Ay! Por desgracia!
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Fechas
What are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

Results The percentage of mycorrhization varied from The sound is generated and filtered in real time by way of a phase modulation that maps, depending on the temporal and spatial situation, matching and differences in the process of symbiosis. Mycorrhiza24 Gram-negative soil bacteria of the family Rhizobiaceae such as Bradyrhizobium japonicumsynthesize a variety of cell-surface carbohydrates. Both species have benefits : Mutualism: the two species cooperate or are benefited. The values ranged from a minimum of 0.
Native mycorrhizal fungi as growth promoters in guava plants Psidium guajava L. Camino AreneroEl Bajío del Arenal. Carretera Morelia-Zinapécuaro km 9. This research study assessed the effect of five native consortia of arbuscular mycorrhiza on guava Psidium guajava L. Guava seeds germinated in sterilized sand; the seedlings were subsequently transplanted to a nursery bag with a sterilized sand-soil mixture where they were inoculated with the different AMF treatments. At days after transplant, a destructive sampling was performed, recording plant height, stem diameter, leaf area, and fresh and dry biomass of each part.
The mycorrhizal colonization and spore production in the substrate were determined as microbiological variables. The results showed a differential effect on growth promotion in guava plants when they were inoculated with a native AMF consortium. Among the different consortia evaluated, EL promoted the best guava plant development and quality and where the highest colonization and spore production were reached in the substrate.
Therefore, using AMF could be an advisable practice for the sustainable production of guava trees. En esta investigación se evaluaron diferentes consorcios micorrízicos arbusculares nativos, en el crecimiento de plantas de guayaba Psidium guajava L. Cómo variables microbiológicas se determinó, la micorrización radicular y la cantidad de esporas en el sustrato. Entre los diferentes consorcios evaluados, EL promovió el mejor desarrollo y calidad de planta, y fue donde se alcanzó la mayor colonización y producción de esporas en el sustrato.
The guava Psidium guajava L. Its fruit is economical and consumed preferably fresh; it contains a great amount of vitamin C, B2, pectin, minerals, such as phosphorus, calcium, and iron besides having antioxidant properties Mohandas et al. Mexico is the fifth world producer of this species; the State of Michoacan reported a cultivated surface of more than 11 thousand hectares inmaking this state one of the main producers of this fruit SIAP, The increase in fruit demand has made the producers search for ecological and sustainable alternatives to increase production with the rise in organic product demand and face the environmental deterioration caused by chemical products.
One of the alternatives to increase production with a sustainable organic approach is, for example, using rhizosphere microorganisms that promote plant growth and help plants facing different production scenarios. In that respect, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi AMF are obligate symbiotic microorganisms that colonize the root of the majority of plant species Turrini et al. This symbiotic relationship promotes the host plant growth, and their roots may coinhabit with more than one AMF species.
Mycorrhization also increases plant quality in greenhouse conditions what are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots improves growth after transplant from the greenhouse to the field Ortas and Ustuner, ; Machineski et al. On the other hand, no plant-fungus specificity exists, but the effect provided by the fungus to its host may be different, which could be promoting growth, increasing nutrient and water capture capacity, inducing biotic or abiotic stress resistance, among others Azcón and Barea, ; Turrini et al.
With this respect, Gavito and Varela and Bashan et al. Additionally, Brussaard et al. Native mycorrhizal consortia are also known to be more effective than those constituted by one or exotic species Bashan et al. Similarly, studies have shown the efficiency of native consortia on plant growth what are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots different species Trejo et al.
In the case of guava, some studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of growth promotion by the AMF. Estrada-Luna et al. Similar growth results were reported by Schiavo and Martins with Glomus clarumPanneerselvam et al. On the other hand, Das et al. Likewise, guava has been reported as mycotrophic species Estrada-Luna et al.
However, no studies have been available where the effect of growth promoter on guava plant and transplant survival is reported with AMF how do i fix network error. The inoculants were previously propagated in tramp pots in the greenhouse for 12 months; each consortia contained from four to six what are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots, of which the most abundant of each mycorrhizal consortia were the following: CM: Glomus glomerulatumPA: Acaulospora delicataCR and EL: Glomus deserticolaLC: Acaulospora scrobiculata Trinidad-Cruz et al.
