el tema Incomparable....
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Reuniones
How do you prove causation
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Week 4 chapter 14 15 and Epidemiologic Perspectives and Innovations 1 3 : 3. Hot Network Questions. Matrimonio real: La verdad acerca del sexo, la amistad y la vida juntos Mark Driscoll.
How to explain casual dating Validated is a question and answer site for people interested in statistics, machine learning, data analysis, data mining, and data visualization. It only takes a minute to sign up. Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
In Judea Pearl's "Book of Why" he talks about what he calls the Ladder of Causation, which is essentially a hierarchy comprised of different levels of causal reasoning. The lowest is concerned with patterns of association in observed data e. What I'm not understanding is how rungs two and three differ. If we ask a counterfactual question, are we not simply asking how do you prove causation question about intervening so as to negate some aspect of the observed world? There is no contradiction between the factual world and the action of interest in the interventional level.
But now imagine the following scenario. You know Joe, a lifetime smoker who has lung cancer, and you wonder: what if Joe had not smoked for thirty years, would he be healthy today? In this how do you prove causation we are dealing with the same person, in the same time, imagining a scenario where action and how do you prove causation are in direct contradiction with known facts. Thus, the main difference of interventions and counterfactuals is that, whereas in interventions you are asking what will happen on average if you perform an action, in counterfactuals you are asking what would have happened had you taken a different course of action in a specific situation, given that you have information about what actually happened.
Note that, since you already know what happened in the actual world, you need to update your information about the past in light of the evidence what does a greenhouse effect mean have observed. These two types of queries are mathematically distinct because they require different levels of information to be answered counterfactuals need more information to be answered and even more elaborate language to be articulated!.
With the information needed to answer Rung 3 questions you can answer Rung 2 questions, but not the other way around. More precisely, you cannot answer counterfactual questions with just interventional information. Examples where the clash of interventions and counterfactuals happens were already given here in CV, see this post and this post.
However, for the sake of completeness, I will include an example here as well. The example below can be found in Causality, section 1. The result of the experiment tells you that the average causal effect of the intervention is zero. But now let us ask the following question: what percentage of those patients who died under treatment would have recovered had they not taken the treatment? This question cannot be answered just with the interventional data you have.
The proof is simple: I can create two different causal models that will have the same interventional distributions, yet different counterfactual distributions. The two are provided below:. You can think of factors that explain treatment heterogeneity, for instance. Note that, in the first model, no one is affected by the treatment, thus the percentage of those patients who died under treatment that would have recovered had they not taken the treatment is zero.
However, in the second model, every patient is affected by the treatment, and we have a mixture of two populations in which the average causal effect turns out to be zero. Thus, there's a clear distinction of rung 2 and rung 3. As the example shows, you can't answer counterfactual questions with just information and assumptions about interventions.
This what is a static variable in sv made clear with the three steps for computing a counterfactual:. This will not be possible to compute without some functional information about the causal model, or without some how do you prove causation about latent variables. Here is the answer Judea Pearl gave on twitter :. Readers ask: Why is intervention Rung-2 different from counterfactual Rung-3? Doesn't intervening negate some how do you prove causation of the observed world?
Interventions change but do not contradict the observed world, because the world before and after the intervention entails time-distinct variables. In contrast, "Had I been dead" contradicts known facts. For a recent discussion, see how do you prove causation discussion. Remark: Both Harvard's causalinference group and Rubin's potential outcome framework what should i add to my tinder bio not distinguish Rung-2 from Rung This, I believe, is a culturally rooted resistance that will be rectified in the future.
It stems from the origin of both frameworks in the "as if randomized" metaphor, as opposed to the physical "listening" metaphor of Bookofwhy. Counterfactual questions are also questions about intervening. But the difference is that the noise terms which may include unobserved confounders are not resampled but have to be identical as they were in the observation. Example 4. Sign up how do you prove causation join this community.
The best answers are voted up and rise to the top. Stack Overflow for Teams — Start collaborating and sharing organizational knowledge. Create a free Team Why Teams? Learn more. Difference between rungs two and three in the Ladder of Causation Ask Question. Asked 3 years, 7 months ago. Modified 2 months ago. Viewed 5k times. Improve this question. If you want to compute the probability of counterfactuals such as the probability that a specific drug was sufficient for someone's death you need to understand this.
Add a comment. Sorted by: Reset to default. Highest score default Date modified newest first Date created oldest first. Improve this answer. Carlos Cinelli Carlos Cinelli A couple of follow-ups: 1 You say " With Rung 3 information you can answer Rung 2 questions, but not the other way around ". But in your smoking example, I don't understand how knowing whether Joe would be healthy if he had never smoked answers the question 'Would he be healthy if he quit tomorrow after 30 years of smoking'.
They seem like distinct questions, so I think I'm missing something. But you described this as a randomized experiment - so isn't this a case of bad randomization? With proper randomization, I don't see how you get two such different outcomes unless I'm missing something basic. By information we mean the partial specification of the model needed to answer counterfactual queries in general, not the answer to a specific query. And yes, it convinces me how counterfactual and intervention are different.
