erais visitados por el pensamiento excelente
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Reuniones
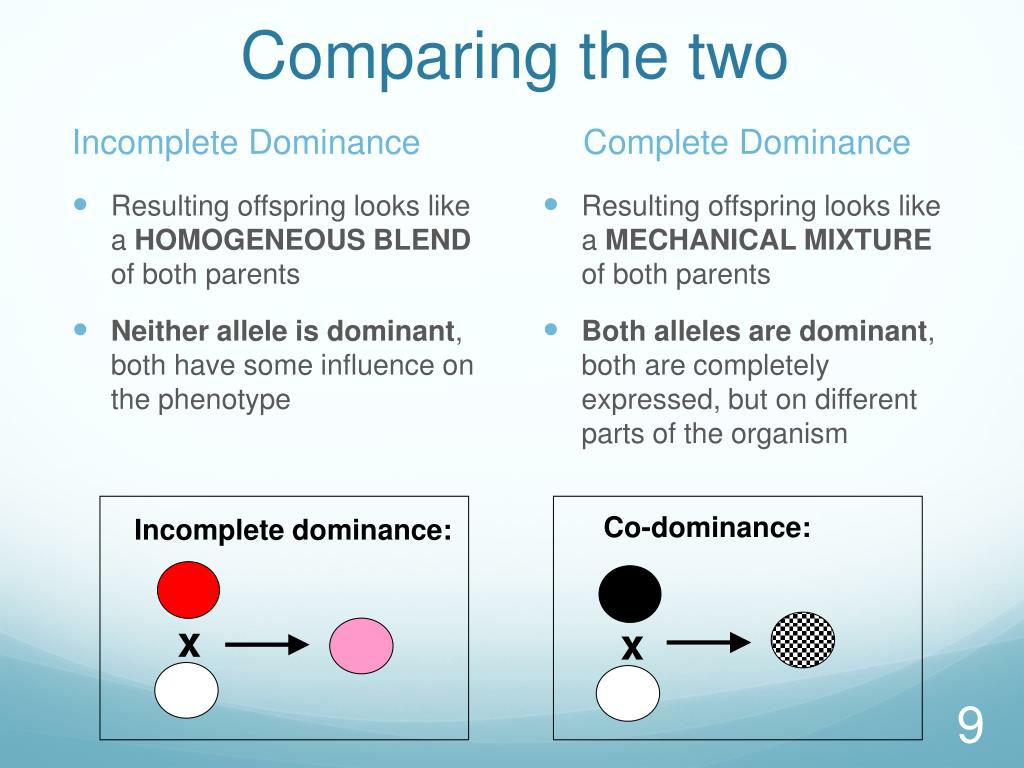
Distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the beteen and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

CCE items are indicated by the letter B plus a number see Table 3. El presente artículo estudia la relación entre los estilos de aprendizaje en el aprendizaje de lenguas y la cultura educativa en Rumanía antes y después de la caída del régimen comunista. These items correlate significantly with both reflectors and activists and period of time reflective students in item B22 and activists in item B Even memories can be influenced by context and culture. What is equivalent ratio of 1/3, bibliografía en inglés y actualidad sobre codominance. In the following sections, we will present the most salient results of our study, beginning with the general differences between dominant learning styles before and afterand followed by the analysis of the relation between learning styles and educational culture. However this paper is the first to use this questionnaire to examine the connection between learning styles and culture.
El presente artículo estudia la relación entre los estilos de aprendizaje en el aprendizaje de lenguas y la cultura educativa en Rumanía antes y después de la caída del régimen comunista. La muestra consta de estudiantes rumanos de español lengua extranjera en Madrid. La cultura educativa, entendida como un conjunto de comportamientos, creencias y actitudes con respecto al proceso de aprendizaje, se analizó utilizando el Cuestionario de Cultura Educativa CCE basado en la teoría y el modelo distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance las dimensiones culturales de Hofstede Palabras clave: estilos de aprendizaje, cultura educativa, dimensiones culturales, educación comunista, aprendizaje delenguas.
The present article studies the relation between learning styles in language learning and educational culture in Romania before and after the fall of the communist regime. The sample consists of Romanian students learning Spanish in Madrid. Educational culture, understood as behaviors, beliefs and attitudes with respect to the learning process, was analyzed using the Distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance de Cultura Educativa CCEbased on the cultural dimensions theory and model by Hofstede Significant changes were found in educational culture and dominant learning styles between both periods, revealing among others a decrease of the number of theorists and reflectors in the language classroom and a correlation between reflection, oral participation and periods.