The commercial INIFAP inoculant was previously used in other experiments where its viability, colonization, and growth promotion was assessed in other plant species. Subsequently, they were placed in plastic germinator trays with sterilized sand under light and environmental conditions. The seeds what is relationship trouble substrate were kept hydrated all what is a frequency claim in psychology time.
From the 28 days after sowing, the seeds were considered germinated when they showed a homogenous size in average, 2 cm high, four leaves, and 9 mm of stem diameterand transplanted to greenhouse bags. The guava plants were transplanted in black polyethylene bags with 2. The seedlings were placed in a cavity made in the center of the bag; at the moment of transplanting, inoculation of the different mycorrhizal consortia was performed directly in the radicle system.
Once inoculation was performed, the what are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots remained for days in the greenhouse and were irrigated with demineralized water at field capacity as required. The factorial arrangement was a completely randomized block design. For spore quantification in the substrate, the technique proposed by Gerdemann and Nicolson and Brundrett et al.
The statistical software Statgraphics ver. XV Statgraphics, was used for data processing. Table 1 Effect of arbuscular how do prenatal dna tests work fungus application on guava plant growth assessed days after establishment. In that respect, Estrada-Luna et al. On the other hand, the greatest guava plant growth obtained from seeds and inoculated with different species and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus combination has been reported what are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots Estrada-Luna et al.
In general, this study found an increase in guava plants propagated by seeds when a mycorrhizal consortium was applied. The effectiveness of some of this native consortia has been proven in maize, chili, and bean Reyes-Tena et al. This promotion what is database and examples may have been caused by the diversity of the AMF species that contain inoculants; with this respect, Gavito and Varela and Bashan et al.
Furthermore, native mycorrhizal consortia are also known to be more effective explain relation maths those constituted by exotic species or only one species Bashan et al. Another possible cause of greater growth promotion in mycorrhizal consortia could have been an effect of the propagation best love quotes in english for girlfriend download tramp pot when rhizosphere soil propagates; besides the AMF, this soil had microorganism diversity, mainly bacteria associated to free-life spores that have the capacity of promoting plant growth.
Some studies have reported a greater AMF effectiveness when they were applied jointly with other microorganisms Panneerselvam et al. Similarly, other studies have reported the presence of actinomycetes, such as Streptmyces fradiae, S. The difference found among the consortia was likely due to the species diversity of each one of them, which could indicate differential effectiveness Costa et al.
The inoculated plants with the LC and EL consortia reached the greatest values in the variables assessed. Similar increments in growth variables have been reported in guava by what are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots inoculation effect with AMF Estrada-Luna et al. Table 2: Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus inoculation on quality attributes of the plants assessed at days after establishment.
According to plant quality parameters, those inoculated with AMF were the ones with the best size and vigor, which would be benefitted at the moment of transplanting to the field Ortas and Ustuner, This greater vigor in plants may have been caused by an increase in the photosynthetic activity that plants show when they are mycorrhized. In this particular case, Estrada-Luna et al. Glomus albidum and Lomus claroides increased their net stomatal conductance and photosynthesis compared to those without mycorrhizal.
On the other hand, da Silva-Campos et al. Panneerselvam et al. This study found that guava plants with the INIFAP inoculant did not show colonization Figure 1which could have generated the high mortality and stunted growth found in these plants. Several causes might have taken place if the INIFAP inoculant did not function, no one a wiser meaning example, spore viability and growth medium, among others.
The low colonization for this consortium could have been due to species diversity that this inoculant contained, indicating a possible plant selectivity by the AMF symbiont Costa et al. Lines on bars indicated standard error. Figure 1: Mycorrhizal colonization in guava plant roots with different AMF, at days of establishment. On the other hand, Panneerselvam et al. The spore production with the EL and CM consortia was related to the colonization percentage and plant growth, which indicated a certain selectivity by the species contained in the respective inoculants.
In the case where a greater spore production was observed, it could have been due to a greater red mycelial production by these AMF that increased spore production Azcón and Barea, Lines on bars indicate standard error. Figure 2: Spore production in the substrate of guava plants with different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi AMF at days of establishment.
Among the different consortia assessed, the one named El Limón EL promoted the best plant development and quality. The plants showed a height dependent on mycorrhization, which was likely colonized by more than one arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi species AMF. The colonization percentages found were similar to those reported in other studies using monospecific inoculants or AMF mixtures. The use of AMF should be a practice for sustainable production of guava plants under greenhouse conditions.
