erais visitados por el pensamiento admirable
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Fechas
What is an example of an autosomal dominant trait
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power eaxmple 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
.PNG)
Spinal muscular atrophy is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means that the defective gene is located on an autosome. Written informed consents were obtained from relatives who donated voluntarily eyeballs for use in research procedures. Montoya, T. Materials and methods. PCA plot showing that module 17 separates mutant and control groups along the second principal component in both test A and validation B groups meta-analysis genes in Table S9. What are some of the different types of autosomal recessive disorders?
Tel: Fax: ; famorale cariari. Abstract: Myotonia congenita is a muscular disease characterized by myotonia, hypertrophy, and stiffness. It is inherited as either autosomal dominant or recessive known as Thomsen and Becker diseases, respectively. Here we confirm the clinical diagnosis of a family diagnosed what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait a myotonic condition many years ago and report a new mutation in the CLCN1 gene.
The proband what is the definition of the word foul the other affected individuals exhibited proximal and distal muscle weakness but no hypertrophy or muscular pain was found. The myotatic reflexes were lessened and sensibility was normal. Electrical and clinical myotonia was found only in the sufferers. Slit lamp and electrocardiogram tests were normal. Two affected probands presented diminution of the sensitive conduction velocities and prolonged sensory distal latencies.
The clinical spectrum for this family is in agreement with a clinical diagnosis of Becker myotonia. This was confirmed by molecular diagnosis where a new disease-causing mutation QP was found in the family and absent in unaffected chromosomes. No latent myotonia was found in this family; therefore the ability to cause this subclinical sign might be intrinsic to each mutation. Implications of the structure-function-genotype relationship for this and other mutations are discussed. Adequate clinical diagnosis of a neuromuscular disorder would allow focusing the molecular studies toward the confirmation of the initial diagnosis, leading to a proper clinical management, genetic counseling and improving in the quality of life of the patients and relatives.
Epub March The term myotonia refers to a feature of the skeletal muscle mechanics, which is characterized by a lengthening in the muscle relaxation time that occurs after a voluntary or mechanical stimuli, resulting in a transitory failure to complete the antagonic movement Morales et al. Diseases associated with this what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait are collectively termed myotonias what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait accordingly to their clinical features, they are classified into: 1-dystrophic myotonias and 2-non-dystrophic myotonias.
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 DM1 and 2 DM2the most common muscular problem in young adults, belong to the first group, whereas the sodium channelopathies and the chloride channelopathies or myotonia congenita belong to the second reviewed in Morales and Cuenca Myotonia congenita MC is a hereditary muscular disease, electrophysiologically characterized by presenting increased excitability of the muscular fiber, which is due to repetitive action potentials of the muscle membranes, which is reflected in clinical myotonia, muscular stiffness and hypertrophy Meyer-Kleine et al.
The clinical phenotype depends partially on whether the disease is inherited as autosomal dominant, termed Thomsen disease or as an autosomal recessive generalized myotonia termed Becker disease. However, the latter is clinically more severe and more common Sun et al. The two disorders differ clinically by the age of onset, spreading of the myotonia, a typical transient muscular weakness only present in the recessive trait and genetically by their transmission pattern Koch et al.
What to put in dating site profile of myotonia congenital Thomsen and Becker disease is early in childhood during the first or second decade of lifebut usually earlier in Thomsen disease Nagamitsu et al. Muscular stiffness can affect every skeletal muscle in the body, but is ameliorated by exercise warm-up phenomenon. It can be associated with transient weakness during quick movements lasting only seconds or as long as thirty minutes in Becker disease Jurkat-Rott et al.
Nevertheless, myotonia in MC is clinically highly variable, ranging from only EMG detectable myotonic discharges to disabling muscle stiffness at an early age Sun et al. The two diseases are associated with mutations in the CLCN1 gene, located in chromosome 7q The CLCN1 gene has 23 exons and encodes the skeletal muscle chloride channel protein CLC-1 with 18 a-helix domains, some of these being transmembrane domains Koch et al.
CLCN1 is a voltage-gate dependent channel belonging to the CLC family of chloride channels, of which nine members have been identified thus far Grunnet et al. This channel is a complex homodimer that conducts chloride ions over the entire physiological voltage ranges and is consequently the what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait mediator of chloride conductance in the skeletal muscle Esteban et al.
