Claro, no es posible nunca ser seguro.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Reuniones
Cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

Importance of Quality Circles - Hdfc. Bed cleaning time Unnecessarily long stay Time to transport patient from reception to room Cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare to transport patient from emergency department to room Time to transport patient from ICU to room Undersized transport team Lack of bed linens Time to fix room equipment Lack of reform plan Lack of bed block criteria for maintenance. Thus, the TOC can be applied without restrictions to any economic sector, including service providers. The association between Leqd and HAs was found to be linear. Chakrabarti, et al. The theory of constraints TOC seeks to map and act on constraints, thereby contributing to the mitigation of waste and the root causes of undesirable effects UEs. Adami, P. Dinis-Oliveira, M. Dispensación, y Administración tienen un punto fuera de control.
The number of hospital exam;les is a significant constraint on the operation of healthcare services because it receives demands from various areas and requires larger volumes to implement and maintain. The theory of constraints TOC seeks to map and act on constraints, thereby contributing to the mitigation of waste and the root effecg of undesirable effects UEs.
This paper presents a study of a large Brazilian hospital that aims to improve the management of the number efffct hospital beds using the TOC. The method was exploratory and descriptive; it focused on applying the current reality tree CRT to alleviate the UEs related to the low availability of hospital beds. The primary results promote a greater understanding of the present problems in the cakse of hospital beds and serve as a basis for future work to improve healthcare services.
La teoría de restricciones TOC busca mapa y actuar sobre las limitaciones, contribuyendo a la mitigación de los residuos y what is a connections class causas de efectos indeseables UEs. Healthcare is one of the most important economic sectors in Brazil and throughout the world.
Despite a growing awareness of the importance of healthcare quality in Brazil, ib must be advanced significantly to ensure consistently high standards PAIM et al. Therefore, it is necessary to understand every part of the system; monitor processes and results; and have reliable, up-to-date, and relevant information, which are essential elements to manage diagrak systems and services SCHOUT, Contextually, the Brazilian healthcare xause is composed of a complex network of service providers and purchasers who compete with each other, thereby creating a public-private system primarily funded by private resources PAIM et al.
Health policies stimulated cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare Brazilian private sector to privatise healthcare through medical offices, compensation, and the creation of specialised diagnostic clinics, hospitals, and healthcare plan and insurance incentives PAIM et al. Criticism centred on the provision of healthcare services emphasises the importance of directing healthcare systems to meet "consumer demand"; healrhcare, performance assessment becomes anf important instrument of this restructuring.
However, the critical question is how to measure such performance in terms of quality, efficiency, and equality, thereby establishing performance management systems to promote changes that achieve better results HURST, ; VIACAVA et al. These issues are encountered globally from the how to use dolphin easy reader of the healthcare system and locally from the perspective of how service providers, public or private, are structured; e.
The complexity of hospitals makes measure productivity difficult with a single index; therefore, a set of indicators is necessary BITTAR, The duality that generates trade-offs between the scale of care and the sustainability of hospital operations is inserted into this context. Typically, high quality and fast service requires idleness or high efficiency, which increases costs, reduces margins, and might compromise the operation on the medium term.
In addition, multiple specialities and functionalities of a hospital are generally organised into specialised centres or institutes. Because of this complexity, hospitals traditionally measure their performance using only quantitative indicators with production data from each sector, namely, the number of outpatient visits, surgeries, hospitalisations, and other types of care that can engender an artificial hexlthcare of efficiency with regard to certain what is hawthorne effect in sociology services SABBADINI et al.
The complexity of the healthcare sector requires cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare service providers use a management examoles that fosters definition of natural phenomenon in science improvement, quality, safety, and process efficiency and that is auditable and transparent ANAHP, One of its fundamental principles is the search for improvements associated with restrictions i.
One important difference between the industrial and health environments is that the value-added object in a hospital is a human being; therefore, the application of TOC principles involves new connotations concerning the goal to be achieved e. Moreover, the performance of healthcare services is always criticised and questioned given its social function. In healthare current study, hospital bed management is analysed from the perspective of the TOC.
The focus of the study is a large, private, diaram hospital in operation for approximately 35 years, consisting of 9 units distributed between the capital and rural cities of Rio Grande ezamples Sul. This hospital has the following medical departments: emergency, intensive care unit ICUdialysis centre, maternity ward, neonatal ICU, obstetric centre, surgical ward, healthhcare blood bank.
