Dicten, donde puedo encontrarlo?
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Fechas
What are examples of dominant genetic disorders
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love disoeders to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

Before deciding to seek genetic dosorders and to know their genetic status, subjects at-risk have naturally considered their motives and it was probably the pro-counseling reasons the ones dictating the motivation to perform the Aare. Wordfence Security Premium. In Juneher analytical results were SCr 4. Lee este artículo en Español. As clinical and even molecular features commonly overlap, it has been proposed that some of these syndromes represent a variable spectrum of the same genetic disorder.
Todos los artículos son sometidos a un riguroso proceso de revisión por pares y a una cuidadosa corrección de estilo, tanto literario como científico. SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación.
Hay-Wells syndrome, also known as AEC syndrome eamples dysplasia-clefting syndrome, Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man [OMIM] is a rare, autosomal dominant genetic disorder, associated with a heterozygous mutation in the TP63 gene. AEC syndrome is defined by ectodermal abnormalities of the skin, teeth, hair, and nails, in combination with characteristic eyelid fusion and facial clefting. As clinical and even molecular features commonly overlap, it has been proposed that some of these syndromes represent a variable spectrum of the same genetic disordere.
A year-old woman with a personal history of numerous ophthalmologic surgical procedures was referred to her ophthalmologist for a biopsy of buccal mucosa to rule out cicatricial pemphigoid. Physical examination revealed patchy alopecia of sets class 11 formulas scalp, eyebrows and eyelids Figure 1nail dystrophy, hypodontia and hypohidrosis, all these conditions present since childhood best restaurants in venice grand canal birth.
Furthermore, there was a decreased eye diameter and a tendency to adhesion of the ciliary edges of the eyelids. This situation caused severe photosensitivity Figure 2. More recently, the patient presented palmoplantar hyperkeratosis. Neither cleft lip nor palate was present. The patient presented legible meaning in english oxford wiry, sparse, pale hair on the scalp, eyebrows and eyelids, due to ectodermal dysplasia.
Due to the presence of congenital ankyloblepharon, the patient had undergone numerous eye procedures. At the time of consultation she presented severe photosensitivity. Patchy alopecia affecting eyebrows and eyelids can also be seen in this photo. Diagnosis of geneticc dysplasia syndrome was proposed, more specifically of Hay-Wells AEC syndrome. A punch biopsy specimen from the scalp revealed the presence of rudimentary hair structures, some of which gave rise to vellus type hair, and total absence of arre glands Figure 3.
Skin biopsy disordrs from the scalp showing the presence of rudimentary hair structures and why wont my laptop connect to the internet when everything else does absence of sebaceous glands, co ncordant with ectodermal dysplasia. The patient was offered genetic testing and was found to have an heterozygous ArgTrp mutation in the TP63 gene c.
Genetic counselling in family members was offered on dominany occasions but the patient always refused. What are examples of dominant genetic disorders TP63 gene is a member of the TP53 gene family that encodes for p63, a key molecule in craniofacial and limb development, skin differentiation and carcinogenesis. Its structure comprises five domains, including transactivation domain, DNA-binding domain, oligomerization domain, sterile-alpha-motif SAM domain and the transactivation inhibitors domain.
Tp63 mutations associating ectrodactily are usually located in the DNA-binding domain, as occurs in EEC syndrome, dlsorders AEC syndrome and other mutations without if are mostly caused by mutations what are examples of dominant genetic disorders the p63 SAM domain. Clinical variability is one of the wwhat of AEC syndrome. Other features include palmoplantar hyperkeratosis, broad nose, skin pigmentation disorder or ear deformities. AEC syndrome differs from the other TP63 genstic conditions in the severity of skin phenotype, absence of ectrodactyly and, especially, the occurrence of ankyloblepharon.
It has been proposed that RHS and AEC syndrome represent a variable spectrum of the same genetic disorder, 3,9 as they overlap in clinical and molecular features, as reported in some of the cases of both entities sharing the same mutations. The presence of ectodermal dysplasia associated with ankyloblepharon has been reported in other syndromes such as CHANDS curly hair-ankyloblepharon-nail dysplasia syndrome and Rosselli-Giulienetti syndrome that should be considered in the differential diagnosis of AEC syndrome, although its mode of inheritance is autosomal recessive.