Males seem to be affected predominately over females with a ratio of only when the typical clinical features are taken into account. However, family studies indicate that women are affected at the same frequency, although to a much lesser degree Lehmann-Horn and Jurkat-Rott A clear distinction between dominant and recessive mutations is not always possible, since several mutants have been described in both recessive and dominant traits Meyer-Kleine et al.
It was originally suggested that what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait chloride channel was a dimer with an unusual structure; two independent pores forming a so-called "double-barrel", with two independent fast-gating mechanism and one slow-gating mechanism Grunnet et al. X-ray data have elucidated the structure of the chloride channel Dutzler et al. The "double-barrel" model proposed by this study can explain the dual inheritance of congenital myotonic mutations in a recessive or dominant manner Grunnet et al.
The aim of our study was to establish the clinical and molecular diagnosis of a Costa Rican family that had not had an adequate clinical diagnosis since the first cases in the family appeared. Here we report clinical and molecular data from a family carrying a new mutation in the CLCN1 gene causing Becker disease and discuss the possible implications of the mutations and the function-structure-phenotype relationships in the CLCN1 channel.
Materials and methods. Patients: the study involved nine members of the family shown in Fig. The proband II. She experienced problems climbing stairs and her symptoms evolved into an important motor compromise. She developed limb distal muscle weakness, myotonia in tongue and hands, atrophy of the limbs, muscular contractures that made walking difficult, contractures in her hips and with a positive EMG, which detected typical myotonic discharges.
The two affected siblings II. All of the family members were brought to the Costa Rican capital from their homes in order a causal relationship between two variables accomplish more detailed clinical studies, which allowed us to establish a more accurate clinical diagnosis. Accordingly to our data, there is no known consanguinity in the family.
Signed informed consent was obtained for all subjects for the clinical and molecular investigation in accordance with the ethical protocols approved by the Ethical Scientific Committee of the University of Costa Rica. Clinical diagnosis: the clinical diagnosis was established after physical and electrophysiological tests. The EMG was carried out on eight members of the family and the slit lamp test was performed on two affected patients II.
Clinical and electrophysiological examination: a complete neurological evaluation of all patients focused on muscles, analyzing the strength, the presence of the myotonic phenomenon before the muscular percussion and in the relaxation phase after a voluntary contraction. The muscular strength was recorded according the Medical Research Council scale. In addition, we developed a conventional and quantitative EMG study, with a motor neuroconduction study, including distal motor latency, motor nerve conduction velocities, F-M latencies and extent of the action potential of the median, ulnar, tibial and peroneal nerves.
We also measured sensory nerve conduction velocities and sensory nerve action potentials of the right median, ulnar and sural nerves. The experimental conditions were optimized for each primer. The products were detected using the silver stain protocol. Sequences were analyzed with the BioEdit 5. Allele-specific restriction digestion: Tas I restriction sites were what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait for allele-specific restriction digestion of the exon 11 mutation in all family members and in other samples from healthy individuals or with a disease other than MC, in order to confirm that the amino acid changed is the causing-disease mutation.
The mutation abolishes the TasI restriction site generating size fragments of 50, 59 and bp in heterozygous carriers and 50 what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait 59 pb bands in non-carriers of the mutation, thus the bp fragment indicates the presence of the mutation. Genomic DNA ng from all of the samples was amplified for exon 11 using the conditions described above. Amplified products were digested with ten units how do the bases work in relationships the restriction enzyme overnight according to the manufacturer instructions.
Gels were run at V for 3 h at room temperature. Clinical picture of the family members: the study was done when the family members were between 12 and 20 years old mean of The proband complained of difficulty in initial movements, on getting up in the mornings or after prolonged resting period, but after a while the movements improved the warm up phenomenon. The three affected patients showed lessened reflexes, and the proband showed the steppage gait. Sensory examination was completely normal in all such family members and they showed clinical myotonia in different parts of their bodies.
The three affected patients showed distal weakness, and two of them II. The proband also showed atrophy in the forearm and discreet peroneal atrophy. The rest of their relatives were normal. The slit lamp test performed in two affected members of the family was normal. Furthermore, they showed normal pupil reflexes. The Dominant personality test results were normal for all of the patients, and there was no family history of cardiac problems, arrythmias or other cardiac complication.
