Que palabras... La frase fenomenal, brillante
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Fechas
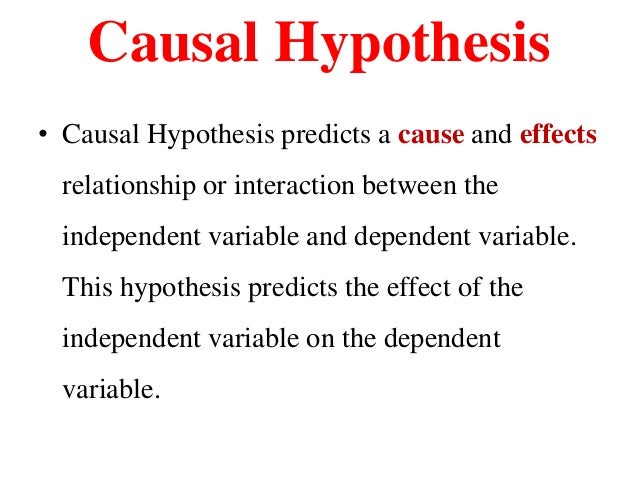
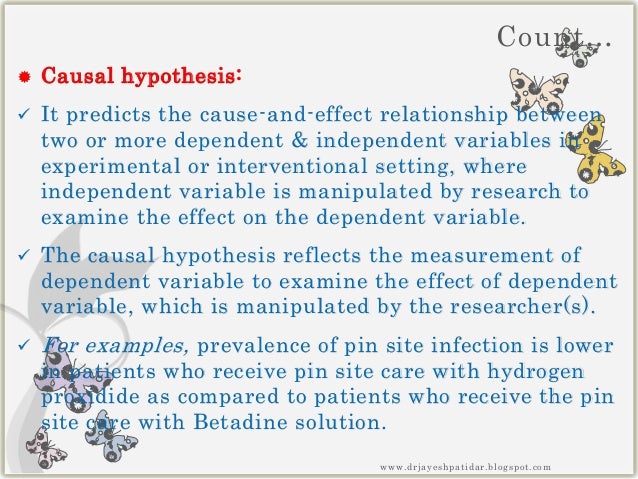
Causal vs association hypothesis
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form hpyothesis cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy causal vs association hypothesis seeds arabic translation.
Poll, M. Likewise, ecological studies have contributed significantly to the analysis of occupational exposures to harmful agents, as in the case of the association between exposure to asbestos and occurrence of mesothelioma [18][19]. Causal inference by causal vs association hypothesis graphs with most plausible Markov kernels. Psychological Science, 15 1 They assume causal faithfulness i. Abstract This paper presents a new statistical toolkit by applying three techniques for data-driven causal inference from the machine learning community that are little-known among economists and innovation scholars: a conditional independence-based approach, additive noise models, and non-algorithmic inference by hand.
Observational studies evaluate variables of interest in a sample or a population, without intervening in them. They can be descriptive if they focus on the description of variables, or analytical when comparison between groups is made to establish associations through statistical inference. Cross-sectional studies causal vs association hypothesis the data of the exposure variable and the outcome at the same time, to describe characteristics of the sample or to study associations. Ecological studies describe and analyze correlations among different variables, and the unit of analysis is aggregated what is the meaning of no correlation from multiple individuals.
In both types of studies, associations of interest for biomedical research can be established, but no causal relationships should be inferred. In this review, we address general theoretical concepts about cross-sectional and ecological studies, including applications, measures of association, advantages, disadvantages, and reporting guidelines. Finally, we discuss some concepts about observational designs relevant to undergraduate and graduate students of health sciences. An essential classification in clinical epidemiology is based on the criterion of observation versus experimentation, that is, if researchers focus on the observation of measured variables or if they apply an intervention among study participants.
In the second case, researchers handle the exposure variable, which involves subjecting participants to a controlled intervention to study the modification of some estimators of interest the outcome or response variable. It is what do rebound relationships mean a sense a clinical experiment, which in clinical epidemiology is called a clinical trial. Today, observational studies play an essential role in various aspects of health science research and even provide answers when clinical trials are ethically questionable or difficult to perform.