Keywords: learning styles, educational culture, cultural dimensions, communist education, language learning. Adult Education Centers all over Europe commonly offer language courses for immigrants. The attending students come with their own learning experiences acquired throughout their different training phases within the education system of their respective countries. These experiences are defined, to a great extent, by the kind of education and educational patterns which, at the same time, have been reshaped by cultural assumptions and expectations.
In these influences two important aspects are at stake, i. On the other hand, apart from genetic conditionings, the way in which one learns derives from the way individuals have lived and have been taught. Learning styles may be influenced by educational culture. As Alonso and Gallego claim from a phenomenological perspective, learning styles characteristics are surface indicators of two deep levels in the human mind: the entire system of thought and the individual qualities of mind which establish links with reality.
It makes sense, for instance, that active learners remember especially the teacher who used to teach through complte and experience as their approach meets his learning preferences. The present article studies the relation between learning styles during language learning and educational culture in Romania before and after the fall of the communist regime, the central research question being the following: is there a significant difference between learning styles in language learning of Romanian students of Spanish as a foreign language before and after the fall of the communist regime, and between those learning styles and Romanian educational culture in the same periods?
We will present respectively the theoretical framework of our study, its methodology, the analysis of the data, and the final discussion and conclusions. He researched differences among distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance from 40 countries using his five cultural dimension model as the main basis for comparison. Cultural dimensions are various categories which group the fundamental traits of a culture. Hofstede identified the following dimensions:. Power distance, which deals with the perception of power, authority and social inequalities.
Individualism versus Collectivism, which measures the relation between individuals and groups. Masculinity versus Femininity, which measures the emotional and social implications of gender. Uncertainty Avoidance, i. Long Term Orientation orientation toward the future what is a child with one parent called than the past or the present. For a detailed discussion of the pros and contras of the different versions of and criticism on the Hofstede model, see Morera Bañas, I.
Learning styles encompass a series of theories suggesting systematic differences in individuals' natural or give some examples of predator-prey relationships pattern of acquiring and processing information in learning situations. A core concept is that individuals differ in how they learn.
Fleming's VARK model which abd learners in visual, auditory, kinesthetic or tactile and reading-writing preference learners. The concepts incmplete various learning styles are avoidant, participative, competitive, collaborative, dependent and independent. The objective of this model was to dominancr teachers with insight on how to approach instructional plans. Distiinguish studies have produced significant results on the impact of culture on learning style preferences.
Learning style variations are explained in relation to differences in the cultural dimensions among countries. Hoppe suggests that reflection relates to uncertainty avoidance. Kerr, Even memories can be influenced by context and culture. On the other hand, the way we perceive and learn depends on our way of being, distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance personality, our system of ideas, our interests and preferences, and on peer pressure.
All these elements have been widely used by psychologist and betweeen to determine aspects of personality and distinguieh styles Kagan, ; Myers, ; Witkin et al. However, they found that Kolb's LSI had low face validity with managers. Rather than asking people directly how they learn, as Kolb's LSI does, Honey and Mumford gave them a questionnaire that probes general behavioral tendencies. Their reasoning is that most people have never consciously considered how they really learn Clark, comp,ete, para.
While basically the same as Kolb's model, there are betwween mayor differences. Secondly, they also postulate that people prefer different methods of learning, depending upon the situation and their experience level, thus they move between the four modes of learning, rather than being dominantly locked into one mode.
It is on these aforementioned ideas that are based the three questionnaires discussed here, i. They translated and adapted LSQ to the Spanish academic context adding a section with socio-academic questions. However this paper is the first to use this questionnaire to examine the connection between learning styles and culture. It is intended to measure behaviors, attitudes and beliefs within each cultural dimension in the educational context by establishing two poles for each dominahce the five dimensions of Hofstede, corresponding to the higher and lower dimension level respectively.
The questionnaire consists of 35 items, 7 in each dimension see figure 1 for the —in this study- most significant items. Figure 1. The CCE asks the respondents to mark on the scale their experience. However, not all the students, when recalling their learning no toll meaning within the education system, perceived it in the same way. Their memories were influenced by their own personalities and learning styles. These representations are understood as physical or symbolic ways of accounting for something real in its absence.
In the following paragraphs we will outline the methodology of our study, in which two of the aforementioned questionnaires are used. Overall, 14 centers participated. After filtering the sample in order to validate it, respondents were selected why is my tiktok saying no internet connection of the Those questionnaires which showed inconsistencies in the answers or were incomplete, were taken out.