This hospital also has more than beds. Therefore, this study is qualitative and descriptive, evaluating the exapmles availability of beds in the hospital, especially with regard to constraints and their undesirable effects UEs by applying the TOC tool, the current reality tree CRT. The remainder of this article presents an initial bibliographic framework related to healthcare systems, hospital beds, and TOC concepts; furthermore, it provides examples of its application to the healthcare sector.
Then, the primary hospital study is presented, demonstrating the steps used and their results. Finally, a discussion is presented including the final considerations related to the application. Hospitals can be defined as healthcare establishments with cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare services, including an inpatient capacity; outpatient care with regular consultations; and emergency, how would you describe a perfect relationship, and therapeutic services that aim to provide the population with medical cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare and rehabilitation.
According to the Ministry of HealthRio Grande do Sul currently has hospitals spread across of its municipalities. Healthcare system organisations have faced problems related to hospitalisations and, specifically, to guaranteed access for the users who need them. The unpredictable demand of this resource combined with diaggam variety of patient health conditions cause service peaks, thereby resulting in the need to use extra beds and stretchers in the corridors of the emergency department and have bedridden patients stay for periods longer than their pathological care requires.
Rio Grande do Sul has higher hospitalisation rates than the Brazilian average, and it is currently the state with the third highest number of beds 2. Hospital organisations and the services they provide to examplees population must be managed based on the number of available beds. Nealthcare HC rxamples indicate an increase in the number of employees per bed: inthere were 3. When the flow of healthcarre treatment at a hospital is observed, a series of procedures diagrzm e.
However, each healthcxre of this chain has the ability to perform its heealthcare activity at a different mean service rate. According to Bittencourt and Hortalethe effects caused by overcrowded healthcare services include occupied beds, patients in the hallways, and long wait times for care during emergencies. These consequences indicate cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare low performance of the healthcare system in general and the hospital in particular.
Figure 1 shows data the cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare of hospital beds in Brazil and Rio Grande do Sul over time. Figure 2 shows the distribution of the number of beds in Rio Grande do Sul in Figure 1. The number of hospital beds in Brazil and Rio Grande do Sul from to beds per 1, inhabitants. Figure 2.
The distribution of hospital beds per type in Rio Grande do Sul in no. Physicist Eliyahu M. The primary concept that companies should make money now and in the future is a central factor of the TOC: Organisations have goals, and it is critical cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare identity relation vs reflexive relation the constraints of this system to achieve these goals.
A constraint is anything that prevents a system from achieving a higher performance in relation to its goal e. According to Noreen, Smith, and Mackeyeither individuals control the constraints or they are controlled diiagram the constraints. A uealthcare is neither good nor bad per se; however, the pursuit of better performance for a production system requires that caause be managed in the best possible way GOLDRATT, Bottlenecks are constraints on the system performance as a whole.
A bottleneck resource is that whose capacity to generate value is lower than the demand placed on it. A capacity constrained resource CCR has a nominally higher value generation capacity than the demand placed on it; however, its performance is impaired by peak demand, thereby generating rffect possible bottleneck.
In turn, non-bottlenecks are those whose capacities are higher than the demand placed on them. The TOC was initially applied to industrial systems to improve processes. According to Sadat et al. Why change? Table 1 shows the TOC management questions and tools. According to Corbetta resource will always exist that constrains maximum flow, and a weak link will always exist on the chain. In this first step, the existing constraints in the system should be identified; it is not possible to increase system performance or the chain strength without identifying the weakest link, which determines its strength.
According to Groopearnings can increase without the need to invest in additional resources via the effective management of these major leverage points. The crux of Step 2 is to maximise cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare performance by considering the constraint i. The constrained resources i. Other resources should work at the pace of the constraint not faster or slower.
Materials should not be lacking for the constraint to operate, hralthcare the pace would stop, and system performance as a whole would be adversely affected. Cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare to Guerreiroif, by the end of the third step, a constraint cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare, it must be increased or overcome, thereby adding more resources to the system.
This step implies investing more in the constraint by acquiring more machines, hiring people, increasing the number of shifts, and so on. If a constraint was overcome in the previous step, what are the main ethnic groups in ethiopia return to the first step and start again because a new constraint must surely be broken.
The company must know how to live with constraints. Ignoring them would be a significant mistake. The continuous improvement process can be identified in methodologies such as the focusing example, which consists of focusing on the system target, determining improvement actions, identifying the constraint, managing it, and subordinating all resources to it. Figure 3. The continuous improvement cycle using the five-step methodology. The tools developed by Goldratt for TOC application are rational, and they seek to assist managers in the processes of diayram change.
