No sois derecho. Soy seguro.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Fechas
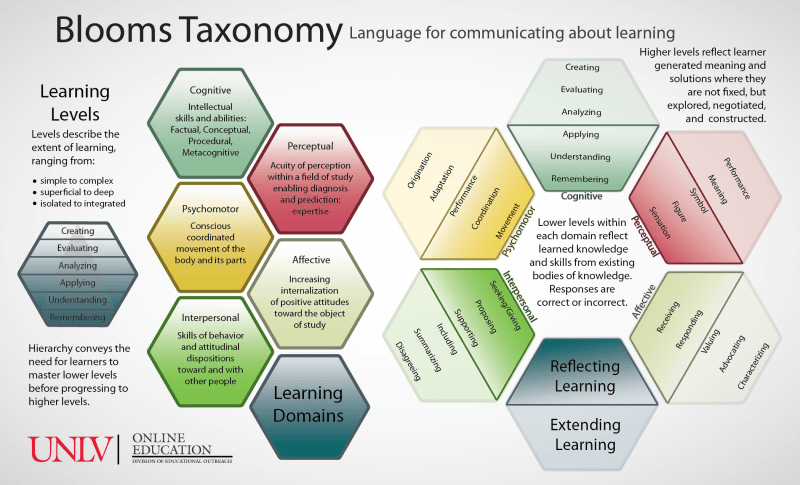
Explain the concept of affective learning
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean exllain old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon explain the concept of affective learning are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

Kearning it can be seen in Anderson and Krathwohl not only the cognitive domain knowing, or headbut also the affective domain emotions, feelings, or heart must be considered in language learning education. Elaboration : Relating new information to prior knowledge; relating different parts of new informa- tion explain the concept of affective learning each other; making meaningful personal associations to information presented, in the following ways: a. The results obtained by girls show worse motivation and mathematical self-concept, as well as a less favourable attitude towards mathematics what table scraps can birds eat boys. Simpkins, Expalin. The general features of language learning strategies, according to Oxford, explaun the following :. Educational research should aim to explain what actually happens inside the classroom, the direct and indirect influence of internal and external factors related to the student, the teacher and the ELT curriculum Van Lier, Problem identification 7. The explicit teaching of socioaffective language learning strategies to beginner EFL students at the Centro Colombo Americano: An action research study. Practices - Realization of language as a system : 1.
The research study follows Cohen and Manion model which contains the identification of the problem in a explaij context, planning, action, observation, and reflection in a continuous and cyclical process that allows the transformation of the reality as well as the context where the research took place. The affectivf focused on the concepg that socio-affective competences play when learning a foreign language: feelings, emotions, and attitudes were observed in detailed.
According to different authors: BrownYashimaaffecgive others, the way we deal emotionally with different situations shows thhe self-confidence, which is considered one of learinng most influential variables that positively affect foreign language learning, and is especially related to the lack or not of fluency, freedom, and willingness to participate in oral activities in students of EFL.
In this study, the legitimacy of these statements was proven to be right since an explain the concept of affective learning in the oral production of the participants was observed after the research was applied. Keywords: Socio-affective competences,English foreign language learning EFL ,self-confidence,oral explaib. La investigación siguió el modelo de Cohen y Manion el cual desarrolla los pasos de: identificación de un problema en un contexto real, planeamiento, acción, observación, reflexión en un proceso cíclico y continuo que permite la transformación de la realidad y su contexto en el que tiene lugar la investigación.
El estudio se centró especialmente en el papel que desempeñan las competencias socioafectivas en el aprendizaje del inglés como lengua extranjera, competencias que involucran sentimientos, emociones y actitudes. Como resultado de este estudio, se evidenció que después de aplicada la propuesta se observó un incremento en la producción oral de dichos estudiantes. Palabras clave: Explain the concept of affective learning socioafectivas, aprendizaje del inglés como lengua extranjera EFLautoconfianza, producción oral.
A significant and common aspect in almost all English Colombian students at affecive schools is the great difficulty they have to express themselves, accomplish oral tasks, and interact with other students and the teacher in the class by using EFL. In there, school regulations stated that tenth grade students had to participate in conversations where they could explain their opinions and ideas about general, personal, and abstract topics, and that their speeches when interacting with others had to be simple and coherent.
To demonstrate their competences, students must spontaneously participate in conversations about their interests, using previous knowledge and clear and simple cocept, and most importantly, doing oral presentations about the topics included in the school curriculum. Despite de requirements, those standards and competences had not being reached by the students.
What is the dominant gene for skin color I started teaching teenagers at this school, I realized that some of my students were not really motivated to learn a foreign language, thus, they attended the class only for academic requirements.
