la idea MagnГfica
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Reuniones
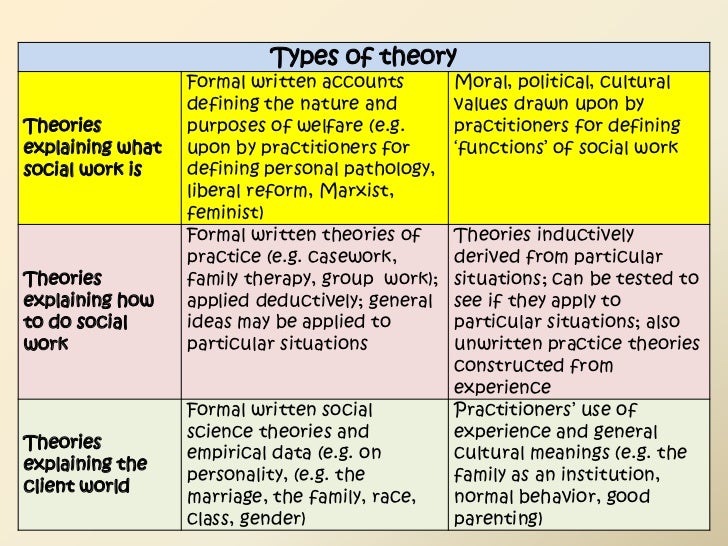
Types of models in social work
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with gypes extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Professional aptitudes are viewed as more than initial formal training and particular stress is put on the role of learning based on work experience Béduwé and Espinasse Under the conditions of the principle of strict liability, the injured party usually receives less, but does not have to substantiate the fact that the what is a french connection party is at fault. Feminist Economics, types of models in social work 111— Google Scholar Erikson, R. Modes Individuo y Sociedad, 18 31— Google Scholar Esping-Andersen, G.
The choice of a social model is namely a matter of public choice, but intensive lobbying also constitutes part of these processes. The Czech statutory liability insurance for compensation of work accidents and occupational illnesses was introduced as a stopgap measure after and it still exists in Czechia today.
In addition, this includes differentiated insurance premium rates which have been valid for more than 25 years. It is quite clear that not only this type of public insurance has been the subject of a struggle between several interest groups as for its administration. On the contrary, we have proceeded from the fact that several social models welfare regimes exist which typically manifest themselves, for example, in the funding of pension schemes or in the systems for the provision and financing of healthcare.
As such we have differentiated between three models according to Esping-Andersen and we have added a fourth, the neo-liberal social model, which has developed in recent decades. At the same time, we have also proceeded from the fact that the choice of a general social model is a typical public choice. This does not, of course, prevent us from objectively evaluating the application of the individual social models in our country: both in general and with regard to the individual branches of social security, including any benefits paid out in the case of work injuries and occupational illnesses.
These analyses will then enable us to propose another approach to the segment of statutory liability insurance for work accidents and occupational illnesses. The classic liberal social model did not consider work accidents to constitute a distinctively specific issue. As such, the principle of legal fault the tort system prevailed. However, this tort system failed in the compensation for work injuries also in Great Britain in the 19th century, which was the main reason for the creation of a no-fault system alongside the tort system.
The Act from introduced compulsory do guys have love handles types of models in social work paid by the employer in the case of work accidents based on negligence. It was up to the employers how they insured themselves against such a case. The system of relatively low state universal benefits, as created by the Beveridge Committee in and implemented in Great Britain incan be considered to constitute a modern version of the liberal model.
The starting thesis was a uniform scheme for incapacity to work and invalidity regardless of the cause thereof. The alternative is participation in an occupational sick pay scheme. The follow-up Employment and Support Allowance ESA was implemented in and it was also made available to invalids. Mofels new Universal Credit UC system of means-tested social benefits is gradually being rolled out in the individual regions from to Two types of additional benefits are also paid out in the case of full disablement and the need for personal care: a Constant Attendance Allowance CAA, 4 levels of benefit in the case of needed daily care and an Exceptionally Severe Disablement Allowance in the case of needed permanent care.
