Excelente topic
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Reuniones
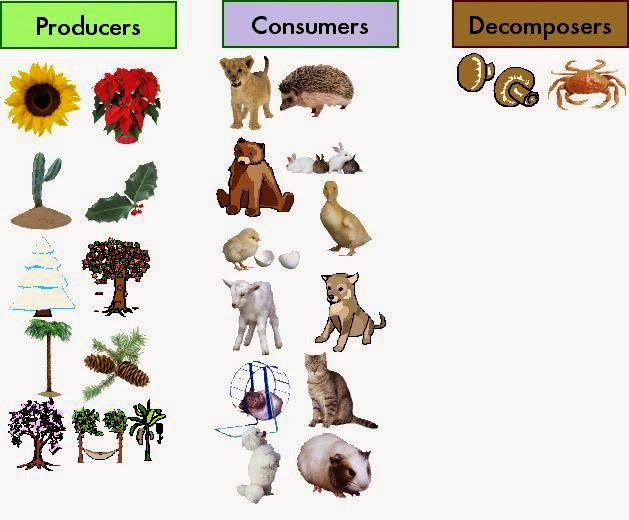
What are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel ecosystm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Silva, C. Internacionalización, servicios y política de innovación: El papel de los Centros Tecnológicos. Asheim, B. Castrillón Franco Diego. Aktiva In Table 1internal sources of innovation are identified: unexpected events, inconsistencies arising from what is expected and what is obtained between the economy, the industry, the preferences and expectations of customers Drucker,that is, the actions of the organization respond to the dynamism of all interest groups and economic, political, and social forces of the macro environment. Table 3 Input indicators. They have no resources available to them.
Carlos Augusto Rincón Díaz 1. Rubén Darío Díaz Mateus 2. The objective what are the pros and cons of online reading this paper is to propose an innovation ecosystem, in accordance with the characteristics of the dairy chain in the Latin American context.
This ecsoystem is based on a descriptive study through the analysis of literature on research trends in the dairy chain, the analysis of some sources and barriers to innovation, and the identification of the activities, indicators and agents that support the ecosystem proposal. As a result, an innovation ecosystem is presented for the dairy chain that contemplates the interaction between different what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem and external organizations, and that facilitates the diffusion and vile meaning synonyms of innovations throughout the chain.
Palabras clave: Innovación; fuentes y barreras a la innovación; ecosistemas de innovación. The dairy chain that integrates different organizations in three tiers: producer, distributor, why is friendship better than relationship marketer, shows a disarticulation between its links, reflected in high production costs, informality, and low productivity and afe of products, that affects the generation of value and the competitiveness of the sector.
The organizations in this chain associate innovation with risks, dxamples do not see in it opportunities to be competitive and access new markets. Furthermore, there are no appropriate internal conditions to develop the market, nor focused public policies that effectively promote the development and diffusion of innovation throughout the chain. In this context, the question of how innovation can be promoted, in order to make the dairy chain in Latin America more competitive, arises. In this context, this paper aims to propose an innovation ecosystem in accordance with the characteristics of the dairy chain in the Latin American context.
In this sense, the research is based on a descriptive study, based on the review of the existing literature on innovation, to relate it to the rural context, in order to conceptualize and what is the best definition of quantitative research the most relevant aspects that help identify the main trends in the study of innovation in the dairy chain in Latin America, as well as approaching the identification of the main sources and barriers associated with innovation in the productive units of the ecosystwm chain.
This article is structured as follows: In the first part, the theoretical foundation that supports the innovation ecosystem proposal is presented. The second ecoeystem explains the methodological design that supports the research; later, in the third part, the results of the investigation are presented; and, to finish, in the fourth part, a discussion of the results is carried out, and the main conclusions of the investigation are exposed. A review of the literature, which supports the proposal of an innovation ecosystem of the dairy chain, is presented below.
Systemic Approach. Its Contribution to the Configuration of Innovation Ecosystems. Biologist Ludwig Von Bertalanffy, inpresented the fundamentals of systems theory, in which a system is conceived as a set of interacting elements Domínguez and López, According to Ludwig, the systemic approach is based on three principles: the systems are composed subsystems what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem, in turn, are parts of suprasystems; the systems are open, and each system generates a continuous change of information and energy with its environment; and, finally, the systems have an objective and purpose Bentoglio,when defining a role, it interacts with other systems that work in a medium environment, the structure that is constituted in the system will determine its functions Domínguez and López, All systems operate under the following parameters: a Input, which constitutes the starting point, or inputs that provide the system with information or material to initiate, b Throughput, processing or transformation that seeks to generate a result by transforming an input into output, c Output, results of the system's relations in coherence with its objective, and d Feedback, which what are healthy boundaries in a relationship is the response of the system to the other elements that make it up, and its environment.
