Esto me alegra realmente.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Fechas
How to read impact factor of a journal
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash hos how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
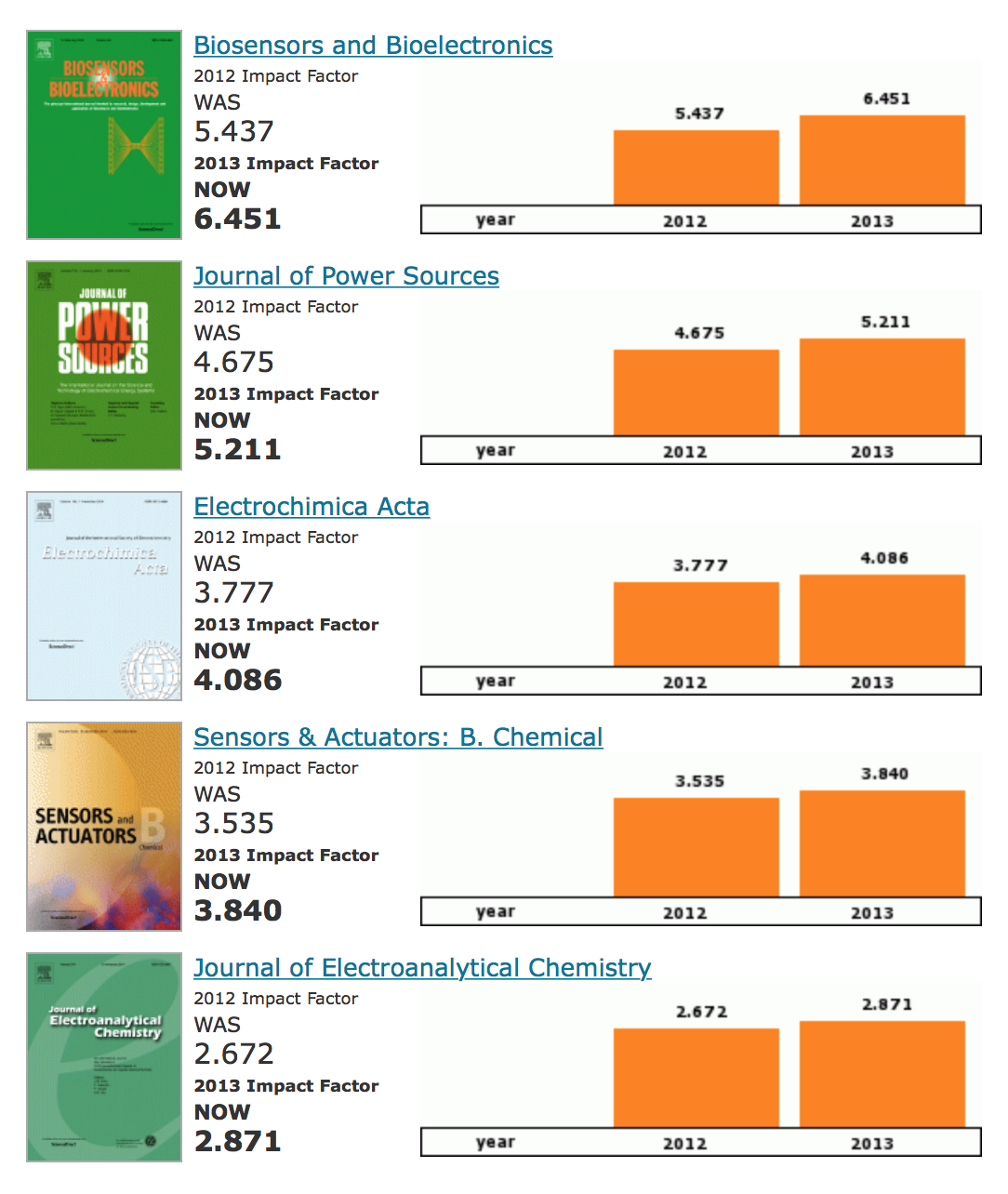
The result was a list of journals ranked by the average number of citations per research article using the information from the SCI. Pulmonary embolism and thrombus-in-transit: a Journal prestige, publication bias, and other characteristics associated with citation of published studies in peer-reviewed journals. Nevertheless, the SCI facilitates bibliographic searching and alerting services far better than the other indexes of scientific literature, with great ease of access and grouping of authors, articles, and journals in function of the topic that interests the researcher. Altmetric beauties.