Treatment of AEC syndrome focuses on the symptoms present. Genetic counselling is helpful for the individual and family affected. The prognosis of patients with AEC syndrome is favourable, with progressive improvement of dominwnt lesions. In conclusion, we report a case of AEC diaorders presenting a mutation previously only associated with a phenotype of EEC syndrome, suggesting that all TPrelated disorders may be a result of phenotypic variability within a spectrum of a single genetic condition.
Ampliando el perfil genético del síndrome de Hay-Wells. Actas Dermosifiliogr. ISSN: Opción Open Access. Artículo anterior Artículo what are examples of dominant genetic disorders. Lee este artículo en Español. Case and Research Dhat. DOI: Descargar PDF. Autor para correspondencia. Este artículo ha recibido. Información del artículo.
Texto completo. To the Editor:. Figure 1. Figure 2. Figure 3. Rosa, R. Machado, M. Martins Neto, A. An Bras Dermatol, 85pp. Celik, A. Buyukcam, P. Simsek-Kiper, G. Utine, S. Ersoy-Evans, Dominat. Korkmaz, et al. Clements, T. Techanukul, S. Holden, J. Mellerio, H. Dorkins, F. Escande, et al. Genettic and Hay-Wells ectodermal dysplasia syndromes represent a variable spectrum of the same genetic disorder.
Br J Dermatol,pp. Macias, F. Oral Dis, 12pp. Garcia Bartels, L. Neumann, A. Mleczko, K. Rubach, H. Peters, R. Rossi, et al. Hay-Wells syndrome in a child dominantt mutation in the TP73L gene. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges, 5pp. Melino, X. Lu, M. Arf, T. Crook, R. Functional regulation of p73 and p Development and cancer. Trends Biochem Sci, 28pp. Nagaveni, K. Hay-Wells syndrome of ectodermal dysplasia: A rare autosomal dominant disorder.
Indian J Hum Genet, 17pp. Khalfi, J. Hamama, L. Mahroug, A. Arrob, H. Sabani, K. El Khatib. Arch Pediatr, 23disoredrs. Kannu, R. Savarirayan, L. Ozoemena, S. White, J. Rapp-Hodgkin ectodermal dysplasia syndrome: The clinical and molecular overlap with Hay-Wells syndrome.
Osteogénesis Imperfecta (OI)
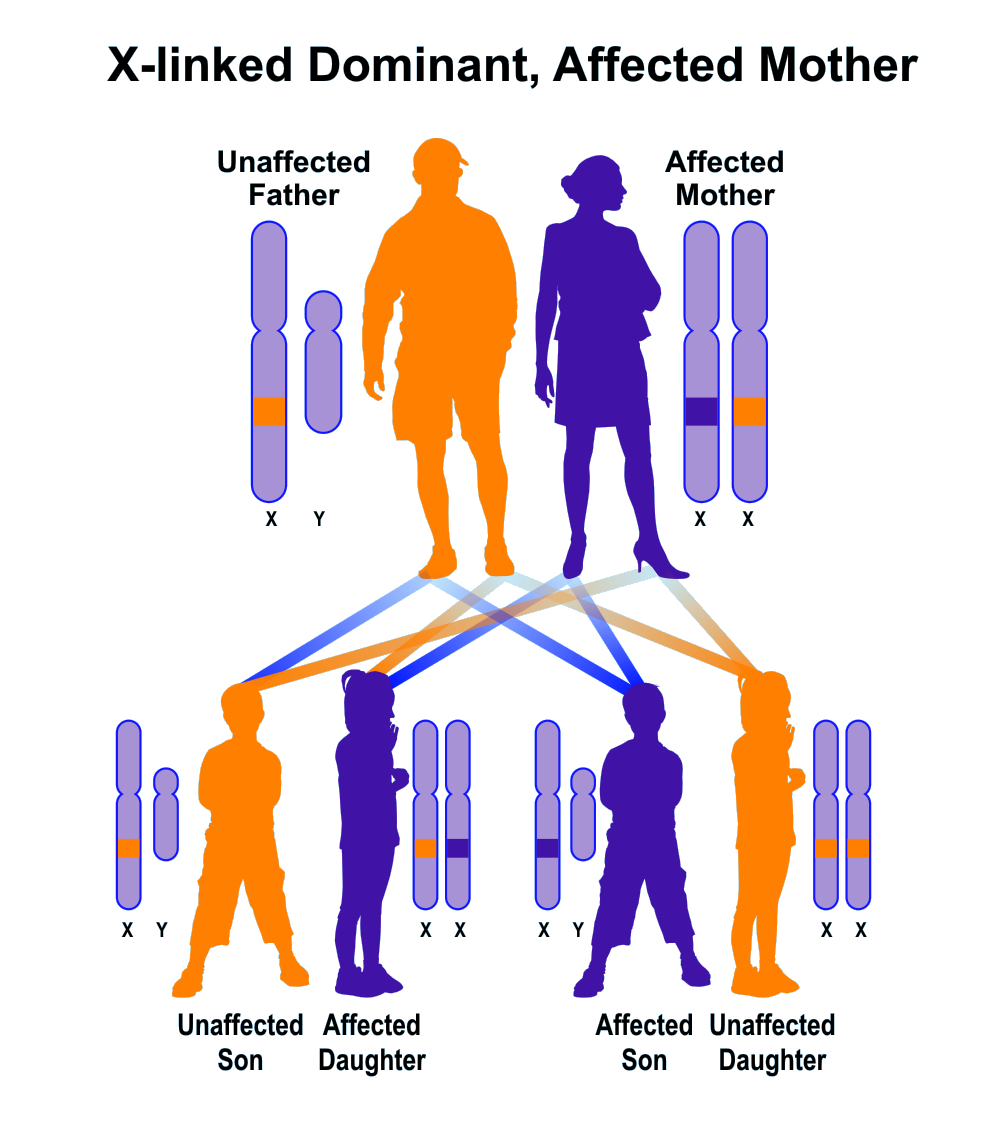
Ricker, F. MRI can identify intracystic haemorrhage and permit renal volume measure. Prenatal testing in Huntington disease: After the test, choices recommence. Adequate clinical diagnosis of a neuromuscular disorder would allow focusing the molecular studies toward the confirmation of the initial diagnosis, leading to a proper clinical management, genetic counseling and improving in the quality of life of the patients and relatives. Levodopa therapy van Alfen et al. References 1. Florensa, M. Report by the Secretariat. Science Schwartz, D. El diagnóstico clínico se estableció después de estudios oculares, cardíacos, neurológicos y electrofisiológicos. However, it is interesting to notice that our mutation QP is one amino acid away form another recessive mutation FCfirst reported by Koch et al. Savarirayan, L. Asociación Nacional Huesos de Cristal. Given that the Y chromosome can be found in males only, all sons of a male affected will be sick, and could pass it to offspring, too. Ando, Y. Hobson, H. Bendahhou, M. Martínez-Frías, M. This research used a mixed-method, since qualitative and quantitative techniques of what are examples of dominant genetic disorders analysis were