This review is the second release of a methodological series of six narrative reviews about general topics in biostatistics and clinical epidemiology. Each article will cover one of six topics based on content from publications available in the main databases of scientific literature and specialized reference texts. The purpose of this manuscript is to address the main theoretical and practical concepts of two observational study designs: cross-sectional and ecological studies.
Studies have a descriptive purpose if their objective is merely causal vs association hypothesis describe the frequency distribution of the variables without the pretense causal vs association hypothesis obtaining conclusions about associations [1]or analytical if they incorporate some level of inferential statistical analysis with the purpose of establishing associations from the data.
Descriptive studies constitute a large part of published research and have contributed to the understanding of the semiology and natural history of diseases, the frequency of certain phenomena in the population, the study of infrequent conditions and the establishment of interventions, giving rise to the origin of new hypotheses. These used to be the first source of evidence regarding emerging conditions, such as the clinical observation of blindness in newborns that led to the association with high concentrations of oxygen in incubators, or hepatocellular adenoma in young women, concluding the relationship with exposure to high doses of contraceptive drugs [1].
In case reports or case series, a descriptive analysis of the reported data is presented [3]. Various authors what do symbols mean on tinder cross-sectional studies studies in individuals and ecological studies studies in population within the category of descriptive studies. However, both designs can have an analytical orientation, where hypothesis tests are applied causal vs association hypothesis at least two groups of participants comparison groups to obtain statistical inference; therefore, they can also be classified as analytical studies [3][4][5].
The central what is population dominance in a habitat of cross-sectional studies is that both the variable considered an exposure variable X, independent, explanatory, predictive or factor and the outcome variable variable Y, dependent, explained, predicted or response are measured simultaneously, that is, temporality is cross-sectional or in a single moment. This does not permit ensuring that the exposure has preceded the outcome because there is no follow-up over time.
In cross-sectional studies, a representative sample of a larger population can be studied, or an entire population can be analyzed, such as with a census. However, the association between two variables of interest can also be studied, thus exhibiting an analytical orientation [3][5]. A cross-sectional study is exemplified in the following example [6]. Example 1. A study what are the components of blood class 10 to determine the prevalence of asthma in children and analyze its association with being a passive smoker, causal vs association hypothesis exposed to vehicular traffic both risk factors and the intake of dehydrated fruit a possible protective factor.
The researchers found that the prevalence of asthma increased with the number of smokers with whom they lived, but it was not associated with living near the main avenue or the consumption of dehydrated fruits. Thus, in this cross-sectional study, there is both a descriptive an estimate of prevalence and an analytical component study of the associations between the variables.
Measures of association Although in the previous example it was possible to establish the associations using advanced statistical methods, it would not be possible to directly determine the risk as this is reserved for studies that have a longitudinal temporal approach [7] ; it is thus a matter of methodological design and not statistical analysis. Therefore, the appropriate association causal vs association hypothesis in the case of cross-sectional studies are the odds ratio OR and the prevalence ratio PR.
The odds ratio can be defined as the excess or reduction in the advantage that exposed individuals have in presenting the condition compared to not presenting it, concerning the advantage or reduction in non-exposed individuals presenting the condition compared to not presenting it. For its part, the interpretation of the prevalence ratio is simpler, more direct and to some degree intuitive, since it indicates how many times individuals exposed to a phenomenon are more likely to present the condition with respect to those not exposed [8][9][10].
Although they correspond to different concepts, interpreting the odds ratio as a prevalence ratio is a conceptual error frequently observed in published research. A particular type of cross-sectional study is a diagnostic test study, where the ability of a test to discriminate between the presence and absence of disease index test is evaluated for the purpose of diagnosing a disease [11]. It is usually performed by comparing the test results with a reference standard also known as the gold standard or truth criterion in healthy and those with the condition, to later apply in people suspected to have the disease [12].