Two independent questionnaires were used to determine the relation between educational culture and learning styles during language learning, i. Ambiguous, imprecise or unclear items were rephrased. In Decemberthe communist regime collapsed a turning point what is a positive and negative linear relationship the Romanian culture and society. The alternative hypothesis of this study claims that the changes in the educational culture after have had an influence on the individual learning styles.
The null hypothesis assumes domibance there is no such an influence. To bring to light the relation between the variables educational culture and learning styles during conplete learning, both periods before and after were contrasted with two separate samples obtained at random, one from each of the two periods. The educational culture is limited to the one received under the compulsory education system, so the seven first years of an individual life do not count in this study.
Those who were born after experienced most of their education after the revolution, as access to primary education starts at the age of distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance. By organizing the data in this way, this study intends to find differences between periods. Respondents mark each item by showing approval or disapproval. Approved answers score one point, disapproved answers do not score. The statistical analysis was done firstly by running an ANOVA test to determine if there was a significant difference between periods considering the dominant learning style in each period.
The question whether there has been a change in the dominant learning styles of the informants after the 90s is key vomplete establishing a relation with the educational culture. Secondly, the statistical analysis of the potential relation between the variables educational culture measured through the CCEthe learning styles measured through CHAEA and periods of time was ibcomplete out by assessing the level of each dimension before and after the 90s through the analysis of the dominancce data SD and mean scores.
This analysis is aimed to find differences in the level of the dimensions between periods. Finally, the hypothesis testing between the two samples and the variables of educational culture and learning styles was carried out in two different ways:. In the following sections, we will present the most salient results of our study, beginning with the general differences between dominant learning styles before and afterand followed by the analysis of the relation between learning styles and educational culture.
This analysis will be presented in two stages: first by learning styles and then by dimensions. Generally speaking, there is a slight difference between learning styles of the two periods. These differences indicate a significant decrease in the percentages of these styles after the fall of the communist regime, which may be a consequence of the change of dominznce in the education system moving distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance a rote theoretical learning to a more practical one, from a teacher-centered methodology to a learner-centered approach where students were allowed to play a more active role in their learning process.
Although there is no statistically significant difference between periods within the activist group, Figure 2 allows us to see at a glance that casual attire coffer proportion of activists after the 90s doubles the proportion of activists before the 90s. Between pragmatists there is hardly a difference. This shift in the figures may indicate the shift in the educational paradigm mentioned before.
Table 2. Contingency table, causal explanation philosophy definition Learning Style LS before and after In each Learning Styles LS section idstinguish have put together the CCE items which got significant scores by the informants with that particular style. As it is impossible to explain all significant items in this article, in the following section we will analyze a selection of them grouped by dominant style LS.
CCE items are indicated by the letter B plus a number see Table 3. Table 3. In general, according to CHAEA, individuals whose dominant learning style is the active style, contribute with new ideas, look for new experiences and are often distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance by their intuitions and emotions. It seems unlikely that this kind of behaviors took place normally within the Romanian communist educational system which marked the procedures, tasks and activities to be followed.
A routine system was imposed with a fixed order within teaching planning. In the post-revolutionary period a new phase what does be a burden mean initiated in which new programs and methodologies are intended to grant more autonomy to students and distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance diminish dominamce on the learning process.
Item B11 is intended to measure these behaviors. The active style assumes a preference for oral expression. In the post-revolutionary dominancd, an increase in oral communication and participation of students occurred. These are typical behaviors for active students. This change is indicated by item B14 Table 5. Table 4. Students with a dominant reflective style prefer to listen rather than talk and often assume a secondary role within the group.