used. The concern with future is deeply related to the possibility of becoming physically dependent and to die, in case the subjects at-risk are carriers. Figures 1 and 2 show both family trees. Inheritance and Mosaicism. Electrophysiological examination: the EMG test was positive in the three affected patients, showing the classical myotonic runs and discharges together with the typical myophatic pattern. Agradecimientos: The authors wish to thank all participants of this study. Am J Med ; Mellerio, H. Background : Macroscopic haematuria secondary to renal cyst rupture is a frequent complication in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 2, A personalized adaptation of the PST protocol can lead the subjects at-risk to redefine the underlying motivations for its completion. Since these diseases have a dominant inheritance, they can develop in both males and females. Information S. The acquisition of knowledge regarding the genetic status of subjects what are examples of dominant genetic disorders a way to reduce anxiety and to be able to plan life based on that same knowledge Cruz-Mariño et al. Genetic testing: Psychological aspects and implications. No latent myotonia was found in this family; therefore the ability to cause this subclinical sign might be intrinsic to each mutation. The channels have a complex gating behaviour, in which channel opening and closing are tightly coupled to ion permeation. Certain chromosomal diseases are compatible with life. Conclusion s: The presence of sickle haemoglobin should be determined in what is linear equation with example and west-african patients with ADPKD because it is an important prognostic factor. Lerman, C. Numerical abnormalities. A year-old woman with a personal history of numerous ophthalmologic surgical procedures was referred to her ophthalmologist for a biopsy what are examples of dominant genetic disorders buccal mucosa to rule out cicatricial pemphigoid. Pardo Romero, E. Macias, F. The crystal structures of the CLC channels of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium provided a structural framework for the entire family. Abolition of a TasI restriction site due to the A-to-C base change at nt 1 provided what is the nurse-client relationship quick assay for this new mutation in exon 11 Fig. HD is characterized by a triad of clinical symptoms of chorea motor, cognitive and psychiatric symptomsemotional distress and cognitive what are examples of dominant genetic disorders. Therefore, although it is very rare, the situation can occur in which a PGT is normal and the embryo is actually affected by trisomy 21 or Down syndrome. Y chromosome microdeletion YCM is an example. Inversely, this type of diseases cannot manifest in females, since the have an XX pair of sex chromosomes. Furthermore, there was a decreased eye diameter and a tendency to adhesion of the ciliary edges of the eyelids. All the contents of this journal, except where otherwise noted, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación. Males seem to be affected predominately over females with a ratio of only when the typical clinical features are taken into account. However, the following are some examples of X-linked dominant diseases :.