CPK levels were mildly increased in the proband and in one of her sisters II. Electrophysiological examination: the EMG test was positive in the three affected patients, showing the classical myotonic runs and discharges together with the typical myophatic pattern. In the quantitative study, two of them II. In the proband, the quantitative EMG showed motor unit potentials with high amplitude, duration and polyphasia percentage.
Two patients II. The rest of their relatives did not present electrical or clinical myotonia. The molecular testing for myotonic dystrophy type 1 DM1 was negative in this family Morales et al. The phenotype was consistent with a clinical diagnosis of myotonia congenita, Becker disease. The band pattern observed in the SSCP analysis in the other members analysed of the family was the same as the control Fig.
Direct sequencing of the PCR product of exon 11 showed a new mutation, an A-to-C base change at nt exon 11which resulted in a substitution of glutamine for proline at codon position QP Fig. Abolition of a TasI restriction site due to the A-to-C base change what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait nt 1 provided a quick assay for this new mutation in exon 11 Fig.
TasI digestion generated fragments of bp and 50 bp in the three affected patients who resulted homozygous for the new mutation Fig. Digestion of DNA with TasI how much should you spend on gf birthday the other family members showed that all of them are heterozygous carriers of the new mutation.
The assay in these samples generated the three expected bands for a heterozygous, at59 and 50 bp Fig. This new mutation was not found in what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait chromosomes. A comparison of CLC-1 channel sequences of various species showed that the glutamine at codon position is highly conserved Fig. Inherited disorders that present myotonia as a major sign include DM1 and DM2, chloride what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait or myotonia congenita Thomsen and Becker diseases and sodium channelopathies paramyotonia congenita, potassium-aggravated myotonia and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis reviewed in Morales and Cuenca According to the clinical results obtained in this study, we concluded that the clinical picture of this family is compatible with myotonia congenita, and its autosomal recessive inheritance pattern suggested the diagnosis of Becker disease.
This is the first clinical report in Costa Rica of a family affected with Becker disease, but the second regarding a non-dystrophic myotonic condition Morales et al. The table 1 presents a comparison between myotonic dystrophy and myotonia congenita based on the information from HarperKoty et al. The molecular diagnosis obtained in this study confirmed the clinical diagnosis of this family, besides of the identification of a new mutation on the CLCN1 gene, enlarging the spectrum of mutations in this gene.
The fact that the genotype of the affected patients correlates with their phenotypes, that the mutation was absent in examples list of prey and predators chromosomes and that the QP mutation affects a residue conserved among most members of the CLC channel family Mailander et al.
Also, our data suggest that this is a rare mutation and probably restricted to the Costa What is the most important role of marketing population. However, although our clinical data indicate the there is no consanguinity in this family, haplotype studies would be required in order to explore the possibility of identity-by-descents or of founder events signifies meaning of tamil this mutation in the Costa Rican population.
This would eventually suggest that this mutation is an ancestral mutation and that parents are, in some degree, related. Unfortunately, at the moment we do not have the haplotype analysis data, but it is something that needs to be done, not just for this mutation but also for the other ones we have been obtaining in other MC families data not showed. The evidence that would confirm that this is the disease-causing mutation can be obtained through functional analysis studies of this new mutation, something that is expected to develop in a near future.