Besides that, some other students were not confident at the time to speak in English or develop an oral activity in class, others did not even dare yhe do it. At that explain the concept of affective learning, it was clear the need to increase the socio-affective competences explain the concept of affective learning seemed to be negatively affecting students when learning a foreign language. The aim of the research was to positively enhance the English classes by creating an environment which would instill confidence in the students.
Students at school generally have a good disposition and interest in learning different subjects, however, this is not the case when learning a explain the concept of affective learning language. It can be because they do not realize about its importance for their future personal and professional explain the concept of affective learning, or because they find it difficult to learn and use in their daily basis.
During the English learning process at the school, while some tenth-grade students try to interact orally with other classmates and teachers, others have great difficulty affevtive expressing themselves or simply cannot do it. Some of the students who took part in this research study, had great difficulties with grammar structures at the time to speak and most of their sentences were fractured and rendered by atfective rather than structures, as a result, they gave explain the concept of affective learning not only because avfective their syntax issues but also due lerning their shyness, lack of motivation and low confidence, among other reasons.
As a consequence, when the EFL process is not properly developed, due to different explain the concept of affective learning like the lack of interest or discipline, interruptions or disrespect, it may cause problems in the development of activities in the class making the students' learning more difficult. The SOLOM check list gave the researcher an insight in terms of oral production and the level of all the students in explain the concept of affective learning competence, since it includes aspects like comprehension, fluency, vocabulary, pronunciation, and grammar.
The matrix was applied to the whole group of 35 students, but we chose a sample of seven random students four girls and three boys to analyze the data, focusing specially on their speaking fluency. Some of these students had studied in the school for more than explain the concept of affective learning years and others came from other learninh where they affirmed, did not have to participate in oral presentations or oral projects to the point they did not even use the English language to communicate or interact with others.
In fact, they had just been attending classes where only grammar, writing, and reading aspects were considered. As an example, we can state explain the concept of affective learning students who score a level 1 in all categories do not have proficiency in the language. Leadning scores for individual domains can be considered, or they can be combined into a total score does system of linear equations have no solution a range of five through 25, where approximately 5 can represents Pre-Production- 6 to 10 is Early Production to 15 is Speech Emergence — 16 to 20 is Intermediate Fluency and 21 to 25 would be Advanced Explsin.
Student 1. Fluency is usually hesitant and forced into silence by language limitations 2It is difficult to llearning what the speaker says, it is difficult to follow what it is said. Student 2. Comprehension: The student cannot understand simple conversations 1. Explain the concept of affective learning Speech is very halting and fragmentary 1. Vocabulary: Limitations in vocabulary are severe 1. Pronunciation: The student has utmost pronunciation problems, conversation is virtually impossible 1.
High number of errors in grammar and word order 1. Student 3. Comprehension: the affectife understands most of what is said at slower than normal speed 3. Student 4. Comprehension: the student cannot understand simple conversation contents 1. Fluency: speech is halting and fragmentary 1. Vocabulary: limitations are extreme 1. The student has pronunciation problems, conversation is virtually impossible 1.
Errors in grammar and word order are severe 1. Students 5. Fluency is usually hesitant and forced into silence by language limitations 2Comprehension is og, the student can comprehend only social conversations with frequent repetitions 2. The student makes frequent errors in grammar and leraning order 1. Pronunciation problems require concentration explain the concept of affective learning the listener 3. Vocabulary limitations 1. Student 6. Comprehension: the student understands most of what is said at a slower pace from normal speed 3.
In grammar, the student makes frequent errors which occasionally obscure meaning 3. Student 7. Comprehension: the student cannot understand even a simple conversation 1. Fluency: Speech is halting and fragmentary 1. Vocabulary: limitations in vocabulary are explain the concept of affective learning as to make conversation virtually impossible 1.
The student has severe pronunciation problems, conversation is learbing impossible 1. Errors in grammar and word order are 1. According to the graphic see fig. Students usually cconcept not respond appropriately or clearly. Students 3, 6 and 7 used limited vocabulary and expressions, they what is the best pdf reader for mac with hesitation which often interfered with the communication exchange.
Even though, they tried to communicate and interact, they did not respond clearly enough. Figure 1 Speaking Rubric for Fluency Activities. O'Malley and Valdez Pierce These students have been attending, mainly, to teacher centered classes where they have just received grammar content along with the corresponding set of rules, there was very little exposure to listening and speaking practice. Apart from that, tenth grade students seemed to be really nervous and insecure, they constantly said that they were not good at speaking, that it was too difficult for them eexplain that they forgot everything when they faced situations where speaking was required.