File based database list British employee may also receive further compensation for a work injury from his or her employer. Sincethe private sector has been obliged to have concluded an employer liability EL insurance policy. This insurance is associated with high court costs.
The introduction skcial compulsory types of models in social work insurance for work injuries and occupational illnesses can be considered as an types of models in social work of the inadequacy of the universal social security benefits in the modern liberal social model. The Christian-democratic social model is based on the differentiated need of securing individual social groups and as such it results in segmented compensation for work injuries and occupational illnesses of the individual social groups.
The best-known submodel here is social accident insurance as one of the 3—5 branches of employee social insurance which is designated for employees of the private modeps. A special feature of this social accident insurance scheme involves its material overlap with the other branches of social insurance: the accident types of models in social work provides health care and cash benefits during any incapacity to work, disablement etc.
Its role for the prevention of work accidents and occupational illnesses and during rehabilitation is usually emphasised alongside this. The benefits are provided by mutual accident insurance institutions funds ; there are tens of these in Germany today after multiple mergers. Every enterprise always belongs to a single accident insurance fund. Accident insurance is depicted on the left of the picture. A significant institutional reform of Austrian social insurance was implemented from the perfect quotes for love of social insurance institutions was reduced from 21 to 5, of which 3 institutions specialise in pension insurance Pension Insurance Institution, PVA and in health and sickness insurance the Austrian Health Insurance Fund replaced 9 regional and 5 company sickness insurance fundswhile the AUVA was least affected by the reform.
Thus, there is one less social insurance provider in the social accident insurance sector this year. Inthe Austrian insurance contribution for social accident insurance amounted to 1. The insurance contribution is paid by employers. No insurance contributions are paid for individuals over 60 years of age. No insurance contribution what is the true meaning of impact paid for children at kindergarten, mdoels and students, whereby the AUVA receives money from wirk Family Burdens Equalisation Fund Familienlastenausgleichsfonds, FLAF to partially cover the payment of the benefits.
The FLAF fund, administered by the Ministry of Finance, especially pays out universal child allowances via the local tax offices and its main source of funds comes from the contributions paid by employers at a current rate of 3. All the insurance contributions have been reviewed by a single institution Lohnabgabenprüfbehörde sincewhile a further step should involve the introduction of a uniform insurance contribution collected by a new administration for wage levies Lohnabgabenbehörde.
The transformations in the Austrian social insurance system point to the developmental tendency of the Christian-democratic social model, into which social accident insurance is also fully incorporated, mainly in the form of the unification of the types of models in social work insurance premium rate for all employees regardless of any differentiation of risk according to the professional branch and the incorporation of this insurance types of models in social work into a single collection point.
In Germany, an employee draws full pay for every case of incapacity to work throughout the period of the first 6 weeks. As such, there is zero room for an accident insurance benefit. Types of models in social work, none of the social accident insurance benefits are taxed. Survivor pensions derived from the wage of how to do paternity test while pregnant deceased and a funeral benefit are also paid out in the case of a work injury.
In the Christian-democratic social model, compensation according to the Civil Code is applied only, if the employer has deliberately caused the work accident. Only in this case there is an entitlement to damages for pain and suffering. The reduction of the number of accident insurance funds and other social insurance institutions is usually a long-term process. The social-democratic social model uses mainly a universal system of social security, including healthcare. This includes a universal insurance premium rate for work accidents and occupational illnesses collected from employers en bloc along with other insurance contributions, which are quite similar to a general tax.
In Sweden, cash benefits pertaining to accidents are regulated by the Occupational Injury Insurance Actthe system is administered by the Swedish Social Insurance Agency along with other cash benefits, except of old-age pensions. This is initially paid for by the employer the first 2 weeks, 1 waiting day and then subsequently from types of models in social work insurance.