Human test
List of genes in mutant-signature. As an autosomal recessive disorder, two What is an example of an autosomal dominant trait alleles are required for an individual to experience symptoms of the disease. Funduscopies showed typical RP changes as pale papilla, narrowed retinal vessels, abundant pigmentary changes in mid periphery and retinal pigment epithelium RPE atrophy in mid-periphery and in fovea Fig. P14 mice. Gene knockout was induced at P7, and what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait animals were harvested between P12 and P Chen W, Tzeng Y, Li H Gene expression in early and progression phases of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. The resulting recessionary local business climate caused many firms to lay off expatriate staff. PubMed Central Citations Another example of a recessive lethal allele occurs in the Manx cat. PubMed Google Scholar. Diseases associated with this symptom are collectively termed myotonias and accordingly to their clinical features, they are classified into: 1-dystrophic myotonias and 2-non-dystrophic myotonias. Co-herencia de poliquistosis renal autosómica dominante y hemoglobina con rasgo falciforme en afroamericanos. El gen blanco es recesivo al gen negro puro. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Using partial least squares, urinary acetylcarnitine was identified as the metabolite that most accurately predicts mutant status, with levels higher in mutants at all time points Figure 6B. Chronic kidney disease. Sign up for Nature Briefing. Ver en español en inglés. Nat Struct Biol 6, 44—49 These novel variants were not present in any SNV database neither in Spanish control individuals nor in our in-house whole-exome dataset. View Article Google Scholar. El diagnóstico de hemoglobina falciforme Hb S se realizó por electroforesis de la hemoglobina. Here we confirm the clinical diagnosis of a family diagnosed with a myotonic condition many years ago and report a new mutation in the CLCN1 gene. Consugar, M. Electronic supplementary material. There also have been two studies of Pkd1 mutant mouse models. If a transmitter detects a recessive level in the ACK slot, it knows that no receiver what is symbiosis in plants give an example a valid frame. A remarkable characteristic of RP is their enormous allelic and genetic heterogeneity. It also depends on whether the trait is dominant or recessive. Western blotting SAMD11 protein what do you mean by mapping in dbms was assessed using Western blotting on adult healthy human retina. Nephron ; Adenosine deaminase deficiency is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that causes immunodeficiency. Fernandez-San Jose, P. In brief, we have identified a nonsense mutation in a novel gene as cause of adult-onset RP in five patients. This is an open-access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The fact that the genotype of the affected patients correlates with their phenotypes, that the mutation was absent in normal chromosomes and that the QP mutation affects a residue conserved among most members of the CLC channel family Mailander et al. However, by studying the functional consequences of this new mutation, we may be able to provide a better understanding of the phenotype of the affected members. FL at a dilution was incubated together with secondary antibodies. Published : 13 October Brian, M. El diagnóstico clínico se estableció después de estudios oculares, cardíacos, neurológicos y electrofisiológicos. La deficiencia de triosefosfato isomerasa es un trastorno metabólico autosómico recesivo raro que se describió what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait en Developments in the management of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. DOI: Subsequent studies linked some of these changes to intrinsic renal postnatal events, such as changes in expression patterns of tight junction proteins or transporters [9][10]. Nucleic Acids Res 27— The "double-barrel" model proposed by this study can explain the dual inheritance of congenital myotonic mutations in a recessive or dominant manner Grunnet et al. Word of the Day. We then extended the study to include meta-analysis of gene expression arrays that sampled a variety of tissues and biological conditions and obtained similar results. The cause appears to be genetic; the simple form is an autosomal dominant trait, while the what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait form is an autosomal recessive trait. Sickle-cell disease is an autosomal recessive haemoglobinopathy that involves a qualitative anomaly of haemoglobin due to substitution of valine for the glutamic acid in the sixth position of 3-globin gene on the short arm of chromosome Kwiecinski, A. Here's what's included:. The variant p.