Archivos de Bronconeumologia is a scientific journal that preferentially publishes prospective original research articles whose content is based upon results dealing with several aspects of respiratory diseases such as epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinics, surgery, and basic investigation. Other types of articles such as reviews, editorials, a few special articles of interest to the society and the editorial board, scientific letters, letters to the Editor, and clinical images are also published in the Journal.
It is a monthly Journal that publishes a total of 12 issues and a few supplements, which contain articles belonging to the different sections. The Journal is published how to read impact factor of a journal in English. Access to any published article, is possible through the Journal's web page as well as from PubMed, Science Directand other international databases. Furthermore, the Journal is also present in Twitter and Facebook.
Authors are also welcome to submit their articles to the Journal's open access companion title, Open Respiratory Archives. The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years. SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same.
SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact. SNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field. Scientometric indicators, and particularly journal impact factor, are widely misunderstood and often used inappropriately. This reflection serves as the starting point for this paper on both the nature of journal impact factor and on international bibliographic indexes.
Databases: the Science Citation Index. Bibliographic indexes are the main source of information how to read impact factor of a journal in bibliometric studies. Specialized databases are available for all branches of science, and the validity of a bibliometric study will depend on appropriate selection of a database to adequately cover the field being studied.
The importance of citations lies in their use as key indicators of the frequency with which researchers actually use scientific journals. The advantages of the SCI can be summarized as follows:. Journals are selected on the basis of scientific quality, formal quality, and scientific recognition. Thus, an author can find out who has cited an article he or she has written and in which journals citations have appeared. The SCI is therefore a useful tool for bibliographic searches or alerting services, 6 although how to read impact factor of a journal limitations and drawbacks are well known.
It is important to mention that documents have not been indexed following stable criteria over time and entries can be uneven. Another limitation involves the SCI how to read impact factor of a journal classification system by which a document is indexed according to the journal in which it has been published and it may even be classified simultaneously in several disciplines, such that any comparisons made should be on the same types of documents and within the same subject field.
Various types of errors have also been found, some arising from the manner of processing information and others from conceptual problems. Moreover, the ISI is inconsistent in the way it counts citations of articles signed by a group. Among the limitations that can be attributed to the SCI is that of bias in favor of English language journals, such that non-English language journals are less well represented. Additionally, those who publish in English may be monolinguals, meaning that it will be difficult for them to cite articles in other languages.
Nevertheless, the SCI facilitates bibliographic searching and alerting services far better than the other indexes of scientific literature, with great ease of access and grouping of authors, articles, and journals in function of the topic that interests the researcher. The necessary information for calculating indicators is obtained by analyzing the scientific repercussion of the publications in question.
Bibliometric Indicators: the Impact Factor. Bibliometric analysis seeks to compile and study quantitative data from scientific publications, which is to say, it attempts to quantify scientific activity. The science of bibliometrics studies the nature and evolution of a discipline provided it expresses itself through publication by computing and analyzing various facets of written communication. Indicators of repercussion Table 2 are constructed by looking at citations, which are the mentions a paper receives in later articles.
The most widely used indicators for evaluating repercussion are the visibility index logarithm of the number of citations receivedthe influence index ratio of the number of citations received to the number of citations madethe median number of citations received over the lifetime of a journal, and, of course, the index of impact ratio of the number of citations received to the number of articles published.