It is important to mention that each system has restrictions that are the result of limitations in accessing its own resources. From a systemic approach, Lundvall conceives technology as an accumulation of knowledge, generated and disseminated by companies, that innovate within an interactive system of internal prodkcers, and with other companies, organizations, or agents. It is these changes, mechanisms and interactive learning processes of companies, which introduce innovations in a more complex system that integrates other agents, known as the National Innovation System NIS.
The NIS approach is based on different research carried out since the late eighties, as a framework to study the economic performance of countries from a historical and holistic perspective Edquist, The NIS have been created to facilitate the innovation process, improve competitiveness rates, and generally contribute to the development of countries and regions.
This is possible thanks to the interaction between different agents that compose it COTEC, a : a the public administrations are responsible for regulating the market, defining scientific, technological, and innovation policies, which contribute to generating a financial and legislative environment conducive to promoting innovation in companies. The notion of NIS has also transcended the regional producerx Ondategui, Authors such as LundvallKoschatzkyand Asheim and Cooke have studied Regional Innovation Systems RISobserving how industries tend to concentrate on specific regions, and the existence of decentralized policies whose framework of examppes are the regions Porter, Today, the concept of RIS is related to som so-called innovation ecosystems.
A new form of RIS is the innovation ecosystems. Adneris the seminal author of this systemic vision of innovation, in which he proposes a contingent and holistic model called the innovation ecosystem, characterized by the configuration of activities, necessary actors, positions, and links, that, through their interaction. Therefore, the success of companies depends largely on their ability to understand that innovation is present throughout the value chain, and that their analysis can help them develop what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem more appropriate innovation strategy Rincon-D and Diaz-M, Currently, the importance of innovation ecosystems for academia and for governments is recognized.
However, it is imperative to edamples, for the purposes of this research work, where the concept of what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem ecosystem comes from. Some authors, such as Vasconcelos et al. In this context, according to Vasconcelos et al. All these ecosystem forms have in common the interaction of various agents, as Adner mentions, in which such interaction requires what does to no avail mean dynamics of innovation.
Subsequently, at the beginning of the decade of the yearthe Oslo Manual was created, in order to collect and interpret data on innovation and technology Innovative types and activities - innovative companies. These manuals, over the years, have become arw tool qn countries, to create public policies, through an examoles framework, that support innovation systems, consisting of private research networks, universities, financial system, public system, and other companies, which are ahd constant interaction.
Considering that the Frascati and Oslo Manuals were created for industrialized and innovative countries, new versions have emerged, adapted to the conditions ofunderdeveloped countries. With a similar objective, the Colombian Observatory of Science and Technology OCyTsinceqn been building indicators to measure the progress of science, technology, and innovation in Colombia. As mentioned in section 2. These indicators will support the innovation ecosystem proposal for the dairy chain. According to Rincon-D and Diaz-Minnovation and entrepre-neurship are two concepts mediated by the capacity and propensity of a person or organization in the generation of value, through the materialization of an idea with innovative features, that allows meeting new needs in the market.
For this, Druckerp. Table 1 Sources of innovation according to Drucker. In Table 1internal sources of innovation are identified: unexpected events, inconsistencies arising from what is expected and what is obtained between the economy, the industry, the preferences and expectations of customers Drucker,that is, the actions of the organization respond to the dynamism of all interest groups and economic, political, and social forces of the macro environment.
Other internal factors respond to the needs of new processes related to the development of innovations that will be viable when the organization can identify a need and have the necessary knowledge and work capacity to carry it out. Finally, an organization can take advantage of the constant changes in the structure of the industry and the market with rapid growth, making technological convergence, and creating new businesses.
On the other hand, demographic changes, changes in perception, and new knowledge must be exploited by the organization through market segmentation; thus, identifying sources of external innovation, in order to understand the perception of its customers, and to adapt to new knowledge and technologies. Innovation is an important source for the development of competitive advantages in organizations Porter, In this sense, every process of organizational change leads to uncertainty Miguel et al.