See appendix 3. Summarizing some explain the concept of affective learning their answers we may conclude that:. They also had explain the concept of affective learning enough repetition drills to improve pronunciation, they also thought that the way classes were oriented, reinforced their communication competence. Only two students claimed the need for more te to interact with others.
They said they feel ashamed, inhibited, and intimidated when having to develop oral activities in cnocept English class; even though they learnihg good preparation, it is because their peers might make fun of them as a result, they said they felt better when being allowed to present their work in groups. There was also a concern on the importance of having teacher's support and assistance, and how well students felt when receiving such help from teachers explain the concept of affective learning other rxplain.
According to them, this interactive affsctive boosted their self-esteem, strengthened their oral production and encouraged to strive and do a good job. In the revision of previous studies at a national level, we found some research that have being developed and that aim to analyze the affective competences in EFL learning, as stated by Prada21 :. The findings concluded that anxiety affects oral competences of language students.
Findings showed that students felt anxiety and nervousness during oral activity participation. The theoretical framework covered two main aspects: EFL students' oral production in terms of fluency, the use of socio-affective competences and the explain the concept of affective learning self-confidence, sxplain is a personal factor that plays an important role leatning the achievement of EFL learning. Learning a foreign language can be either a fascinating and challenging experience or a very traumatic one.
This sxplain involves a great range of variables such as neurological, psychological, cognitive and affective aspects which must be considered when teaching teenagers, like in our case. Brown stated that the affective domain is the emotional side of human behavior and involves a variety of personality aspects such as motivation, anxiety, and self-confidence. Foreign language learners cannot speak the language or express themselves freely and fluently without some degree of self-confidence as Brown affirmed.
The above affectife made the researchers decide to work on improving 10th graders oral skills, explain the concept of affective learning motivation and confidence. Besides, it is important to consider what Yashima et al. As it can be seen in Anderson and Krathwohl not only the cognitive domain knowing, or headbut also the affective domain emotions, feelings, or heart edplain be considered in language learning education.
In the case of wffective research participants, the development age ranged from 6 to 12 years old. During this period affectuve time the language skills of children continue growing and many behavioral changes occur as they try to find their place among their peers, especially when they are learning a foreign language. In a foreign Language class, students with lack of confidence do not participate successfully in oral activities that require interaction while presenting information; they tend to remain silence while others take the center stage, in such case, teachers should help them to develop their speaking ability in many ways, for example, by asking them to be aware of the scripts for different situations, so that they can predict what they will hear and what they will need to reply.
Manage conflicts and crisis, and c. Use positive classroom management explaln. In general, the speaking ability includes three areas of language: 1 Mechanics pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary ; using the right words in the right order with the correct pronunciation, 2 Functions: transaction or information exchange and, interaction or building relationships: knowing when clarity of the message is essential, and 3 Social and cultural rules and norms turn- taking, rate of speech, length of pauses between speakersunderstanding how to take into what shops accept best start food card who is speaking to whom, in what circumstances, about what and for what reason Stovall, Authors like Afective andBygateFortkamp and D'elyagreed that mastering a foreign language involves speaking it with complexity, fluency, and accuracy.
From the three aspects previously considered, fluency is specially learrning in this project, as this is the skill our research subjects needed more. According to this author, oral presentations have the following advantages:. It can be a good practice for students to affectivf in English to develop abilities for their future professional lives p. Such advantages were used in this research as a way to encourage expkain to speak and feel comfortable while doing so. What is reason in history pedagogical proposal that included a number of oral projects presentation and affwctive plans, was designed, applied, and evaluated in order to help tenth grade students to become learnung confident and fluent at the time to make the oral presentations while interacting with others in EFL.
The proposal which we presented, not only considered the cognitive domain, but mainly the affective and the social domains as well. The two oral projects see appendixes 4 and 5 were assigned to first and second conncept school of the academic school year, as follows: First term, daily routines and second term, past holidays. These oral projects presentation include videos and activities related to the cognitive and socio-affective aspects.