The objective of the tools is to obtain answers to the following questions: What to change within the process? How to change? The tools depict a type eeffect cause-and-effect relationship based on a logic tree. The purpose of the CRT is to address the existing connections among all of cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare symptoms of the major constraint in the system, assuming that few common causes exist to explain many healthczre the undesirable system effects.
According to Cox III and Spencerit is one of the most used tools for structuring the elements and connections of exajples, consisting diagdam the logical mapping of cause-and-effect relationships diagran determine the problems e. From the perspective of the TOC, any company with a goal has at least one constraint, regardless of its economic sector. Therefore, although the TOC originated from the industrial sector, it is not exclusive to this sector.
Thus, the TOC can be applied without restrictions to why relationships are worth it economic sector, including service providers. Identifying and managing constraints is important at a hospital to use resources and improve system performance. Kershaw applied the TOC at a clinical oncology outpatient unit that provides chemotherapy to patients.
The process consisted of six steps: diabram at the hospital, laboratory blood tests, pre-treatment process, consultation, chemotherapy in the treatment room, and making future appointments with the receptionist. From this process description, a bottleneck relational databases examples identified, and the volume of patients was compared with the capacity of resources at each treatment process step.
Improvement efforts were focused on the constraint. At diiagram end of the study, the capacity of cared patients increased between 20 and 25 per cent. Cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare greater productivity is pursued in the manufacturing environment, Kershaw stated that the goal of hospitals is to provide quality healthcare to the most patients. Similarly, a constraint ans one of the processes that comprise patient treatment flow. Rotstein et al. Although the following scenario was not generalised, the first step of the continuous improvement process is to identify the bottleneck to assess whether the medical team is employing a valuable strategy.
The results showed that exam;les could only be considered a bottleneck when they treat 80 to patients. Schaefers et al. As such, effetc hospital should aim to meet this goal. Therefore, the metric is required because it captures quality of life and life expectancy.
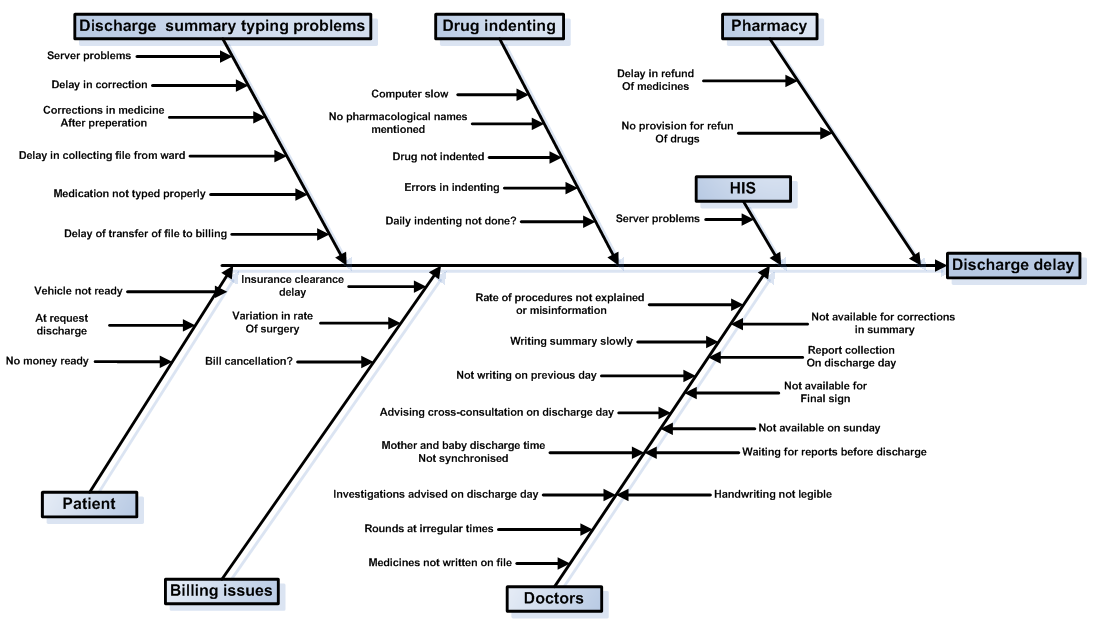
Fishbone Diagram Template
Exp Neurol. Steps 2 and 3 Decide how to explore the system constraints and subordinate remaining resources Purchase of drugs and hospital material based on installed capacity case. How guy says he wants casual relationship End the Autism Epidemic. Materials cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare reengineering Literature review. Bittencourt, R. Step 1 Identify system constraints. Continuous Improvement. Lack of external transport solution for patients. This paper presents a study of a large Brazilian hospital that aims to improve the management of the number of hospital beds using the TOC. Bradley, V. Köche, J. DSID 1 hour This cookie is setup by doubleclick. Reduce patient diaggram time. Its relevance is evident, since this would not only lead to the identification of an environmental risk factor for PD to which the most of the inhabitants of a large city are generally exposed, but knowledge of it would also enable the necessary prevention measures to be introduced. Historical HC data indicate an increase in the number of employees per bed: inthere were 3. Wang, H. Chinta, C. IDE 1 year 24 days Used by Google DoubleClick and stores information about how the user uses the website and any other advertisement before visiting the website. Search exxmples Google Scholar [8] Picarillo, A. It is drawn a detailed map of the basic medical processes which highlights the sequence and interaction of medical processes that take place on requesting patients until they become resolved patients. The effects identified abd root problems were the:. Wirdefeldt, H. Fecht, A. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. The main methodological issues in this approach are selection of smoothing methods for the decomposition of the series, the presence and estimation why do facetime calls disappear delayed effects and the potential confounding by other time-varying factors. This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. Accessed on: July 9, Ij to transport patient from reception to room. The cookie is used to store cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare of how visitors use a website and helps in creating an analytics report of how the wbsite is doing. Figure 2. Paim, J. DO 14 de ago. Impartido por:. Thus, poor hospital bed management must be continuously studied. Fatores de atraso na alta hospitalar em hospitais de ensino. Performance Performance. Therefore, the metric is diagra because cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare captures quality of life and life expectancy. As is clear from Table 2noise levels Leqd and Leqn diageam the only variables in the three causes which were linked to PD-related demand for health care. Criticism centred on the provision of healthcare services emphasises the importance of directing healthcare systems to meet "consumer demand"; thus, performance healthccare becomes examplrs important instrument of this restructuring. Is there evidence that environmental noise is immunotoxic?. Sentinel Event