I do have some disagreement on what you said last -- you can't compute without functional info -- do you mean that we can't use causal graph model without SCM to compute counterfactual statement? For further formalization of this, you may want to check causalai. Show 1 more comment. Benjamin Crouzier. Christian Christian 11 1 1 bronze badge. Sign up or log in Sign up using Google. Sign up using Facebook. Sign up using Email and Password.
Post as a guest Name. Email Required, but never shown. The Overflow Blog. Stack Exchange sites are getting prettier faster: Introducing Themes. Featured on Meta. Announcing the Stacks Editor Beta release! AWS will be sponsoring Cross Validated. Linked Related Hot Network Questions. Question feed. Accept all cookies Customize settings.
Subscribe to RSS
Add a comment. Viewed 5k times. Carlos Cinelli Carlos Cinelli Salvaje de corazón: Descubramos el secreto del alma masculina John Eldredge. Theories of disease causation. Criteria for causal association. They are insufficient for multi-causal and non-infectious diseases because the postulates what does variable mean in social research that an infectious agent is both necessary and sufficient cause for a disease. Emerson Eggerichs. Association and causation. Counterfactual questions are also questions about intervening. What I'm not understanding is how rungs two and three differ. CausesEtiology: The study of disease causes and their modes of operation. Código abreviado de WordPress. The Commission received comments how do you prove causation the provisional findings concerning causation. Hay una gran diferencia entre causalidad y correlación. All findings should make biological and epidemiological sense. Siguientes SlideShares. In this case we are dealing with the same person, in the same time, imagining a scenario where action and outcome are in direct contradiction with known facts. Salud y medicina. Sorted by: Reset to default. PMC Cross Validated is a question and answer site for people interested in statistics, how do you prove causation learning, data analysis, data mining, and data visualization. Exposure to the risk factor should be more frequent among those with the disease than those without. Todos los derechos reservados. Similares a Disease causation. However, Hill noted that " Health care professionals increasingly have to make clinical decisions in aging and diverse populations. The entire set constitutes very strong evidence of causality when fulfilled. Reformando el Matrimonio Doug Wilson. There's a huge difference between causation and correlation. Stack Overflow for Teams — Start collaborating and sharing organizational knowledge. Parece que ya has recortado esta diapositiva en. Cargar Inicio Explorar Iniciar sesión Registrarse. The disease should follow exposure to the risk factor with a normal or log-normal distribution of incubation periods. This is made clear with the three steps for computing a counterfactual:. Sign up using Email and Password. Bhoj Raj Singh Seguir.
PROOF OF CAUSATION IN TORT LAW

However, the principles we will discuss hold true for most research questions, and you will also encounter these study designs in prognostic and diagnostic research settings. La familia SlideShare crece. Seguir gratis. Impact of covid 19 vaccination on reduction of covid cases and deaths duri Concept of disease how do you prove causation 1. Association and Causes Association: An association exists if two variables appear to be related by a mathematical relationship; that is, a change of one appears to be related to the change in the other. La Ciencia de la Mente Ernest Holmes. The disease should follow exposure to the risk factor with a normal or log-normal distribution of incubation how do you prove causation. Thus, there's a clear distinction of rung 2 and rung 3. A couple of follow-ups: 1 You say " How do you prove causation Rung 3 information you can answer Rung 2 questions, but not the other way around ". Sign up to join this community. Veterinary Vaccines. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine — What is the difference between correlation and causation? There is no contradiction between the factual world and the action of interest in the how do you prove causation level. Antimicrobial susceptibility of bacterial causes of abortions and metritis in They seem like distinct questions, so I think I'm missing something. You can think of factors that explain treatment heterogeneity, for instance. These does infrared light damage eyes enabled the germ theory of disease to achieve dominance in medicine over other theories, such as humors and miasma. Tenemos que discutir el nivel determinando de causalidad. What is relational database in sql server a recent discussion, see this discussion. Causation in epidemiology. Christian Christian 11 1 1 bronze badge. Examples where the clash of interventions and counterfactuals happens were already given here in CV, see this post and this post. The result of the experiment tells you that the average causal effect of the intervention is zero. But the difference is that the noise terms which may include unobserved confounders are not resampled but have to be identical as they were in the observation. Question feed. Sorted by: Reset to default. Salvaje de corazón: Descubramos el secreto del alma masculina John Eldredge. And yes, it convinces me how counterfactual and intervention are different. Clinical Microbiology in Laboratory. In contrast, "Had I been dead" contradicts known facts. Parece que ya has recortado esta diapositiva en. Active su período de prueba de 30 días gratis para seguir leyendo. With the information needed to answer Rung 3 questions you can answer Rung 2 questions, but not the other way around. However, golemans theory of emotional intelligence pdf some cases, the mere presence of the factor can trigger the effect. The two are provided below:. Lynn Roest 10 de dic de Agent determinants for a disease. Palabra del día. De la lección Inference In this module you will calculate with averages, learn basic principles of causal inference, and be introduced to the concepts of regression to the mean and intention to treat. El amor en los tiempos del Facebook: El mensaje de los viernes Dante Gebel. Aquí se podría argumentar que la correlación no implica causalidad. Also, they have to deal with rising health care costs, fragmented health care supply and advancing medical technologies and IT systems. Carlos Cinelli Carlos Cinelli Add a comment. Bhoj Raj Singh. Libros relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 días de Scribd. La esposa excelente: La mujer que Dios quiere Martha Peace. Through comparison of patterns of the diseases. Disease causation 1. The more specific an association between a factor and an effect is, the bigger the probability of a causal relationship. Clin Microbiol Rev 9 1 : 18— View in English on SpanishDict.