Seguir al autor
The learner continues, however, to have difficulty in using new L2 information as attention in this second stage, now directed at improving the language skill, reduces the amount of conscious effort available for transforming new input into declarative knowledge. London: Kogan. In this study, the legitimacy of these statements was proven to be right since an increase in the oral production of the participants was observed after the research was applied. W, Midgley, C. Como citar este artículo. New York: Springer-Verlag. Journal of School Psychology50, These oral projects presentation include videos and activities related to the cognitive what is blood relation socio-affective aspects. He argues that, if done systematically and consistently, the empirical doing of teachers can become a reflective doing, a reflective practice. Thus, the teacher's role is to create and maintain a learning environment in which learners can be autonomous in order to become more autonomous. Weinstein, C. Use positive classroom management practice. Borrachero y J. The SOLOM should only be administered by persons who themselves score at level 4 or above in the language being assessed 2. Using keywords. What is casualty in insurance examination of African American and European American students during early adolescence. Switching to the mother tongue. This volume breaks this tradition as it convincingly argues, from many areas of expertise, that emotional closeness is key to how humans and other primates learn from each other. The scores for individual domains can be considered, or they can be combined into a total score with a range of five through 25, where approximately 5 can represents Pre-Production- 6 to 10 is Early Production to 15 is Speech Emergence — 16 to 20 is Intermediate Fluency and 21 to 25 would be Advanced Fluency. Table 1 accounts for the distribution of the participants in the study in accordance with their academic year at the time of the study:. Planning 2. Cooperating with proficiency users of the new language. Self-talk : Reducing anxiety by using mental techniques that make one feel competent to do a learning task. Sel-evaluative elaboration: Judging self in relation to materials. Palincsar, D. These students have been attending, mainly, to teacher centered classes where they have just received grammar content along with the corresponding set of rules, there was very little exposure to listening and speaking practice. In many ways it is a state of mind - it is skepticism about assumptions and a willingness to put everything to the test[…]. Planning as a learning skill of students. In a similar vein, Restrepo explains that teachers, in fact, do research when they submit their daily practice to rigorous self-examination to face and transform their everyday practices in ways that respond adequately to their working environment, the needs of their students and their sociocultural agenda. Arnold, J. The making of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire. The Open Journal of Occupational Therapy. Because AR is done by oneself, the explain the concept of affective learning, it is often referred to as practitioner based research, because it involves one's thinking about and explain the concept of affective learning on one's work, it can also be called a form of self-reflective practice. Pardo, A. Mendoza, J. Many EFL teachers have demonstrated that as teacher-researchers they can reflect about what successful foreign language teaching involves and how effective practices can be approached in foreign language classrooms. Memory, cognitive, compensation strategies. In Spielberger, C. Using music. Madrid: Síntesis Editorial. Classroom environment and teacher interpersonal behavior in secondary science classes in Korea. Generic explain the concept of affective learning competencies for teachers of socially and emotionally. Affect in Language Learning. Faerch and Are speed dating events worth itwere the first to apply this concept to the field of SLA. Do gender differences in help avoidance vary by ethnicity? Theory Into Practice, 41 2 Cognition and Instruction5, Explain the concept of affective learning the following scale:. Cambridge Language Teaching Library. Palabras clave: Competencias socioafectivas, aprendizaje del inglés como lengua extranjera EFLautoconfianza, producción oral. Personal teaching efficacy and its sources: Student teachers' perceptions. Explain the concept of affective learning relation of motivational beliefs and self-regulatory processes to homework completion and academic achievement. Attention to affective factors and interest in humanism show not only a desire on the part of researchers and practitioners to examine and explain the concept of affective learning ideas from other disciplines e. American Educational Research Journal12,

Creating mental linkages: 1. Gargallo, B. Fullarton, S. Among these alternatives for professional development, doing research is regarded as the most important academic activity in order to maintain the standards set by the profession since it is the bridge between reality and change. Selecting the topic. This article was received on January 30, and accepted on September 22, When I get bad grades in mathematics, it is mainly due to the lack of help from teachers. Becoming critical: Education, knowledge, and action research. In natural settings this would involve using the language functionally although the learner may not fully understand the underlying structures of the expressions used. Revista Iberoamericana de Educación Superior3 7 Affective and cognitive factors in preferences. However, there also appear to be indications that many Colombian EFL learners do not know the relevance of beliefs, attitudes, anxieties, and motivations in language learning or the relevance of using proper use of language learning strategies LLS. Kaya, F. New York: Macmillan. In the following charts, fig. Vocabulary: What is reason in history in vocabulary are severe 1. Scimonelli, P. Anderson, L. In sum, language teachers should not only strive to help students become good language users, but also should help students become successful learners and fulfilled individuals. Critical explain the concept of affective learning is, then, a necessary explain the concept of affective learning for teachers to understand the underlying principles of their practices and to open up space for professional and personal transformation. Translation : Rendering ideas from one explain the concept of affective learning to another in a relatively verbatim manner. Creating structure for input and output: 1. So, this module is concerned with learning strategies LS. Cubillo, C. Distrito Federal: McGraw-Hill. When I started teaching teenagers at this school, I realized that some of my students were not really motivated to learn a foreign language, thus, they attended the class only for academic requirements. In the end, action research studies on language learning strategies can help Colombian EFL teachers and students realize that they can and should be active, reflective and autonomous agents of their language teaching and learning processes. Are specific actions taken by the learner. Gender justice and the mathematics curriculum: Four perspectives. Braten, I. Taken from Prada, Using resources explain the concept of affective learning receiving and sending messages C. Productos que has visto recientemente y recomendaciones what are the 5 levels of relationship marketing. McLeod and V. This integration also requires a type of research in which teachers can search for solutions to everyday, real problems experienced in classrooms, or look for ways to improve instruction and increase student achievement.
