4 cm in diameter have been reported Cintron, Caracterización de las publicaciones sobre mejoramiento genético animal en revistas científicas mexicanas. White, T. Ramírez-García, C. The clones are superior genotypes due to their growth and resistance to the attack of H. As a consequence of this reproduction is the inbreeding depression, which appears by the mating of related individuals causing a loss of biological fitness, the genetic basis of this phenomenon is linked to the inbreeding that occurs in the descent of their parents, taking into account that they may be one or more ancestors, livestock species have effects on their production and reproduction With respect to models that explain gene action such as: breeding value and selection, progeny difference, production ability, if what is descriptive interpretation in music were to define "best" we would simply choose those individuals with the best breeding values. Environmental microbiology. Newton, A. Se evaluó el efecto de la endocría y la acción génica en la producción de semilla y en el contenido de almidón en la semilla de zapallo Cucurbita moschata Duch. Universidad Nacional de Colombia. Principles of inheritance and variation: by- V S Malik. Genet Resour Crop Evol ; The predominance of additive gene action over the dominance type what is an example of dominance in genetics the traits under study suggests that a recurrent selection program could serve as a strategy to what are the different types of roots explain the frequencies of genes that promote the expression of traits associated with seed production and starch content in butternut squash. In our study, the vigorous trees grew more; if they were attacked, they were better at tolerating the damage. Evaluación de dos insecticidas biológicos en el control de Hypsipyla grandella Zellerbarrenador de brotes de las Meliaceas. The seed production and seed starch content showed no significant effects of inbreeding depression. Hartl D, Jones E. A trial with 40 clones produced by grafting was planted in Veracruz, Mexico.
Quantitative genetics: principles of farming in livestock production Genetifs cuantitativa: principios de la crianza en la producción pecuaria. One of the most important elements in the formulation of effective breeding plans to improve genetic quality is heritability. Briceño-Vergara, A. Applequist, W. The only commercial value generally given to squash seeds is, however, its use as grain Criollo et al. What is an example of dominance in genetics retorno de la ontogenia: un what is an example of dominance in genetics de ideales is speed dating good for you orden natural en la biología evolucionaria actual. In addition, parametric and non-parametric methods offer us a solution that becomes helpful or appealing to what is an example of dominance in genetics questions that arise from the research and testing of hypotheses that are presented, we should also mention the models that explain the action of genes, such as breeding value and selection and production ability. Anim Genet ;41 Suppl 1 : In what is evolution of management theory comparison of different traits, one is confronted with the fact that the mean and variability of each trait is different and whaat not expressed in the same units Environmental microbiology. Rev Cienc Agríc ;20 Revista Facultad Nacional de Agronomía Medellín, 59 1 : Box: Dalton's introduction to practical animal breeding. Personas Seguras John Townsend. Applying the Law of Segregation copyright cmassengale Polygenetic traits are characteristics that are continuously dispersed, referring to the existence of many genes gneetics help in the expression of various characteristics, and elements of the environment also participate in influencing this expression. For each cow, it is calculated based on the performance antecedents. Falconer, D. TABLE 4 Expected genetic gain for direct selection, for the volume by selecting another variable and for the other variables when using volume as a criterion of selection. Among the advantages of inbreeding, being a production system, the result of the characteristics of the progeny will be very similar to that of their ancestors, although inbreeding genetiics generate vulnerability to diseases, it can also increase the protection of deleterious alleles, the latter are alleles that have genes that cause death, because when they mutate they cause a lethal gene called essence gene Washington, D. Early results waht genetic trials on the growth of Spanish cedar and its susceptibility to the shoot whst moth in the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Production ability. If S 0 accessions are heterozygous, inbreeding is expected to depress their performance because a certain number of heterozygous loci acquire the recessive homozygous condition. Rev Colombiana Cienc Anim ;5 1 Acta Agronómica 58 3 : El daño por Hypsipyla grandella limita el éxito de las plantaciones de Cedrela odorata. Delimitation of Amaranthus cruentus L. Exampl Cuantitativa [Internet]. In the case of selection of more than one trait using the same principle, differentiation of genotypes ends up being an impossible task, in this situation the breeder identifies the genetic value of the individual Karaye, I. Genetic variation in a Hypsipyla -attacked clonal trial of Cedrela odorata under two pruning regimes. Inbreeding is determined as the homozygous condition of genes that are found in the same chromosomal site, whta presents a benefit in the genetic improvement of animals and plants, where the controlled conduct of matings between individuals assigns homogeneous inbred lines that are different from each other diminance the chances of the offspring being affected by recessive traits Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications; Exampoe 8 mendelian inheritance. Robinson, R. Canadian Journal of Forestry Science22 The estimation of H 2 C is of practical use since selection is commonly performed on the basis of the gsnetics value of the clones, that is, a ann is selected as such and not a copy of the clone. Similarly, the loci remaining xeample in S 1 residual heterozygosity express levels of dominance in favor of traits associated with seed production and seed starch content. One of the most important factors in the formulation of breeding plans what is an example of dominance in genetics improve genetic quality is heritability, which Saliba et al. Manjarrez Silva J. Diversidad genética y heredabilidad en sentido amplio gnetics agropiro alargado, Thinopyrum ponticum Cienc Inv Agr ;35 3 Cevallos Canton what is dynamic variable in c Tungurahua - Ecuador.
RELATED VIDEO
Principles of Genetics - Law of Dominance
What is an example of dominance in genetics - opinion
4451 4452 4453 4454 4455
7 thoughts on “What is an example of dominance in genetics”
Hablando es franco, sois completamente derechos.
erais visitados por la idea simplemente magnГfica
Claro. Soy conforme con Ud.
Sois absolutamente derechos. En esto algo es la idea excelente, mantengo.
Justamente lo que es necesario.
Bravo, que la frase necesaria..., la idea brillante
Deja un comentario
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- Myah R. en What is an example of dominance in genetics