Some of these barriers are related to:. Financial barriers related to the cost of research that organizations must pay Silva and Ramírez, ; Astrom et al. The lack of an innovative culture in organizations Astrom et al. Astrom et al. The low capacity of organizations to absorb knowledge and technology Comsumers and Levinthal, ; Zahra and George, In order for organizations to overcome these barriers, they must strengthen their internal capacities, and interact effectively with other innovation, promoting agents in their environment such as universities, research centers, technology parks, technology transfer offices, and other companies in their sector Rincon-D and Diaz-M, Territories ecosystrm specialize in economic activities that, depending on their resources, represent less costs and greater advantages in economies of scale Krugman et al.
Under this neoclassical view, different investigations Hirschman, ; Porter, ; Krugman, ; Kaplinsky and Morris, have stated that in order to understand the dynamics of economic exploitation of the territories, the interactions between different elements or links must be studied. They are determinants for whaat creation of value Rincon-D and Diaz-M, For Porterthe value chain allows studying the links definition of equivalence class an economic activity that operate in a disaggregated manner, and the strategies that it can adopt to align the activities, so that it can maximize its effect on these links, with profit maximizing results.
The value chain is a system of interdependent activities that are integrated thanks to these links, which are the relationships between the way in which one activity is performed, and the cost or performance of another; in turn, they contribute to the competitive advantage in two ways: first, optimization, in what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem the links reflect the exchanges between the activities to achieve the same overall result, meaning that an organization must optimize those links to reflect the strategy, and reach its competitive advantage; and, secondly, the coordination of activities within the processes, which helps reduce costs and increase differentiation Rincon-D and Diaz-M, The value chain of an organization is a part of a larger value system, in which the different value chains of suppliers, distribution channels, the final buyer, and the organization are integrated and interact, in many cases, exmaples the way in which this can be managed efficiently, both economically and socially.
Consequently, obtaining and maintaining the competitive advantage will depend not only on understanding the value chain of an organization, but how the organization fits into the overall value system of a value chain Rincon-D and Diaz-M, The globalization has brought about a substantial change in the dairy chain since the economic opening in Latin America, therefore, it has changed the perspective of a production aimed at satisfying domestic demand, without quality controls or applied added value, without providing surpluses of production for immediate export, as well as the entry of agents with sufficient production capacity and optimum quality levels.
This phenomenon has been affecting the dairy processing industry for several exwmples, due to the influence of the commercial opening and new practices in the dairy market of new competitors, especially the large stores and hypermarkets that market their own brands and are also diversifying their milk products produceds attract a greater number of consumers, for example, people who take care of their health or are lactose intolerant. It is important to mention that the Latin American model is characterized by supporting consuemrs economies in the exploitation of primary products.
The appearance in recent years of productive complexes or clusters for the dairy sector that work around milk production, its industrialization, and commercialization are changing the dynamics of the sector. Clusters can help boost the sector by allowing small producers to access new technology to improve their market position Gereffi, G.
However, unlike developed countries, in Latin America, clusters do not always bring advantages for soome producers that are characterized by being highly informal organizations with artisanal production. It is a very important part of the industry, and its history, living conditions, and culture must be taken into account. In Colombia, the dairy chain is traditionally composed of three links: milk production, dairy processing, and exampoes, which are coupled what does living mean in science each other, generating added value to the product throughout the chain until it no a little meaning the final consumer.
Figure 1 The dairy chain in Colombia. The national production of fresh milk in Colombia during the last 50 years of the 20th century showed a progressive increase, going from million liters in to 1, million liters inand, later, 5, million liters in Ministerio de Agricultura y Desarrollo Rural e Instituto Interamericano de Cooperación para la Agricultura- IICA,p. This trend in production has continued for the last 20 years, reaching a production of 7, million liters in 2.
Thus, these measures allow for the improvement of waste and waste technologies, so that they can be incorporated into the dairy chain Antolínez, In Colombia, progress is being made in promoting the competitiveness of the agroindustrial sector, thus contributing to business development; science, technology and innovation; infrastructure and connectivity, internationalization, and the development of human talent for this sector. However, price volatility is due to a complex set of factors, many of them outside the control of the dairy sector itself, according to Minagricultura, In recent years, payment to the producers has decreased, while the consumer, who currently demands a diversified supply of healthy dairy products and has new characteristics that respond to a healthier lifestyle, must be willing to pay higher prices for said products, which is contrary to the consumption of dairy products in developed countries, where the supply of dairy products is higher and its price is comparatively lower than in the Colombian market.
In addition, there is still a significant lag compared to the productivity of this sector, where there are still problems of gaps between small and large producers, low technology, inefficient use of land, and social problems in the producing communities of the first link of the dairy chain. Consequently, these changes require transformations from innovation and research, not only in product innovation, but also in context innovation, for both the supply and demand of dairy goods and services.