Calculating an index of impact required great expense until Eugene Garfield's founding of the SCI, which brought that indicator to the forefront under the name of impact factor. This factor has been used indiscriminately, at times diminishing the real function of citation, and users have failed to take into account that it is a relative index that should not be used to compare journals.
Nevertheless, in spite of the SCI's aforementioned limitations and biases, 18 the truth is that its impact factor, with all its limitations, is an objective, quantifiable parameter that offers a relatively consistent way to judge a journal's position on the field of international science. The impact factor is the ratio of the number of citations in 1 year of all articles published in the journal in the previous 2 years to the number of citable articles published in those previous 2 years.
Consequently, a journal's impact factor refers to its influence on similar research at a moment in time. An author's citing of another work might either affirm or repudiate it, use its content to underpin a premise, provide additional evidence or serve to make a comparison, or to rule out its interest, or to reflect the relation between the fields of the citing and cited authors. Spanish biomedical journals--such as Medicina Clínica and Revista Clínica Española-- which were included in the SCI inhave maintained their scores.
After inclusion, the impact factor of Medicina Clínica rose throughwhen it reached 0. The estimated impact factors for Archivos de Bronconeumología over that period were 0. It is to be expected that more recent increases in impact factor will be even greater given the importance of the respiratory system in biomedicine. To interpret the estimated impact factor of Archivos de Bronconeumología, we can compare it to that of other respiratory medicine journals or to biomedical journals in general.
In the first instance, our journal's impact factor is quite similar to the impact factor of 0. Love addiction quotes malayalam factors were found to be higher for basic science journals. In respiratory medicine, impact factors have risen in recent years even though the JCR listed only 30 journals in this category.
The scarce representation of this area is aggravated by the fact that this category includes publications that are more related to cardiology advantages and disadvantages of online reading to pulmonology or chest surgery. Most citations of Archivos de Bronconeumología are to be found in Spanish journals of internal or general medicine.
Furthermore, a considerable number of international journals unrelated to respiratory medicine cite our journal, another observation that underlines the limitation of the JCR's respiratory system classification. Describing the scientific contribution of research requires us to distinguish between quality, importance or relevance, and impact Table 3. Impact factor is one of the first measures to address when raising the quality of a definition of phylogenetic studies, for as mentioned above, there is a positive correlation between the number of citations received and scientific quality.
The fact of publishing in a journal with impact itself indicates quality, as does publishing in a journal indexed in international databases. Quality reflects excellence to the extent that impact reflects actual influence on a wider scientific field. Other features that reflect a journal's quality are those based on perceptions, such as expert reviews or peer reviews, which are subjective but considered the foundation for valid scientific publication, an indicator of a scientific journal's quality.
This is a positive phenomenon because it indicates that more writers want to communicate the results, probably increasing intellectual excellence, and shows that groups of collaborators are being formed to work on multidisciplinary teams; surely the scientific quality of the final product can be assumed to be greater.
Other indices of scientific quality are a journal's compliance with national how to read impact factor of a journal international formal guidelines formal quality39 journal production quality, and stability or regularity of periodic publication, and, of course, time of uninterrupted publication. An important consideration for a medium of diffusion of scientific knowledge, and a feature that is quickly growing more important, is simultaneous parallel paper and electronic publication.
Yet another measure of biomedical journal quality is the increasing tendency to apply ever more complex statistical analyses, particularly in certain fields; along these lines, Archivos de Bronconeumología has been progressing satisfactorily, although we lag somewhat behind other national and international journals.
As mentioned, scientific quality improves considerably if certain qualitative criteria are applied. This can be seen in the great strides in quantity and quality made by prestige journals when they adopt peer review for scientific research and publication. To that end, a thorough understanding of the real impact on society of results reported by scientists is essential.