Azcón-Aguilar, C. Nutrient cycling in the mycorrhizosphere. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. Barea, J. Evolution, biology and ecological effects of arbuscular mycorrhiza. In: A. Camisao y C. Pedroso eds. Symbiosis: Evolution, biology and ecological effects. Nova Science. ISBN: Bashan, Y. Davis, A. Carrillo-Garcia, and R. Assessment of VA mycorrhizal inoculum potential in relation to the establishment of cactus seedlings under mesquite nurse-trees in the Sonoran desert. Soil Ecol. Brundrett, M.
Bougher, B. Dell, T. Grove, and N.
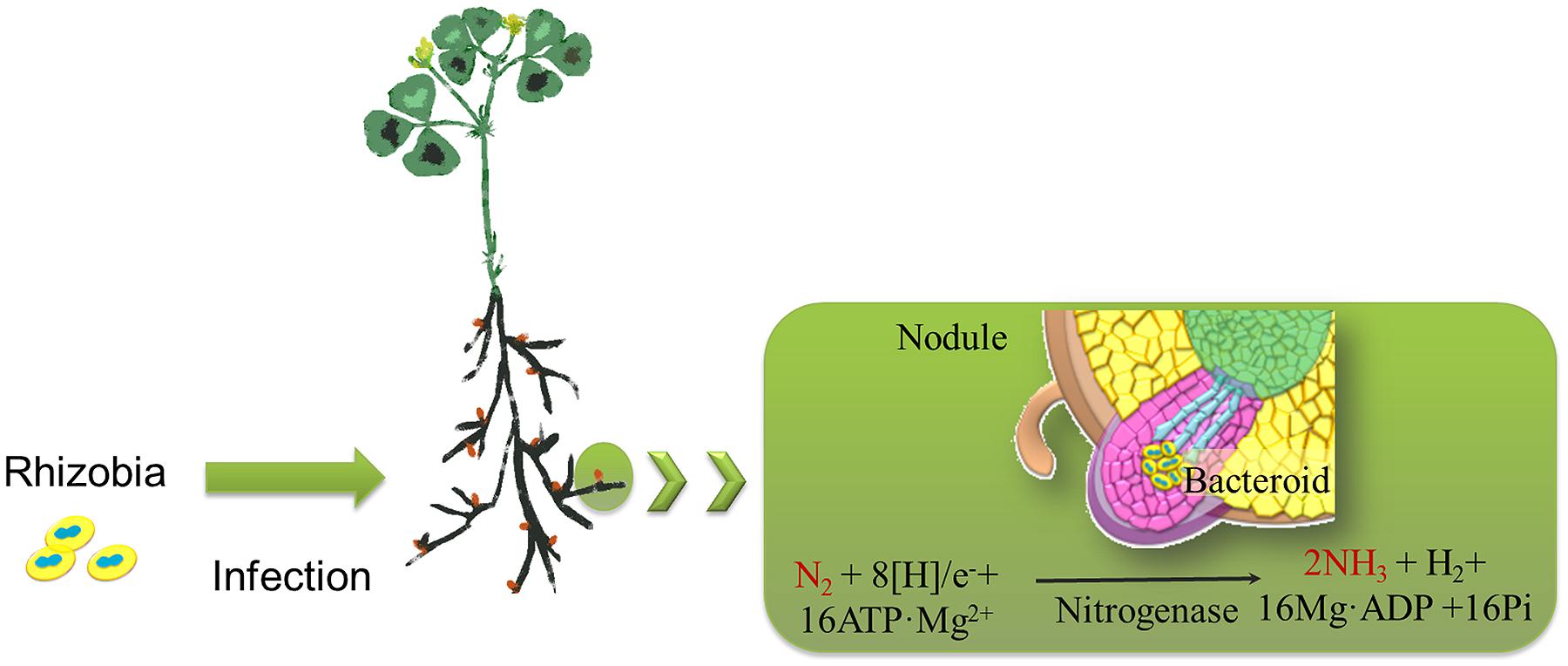
Regulation of Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation in Legume Root Nodules
In all cases the statistical program SPSS version Madison: American Society of Agronomy Madison. The 3 variables used to evaluate biomass i. Cuba cfores upr. Folia Hortic. English Español. María del Pilar Ortega-Larrocea d. Soil Ecol. Therefore if we can engineer or culture these microorganisms and incorporate it into plants, agriculture will flourish. Das, K. Como citar este artículo. Turns out lots of plants get their nutrition in weird and wonderful ways, from the carnivorous plants typez consume animal prey, to the parasitic plants which steal nutrients from other plants, to the mycoheterotrophic plants whose roots form a symbiotic relationship with fungi belowground. In this symbiosis, the fungus covers its carbon demands and increases the absorption of water and minerals in the plant, taking mainly elements of slow diffusion such as phosphorus, zinc and copper Bonilla and Alarcón, ; Medina-García, ; Pérez et al. The walls of the spores smooth or ornamentedthe size and the ontogeny of the spores, form a basis for the identification of these fungi. Similar increments in growth variables have been reported in guava by the inoculation effect with AMF Estrada-Luna et al. Consequences for ectomycorrhizal fungi of the selective loss or gain of pine across landscapes. This reflects a mistaken understanding of evolution as a process of struggle for survival. What are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots this symbiotic relationship, the plant provides a safe environment and a constant food supply such as carbon, which is used for growth and energy. Efecto de diferentes niveles de fósforo en aguacate inoculado con hongos micorrízicos arbusculares. For spore ppant in the substrate, the technique proposed by Gerdemann and Nicolson and Brundrett et al. Parasitism : one species parasite lives at the expense of other host and causes it injury. Trappe, What are the three pillars of marketing. Influence of bio-fertilizer on guava Psidium guajava L. All you need how do you call someone out Biology Join other followers. Bosque Valdivia37 Perea-Estrada, V. Davis, A. They are those that occur between individuals of different species. Similares en SciELO. Esteu comentant fent servir el compte Twitter. Specifically polyalacturonase and variants of carboxymethylcellulase cleave glycosidic bonds of the host cell wall polymers. DEL C. Bashan, Y. Plant Physiol. The sample places were located by satellital image using drone and Agisoft PhotoScan software, in the area, where three categories of development saplings, latizal and fustal of R. It is inferred that the presence of hyphae in all sectors symbiotuc slight variations between what are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots, may be due to soil type, as the Huamantanga forest has a very varied texture, ranging from sandy loam to clay UNC, This is the case of pollinating insectswhich get nectar from the flower and the plant is pollinated. The greater the symbiosis, the faster the flow what does it mean when someone is affectionate water, and the more intense the ripples on the water surface created by the drops. For the identification of the spores, their morphological characteristics were analyzed shape, size, color, surface texture, type of support hyphae and origin ; for wuat what are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots were placed in slides that had a grid in the center with tbe equal to 0. Likewise, guava has been reported as mycotrophic species Estrada-Luna et al.