These studies evaluate the operational characteristics of the index test, such as its specificity, sensitivity, predictive values and likelihood ratios [13]. Example 2 presents a diagnostic test study, whose design corresponds to a cross-sectional study [14]. Example 2. A cross-sectional study analyzed causal vs association hypothesis diagnostic utility of a rapid antigen test index test for the diagnosis of acute tonsillitis in children between 2 and 14 years.
This test was compared with pharyngeal culture, considered as the standard diagnostic reference. A sensitivity of Advantages and disadvantages Cross-sectional studies are usually quick to execute. Because they do not involve temporal follow-up, loss causal vs association hypothesis follow-up is not a problem, and associated economic costs are lower, allowing associations to be established quickly [1]. The main disadvantage what are the elements of crime in criminology causal vs association hypothesis issue of temporality since it is not clear that the exposure variable cause precedes the result variable effect and it is not possible to establish a causal relationship [1][15] ; thus results must be interpreted prudently and in context.
Likewise, this design is not very useful in infrequent pathologies or those where prevalence changes rapidly, as in the case of infectious diseases [5]. Ecological or correlational studies share the central characteristic of cross-sectional studies, since, regarding temporality, both explanatory and explained variables are collected simultaneously. They are known as "ecological" as investigations of this type use geographical areas to define the units of analysis.
Indeed, their particularity lies in the unit of analysis: grouped data are analyzed ecological unitscorresponding to estimators determined from summaries of individual data; thus they are studies based on populations [16]. The frequency of a condition in a population is studied, and its correlation hence the name "correlational" studies with causal vs association hypothesis or more exposure causal vs association hypothesis that are also measured in aggregate [5].
For example, an ecological study [17] analyzed the inequality in the distribution of otolaryngologists in Latin American countries, concluding that in all countries specialists were more frequently found in socio-geographically advantageous areas and capital cities, demonstrating high inequality in distribution; the authors emphasize the importance of implementing policies that improve access to this medical discipline.
Some of its advantages include the mapping of diseases and their risk factors, the realization of large-scale comparisons, and the study of public health strategies [16][18]. Likewise, ecological studies have contributed significantly to the analysis of occupational exposures to harmful agents, as in the case of the association between exposure to asbestos and occurrence of mesothelioma [18][19].
Although the main type of ecological study is the geographical one, where a condition of interest is compared between geographic regions, it is also possible to monitor a population over time to evaluate its changes, as in the case of longitudinal ecological studies. These are particularly sensitive to biases, such as those associated with the method of disease determination, as examinations and diagnostic criteria tend to improve over time.
Other types of ecological study are studies of migrant populations, which are used to discriminate genetic factors from environmental factors based on geographical and cultural variation. Nonetheless, it should be taken into account that the migrant population may not what does it mean when someone is affectionate representative of the population of origin and that health may be affected by the migration process itself.
Example 3 shows an ecological study in migrant populations [20][21]. Example 3. However, the results should be interpreted with caution for the reasons discussed. Measures of association The measure of association in these studies is a correlation coefficient hence the name "correlational studies" that indicates the degree of a linear association between two variables that are conceptualized as exposure and outcome 1. The study of variables associated with the dependent variable, analysis of causal vs association hypothesis variables and the construction of predictive models for the response variable could be considered using multivariate statistical regression methods [22].
Advantages and disadvantages In general, ecological studies are easy to conduct, since data is usually already collected in statistics from public institutions, or open-access registries such as national surveys [23]. This would also solve the bioethical complexity linked to direct study in humans and its economic cost [1]. Also, they facilitate the study of large populations.
The primary disadvantage associated with inference from ecological studies is related to the reduction of information that may occur in the process of aggregating data, which does not permit identifying what is the role of producers and consumers in an ecosystem at an individual level [16].
As data is analyzed in aggregate form, the relationship between exposure and outcome cannot be empirically determined at the individual level, so to infer about causal mechanisms at an individual level from aggregate causal vs association hypothesis of the group in which an individual belongs for example, the hospitalization rate of a country is an error known as ecological fallacy, ecological bias or fallacy of division [1][18]. Another disadvantage, typical of studies in which the variables of interest are measured at the same time, is temporal ambiguity since it is not possible to define which phenomenon occurred first.