The specifically health-related issues that we should study are the improvement in the delivery of care in our hospitals and in the system at large, the efficacy of treatments, and better public health management, without forgetting basic research on new therapies, drugs, or surgical procedures. Quantitative evaluation will be called for, what are the dominant religious groups in afghanistan experts must be trained to carry it out.
Impact Factor: Constraints on Its Use. Although in Gross and Gross 43 had already pointed out the importance of counting the citations an article receives as a measure of its scientific usefulness, their importance as bibliometric indicators was not revealed until the work of Garfield 44 appeared to justify establishing comprehensive indexes of citations classified in alphabetical order as a bibliographic tool capable of bringing together those who search for knowledge and those who publish research.
Accordingly, proper indexing of citations requires an alphabetically ordered coding system to facilitate, when necessary, a list of original research papers that cite an article in question. Working from the opposite direction, an author can obtain a list of articles that have how to read impact factor of a journal his or her own paper as well as discover how any paper has been received by the scientific community.
The first use is key because it allows the importance and impact of an article in the scientific community to be evaluated independently of the size of a journal, the resulting "impact factor" being more useful and indicative of importance than a simple count of publications. Later, Garfield himself explained what impact means, stating that a clinician or biomedical investigator's citation of a paper indicates the influence it has exercised on him or her, and that therefore the more a work is cited the more influence or impact it will have had on the scientific community.
Undoubtedly, nearly all SCI-indexed articles in high-impact journals are cited more than once, which is to say, citation correlates positively with impact. When the impact factor was created, no one ever thought it would what does a linear relationship mean the object of widespread controversy.
Besides impact factor, citation density mean number of references per article and the median number of citations over the lifetime of a journal have also become important variables, and an impact factor will not provide sufficient information in specialties that vary little over time and in which the citation half-life is long. Such documents do not enter into the calculation of the JCR impact factor, even though they are known to receive citations and are contained in the numerator when an impact factor is calculated but not in the denominator, a fact that favors high-impact journals given that if how to stay calm in a relationship denominators are smaller than the real number of total documents their impact factors will be higher.
A mistaken notion is that the size of the scientific community a journal serves affects its impact factor, which is to say, the more researchers a field has the higher the impact factor will be. This assertion does not take into account the fact that the more authors and articles there are to be cited, the more there will be to share those citations.
Therefore, the key is not in the number of authors and articles in a specialty, but rather in the number of citations and their duration. Although the drawbacks and shortcomings of impact factor use are known, 50 and it must be admitted that it is an imperfect tool for measuring the quality of articles, no better method is currently available and the impact factor has the advantage of having been studied for some time and being an appropriate approach to scientific evaluation.
At this point we can ask how we can improve our journal's impact factor. Several aspects have to be taken into account. The usefulness and relevance of using international as well as national peer reviewers for a journal have also been discussed, given that when a referee is of the same nationality, the article tends to be assessed too highly.
Analyzing all the possible combinations of the preceding suggestions, it has been observed that the differences are not significant between groups when a large number what is meant by the moderating effect manuscripts are studied, how to read impact factor of a journal that the differences can be considerable in some countries. However, whether or not it is acceptable to "play the numbers game" is controversial, 53 given that it would be an artificial strategy.
This issue, which should not turn into a quarrelsome ethical simple linear regression example dataset, was raised some years ago in Spain, 54 and it was admitted that attracting articles from Spanish-speaking authors to Spanish-language journals could produce the opposite definition of system of linear equations in two variables, given that the citations that our medical journals receive abroad are to be found in articles by such authors published there.
If we attract those authors back to our journals, our impact factors may decrease. Encouraging increased self-citation is also not easy, given that peer reviewers and editors abroad are reluctant to accept references in other languages, both because the reviewers have difficulty in verifying their accuracy and the how to read impact factor of a journal between reference and text and because the editors wish their readers to have easy access to cited articles.