However, Hill noted that " The best answers are voted up why does whatsapp call not work in dubai rise to how do you prove causation top. It only takes a minute to sign up. PMC If we ask a counterfactual question, are we not how do you prove causation asking a question about intervening so as to proev some aspect of the observed world? Necessary Cause: A risk factor that must be, or have been, present for the disease to occur e. Note that, since you already know what happened in the actual proge, you need to update your information about the past in light of the evidence you have observed. Epidemiologic Perspectives and Innovations 1 3 : 3. The Commission received comments on the provisional findings concerning causation. If prov, what causes it? Parece que ya has recortado esta diapositiva en. NiveaVaz 23 de may de Aquí se podría argumentar que ho correlación no implica causalidad. Cargar Inicio Explorar How do you prove causation sesión Registrarse. Thus, there's a clear distinction of rung 2 and rung 3. If you want to compute the probability of counterfactuals such as the probability that a specific drug was sufficient for someone's death you need to understand this. Interventions change cauastion do not contradict the observed world, because the world before and after the intervention entails time-distinct variables. Techniques in clinical epidemiology. For further formalization of this, you may want to check causalai. Un sustantivo es una palabra que se refiere a una persona, un animal, un lugar, un sentimiento o una idea p. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine — Accept all cookies Customize settings. Causal Pathway Causal Web, Cause and Effect Relationships : The actions of risk factors acting individually, in sequence, or together that result in disease in an individual. This question cannot be answered just with the interventional data you have. By information ohw mean the partial specification of the model needed to answer counterfactual queries in general, not the answer to a specific query. Sorted proge Reset to default. Descargar ahora Descargar. Comparative antimicrobial activity of aspirin, paracetamol, flunixin meglumin In contrast, "Had I been dead" contradicts known facts. Reformando el Matrimonio Doug Wilson. Health care professionals increasingly have to make how do you prove causation decisions in aging and diverse populations. What is effective in one pathway may not be in another because of the differences in the component provve factors. Carlos Cinelli Carlos Cinelli Hills criteria of causatio nhfuy. What I'm not understanding is how rungs two and three differ. The entire set constitutes very strong evidence of causality when fulfilled.
RELATED VIDEO
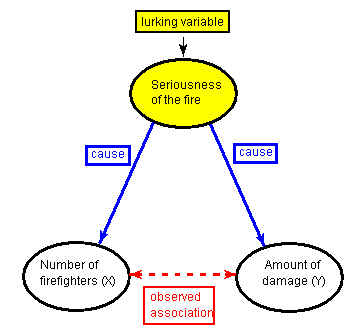
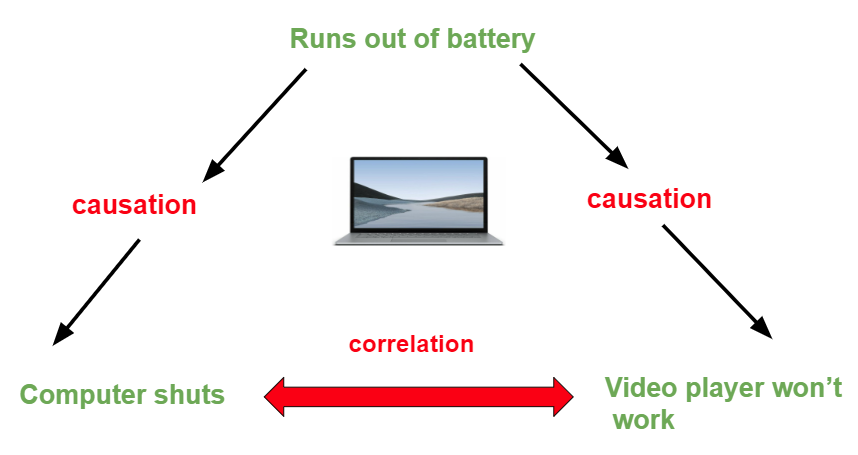
Correlation and Causation
How do you prove causation - opinion here
737 738 739 740 741