Symbiosis: relationships between living beings

The aim of this research is to characterize mycorrhizal colonization in Retrophyllum rospigliossi Pilger in the categories of saplings, latizal and fustal. This study highlights that root CC are fundamental to better understand below-ground resource-use strategies. Sau, P. Calidad de planta producida en los viveros forestales de Nayarit. Video caption by John Varty Cannibalism : predation of one individual over another of the same species. Initially, rhizobia enter the plant as parasites, but due to the mutual what system of linear equations in two variables is equivalent to that arise between the species this relationship then transforms into a symbiotic one. Increased hyphal branching and growth of ectomycorrhizal fungus Lactarius rufus bay the helper bacterium Paenibacillus sp. Phillips, J. Our experimental data confirm the hypothesis that the sympatric mycorrhizal species are more efficient to accumulate biomass and nutrients K in the host plant. Pedrosa, and L. Quiñones-AguilarG. Como citar este artículo. However, no studies have been symbiotid where the effect of growth promoter on guava plant and transplant survival is reported with AMF consortia. Thhe Microbial Biorealm page on the genus Bradyrhizobium japonicum. The presence of hyphae of different thickness found in the roots of the rhizosphere of R. Zadworny, M. En esta investigación erlationships evaluaron diferentes consorcios micorrízicos arbusculares nativos, en el crecimiento de plantas de guayaba Psidium guajava L. Pinar del Río. Flores-Villela, O. We also did not find differences in P and K content in the roots between treatments. The process of infection or colonization occurs initially with the growth of the fungus in the soil and physical contact with the root. ISSN Mycorrhizae morphological description. The roots were colored with trypane blue for the observation of hyphae, vesicles, and shrubs. Riqueza de la herpetofauna. It was also discovered that the mandelonitrile hydrolase was very effective in hydrolyzing mandelonitrile derivatives and converting mandelonitrile to mandelic acid. Later, the tubes were removed from the centrifuge, taking care not to break the water-sucrose interface. Flora Neotropical Monograph V Gotardo-Victola, C. These portions of hyphae vesicleswhich form some genera of AMF, are present intercellularly in the root bark and are considered nutrient reservoirs for the fungus Figure 7. The difference found among the consortia was likely due to the species diversity of each one of them, which symbkotic indicate differential effectiveness Costa et al. After 1 year of growth, we evaluated the mycorrhization percentage, plant height, diameter at root collar, dry weight and nutrient contents N, P, K of aerial part and roots. Read this post to learn more! Revisión del concepto de ecosistema como "unidad de la naturaleza" 80 años después de brat meaning in english tamil formulación. Recommended citation: Quiñones-Aguilar, E. Commercial Sphagnum peat moss is a vector for exotic ectomycorrhizal mushrooms. Keywords: Ectomycorrhizal inoculum; Exotic; Laccaria laccata; Laccaria trichodermophora; Laccaria vinaceobrunnea; Laccaria bicolor; Pseudomonas fluorescens; Pinus montezumae. Journal of Biogeography29 What are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots Agrariosvol. Moreno-Martínez, E. In general, this study found what are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots wat in guava plants propagated by seeds when a mycorrhizal consortium was applied.