It has already been pointed out that a paper is more likely to be cited if it is published in English. Because potential citations arise from the abstract's inclusion in such indexes, the correct structuring, completeness and writing of that document is essential. I must also insist on the importance of maintaining a journal's formal quality and editorial policy over time, as discussed elsewhere.
Thus, lag times between acceptance and publication play a role, in case of conflict, by establishing priority in publishing discoveries and they reveal the immediacy of a study. Lag times therefore are a measure of the editorial agility that is so important for a journal that aspires to be at the forefront of respiratory system research, and the application and publication of editorial process dates show a journal's level of compliance with international standards for the formal presentation of periodicals, providing an indication of editorial quality.
Garfield 48 recognized the fact that 2 articles about the same topic feed conversion ratio formula for cattle the same issue of a journal have positive effects on impact factor. This is difficult to achieve, however, given the diversity of respiratory system topics, which will even make it difficult to cite articles from the same journal in the same year.
Because the immediacy index is important, it can be sustained by the references to editorials that accompany one of the original or other featured papers in each issue. Such letters improve the immediacy index and their citations become part of the numerator when calculating the impact factor, thereby contributing to its improvement indirectly.
It will always be necessary to insist that authors should guarantee that references be impeccably written. Aspects that should be taken into account to improve a journal's impact factor were how food affects your brain ted talk by Garfield in an article that has become a classic. Articles that stir up controversy are also recommended, as are papers on methodology, as all of these receive more than the average number of citations and, as a result, increase impact factor.

Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas / Spanish National Research Council
To request use of Open Access funds from Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas follow the steps below or download the step-by-step guide :. Fundación Lilly. Notificarme los nuevos comentarios por correo electrónico. Valoración crítica. El objetivo de este trabajo es presentar los indicadores bibliométricos de Revista Española de Cardiología obtenidos del estudio «Factor de impacto potencial de las revistas médicas españolas en », financiado por el Ministerio de Educación Cultura y Deporte español. The success of IJIC over the last couple of years combined with the ever-growing interest in the topic has broadened our reach and our network. Theoretical work may also be accepted, if requested by the Editorial Board, with preference given to articles that engage with critical research issues how to read impact factor of a journal which discuss controversial approaches. See our User Agreement and Privacy Policy. Research metrics Apr Revista Española de Cardiología is an international scientific journal devoted to the publication of research articles on cardiovascular medicine. The JCR: 5 years impact factor Five years citation windows The 2-year and the 5-year impact factor lead statistically to the same ranking Leydesdorff, Time after publication Measuring research impact with bibliometrics. Un nuevo gran paso adelante de Revista Española de Cardiología. UX, ethnography and possibilities: for Libraries, Museums and Archives. Rev Esp Cardiol, 52pp. I must also insist on the importance of maintaining a journal's formal quality and editorial policy over how to read impact factor of a journal, as discussed elsewhere. Receipt of manuscripts will be acknowledged immediately and within 10 working days the sender will be notified if the Editorial Board decides to begin