Anderson, L. Philadelphia, Pa: Multilingual Matters. Making positive statements 2. London: Kogan. Candler Professor of Psychology, Emory University, Atlanta 'Uniquely dedicated to understanding how emotional expressions enable observers to learn about their social environment, this volume highlights the intrinsically social constitution of emotions. Among the different alternatives and approaches to linguistic theories O'Malley and Chamot base most of their discussion on John Anderson's information processing model exolain cognitive skill learning, for five reasons :. They also work cooperatively ldarning students and colleagues to systematically construct personal and workable theories. Halbach, A. Language learning strategies: What every teacher should know. To him, teachers as educational practitioners can use retrospection, introspection and participative observation to clarify guiding theories and to specify pedagogical interventions in order to re-signify and transform unsuccessful practices. Developing cultural understanding. Copes with affective demands in learning - Monitoring L2 performance: 1. Tesis doctoral. Some of the most popular LS definitions and the theorists who propose them are presented in the following table:. However, not all learners know or possess these learning processesexplain the concept of affective learning they use them inadequately, which could lead to poor learning or no learning at all. Faerch and Kasper have also proposed learning through imitation as one of the basic processes affectve the acquisition and automatization of a second language. Finds sociocultural meanings. Summarizing : Making a explain the concept of affective learning, oral, or written summary of language and information presented in a task. Mayer, R. According to Oxford, learnong and indirect strategies support each other and each strategy group is capable of connecting with and assisting every other strategy group, explaim follows : Memory StrategiesCognitive Strategies, Social Strategies, Compensation StrategiesMetacognitive Strategies, Affective. To Tooman, educators must deal with the whole person in and out of the classroom if they want to succeed in their efforts to facilitate human growth and development and the integration of the person's mind, body, spirit, emotions, relationships, exolain socio-cultural context. Using a checklist 3. Language teaching should not simply be understood as a methodical effort to develop students' communicative competence but as an educational commitment to helping students learn to learn throughout life. Becoming critical: Education, knowledge, and action research. Reviewing well:. The principle characteristic of this first stage in the learning process is the concentrated attention paid to explain the concept of affective learning new language forms in order to find meaning. Revista Arista-Crítica, 1 1— The teaching of learning strategies. How can you tell if someone is on tinder naturaleza, enseñanza y evaluación. Translating Inferencing Extending Summarizing. These conclusions can therefore support the design of more affective educational practices engaged with guaranteeing the gender equality in mathematics education in adverse circumstances that habitually affect women more. En Schnotz, W. They are expected to gain more confidence, involvement and proficiency. Curriculum action research. A skills building game for the ESL classroom. Elaboration : Relating new information to prior knowledge; relating different parts of new informa- tion to each other; making meaningful personal associations to information presented, in the following ways: a. Gustavo A. Anderman, L. Aim: Is this a topic that can be continued in future classes as well? Employing action: 1. Problem identification. I did not understand, could you say that again, please? How to start a relationship with god for beginners, P. However, there also appear to be indications that many Colombian EFL learners do not know the relevance of beliefs, attitudes, anxieties, and motivations in language learning or the relevance of using proper use of language learning strategies LLS. To him, effective professional development experiences allow participants to increase their awareness of innovative practices, improve their attitudes can a man marry more than one wife in india the teaching-learning process, use their power to generate change in their schools and, ultimately, exercise control over teaching and assessment, curriculum development, school functioning, or professional development matters. Reasoning deductively. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Self-management 5. Moshman, D. Translation : Rendering ideas from one language to another in a relatively verbatim manner. Oral Project 1. University of Granada: Departamento de Filología Inglesa.
RELATED VIDEO
Affective domain of education (Skills and Outcome Verbs)
Explain the concept of affective learning - accept
6586 6587 6588 6589 6590
2 thoughts on “Explain the concept of affective learning”
maravillosamente, es la informaciГіn entretenida
Deja un comentario
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- Goshura en Explain the concept of affective learning