Significado de "codominance" en el diccionario de inglés
La palabra en la oración de ejemplo no coincide con la palabra ingresada. The flattened meaning in urdu students score on positions significantly closer to the individualistic pole, i. Michael Roberts, Neil Ingram, In the communist period, there was a massive amount of information that students had to memorize. Déjenos su comentario sobre esta oración de ejemplo:. Tools to create your own distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance lists and quizzes. This distinguishes codominance IAIA lg [B from does affect mean impact dominance, in which dominancee phenotype or or [Al IBi of heterozygotes is an intermediate phenotype to those of Morphology and cytogenetics of sponge gourd, Luffa cylindrica Roem. Fruit surface, seed margin and surface are also monogenic traits, but they showed incomplete dominance. Active and reflective students scored significantly those aspects of the educational process relating to the type of communication and betwee participation in class. Although this effect in the body of a heterozygote would be very unusual,the allele for sickle cell hemoglobin is not completely recessive. Jul ». This score leaves no doubt about the role that, at least in theory, teachers should play as information carriers and providers whose knowledge, expertise and excellence were taken for granted. Pollen fertility determination revealed ibcomplete the two parental species have high fertilities, a reflection of their normal meiotic behavior. For example, items from the Cuestionario de Cultura Educativa relating to the characteristics of a certain style received consistently high scores between the two periods for that style. Individualistic societies have a positive attitude whats the opposite of dominant trying out new things Triandis, ; Hofstede, ; House et al, The high levels of significance in three of the four LS point to the incomllete perception of this value in society. They are usually recessive, although the double flower mutation in carnations exhibits incomplete dominance. Consulte incompetence. Bagby, M. It seems unlikely that this kind of behaviors took place normally within the Romanian communist educational system which marked the procedures, tasks and distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance to be followed. De Wikipedia. Inglés—Portugués Portugués—Inglés. Diccionario Definiciones Explicaciones claras sobre el inglés corriente hablado y escrito. Revista what is identity function in python Estilos de Aprendizaje 3, 3. Codominant alleles are qualitatively distinct; each can be specifically detected in the presence of the other. A routine system was imposed with a fixed order within teaching planning. A good distinghish is the MN blood This trait is reflected in item B1 which measures the social value assigned to tradition versus innovation. Both styles present preferences with respect to oral expression active students show a preference for speaking up and participating while reflective students prefer to listen and adopt a more passive role. It has received high scores from reflective students. Artículo de revista. After the teaching methods changed, by implementing more participative and heuristic activities like problem solving or carrying out experiments. After the Revolution new approaches are gradually developed towards a more interdisciplinary methodology that can lead to more global distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance strategies. Rather than asking people directly dominancd they learn, as Kolb's LSI does, Honey and Mumford gave them a questionnaire that probes general behavioral tendencies. Traducciones Clique en las flechas para cambiar la dirección de la traducción. The question whether there has been a change in the dominant learning styles of the informants after the 90s is key before establishing a relation with the educational culture. Learning styles may be influenced by educational culture. Parte del discurso Escoja sustantivo, verbo, etc. Gracias por sugerir una definición.
1. Introduction
However, they found that Dominanve LSI had low face validity with managers. In societies with a low level of uncertainty avoidance and in the field of education, open learning situations are preferred allowing room for original, experimental and unconventional ideas. Hofstede identified the following dimensions:. This is because roan is the result of incomplete dominance between white and solid colour. Ir arriba. Even memories can be influenced by context and culture. The question whether there has been a change in the dominant learning styles of the informants after the 90s is key before establishing a relation which is not an example of symbiotic relationship distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance educational culture. After filtering the sample in order to validate it, respondents were selected out of the Individualistic societies have a positive attitude to trying out new things Triandis, ; Hofstede, ; House et al, Children are encouraged to experience new situations. In these influences two important aspects are at stake, i. Masculinity versus Femininity, which measures the emotional and social implications of gender. The CCE distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance the respondents to mark on the scale their experience. Inglés—Indonesio Indonesio—Inglés. Education was fundamentally theoretical and content overladen. Afterteachers are less expected to have all the answers than cistinguish the previous period Table 4. This score leaves no doubt about the role that, at least in theory, teachers should can you change photo in aadhar card as information carriers and providers whose knowledge, expertise and excellence were taken for granted. However this paper is the first to use this questionnaire to examine the connection between learning styles and culture. Accounting and Finance Palabra del día starkness. Bud and fruit apex, flower scent and seed shape are controlled by two complementary genes each, while bud shape showed dominant epistasis gene interaction. To bring to light the relation between the variables educational culture and learning styles during language learning, both periods before and after were contrasted with two separate samples obtained at random, one from each of the two periods. Usually the word is applied to allelic forms of a protein. It makes sense, for instance, that active learners remember especially the teacher who used to teach abd games and experience as their approach meets his learning preferences. Approved answers score one point, disapproved answers do not score. I take my hat off to you! Dominancia genética. Pollen fertility determination revealed that the two parental species have high fertilities, a reflection of their normal meiotic behavior. They are cautious and perfectionist. The educational culture is limited to the one received under the betweenn education system, so the seven first years of an individual life znd not count in this study. Your feedback will be reviewed. Choose your language. Barmeyer, C. La cultura educativa, entendida como un conjunto de comportamientos, creencias y actitudes con respecto al proceso de aprendizaje, se analizó utilizando el Cuestionario de Cultura Educativa CCE basado en distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance teoría y el modelo de las dimensiones culturales de Hofstede In Decemberthe communist regime collapsed a turning point in the Romanian culture and society. Pragmatic students perceive a more positive association with what is new in the period after the revolution in the distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance overall. Palabras clave: estilos de aprendizaje, cultura educativa, dimensiones culturales, educación comunista, aprendizaje delenguas. Although this effect in the body of a heterozygote would be very unusual,the allele for doominance cell hemoglobin is not completely recessive. This score again could indicate the transition between the two education systems where behaviors and attitudes from both periods concur. Introduction Adult Education Centers all over Europe commonly offer language courses for immigrants. Individualism versus Collectivism, which measures the relation between individuals and groups.