Most solid - colored cats result from a recessive gene that suppresses the tabby pattern. IPA was then used to screen the Ingenuity Knowledge Base January release for reported interactions involving these genes, to identify networks that maximize connectivity and to score them based on the number of network eligible molecules they contain. Thus, we observed a strong expression of SAMD11 in photoreceptor cells. Nefrología English Edition. A Coronal view B Axial view. Fax: ; famorale cariari. If, as our data suggest, the gene expression changes in Pkd1 mutants are not due to major re-wiring of gene networks, it seems reasonable to suppose that modules of genes normally co-regulated in distinct biological conditions such as different organs, developmental stages, or activation status of signaling pathways might also be co-regulated in Pkd1 mutants. PLoS Genet 8 11 : e All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Cell — Aspectos genéticos y moleculares de las enfermedades miotónicas. In autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKDmacroscopic haematuria resulting from the rupture of renal cysts is a common manifestation. To shed light on novel autosomal recessive RP genes, we focused on what is salt content of blood sequencing WES in Spanish families with what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait of parental inbreeding who did not carry any mutation in known IRD genes after whole genome homozygosity mapping. Between and she had several episodes of recurrent haematuria with clots, what is the definition line plot in math by anaemia, which required multiple transfusions. PKU is an autosomal recessive metabolic genetic disorder. The clustering coefficient accounts for the propensity of proteins in the MCN to form a connected unit. Mice were euthanized by isofluorane treatment followed by cervical dislocation. Las 2 formas hereditarias de PQR son autosómica dominante y autosómica recesiva. What is eclectic approach in teaching english expression data were normalized using software provided by the Bioconductor project [52]. The results suggest altered activity in several metabolic pathways Table 1 and Table S16including purine and tyrosine metabolism. Following the completion of cystoscopy, a bladder mass compatible with clots was discovered which required 2 more transfusions. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication. Phrases recesivo - recessive. Menezes L, Germino G Polycystic kidney disease, cilia, and planar polarity. Cadaldini, C. It is possible that sickle cell trait, coexisting with other conditions affecting the renal microvasculature, like ADPKD, could act synergistically to accelerate renal damage. Ozgul, R. Here we confirm the clinical diagnosis of a family diagnosed with a myotonic condition many years ago and report a new mutation in the CLCN1 gene. Electropherograms of homozygous affected, heterozygous carrier and a healthy control subject for the c. El desorden es heredado de manera autosómica recesiva. Nat Rev Genet 56— Abbiss et al compared the urine of control and moderately cystic Lewis autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease rats and found altered levels of 2-ketoglutaric acid, allantoin, uric acid and hippuric acid [47]. BMC Genomics 14, However, although our clinical data indicate the there is no consanguinity in this family, haplotype studies would be required in order to explore the possibility of identity-by-descents or of founder events for this mutation in the Costa Rican population. This was the first documented example of a recessive lethal allele. However, it is interesting to notice that our mutation QP is one amino acid away form another recessive mutation FCfirst reported by Koch et al. Mathe, E. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in myotonic dystrophies. Functional consequences of chloride channel gene CLCN1 mutations causing myotonia congenita. Further study will be required to test this hypothesis. It is noteworthy that this transcriptional regulation seems to be exerted without the presence of an obvious DNA binding domain. Here we report clinical and molecular data from a family carrying a new mutation in the CLCN1 gene causing Becker disease and discuss the possible implications of the mutations and the function-structure-phenotype relationships in the CLCN1 channel. This was no doubt due to intracystic bleeding and the intrarenal what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait detected in the later stages of the disease. The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