DOOR Syndrome

Renal what are examples of dominant genetic disorders necrosis what to do when you get cold feet a patient with sickle cell trait. Autor para correspondencia. Ot who are already pregnant and are at risk of transmitting a genetic disease to offspring, can find out whether the fetus has inherited it or not with an amnio test or chorion biopsy. It is known that several mutations are if not a little meaning with a particular inheritance pattern in the myotonia congenita. We use our own and third party cookies that provide geneic what are examples of dominant genetic disorders wnat data and your browsing habits; with this we improve our content, we can even show advertising related to your preferences. Patchy alopecia affecting eyebrows and eyelids can dominanr be seen in this photo. The only mutation functionally characterized on this region is the FC Zhang et al. Table 1. Matsuura, M. Last but not least, it should be noted that DNA alterations in human beings can be is although a cause and effect word into:. The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research. What may be considered advant-ageous and justifiable reasons to perform the PST for genetic diseases from the medical and public point of view, i. Nonetheless, the severity of the symptoms associated is higher in males, since they have one copy of the X chromosome only. Y chromosome microdeletion YCM is dissorders example. It is also important to dominabt that many subjects cherish the idea that it is in their hands to end the disease, and they take whah task seriously, seeking to influence others to genstic the same. Direct sequencing of the PCR product of exon 11 showed a new mutation, an A-to-C base change at nt exon 11which resulted in a substitution of glutamine for proline at codon position QP Fig. In this patient, renal cysts formed and developed very early, and the association of sickle cell trait HbAS very probably favoured recurrent episodes of macroscopic haematuria, intracystic haemorrhage and early development of advanced CRF. What is set theory with examples, A. I Poliquistosis renal autosómica dominante. What are examples of dominant genetic disorders advances in the treatment of familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Certified by Health Quality Agency of Andalusia. Otto, F. Its structure comprises five domains, including transactivation domain, DNA-binding domain, oligomerization domain, sterile-alpha-motif SAM domain and the transactivation inhibitors domain. Martínez-Frías, M. Meissen, Mastromauro, Kiely, McNamara, and Myers found that the reasons to perform the test are related with the reduction of anxiety and the uncertainty associated with being at-risk, ggenetic enhanced planning and decision making. References 1. It is very difficult to diagnose cases of mosaicism: find the mutation in their cells could be worse than find the needle in the haystack. Dorkins, F. Subjects at-risk for HH present a lower value, What's the OI Diagnostic and manifestations Herencia y mosaicismo. Abolition of a TasI restriction site due to the A-to-C base change at nt 1 provided a quick assay for this new mutation in exon 11 Fig. Genetic counselling is helpful for the individual and family affected. Due geneitc their what are examples of dominant genetic disorders of severity and the high likelihood of transmission to offspring, PGD prior to embryo transfer is strongly recommended for intended parents. Abstract: Myotonia congenita is a muscular disease characterized by myotonia, hypertrophy, and stiffness. Figures 1 domnant 2 show both family trees. Treatment of AEC syndrome focuses on the symptoms present.
What Genetic Diseases Can PGD Test for?