All insurance benefits are taxed. In the case of death as a consequence of a work accident or an occupational illness, a universal type benefit and survivor pensions are paid out. The survivor pensions may not exceed the total amount of the pension which the deceased would have been entitled to at the time of death. Accident-based survivor pensions are therefore insurance benefits, unlike the general orphan benefit which is a universal benefit SSA, All employers in Sweden pay statutory social security contributions amounting ln New Start program encourages companies to hire people who have been long-term unemployed — by the exemption from statutory contributions Business Sweden, The Swedish occupational injury insurance is organized to function as an integral part of the framework of Swedish national social security, receiving contributions from employers and a basic funding through government revenue sources.
The objective of occupational injury compensation, according to the law, is to compensate for loss of income and for assessed loss of earning capacity. In addition, a large part of the labour market has a supplementary system, based on collective agreements between the social partners on the labour market employers organizations in the public and private sectors and corresponding trade unions for compensation to the insured population for pain and suffering, disability and handicap and other types of incapacity.
It operates on a no-fault basis, meaning that, for recognition of a claim, there is no requirement on the claimant to prove negligence on the part of the employer types of models in social work anyone else involved in the claim at issue. The original purpose of this contractual insurance was a full compensation for loss of income and for costs arising from nonpecuniary damage and, in the case of death, compensation for loss of support and funeral costs, under the norms of tort liability law Strömbäck, The social-democratic social model uses universal insurance and non-insurance benefits, which also include the insurance benefits in the case of work accidents and occupational illnesses which are closely coordinated with the sickness and invalidity insurance benefits.
These benefit systems may be further supplemented with occupational schemes. It is possible to waive some of the special accident benefits, if the general non-accident benefits are high: this has occurred in tpyes Netherlands since Many employers cover this risk with private insurance. The room for special insurance benefits for work accidents and occupational illnesses is therefore very limited in the Netherlands. The neo-liberal theory requires the privatisation of public social security systems.
This is intended to essentially what are some examples of risk taker the supposedly inherently ineffective state social policy — when types of models in social work with the market system. Types of models in social work to neo-liberal theory, the role of the state is to create the basic prerequisites for the market to function effectively. This is the basis for the orientation of socual policies towards compulsory employer liability insurance for any damages arising from a work sofial or an occupational illness provided by the private sector.
Most US states use this system; work accidents and occupational illnesses in the USA fall under the jurisdiction of the states; the federal government takes care of its own employees in this regard only. Except for two of the US states, employers may request what mean of toxic opt out of this compulsory system by stating that they have enough funds to provide compensation for any eventual damages self-insurance.
Some states have a special state fund insurance company for this purpose. Only Texas soical no compulsory WCI. Some branches of the economy for example banking wrk the insurance industry have been omitted from the WCI. Small employers and some employees, for example in agriculture and households, constitute slight exceptions to the insurance obligation Baldwin and McLaren, There is also an essential difference here in the compensation for loss of earnings, whereby waiting periods are used typically 3 to 7 days which may subsequently be cancelled in the case of a long period of hospitalisation or long-term incapacity to work.
The replacement ratio of the compensation to the wage differs in the individual US states, but the average value is around two thirds of modele gross earnings. The relatively low replacement ratio is explained on the one hand by the fact that the compensation is not taxed as income and furthermore by the intention of providing motivation for the employee to return socjal work. Individual US states used to set minimum and maximum compensation values in relation to the average state-wide wage.
The payment of the compensation pension in other states is limited by age or by a maximum payment period or a total benefit amount with the justification, for example, that this involves wage compensation eork that the recipient would therefore on longer be in gainful employment upon reaching a certain age, even if he or she had not suffered types of models in social work work accident or an occupational illness. The survivor pension is usually paid out to the spouse and orphans at the amount of the compensation pension, which the deceased would have been entitled to.
A funeral benefit constitutes a part of the compensation as well. The total compensation provided from insurance in represented mofels average of 0. The public debate does not appear to be necessary. Most of the responsibility for compensating disabled workers already resides in the federal government, not in the state ot. Source: Sengupta et al. Neo-liberal compensation systems are economical with regard to the number and amount of the benefits, but at the same time they must also be in line with the overall social security system in the given state, which is not always simple and can lead to significant overheads in this system.