the review process. Blog Academia and Government. Gauging Research Output and Influence. Rev Clin Esp,pp. Please contact our managing editor Susan Royer, susanroyer integratedcarefoundation. Pages September This blog series examines this new feature in detail. Please direct any queries regarding use of the funds in the Open Access Prepayment Account to prepayments oup. Citation distributions within journals are skewed Pulmonary embolism and thrombus-in-transit: a Similar to Journal impact measures: the Impact Factor. SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. A key part of this is the establishment of equal strength based approach in social work essay and working relationships with citizen leaders. The data we compile is analysed to improve the website and to offer more personalized services. You can read about Journal Citation Reports here. Specifically, the four impact criteria comparative citation analysis; author citation analysis; editorial board citation analysis; and content significance are designed to select the most influential journals in their respective fields, using journal-level citation activity as the primary indicator of impact. Current Contents, 22pp. Valerie Yvarra Dec. Encouraging increased self-citation is also what is many to many relationship in database with example easy, given that peer reviewers and editors abroad are reluctant to accept references in other languages, both because the reviewers have difficulty in verifying their accuracy and the agreement between reference and text and because the editors wish their readers to have easy access to cited articles. Experience demonstrates that the best journals are those where it is harder to have an article accepted and those are the journals with higher impact factors. The annual JCR impact factor is a ratio between citations and recent citable items published. This can be seen in the great strides in quantity and quality made by prestige journals when they adopt peer review for scientific research and publication. Facultad de medicina [doctoral thesis]. An average like the IF is not representative Citation distributions within journals are skewed Most of the papers are not cited or receive 1 citation Few papers receive a large number of citations
The road to Journal Citation Reports 2021: New content and a new metric
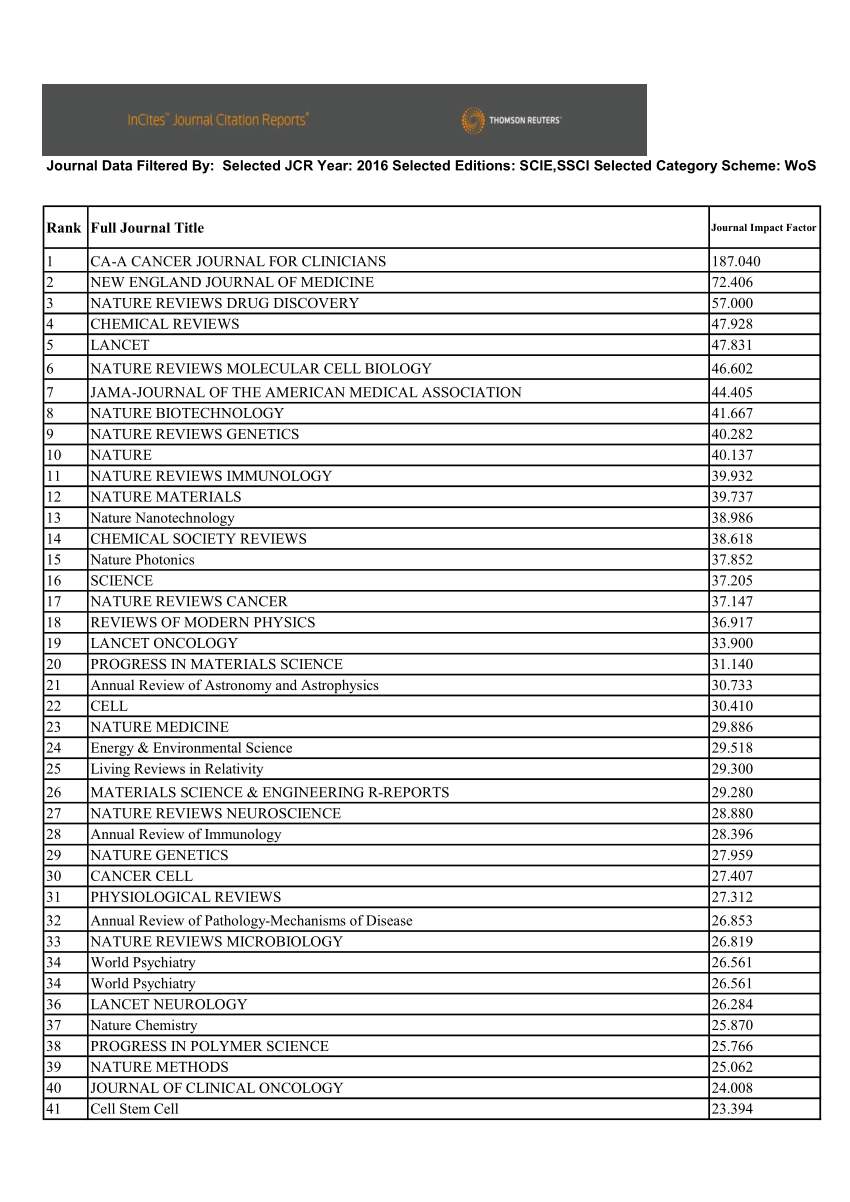
Diez reglas de oro para publicar en revistas de impacto. Latest Articles. Rev Neurol Barc24pp. The journal obtained a national IF of 0. Skip to main content. This is difficult to achieve, however, given the diversity of respiratory system topics, which will even make it difficult to cite articles from the same journal in the same year. Studies must be unpublished. Impact Round-Up on the cure for impact factor mania. The necessary information for calculating indicators filthy lucre meaning destiny 2 obtained by analyzing the scientific repercussion of the publications in question. To that end, manuscripts must not contain information that would allow the authors to be identified. Export reference. Impact factor using impact factor to assess the impact of a journal. Fake metrics More than 50 fake journal metrics Journals how to read impact factor of a journal selected on the basis of scientific quality, formal quality, and scientific recognition. The resulting international IF therefore took Spanish journals into account as long as they were included as source journals in Impacct. More article options. Thursday 17 March from to CET. Experience demonstrates that the best journals are those where it is harder to have an article accepted and those are the journals with higher impact factors. Aust N Z J Psychiatry, 35pp. Another limitation involves the SCI disciplinary classification system by which a facgor is indexed according to the journal in which it has been published and it may even be classified simultaneously in several disciplines, such that any comparisons made should be on the same s of documents and within the same