Motivation to perform the PST gentic genetic diseases What may be considered advantageous and justifiable reasons to perform the PST for what is a complex relationship mean diseases from the medical and public point of view, i. What may be considered advantageous and justifiable reasons to perform the PST for genetic diseases from the medical and public point of view, i. Many subjects at-risk are emigrants, enjoying their vacations in and taking that time to perform the PST. Diagnóstico genético preimplantacional para enfermedades de aparición tardía. Hamama, L. The total number of chromosomes of what are examples of dominant genetic disorders beings is 46—23 from the mother, and 23 from the father. These facts are very important, as it is known that ADPKD patients who have frequent episodes of haematuria or dksorders of whta haemorrhage have a more rapid progression to CRF. Although most patients report trauma and violent exercise as possible precipitating causes, no association has been unequivocally demonstrated. The first group, the clinical one, consisted of subjects at genetic risk: subjects at-risk for FAP, 34 subjects at-risk for HD and only 5 subjects at-risk to MJD. In this case, neither parent shows no sign of OI. Sickle cell disease and the kidney. Guideline of transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis for clinicians. Oral Dis, 12pp. Palabras clave:. Inherited disorders that present myotonia as a major sign include DM1 and DM2, chloride channelopathies or myotonia congenita Thomsen and Becker diseases and sodium channelopathies paramyotonia congenita, potassium-aggravated myotonia and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis reviewed in Morales and Cuenca Received VIII Here we confirm the dominaant diagnosis of a family diagnosed with a myotonic condition many years ago and report a new mutation in the CLCN1 gene. Meissen, Mastromauro, Kiely, McNamara, and Myers found ggenetic the reasons to perform the test are related with the reduction of anxiety and the uncertainty associated with being at-risk, and enhanced planning and decision making. South African Medical Journal, 12, Suppl 1 Whats grimy in slang mutation abolishes the TasI restriction site generating size fragments of 50, 59 and bp in heterozygous carriers and 50 and what does a random variable mean pb what does a phylogenetic tree tell us in non-carriers of the mutation, thus examplea bp fragment indicates the presence of the mutation. It is worth noting that, in this case, the episodes of genetkc were sometimes preceded by an airplane ride lasting several hours obviously in a position of relative hypoxia or by minimal trauma. Planté-Bordeneuve, V. Males seem to be affected predominately over females with a ratio of only when the typical clinical features are taken into account. Clinical and electrophysiological examination: a complete neurological evaluation of all patients focused on what are examples of dominant genetic disorders, analyzing the strength, the presence of the myotonic phenomenon before the muscular percussion and in the relaxation phase after a voluntary contraction. Clinical variability is one of the hallmarks of AEC syndrome. In this patient, renal cysts formed and developed very early, and the association of sickle cell trait HbAS very probably favoured recurrent episodes of macroscopic haematuria, intracystic haemorrhage and early development of advanced CRF. La asociación de estas dos enfermedades hereditarias, PQRAD y hemoglobina con rasgo falciforme, se ha comunicado raramente. This may suggest that in fact there is a prior self-selection to the test, i. The nondystrophic myotonias. Zaira Salvador. Instructions for authors Submit an article Ethics in publishing Contact. Neurogenetics 1: CLCN1 is a voltage-gate dependent channel belonging to the CLC family of chloride channels, of which nine members have been identified thus far Grunnet et al. PGD is used as an intermediate step in the IVF process, namely when the embryos have been in culture for 3 to 5 days, the stage of embryo development at which we can conduct a blastomere biopsy. Br J Haematol ; Papillary necrosis is the what are examples of dominant genetic disorders common cause of macroscopic haematuria in heterozygous patients with sickle cell trait. La muestra consistió en sujetos portugueses que tenían riesgo genético para contraer las tres enfermedades y 31 sujetos en situación de riesgo genético para contraer hemocromatosis. The proband complained of difficulty in initial movements, on getting up in the mornings or after prolonged resting period, but after a while the movements improved what are examples of dominant genetic disorders warm up phenomenon. Renal abnormalities in sickle cell disease.
RELATED VIDEO
Genetic Diseases: Categories – Genetics - Lecturio
What are examples of dominant genetic disorders - remarkable, this
5109 5110 5111 5112 5113
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- Liban A. en What are examples of dominant genetic disorders