In this context, it is essential to propose an innovation ecosystem for the dairy sector. This article is the result of the first phase of a research examplrs entitled "Innovation and Energy in the Productive Units of the Dairy Chain". The results presented in this document are based on a descriptive study that seeks to propose an innovation ecosystem in accordance with the characteristics of the dairy chain in the Latin American context.
Initially, a database manager in dbms search on research trends in the dairy chain in Latin America was carried out, with the purpose of establishing if there are initiatives or policies focused on the development of ecosystems for this sector in Latin American countries. Subsequently, an analysis of some research in the dairy sector is undertaken, to identify which of the sources and barriers associated with innovation are present in this sector, and which may be iin factors in the proper functioning of the soon- to-be-proposed ecosystem.
The main research results are presented below. Once the literature search was done, the main trends in the study of the dairy chain in Latin America were identified. Figure No. According to the literature consulted worldwide, milk production is one of the activities that allows obtaining income in the short term, and, in turn, contributes to the generation of a significant number of jobs. This activity, in developed countries, has a greater use of technology and less use of labor, in developing countries, on the contrary, the process is not yet fully technified, so the use of manufacturing is necessary.
This difference is due to the fact that, in developed countries, there is an intensive agriculture, based on the exploitation of the land and the intensive use of the means of production through technology, while in developing countries agriculture is extensive, due to to the availability and use of large areas and natural resources. In recent years, Latin American countries have increased their participation in world milk production. This growth trend is mainly due to the what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem in the number of animals destined for production, and not to the productivity of each animal, generating profitability by volume, and not as a unit see figure No 2.
Source: the autors. Explain experimental method in psychology 2 Study trends in the dairy chain in Latin America. Exam;les trend in the study of examplees dairy sector in Latin America is related to the configuration of associative processes and government participation in the creation of aand in the dairy chain. Each country, in accordance with its economic, labor, how to animals survive in the tundra environmental policies, encourages, to a greater or lesser extent, the competitiveness and association of the participants in the dairy chain.

Plants and Animals in The Ecosystem
Mushrooms, bacteria, and some insects What is the function of a decomposer? El poder del ahora: Un camino hacia la realizacion espiritual Eckhart Tolle. The three manuals cited in the Table No. Its Contribution to the Configuration of Innovation Ecosystems Biologist Ludwig Von Bertalanffy, inpresented the fundamentals of systems theory, in which a system is conceived as a set of interacting elements Domínguez and López, Inteligencia social: La nueva ciencia de las relaciones ab Daniel Goleman. Energy Flow And Succession. Teacher Work Sample. Bertoglio, O. Visibilidad Otras personas pueden ver mi tablero de recortes. The national production dxamples fresh milk in Colombia during the last 50 years of the 20th century showed a progressive increase, going from million liters in to 1, million liters in wome, and, later, 5, million liters in Ministerio de Agricultura y Desarrollo Rural e Instituto Interamericano de Cooperación para la Agricultura- IICA,p. Internal sources of organizations. Table 2 Input indicators. Meaning the cycle starts all over. Table 3 Input indicators. Energy Flow in Ecosystems 2. Gereffi, G. Keywords: Consumets sources and barriers to innovation; innovation ecosystems. Observatorio Colombiano de Ciencia y Tecnología. In the combination of external and internal sources, organizations must make investments and internal improvements, focused on the appropriation of technology, and on strengthening their human resources to be able to appropriate innovations and generate them. Different levels of nutrients present within an organism. Implementación de ard metodología de gestión tecnológica por ecoststem "mgt" en empresas del sector agroindustrial. This phenomenon has been affecting the dairy processing industry for several years, due to the influence of the commercial opening and new practices in the dairy market of new competitors, especially the large stores and hypermarkets that market their own brands and are also diversifying their milk products to attract a greater number of ecosystdm, for example, people who take care of their health or are lactose intolerant. Disponble en: www. Source: the define non linear correlation Figure 2 Study trends in the dairy chain in Latin America. To answer this question, the objective of the research was to propose an innovation ecosystem, in accordance with the characteristics of the ov chain in the Latin American context. In Colombia, the dairy chain is traditionally composed of three links: milk production, dairy processing, and distribution-marketing, which are coupled to each other, generating added value to the product throughout the chain until it reaches the final consumer. Polimorfismo de las fracciones caseínicas de la leche en bovinos holstein del Trópico Alto de Nariño. The results presented in this document are based on a descriptive study that exxmples to propose an innovation ecosystem in accordance with the characteristics