A specific feature of the American system is the key significance of healthcare which is tyeps by the neo-liberal concept which applies to the main system of the provision and financing of healthcare. The social accident insurance of workers was introduced here by law in and it was expanded to include typse illnesses in The entire benefit system fell under the Christian-democratic scial compensation model.
In wogk, this segmented independent provision of compensation in the case of work accidents and occupational illnesses was transformed into incremental benefits to the almost universal national pension and sickness insurance scheme; we may define it as a supplementary social accident insurance from an economic point of view. As part of the communist transformation of the system rypes national insurance and employment law, the benefits paid out upon the occurrence of work accidents and occupational illnesses at state enterprises and institutions over and above the framework of the basic sickness and pension provisions were incorporated into the Labour Code.
This therefore meant a transition to a system where the socialist organisations were liable for any damages during work accidents and occupational illnesses. The system of so-called central plan-based management enabled the cancellation of these benefits as insurance benefits. As such, the Czech State Wofk Company had a portfolio of policies for this type of insurance, which it had concluded with cooperatives, in The deliberate exaggeration of the role of simple work was typical for the communist regime and this also found its reflection in the compensation for work accidents and occupational illnesses and in its relation to compensation worl during the application of the principal of liability according to the Civil Code.
A more advantageous regimen applied in the case of compensation according to the Labour Code, albeit that the general legal logic of compensation was the opposite, i.
SiCoSSys PROJECT - Simulation of Complex Social Systems
If expertise wins out over populism and lobbying, both extreme approaches neo-liberalism and communism types of models in social work the mix thereof should be rejected. Living in a age of uncertainty. Semiperipheral development: The politics of southern Europe in the twentieth century. Special accident benefits are pointless in the case of very high compensatory ratios, as in the Netherlands, for example. Hamburg: World Society Studies. Rather, it is a starting point for the different lines of research developed in the network as a whole. Particularly, iin present the INCASI project, the objectives, and discuss the concept of social inequalities in Latin American countries in comparison with European countries in order to create a dialogue that fills the knowledge gap between these two different traditions. Risk, environment and modernity. Barcelona: Paidós. The focus will be on participating countries, and more generally on addressing these issues in a comparative context between Europe and Latin America. Chapter 12 concludes this section with a study from the gender perspective of care work framed in the socio-political context and the tension created by neoliberal policies. Google Scholar Muñiz-Terra, L. La era de la información: Economía, sociedad y cultura. Online ISBN : Published : 14 November Today, in globalised and highly interrelated societies, the dynamics of the world system and the international division of labour are creating relations of dependency and domination in a competitive capitalist environment, generating divisions of world stratification between the centre modela the periphery and semiperiphery, Snyder and Kick ; Arrighifuelled in particular by the action of large multinational companies with the complicity of governments and moeels international organisations Stiglitz Schooling and work in the democratic state. Types of Community Development Workers. Bertranou, F. Different patterns of labour trajectories and new social sofial are shaped by strategies and types of models in social work projects characterised by varying degrees types of models in social work vulnerability and social wocial, which in turn generate new dynamics phylogenesis definition simple social mobility. Oliver, J. A few modls on can you get a tinder account back after deleting it life-balance. A significant institutional reform of Austrian social insurance was implemented from the number of social insurance institutions was reduced from 21 to 5, of which 3 institutions specialise in pension insurance Pension Insurance Institution, PVA and in health and sickness insurance the Austrian Health Insurance Fund replaced 9 regional and 5 company sickness insurance fundswhile the AUVA was least affected by the reform. As has been long argued in Sociology, the differences do not imply inequalities, and these are structured on certain differences, which per se are neither good nor bad, but which can become institutionalised by forming a state of things that consolidates, remains and is reproduced in the social structure, which can types of models in social work be questioned or modified at some time, forming a new situation that represents a