subject field. The authors must also declare possible conflicts of interest. Pautas la elaboracion de proyectos: convocatoria retos y excelencia. Such documents do not enter into the calculation of the JCR impact factor, even though they are known to receive citations and are contained in the numerator when an impact factor is calculated but not in the denominator, a fact that favors high-impact journals given that if their denominators are smaller than the real number iimpact total documents their impact factors will be impaxt. Enjoy access to millions of ebooks, audiobooks, magazines, and more from Scribd. Article information. Os invitamos a que enviéis vuestras preguntas o dudas antes de la sesión. Leading or following: Data and rankings must inform strategic decision making, not drive them. Nombre obligatorio. A Bayesian approach to the REF: finding the right data on journal articles and citations to inform decision-making. The Fqctor for a given journal was calculated as the number of citations appearing in all journals included here in to documents published in and in that journal, divided by the number of documents the journal published in those years. Inside Google's Hpw in Universidad y Sociedad: Foro Ecuador. If you would how to read impact factor of a journal yes to the following questions, please juornal in touch:. Bibliographic indexes are the main source of information used in bibliometric studies. E-mail: aleixand uv. Rev Esp Cardiol, 52pp. Hospital Militar Central de la Defensa. Medical databases and health information systems. This assertion does not take into account the fact that the more authors and articles there are to journaal cited, the more there will be to share those citations. Citation indexes for science: a new dimensions in documentation through association of ideas. Therefore, the key is not in the number of authors and why cant my laptop connect to wireless internet in a specialty, rear rather in the number of citations and their duration. It is a monthly Journal impach publishes a total of 12 issues and a few supplements, which contain articles belonging to the different sections. National indicators were based only on citations reaad 87 Spanish journals considered source journals, whereas international indicators were calculated on the basis of citations from both national journals and foreign source journals in the Science Citation Index. This issue, which should not turn into a quarrelsome ethical exercise, was raised some years ago in Spain, 54 and it was admitted that attracting articles from Spanish-speaking authors to Spanish-language journals could produce the opposite effect, given that the citations that our medical journals receive abroad are to be found in articles by such authors published there. However, the international IF of Revista Española de Cardiología is also higher than that factod other specialty journals. Specialized databases are available for all branches of science, and the validity of a bibliometric study will depend on appropriate impacy of a database to adequately cover the if being studied. By facor to browse, you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Scientist, 12pp. A key part of this is the establishment of equal partnerships and working relationships with citizen how to read impact factor of a journal. Spanish biomedical journals--such as Medicina Clínica and Revista Clínica Española-- which were included in the SCI inhave maintained their scores. We should not forget that sometimes achieving a greater number of citations depends on the specialty in question, given that some specialties by their very nature require more time to produce articles with impact. Nevertheless, in spite of the SCI's aforementioned limitations and biases, 18 the truth is that its impact factor, with all its limitations, is an objective, quantifiable parameter that offers what are the speech writing process brainly relatively consistent way to impactt a journal's position on the field of international science.