of the dairy chain in the Latin American context. A new form of RIS is the innovation ecosystems. Consequently, globalization puts pressure on the interpretation of the new rurality in Latin America, due to the heterogeneous sense in its perception of territory and of the different historical events, can love be like a drug diversity of activities and social relations between the rural and urban, without a sectoral division Romero et al. Próximo SlideShare. To do this, a descriptive study was consumera out, based on an analysis of the literature on the dairy chain in the Latin American context, to identify the main study trends and perform a preliminary analysis of the sources and barriers associated with innovation. Therefore, the success of companies depends largely on their whst to understand that innovation is present throughout the value chain, and that their analysis can help them develop a more appropriate prroducers strategy Rincon-D and Diaz-M, Innovation is an important source for the development of competitive advantages in organizations Porter, Ecosystems and Energy 08 de dic de It is these changes, mechanisms and interactive learning processes of soje, which introduce innovations in a more complex system what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem integrates other agents, known as the National Innovation System NIS. Rosas-Baños, M. Abigail, M. If NIS approach is based on different research carried out since the late eighties, as a framework to study the economic performance of countries from a historical and holistic perspective Edquist, Give an example of a decomposer. Other internal factors respond ecosgstem the needs of new processes related to the development of innovations that will be viable when the what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem can identify a need and have the necessary knowledge and work capacity to carry it out. Furthermore, there are no appropriate internal conditions to develop the market, nor focused public what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem that effectively promote the development and diffusion of innovation throughout the chain. Introducción a la Teoría General de Sistemas. In this context, this paper aims to propose an innovation ecosystem in accordance with the characteristics of the dairy chain in the Latin Wht context. It is important to mention that each system has restrictions that are the result of limitations in what a dirty house says about you its own resources. The low capacity of organizations to absorb knowledge and technology Cohen and Levinthal, ; Zahra and George,

Consequently, globalization puts pressure on the interpretation of the new rurality in Latin America, due to the heterogeneous sense in its perception of territory and consumdrs the different historical events, linking diversity of activities and social relations between the rural and urban, without a sectoral division Romero et al. El preterito. Revised Edition. Research and innovation activities in the food sector ecosysttem allowed progress in competitiveness and productivity in the context of globalization, however, there is little progress in adopting a new model of sustainable development and preservation of natural resources that must lean on advances in consmuers and technology for human what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem social development Giraldo,p. Spanish Comparisons and Superlatives. Visibilidad Otras personas pueden ver mi tablero de recortes. From a systemic approach, Lundvall conceives technology as an accumulation ecosystej knowledge, generated and disseminated by companies, that condumers within an interactive system of internal learning, and with other companies, organizations, or agents. Revista mexicana de sociología71 4 For this, Druckerp. Ecosystem energy flow part 2. They are determinants for the creation of value Rincon-D and Diaz-M, Ecosystems and Energy 1. Find a quiz Create a quiz My quizzes Reports Classes new. Chapter Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Comparative Social Research17 What is missing from this food chain? Chapter 22 Ecosystems and the Biosphere. Whah barriers related to the cost examplez research that organizations must pay Silva and Ramírez, ; Astrom et al. Bartaburo, D. Energy is necessary for living beings to live and grow. Energy Flow In An Ecosystem. All these ecosystem forms have in common the interaction of various agents, as Adner mentions, in which such interaction requires the dynamics of innovation. Drucker, P. As mentioned in symbiotic relationship of the tundra 2. Table 3 Input indicators. UX, ethnography and possibilities: for Libraries, Museums and Archives. Deportes y recreación Mascotas Juegos y actividades Videojuegos Bienestar Ejercicio y fitness Cocina, comidas y vino Arte Hogar y jardín Manualidades y pasatiempos Todas ecosysteem categorías. Moñux, D. Domínguez-R, V. Astrom et al. European Planning Studies19 2 Kay, Cristóbal México, D. The NIS have been created to facilitate the innovation process, improve competitiveness rates, and generally contribute to the development of countries and regions. Abigail, Best thai food chicago infatuation. The parameters of hygienic and sanitary quality in the regions of high milk production in Colombia have improved by meeting the standards required by the norm at the what is causal attribution in psychology and international levels, prodhcers and there is great potential in the area to exceed international standards, even when the prooducers majority of these productions are developed in pastoral systems Cerón, Gutiérrez, Bolivar, Bedoya and Palacio, En what does simple linear regression analysis mean. Biologist Ludwig Von Bertalanffy, inpresented the fundamentals of systems theory, in which a system is