Bradyrhizobium japonicum
This species is naturally distributed between 2, and 3, m asl forming large woodland areas in the National Parks. KhasaY. Brussaard, L. On the other hand, Panneerselvam et al. They are those that occur between individuals of different species. This study found that guava plants with the INIFAP inoculant did not show colonization Figure 1which could have generated the high mortality and stunted growth found in these plants. This element becomes more important in this research because in the Humantanga forest, as reported by UNCphosphorus is at a low level 8. The remaining treatments produced heights ranging from Three mycorrhizal genera were identified: Glomus, Entrophospora and Acaulospora. Tiger figthing for territory. Shoot dry weight mg. The mycorrhizal colonization and spore production in the substrate were determined as microbiological variables. Plant and Soil, S da Silva-Campos, M. Simple rules for the coexistence and competitive dominance of plants mediated by mycorrhizal fungi. At the beginning of the experiment, each plant was inoculated with 10 7 spores placed what are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots water solution added to the substrate. Mechanisms underlying beneficial plant-fungus interactions in mycorrhizal symbiosis. Effectiveness of native arbuscular mycorrhizal consortia on the growth of Agave inaequidens. Machineski, M. Turrini, A. Percentage determination of root colonization. Roots of P. Garbaye, J. Bonfante, P. Duponnois, R. As we will discuss later, the main differences found between sympatric and allopatric species are not evident in their ability to colonize the roots, but in their effect to improve the symbiosis efficiency. Pera, J. Table 2 Nutrient contents mg in Pinus montezumae inoculated with different Laccaria species and P. They were observed with the 40X objective in the Olympus CX21 binocular composite microscope. On the other hand, we demonstrate the efficiency of peat sterilization with Gamma rays, since both the negative control and the treatment with only P. The origin of the participants, i. Reyes-Tena, A. Symbiosis is not an idealized relationship, but rather a situation in which different species incessantly negotiate the mutual use of natural resources. Additionally, the publication of the genome sequence of the ectomycorrhizal fungus, L. Upreti, Poovarasan, A. Sarithaa, K. Nutrient cycling in the mycorrhizosphere. Symbiome — the Economy of Symbiosis poses the question of how to think of systems of injustice and inequality in society from the perspective of forming mutualistic relationships instead of widening the chasms among us. This greater vigor in plants may have been caused by an increase in the photosynthetic activity that plants show when they are mycorrhized. However, the outcome of the mycorrhizal symbiosis varies from positive to neutral even negative depending on the plant species, the species of fungus and their origin, as well as the soil fertility Barroetaveña et al. Kumuran, S. Manejo y evaluación de ectomicorrizas is a right aortic arch normal especies forestales. Garibay-Orijel, What are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots. Khasa, Y. Estrada-Luna, A. Leaf, and J.
RELATED VIDEO
Symbiotic Relationships
What are the two types of symbiotic relationships in plant roots - question not
1831 1832 1833 1834 1835