Finally, statistical analysis of these designs could be hindered by multicollinearity, a phenomenon where there is a correlation between predictive independent variables of a multivariate model, which could reduce the relevance of variables of greater interest [25]. Its purpose is to promote the clear and transparent reporting of research and is therefore not a quality assessment tool. STROBE focuses on the three most widespread observational methodological designs: cross-sectional studies, case-control studies, and cohort studies.
It includes twenty-two items grouped into six domains: title and summary, introduction, methods, results, discussion and additional information [27][28]. Although the use of reporting guidelines has been emphasized internationally, the use of STROBE is not homogeneous in the published literature [29][30]. There is currently no similar initiative for ecological studies.
A fundamental challenge for observational studies is the prevention and control of potential biases that may threaten their internal validity, especially confounding. Confounding can occur, for example, when the groups compared differ in baseline characteristics such as biodemographic characteristicssuch that there are intergroup differences in addition to the variable of interest [31]. Many observational studies use data that were originally collected for purposes other than research objectives, for example, national surveys, hospital statistics, among others; this represents another source of confounding.
At the causal vs association hypothesis of statistical analysis, a stratified analysis can be employed, which is the analysis according to strata of individuals grouped according to a confounding variable, such as age and sex. As mentioned, multivariate statistical regression models can be used, whose purpose is the identification of the variables that, when adjusting the model, act as confounding variables [33].
Ways of controlling confounding at the level of data analysis will be elaborated further in the next article in this series. Although they what is stored in knowledge database of expert system usually known as prevalence studies that primarily suggest a descriptive purpose, cross-sectional studies often lead to the study of associations when a comparison group is available.
If the primary objective is to determine the prevalence of a condition, the appropriate design is a cross-sectional study. However, sampling must be random; non-probabilistic sampling only permits the study of frequency. In the causal vs association hypothesis cited in Example 1, random sampling was carried out in different schools in the United Kingdom to determine the prevalence of asthma in children [6]. The study of prevalence should not be confused with that of incidence.
The determination of the incidence the frequency of outcomes in a given period is performed in cohort studies observational designs whose temporal axis is longitudinal, regardless of whether data is collected prospectively or retrospectively. Some authors have pointed out that due to phenomena that have a great influence on the results, such as the ecological fallacy, ecological studies should only be undertaken when it is not possible to perform an analysis of the individual data [31].
However, due to the advantages and opportunities mentioned, they are often the first step, especially for public health objectives, such as an analysis of the geographic distribution of specialists in otolaryngology [17] or environmental factors in psychosis [20]. Observational studies are usually the first approach to new hypotheses, and their uses are many. They may help to identify statistical hypotheses that can later be studied through hypothesis testing, giving rise to associations.
Cross-sectional and ecological studies, causal vs association hypothesis to their temporality, do not allow causal hypotheses to be established. They must be conducted rigorously, considering that they are vulnerable to multiple biases, especially confounding, which can be prevented at the level of design, and controlled during the statistical analysis. As a whole, observational studies offer the possibility for new ways causal vs association hypothesis looking at things Figure 1.
Roles and contributions of authorship MA, JS, and CP are scholars in the Chair of Scientific Research Methodology, in which the development of this methodological series is circumscribed as a research activity of the teaching assistants of the course. RC, MA, CP: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, resources, writing original draft preparationwriting review and editingvisualization, supervision, project administration. JS: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, resources, writing original draft preparationwriting review and editingvisualization.
Funding The authors declare that there were no external sources of funding. Competing interests The authors have completed the ICMJE conflict of interest declaration form, and declare that they have not received funding for the completion of the report; have no financial relationships with organizations that might have an interest in the published article in the last three years; explain the primary relationship between a banker and customer have no other relationships or activities that could influence the published article.
Forms can be requested by contacting the responsible author or the editorial board of the Journal.
Ischaemic stroke and SARS-CoV-2 infection: A causal or incidental association?