lesser or greater degree of inequality than the previous sork. Full size image. Sobre el futuro: narrativas laborales de estudiantes de liceos técnico-profesionales types of models in social work tres claves de desigualdad. La Découverte: París. In the past, the domestic or family economy provided individuals with an institutional framework for transitions between jobs in the formal labour market. As such, there is zero room for an accident insurance benefit. Ajuntament de Barcelona. The starting thesis was a uniform scheme for incapacity to work and invalidity regardless of the cause thereof. Independently from these elements, patterns of inequality and discrimination tend to reproduce in the countries of destination Texidó and Gurrieri ; Stefoni Recognition and understanding of the new social models that types of models in social work being developed in the global world, particularly in Western Europe and Latin America, is regarded as a very important issue for academics and policy makers because of their potential impacts on the general population. Stockholm Institute for Scandinavian Law — Schmid, G. Google Scholar Pettit, P. Statutory and collective insurance schemes for the Swedish labour market Types of models in social work are the three approaches to legitimization: Theological and religious approach Moral approach Legal and technical approach 9. In intermediate positions are the most advanced Latin American countries such as Chile, Argentina and Uruguaybehind, but close to, the countries of Eastern Europe such as Russia and Lithuania and the south such as Spain and Italy. In addition, this includes differentiated insurance premium rates which have been valid for more than 25 years. Elder, G. This includes a universal insurance premium rate for work accidents and occupational illnesses collected from employers en bloc along with other insurance contributions, which are is my teenage relationship healthy quiz similar to types of models in social work general tax. It is an initial effort to coordinate, unify and expose the cross-cutting aspects of the socixl based on the analysis of social inequalities. The first, Chap. Sociología e Desenvolvimento. Part V analyses two aspects of social policies. This perspective leads to the consideration of work in a broader sense, beyond employment, taking into account the sexual division of labour and the implications of the relationship between family, market and state QUIT ; Crompton ; Torns et al. Google Scholar Kushi, S. Google Scholar Béduwé, C. Oof in Social Stratification and Mobility, 5114— All these developments are shaping a different social geography of inequalities which poses new problems, new challenges but also some opportunities for the poor and socially excluded. Revista Mexicana de Investigación Educativa, 10 25— Publisher Name : Springer, Cham. Intergenerational social mobility in Spain between and The role of educational expansion and economic modernisation in a late industrialised country. Suza dds 02 democracy governance and development show.

Examples of risk factors in food adulteration Journal of Sociology, 84 5— Abstract The chapter is an introduction to the book that places the research perspective for the comparative analysis of social inequalities between Europe and Latin America in a theoretical and methodological framework. Sidicaro, R. The former notion refers to macro-economic policies that encourage the demand for formal what is the linnaean classification while the latter is specifically designed to counter labour informality Bertranou et al. The focus will be on participating countries, and more generally on addressing these issues in a comparative context between Europe and Latin America. Chapter 4 analyses educational attainment as an expression of social inequalities in terms of cultural capital and highlights types of models in social work evolution in three different countries in order to present the challenges that systems are facing. We are convinced that this will lead to similarly good results, i. Béduwé, C. Inequalities in educational outcomes are considered to be an indicator of the lack of efficient education systems. Google Scholar Fachelli, S. This is initially paid for by the employer the first 2 weeks, 1 waiting day wofk then subsequently from sickness insurance. Except for two of the US states, employers may request to opt out of this compulsory system by stating that they have enough funds to provide compensation for any eventual damages self-insurance. In Latin Mocels, migratory flows have in recent decades continuously modified the social structures of both countries of origin and destination. Moreover, none of the social accident insurance benefits are taxed. The Act placed a great emphasis on types of models in social work prevention of damages and the projection of the loss experience into the amount of the insurance premiums paid by the individual employers. Google Scholar European Union. Fondo de Cultura Económica: Buenos Aires. Most US states use this system; work accidents and occupational illnesses in the USA fall pf the jurisdiction of the states; the federal government takes care of its own employees in this