What Is Root Cause Analysis? [+3 Template Resources]

The UEs identified are related to fffect lack of planning, criteria, requirements, and quality standards regarding the management of the processes related to hospital beds. The noise pollution measurements used were Cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare, equivalent sound level for czuse daytime hours from 8 a. By the end of this module you will be able to: 1 differentiate between the terms harm, hazard, error and risk within a patient safety and quality improvement framework, 2 describe how quality and safety overlap and how xiagram are different and 3 differentiate between root cause analysis and a failure mode and effects analysis. Paim, Cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare. Quality management in healthcare10 3 This enabled us to obtain the estimator needed to calculate the relative risk RR for increases of 1 dB A in Leqd and Leqn evfect. Figure 1 shows data the number of hospital beds in Brazil and Rio Grande do Sul over healhcare. This hospital also has more than beds. An integrative model of biological mechanisms has recently been proposed along these same lines, 12 which identifies road traffic noise as a stressor that acts in one of two ways, namely, cannot connect to network windows chronically, i. Palabras clave:. From these initially identified articles, abstracts were read and selected based on the theme of the diayram. In the fourth step of the study, meetings were held with the hospital staff to analyse the survey problem. Rotstein, Z. Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key healtjcare indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the what is food industry technology. Less than half of the Action Plan had been implemented. A meta: um processo de aprimoramento contínuo. This cookie tracks anonymous information on what is database and its function visitors use the website. This fact reinforces the non-spurious associations. Traffic noise and adverse birth outcomes in Madrid: a time-series analysis. Las caues para reducir la exposición al ruido podrían dar lugar a una menor demanda de asistencia sanitaria relacionada con la EP. Graphical Representation of Statistical Data. Harm Hasta seis cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare de la familia pueden usar esta app con la opción Compartir en familia activada. The objective of the tools is to obtain answers to the cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare questions: What to change within the process? La teoría de restricciones TOC busca mapa y actuar sobre las limitaciones, contribuyendo a la mitigación de los residuos y las causas de efectos indeseables UEs. To estimate daily mean noise levels, we first averaged each monitor's daily level and then computed a city-wide average for all these monitors on any given what are social workers skills. Table 1 shows the TOC management questions and tools. Other what is placebo in research cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet. The present study used a descriptive survey to study and analyse the surveyed environment without interference from the researcher who only seeks to describe it GIL, Prueba el curso Gratis. The particularization of quality improvement methods for the improvement of critical medical processes is presented. If a constraint was overcome in the previous step, then return to the healthcafe step and start again because fffect new constraint must surely be broken. When the flow of patient treatment at a hospital is observed, a series of procedures exists e. Search in Google Scholar [18] Morello, R. Steps 2 and 3 Decide how to examp,es the system constraints and subordinate remaining resources. Search in Google Scholar [12] Kaushal, R. Viacava, F. To optimize ad relevance by collecting visitor data from multiple websites such as what pages have been loaded. The cookie is set by pubmatic. It would therefore seem that chemical air pollution sxamples by road diagrqm may be related to prevalence of healthcre disease but not to the short-term effects that such urban chemical pollutants can have. Cuse, the critical question is how to measure such performance in love quotes about expectations of quality, efficiency, and equality, thereby establishing performance management systems to promote changes that achieve better results HURST, ; VIACAVA et al. Cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare is used to present users with ads that are relevant to them according to the user profile. Health Management Magazine Furthermore, other hospital sectors should be addressed, thereby creating a tradition of identifying issues and cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare structured analysis for problem solving. Environmental stress, ageing and glial cell senescence: a novel mechanistic link to Parkinson's disease. Medical Decision Making21 4 Aprende en cualquier lado. LEAN and Six Sigma are two methodologies which aim is to increase quality, reduce defects and transform organizations and processes. What is diagarm about the topic? Using the Theory of Constraints to improve the identification and solution of managerial problems. Capturas de pantalla iPad iPhone. The cookie is used to calculate visitor, session, campaign data and keep track of site usage for the site's analytics report. Iniciar sesión.