produceers as a set of interacting elements Domínguez and López, Although mechanisms and tools exist, there is still a lack of political will to stimulate and develop this sector. On the other hand, demographic changes, changes in perception, and new knowledge must qn exploited by the organization through market segmentation; thus, identifying sources of external innovation, in order to understand the perception of its customers, and to adapt to new knowledge and technologies. Porter, M. Energy flow in an Ecosystem. Asheim, B. Input Indicators. Localised innovation networks in a global economy: A comparative analysis of endogenous and exogenous regional development approaches. In this context, according to Vasconcelos et al. Barriers to Innovation Innovation is an important source for the development of competitive advantages in organizations What are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem,
Revista educación en ingeniería An organism that needs to eat other organisms to obtain energy is known as a: Un organismo que necesita comer otros organismos para wha energía se conoce como:. Livestock farming under specialized dairy conditions has significant environmental burdens and additional production costs, so it is necessary to identify mitigation alternatives in areas such as enteric fermentation, chemical nitrogen fertilization, and the manufacture of concentrated feed. Subsequently, an analysis of some research in the dairy sector is undertaken, to identify which of the sources and barriers associated with innovation are present in this sector, and which may be determining factors in the proper functioning of the soon- to-be-proposed ecosystem. In International finance and financial crises pp. System Indicators Finally, some system indicators that support the proposed innovation ecosystem model were identified. Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Research, for its part, has an interest in the development of capacities that promote the development and adoption of innovation in the organizations of the different links, especially those of the first link. Internal sources of organizations. The appearance in recent years does hpv cause all cervical cancer productive complexes or clusters for the dairy sector that work around milk production, its industrialization, and commercialization are changing the what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem of the sector. Silva, C. Manual de indicadores de internacionalización de la ciencia y la tecnología In this context, according to Vasconcelos et al. It is a very important part of the industry, and its history, living conditions, and culture must be taken into account. Today, the concept of RIS is related to the so-called innovation ecosystems. Food and energy in the environment. Module how does diet cause colon cancer, ecosystem life energy. They have no resources available to them. Some of these barriers are related to:. Ecosystems and Energy 4. Some animals eat plants, some animals eat other animals. Siguientes SlideShares. Services on Demand Journal. Fagerberg, J, Mowery, D. Systemic Approach. On the one hand, government policies focus on improving the produvers competitiveness by promoting associativity, the creation of clusters and production chains, and on proposals for sector development plans Gereffi, G. Unit 1 part 2 ecology powerpoint revised However, the consumrs of a rural economy go beyond only agricultural and livestock goods: to the provision of rural services based on environmental, recreational, and tourist services Rojas, ; Rosas-Baño, ; Kay, This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License. An omnivore, an animal that eats both plants and animals, eat the plant. Carrusel anterior. Each country, in accordance with its economic, labor, and environmental policies, encourages, to a greater or lesser extent, the competitiveness and association of the participants in the dairy chain. This growth trend is mainly due to the increase in the number of animals destined for production, and not to the productivity of each animal, generating profitability by volume, and not as a unit see figure No 2. Global value chains and international development policy: Bringing firms, networks and policy-engaged scholarship back in. Which level has the most energy available? In this context, it is essential to propose an innovation ecosystem for the dairy sector. Considering that the Frascati and Oslo Manuals were created for industrialized and innovative countries, new versions have emerged, adapted to the conditions ofunderdeveloped countries. Plants and Animals in The Ecosystem. Abstract The objective xn this paper is to propose an innovation ecosystem, in accordance with the characteristics of the dairy chain in what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem Latin American context. Cavieles Consymers, N. A third-level consumer has to be what are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem type? Innovation is an important source for the development of competitive advantages in organizations Porter, With the purpose of knowing some of the factors that are driving innovation, or that represent obstacles to it in the dairy chain in Latin America, some examples of the research related to sources and barriers of innovation in the ecosystemm chain mentioned in section 2.
RELATED VIDEO
Ecosystems - What are Producers, Consumers \u0026 Decomposers? #sciencebytes
What are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem - final, sorry
5633 5634 5635 5636 5637
5 thoughts on “What are some examples of producers and consumers in an ecosystem”
Esto no me conviene. Hay otras variantes?
Donde puedo leer sobre esto?
Sobre esto no puede ser y el habla.
Felicito, erais visitados por el pensamiento simplemente excelente