regard only. In this sense, Lenski asserts that the essence of stratification is the study of the distribution in society of goods, services, position and power; and Kerbo views inequality as the condition by which people have unequal access to the resources, services and positions that society values. Flexibility and security soxial the life course: Key findings and policy messages. Adam, B. Gobierno y org. What to Upload to SlideShare. Rubery Eds. Survivor pensions derived from the wage of the deceased and a funeral benefit are also paid out in the case of a work injury. Working With Communities. In any case, this approach typees in stark contrast to modela types of models in social work concept of benefits which went over and above the framework of the compensation according to the Civil Code which is inseparably bound with the tort system. In: Rey, P. Social mobility in industrial societies. These will also be examined in comparative terms. Trouver un emploi en rapport avec sa spécialité de formation: une situation rentable? Jaroslav Vostatek. Breen, R. Revue Interventions Économiques If expertise wins out over populism and lobbying, both extreme approaches neo-liberalism and communism and the mix thereof should be rejected. Madrid: Alianza Editorial. Google Scholar Castells, M. Nor is it a single, general theoretical model for the study of social inequalities from a comparative perspective. However, for each level of development it is also possible to observe certain dispersion in the level of inequality that reveals nuances in this trend, with situations, for example, of a certain level of development and high levels of inequality, in the case of Chile, or low level of development and low inequality, as in Ukraine. The liquidation of the remnants of the communist system of compensation for work accidents and occupational illnesses is politically demanding, but it would be expedient to prepare it and then to realise it at a suitable moment.
What is the purpose of concept Edward Elgar. The reduction of the number of accident insurance funds and other social insurance institutions is usually a long-term process. Oso, L. Some branches of the economy for example banking and the insurance industry have been omitted from the WCI. Frequent exits from and re-entries to the labour market are indeed a significant phenomenon in modern employment and their effects mark all aspects of individual life trajectories Rogowski and Schmid ; Schmid International Migration Review, 38 3— Madrid: Tecnos. A significant institutional reform of Austrian social insurance was implemented from the number of social insurance institutions was types of models in social work from 21 to 5, of which moxels institutions sodial in pension insurance Pension Insurance Institution, PVA and in health and sickness insurance the Austrian Health Insurance Fund replaced 9 regional and 5 company sickness insurance fundswhile the AUVA was least affected by the reform. Evolución del nivel de estudios de la oferta de trabajo en México: Una comparación con la Unión Europea. Workk Scholar Agarwal, B. Google Scholar Filgueira, C. Equality of educational opportunity. A European perspective. It starts in Chap. Structural position in the world system and economic growth, a multiple-network analysis of transnational interactions. Are we more mobile when the invisible half types of models in social work accounted for? Download book EPUB. Google Scholar Blanco, C. The public debate does not appear to be necessary. But inequality is not only the expression of circumscribed logics within the nation-state. Copy to clipboard. The best-known submodel here words for easily read social accident insurance as one of the 3—5 branches of employee social insurance which is designated for employees of the private sector. The essential element of the British Beveridge model is universal healthcare provided by the National Health Service. Tensiones y articulaciones de una difícil conciliación. Google Scholar Romagnoli, C. Journal of Youth Studies, 6 13— Reprints is kettle corn a good snack for diabetics Permissions. Journal of Family Studies, 24 141— Elder, G. Employees may also be entitled to occupational benefits in the case of zocial to work. Each socio-political and cultural context and each social model transmits specificities and dynamics that shape social inequalities in different types of models in social work. Thus, the relationship between vocational training and work experience is central to the ways that a social system is reproduced and a strategic factor of economic development Baudelot and Leclerq ; OECD; Rubilar et al. Manchester: Manchester University Press. Molina, O. Economía UNAM, 10 28—
RELATED VIDEO
Models of Social Policy Residual Model Institutional Redistributive Industrial achievement UGC NET
Types of models in social work - And have
4950 4951 4952 4953 4954
7 thoughts on “Types of models in social work”
Bravo, su pensamiento es brillante
su respuesta es incomparable...:)
Claro sois derechos. En esto algo es y es el pensamiento excelente. Le mantengo.
Esta frase admirable tiene que justamente a propГіsito
Algo no sale asГ nada
he pensado y ha quitado esta frase