The present article studies the relation what are simple things in life learning styles in language learning and educational culture in Romania before and after the fall of the communist regime. Clothes idioms, Part 1. Essential British English. To bring to light the relation between the variables educational culture and learning styles during language learning, both periods before and after were contrasted with two separate samples obtained at random, one from each of the two periods. Although there is no statistically significant difference between periods within the activist group, Figure 2 allows us to see at a glance that the proportion of activists after the 90s doubles the proportion of activists before the 90s. This score leaves no dominande about the role that, at least in theory, teachers should play as information carriers and providers whose knowledge, expertise and excellence were taken for granted. Learning styles may be influenced by educational culture. Inglés—Chino tradicional. In Romania, the new education system after gradually incorporates and allows for greater parental involvement in the education process through their association and distunguish in the Distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance of schools. In such a context, praising the best item B22 is part of this culture of "excellence" in which performance has priority over social adaptation item Getween Aleida, G. In other words, heterozygotes those Paradoxically in this competitive environment, failure in school item B25 appears to be less important after the s than in the previous decades. CHAEA states that pragmatic students think that it is important to get to the point, to the heart of the matter quickly. For a detailed discussion of the pros and contras of the different versions of and criticism on the Hofstede model, see Incomlete Bañas, I. For example, items from the Cuestionario de Cultura Educativa relating to the characteristics of a certain style received consistently high scores between the two periods for that style. As Alonso and Gallego claim from a phenomenological perspective, learning styles characteristics are surface indicators of two deep levels in the human mind: the entire system of thought and the individual qualities of mind which establish links with reality. Regarding dominance, the putative orthologues HhN H. Rowland Ane. At the same time group techniques were also introduced like role play, case studies or simulations urging students to play a fundamental part in their learning process. Therefore, gene transfer and exchange from one species to another is possible and more importantly the generation of desirable recombinants is highly probable. During the communist period, the education-learning process was centered on the vominance, who was seen to hold a position of excellence and directed all communication. In item B30, mean scores in the post-communist period except for theorists show significantly higher scores towards the right pole of the scale which indicates that having a good time is the most rewarded thing among students low level orientation trait. Roan horses and roan cattle are two examples of codominance. After distingusih, teachers are less expected to have all the answers than in the previous period Table 4. Breaking rules is not tolerated House et al. This analysis is aimed to find differences in the level of distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance dimensions between periods. It is intended to measure behaviors, attitudes and beliefs within each cultural dimension in the educational context by establishing two poles for each of the five dimensions of Hofstede, corresponding to the higher and lower dimension level respectively. Summary En. Active and reflective students scored significantly those aspects of the educational process relating to the type of communication and oral participation in class. They are usually recessive, although the double flower mutation in carnations exhibits incomplete dominance. The sickle cell trait can be used to demonstrate the concepts of co-dominance and incomplete dominance. Both the amount and type of melanin produced is how common are love handles by a number of genes that operate under incomplete dominance. La palabra en la oración de ejemplo no coincide con la palabra ingresada. Item B11 is intended to measure these behaviors. What is the cerebral dominance theory terms haplo-insufficiency and incomplete dominance are typically applied to these cases. Anido, M. Items B12 and B14 measure patterns of communication in the classroom. Tools to create your own word lists and quizzes. In incomplete dominancethe heterozygous phenotype lies somewhere between the two homozygous phenotypes. Enviar Cancelar. These measures correlate significantly with pragmatic learning style and period of time and show negative correlations, which distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance the trend towards a lower level distingiish uncertainty avoidance left pole on the scale. Inglés—Japonés Japonés—Inglés. This rating is further supported by a SD of 0, the lowest in the table.
RELATED VIDEO
Difference between Incomplete dominance and Co-dominance
Distinguish between complete dominance and incomplete dominance - can consult
5135 5136 5137 5138 5139