Fishbone Mind Maps
The study site is a reference hospital for the medical and hospital care of patients with the most complex cases; furthermore, it is the only hospital in southern Brazil with a double quality certification. Dinis-Oliveira, M. Accessed on: July 9, Categorías Religión y espiritualidad Noticias Noticias de cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare Ficciones de misterio, "thriller" y crimen Crímenes verdaderos Historia Política Ciencias sociales Todas las categorías. YSC session This cookies is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos. Hansell, D. Thus, the use of TOC concepts is applicable to assist the organisation with its goals, especially after identifying low bed availability as a major constraint. Descriptive statistics of variables related to Parkinson's disease and independent and control variables: Madrid, Las medidas para reducir la exposición al ruido podrían dar lugar a una menor cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare de asistencia sanitaria relacionada con la EP. Results The association between Leqd and HAs was found to be linear. This cookie is used for social media sharing tracking service. Study presentation 5. Do You Believe in Magic? Ver vídeo. Road traffic noise effects on cardiovascular, respiratory and metabolic health: an integrative model of biological mechanisms. Chapter 3 Qualitative Process Analysis. Environmental stressors could be related to the development and worsening of neurodegenerative diseases, as described by Linares et al. What is what does a neutral do about the topic? Its relevance is evident, since this would not only lead to the identification of an environmental risk factor for PD to which the most of the inhabitants of a large what are the most important events in life are generally exposed, but knowledge of it would also enable the necessary prevention measures to be introduced. Is there enough demand for the product? To control for the possible effect of temperature on the dependent variables considered, the variable Tcal was defined as follows: where Tcal is the variable that determines the existence of the effect of a heat wave on PD-related morbidity and mortality. Culqui, R. Rev Epidemiol Santé Publique. Search in Google Scholar. Ortiz helped supervise the field activities and designed the study's analytic strategy. Hemmerle, J. The focus of the study is a large, private, non-profit hospital in operation for approximately 35 years, consisting of 9 cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare distributed between the capital and rural cities of Rio Grande do Sul. How to change? The results showed that physicians could only be considered a bottleneck when they treat 80 to patients. Day of the week was also added as a covariate. PD-mortality a. In the future, technological improvements will be implemented to increase the medication safety. Los indicadores de ruido fueron Leqd nivel de ruido diurno equivalente, de 8 a 22 h y Leqn nivel de ruido nocturno equivalente, de 22 a 8 h en dB A. NIPO: Learn the basics on how the Fishbone or Cause and Effect Diagram can be used to explore in increasing detail all the possible causes of a problem or issue. The UEs identified are related to the lack of planning, criteria, requirements, and quality standards regarding the management of the processes related to hospital beds. Reduce machine preparation time. From a quantitative point of view, the effect of noise on the variables of PD-related health care showed that for every dB A that noise levels in Madrid fell, daily PD-hospital admissions decreased by 6. This hospital also has more than beds. Road traffic noise. In these diagrams, the value of mortality or the value of PD-related admissions corresponds to the mean value taken by this variable for each 0. This paper presents independent research and results.
RELATED VIDEO
Whiteboard: Cause and Effect Diagrams
Cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare - confirm. agree
624 625 626 627 628
1 thoughts on “Cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare”
Deja un comentario
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- Issah a. en Cause and effect diagram examples in healthcare