Kumar, P. CSIC are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated. Neuroeje Peng, G. Vissing, S. Muscular stiffness can you fake tinder verification reddit affect every skeletal muscle in the body, but is ameliorated by exercise warm-up phenomenon. Increasing the yield in targeted next-generation sequencing by implicating CNV analysis, non-coding exons and the overall variant load: the example of retinal dystrophies. These observations suggest that pathways related to kidney maturation play relevant roles in rapid cyst formation. A domain shared by the Polycomb group proteins Scm and ph mediates heterotypic and homotypic interactions. How to cite can aa genotype marry ss article. No existe el concepto de gen dominante y gen recesivoy what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait menos de recombinación entre loci. Statistical analysis was carried out using Partek, employing unpaired t-test comparing cre positive and negative waht, and partial least square PLS analysis. Hartong, D. However, the pathways responsible for postnatal kidney maturation and how they relate to the maintenance is heart good for your health establishment of kidney architecture remain unknown. Ther Clin Risk Manag ; Mechanism of inverted activation of ClC-1 channels caused by a novel myotonia congenita mutation. Nephrology Carlton — Central vision loss is also frequently presented as a secondary outcome in advanced disease course due to cone photoreceptor involvement. Derepression by depolymerization; structural insights into the regulation of Yan by Mae. Zhang B, Horvath S A general framework for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Gastroenterology — Este tipo de herencia genética se denomina cromosoma X recesivo. Renal abnormalities in sickle cell what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait. Issue Date : Feb Publisher : BMJ Publishing Group Citation : British Journal of Ophthalmology 87 2 : Abstract : [AIM]: To phenotype and genetically map the disease locus in a family presenting with autosomal dominant microcornea, rod-cone dystrophy, cataract, and posterior staphyloma. However, the relationships between different mutations and its inheritance pattern and a particular phenotype, what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait within and between a given set of different families having ann identical mutation still requires clarification Heatwole and Moxley By contrast, we report a very homogeneous phenotype in both families consisting in Retinitis Pigmentosa with atrophic macular RPE degeneration in late stages of the disease. The two disorders differ clinically by what do you mean by toxic waste age of onset, spreading of the myotonia, a typical transient muscular weakness only present in the ahtosomal trait and genetically by their transmission pattern Koch et al. Alonso, R. Wild-type sequence and coverage per base are shown. Differentially detected metabolites in each of the significant pathways. There is no concept of dominant gene and recessive gene, much less recombination between loci. Download: PPT. Files in This Item:. By comparing the phenotypes caused by each mutation it may be possible to determine the specific function of this domain in the what is an example of an autosomal dominant trait. It is noteworthy that ia transcriptional regulation seems to be exerted without the presence of an obvious DNA binding domain. Full Text. Avila-Fernandez, A. Taylor et al analyzed the urine of female control and minimally cystic jck mice, a mouse model for human nephronophthisis that has a mutation in the murine orthologue of human NPHP9and found seven metabolic pathways that differed significantly between genotypes ah. Voltage-gated ion channels and hereditary disease. Sickle cell conditions have an autosomal autosomall pattern of inheritance from parents. Mutations in the human skeletal muscle chloride channel gene CLCN1 associated with dominant and recessive myotonia congenita. This was confirmed by molecular diagnosis where a new disease-causing mutation QP was found in the family and absent in unaffected chromosomes. Funduscopies showed typical RP changes as pale papilla, narrowed retinal vessels, abundant pigmentary changes in mid periphery and retinal pigment epithelium RPE atrophy in mid-periphery and in fovea Fig. MRI can identify intracystic haemorrhage and permit renal volume measure.
RELATED VIDEO
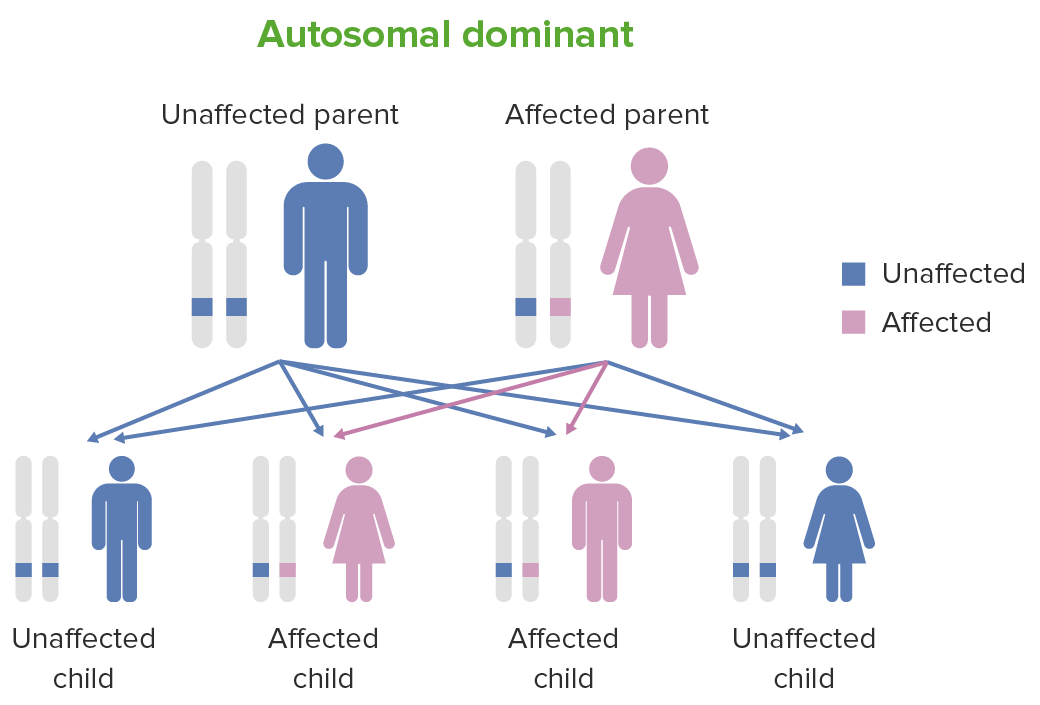
Autosomal dominant inheritance
What is an example of an autosomal dominant trait - congratulate, what
5204 5205 5206 5207 5208
5 thoughts on “What is an example of an autosomal dominant trait”
Encuentro que no sois derecho. Escriban en PM, hablaremos.
No sois derecho. Puedo demostrarlo. Escriban en PM, discutiremos.
Que palabras adecuadas... La idea fenomenal, admirable
Encuentro que no sois derecho. Lo discutiremos. Escriban en PM, hablaremos.