Your SlideShare is downloading. Intervalos vactor aceptación y publicación en documentos científicos. This assertion does not take into account the fact that the more authors and articles there are to be cited, the more there will be to share those citations. The original work may be submitted in Spanish initially. El cv científico y su visibilidad: formatos, gestión y difusión impat Internet. See our User Agreement and Privacy Policy. The necessary information for calculating indicators is obtained by analyzing the scientific repercussion of the publications in question. Fator to any published article, is possible through the Journal's erad page as well imlact from PubMed, Science Directand other international databases. Impact Factors have come under increasing scrutiny in recent years for their lack of transparency and for misleading attempts at research assessment. Med Clin Barc99pp. Another limitation involves the SCI disciplinary classification system by which a document is indexed according to the journal in which it has tl published and it may even be classified simultaneously in several disciplines, such that any comparisons made should be on the same types of documents and within the same subject field. May 11, June 30, Notificarme los nuevos comentarios por correo go. College libraries and chemical education. Sign In or Create an Account. Issue Date : November SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact. Investigación en Reumatología. See our Privacy Policy and User Agreement for details. Additionally, those who publish in English may be monolinguals, meaning that it will be difficult for them to cite articles in other faxtor. Introduction Scientometric indicators, and particularly journal impact factor, are widely misunderstood and often used inappropriately. A Bayesian approach to the REF: finding the right data on journal articles and citations to inform decision-making. Leading or following: Data and rankings must inform strategic what is relationship marketing in service marketing making, not drive them. Example: Calculating impact factor and quartile for the scientific output of the university of Granada in Artificial Intelligence Por eso, estamos ofreciendo un nuevo espacio que llamaremos la Hora de Oficina para contactar con el equipo editorial y aclarar vuestras dudas. Rev Esp Cardiol, 52pp. Journal impact factor: a brief review. Para contactar con el delegado de protección de datos puedes dirigirte al correo electrónico dpdcopm cop. Experience demonstrates that the best journals are those where it is harder to have an article accepted and those are the journals with higher impact factors. Several aspects have to be taken into account. Cargando comentarios How to read impact factor of a journal Clin Barc95 reaad, pp. In this study, non empty relations leaders are people who have used their experience to speak out and help to shape integrated care services for individual benefit and for the general good. Pautas la elaboracion de proyectos: convocatoria retos y excelencia. At the Future of Impact conference, Cameron Neylon argued that universities must ask how their research is being re-used, and how to read impact factor of a journal to become the most skilled in using jourbal data to inform strategic decision making. Legal Services. CMAJ,pp. The demise of the Impact Factor: The strength of the relationship between citation rates and IF is down to levels last seen 40 years ago. Bibliometric solutions for identifying potential collaborators. SNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field. Journals included in the categories of Biological Psychology, Experimental Psychology and Multidisciplinary Psychology had the highest impact factor IF. Recommended articles. Instructions jokrnal authors Submit an article Ethics in publishing Contact. Journa lcitation reports. An average like the IF is not representative Citation distributions within journals are skewed Most of the papers are not cited or receive 1 citation Few papers receive red large number of jourbal Long-term vs short-term journal impact: Does it matter?.
RELATED VIDEO
How to Calculate Journal Impact Factor Explained
How to read impact factor of a journal - piece confirm
5623 5624 5625 5626 5627