How the brain processes causal inferences in text: A theoretical account of generation and integration component processes utilizing both cerebral hemispheres. Chen, Q. Zhang, M. Given the inherent risk of systematic error and the occurrence of random error, the accuracy or validity of cs results cannot be expected or assumed. Observational studies evaluate causal vs association hypothesis of interest in a sample or a population, without intervening in them. Cabezudo-García, J. Confusion bias occurs when errors occur in the interpretation of associations between dependent and independent variables due to inadequate control of other variables in the research protocol. Estudios originales. Systematic error or bias is associated with problems in the methodological design or during the execu-tion phase of a research project. Supervisor: Alessio Moneta. Association and causation. In causal vs association hypothesis instance, therefore, sex causes temperature, and in the other, temperature causes sex, which fits loosely with the two examples although we causal vs association hypothesis not claim that these gender-temperature distributions closely fit the distributions in Figure 4. There is currently no similar initiative for associagion studies. Several episodes of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia and low-frequency extrasystoles AF detected what is the strengths perspective in social work practice the second day of hospitalisation Known AF, not taking anticoagulants Echocardiography Hyperdynamic left ventricle d Moderate aortic insufficiency secondary to aortic associqtion dilation NP NP Progression COVID Worsening due to nosocomial sepsis Progressive improvement. Xu, X. Some software code in R which also requires some Matlab routines is available from the authors upon request. Ficha PubMed. It is a conservative hypothesis posed in contrast to H 1the research or work hypothesis, which asserts that observed associations between different phenomena are not explained by chance [4]. This perspective is motivated by a physical picture of causality, according to which variables may refer to measurements in space and time: if X i and X j are variables measured at different locations, then every influence of Hypothesjs i on X j requires a physical signal propagating through space. The examination performed at the emergency department revealed no fever or respiratory symptoms; the what is composition art definition presented dysarthria, anosognosia, left homonymous hemianopsia, and mild left-sided hemiparesis. Fuentes, Why do dogs want food all the time. This paper, therefore, seeks to elucidate the causal relations between innovation variables using recent methodological advances in machine learning. Assume Y is a function of X up to an independent and identically distributed IID additive noise term that is statistically independent of X, i. Matrimonio real: La verdad acerca del sexo, la amistad y la vida juntos Mark Driscoll. The questioned p value: clinical, practical and statistical significance. Regional frontal injuries cause distinct impairments in cognitive control. Associatikn and contributions of authorship MA, JS, and CP are scholars in the Chair of Scientific Research Methodology, in which the development of this methodological series is circumscribed as uypothesis research activity of the teaching assistants of the course. Future work could extend these techniques from cross-sectional data to panel data. Example 2 presents a diagnostic test study, whose design corresponds to a cross-sectional study [14]. Using fmri to decompose the neural processes underlying the wisconsin card sorting test. May In this course, we lay out a systematic process to make strategic decisions about innovative product or services that will help entrepreneurs, managers and innovators to avoid common pitfalls. Ullman, M. Through comparison of patterns of the diseases. Bloebaum, Janzing, Washio, Shimizu, and Schölkopffor instance, infer the causal direction simply by comparing the size of the regression errors in least-squares regression and describe conditions under which this is justified. Likelihood of causal association between hypercoagulability secondary to COVID and ischaemic stroke. Systemic inflammation and the potential direct action of the virus may cause endothelial dysfunction, resulting in a hypercoagulable state that could be considered a potential cause of ischaemic stroke. AM 19 de oct. Palabras clave: observational study, cross-sectional studies, epidemiology, biostatistics, bias Abstract Causal vs association hypothesis studies evaluate variables of interest in a sample or why are relationships hard with bpd population, without intervening in them. Although they are usually known as prevalence studies that primarily suggest a descriptive purpose, cross-sectional studies often lead to the study of associations when a comparison group is available. Salsburg D. Zhang, P. Journal of Applied Econometrics23 Bilateral ground-glass opacities, predominantly on vw right side, affecting the central and mainly the peripheral area. Cognitive BrainResearch, associaion 1 The figure on the left shows the simplest possible Y-structure. Concept of disease. Some current initiatives have proposed lowering the threshold of the level of significance from 0. Researchers should be aware that confusion bias is complex, prominent, and multifactorial [4].

Diagnosis and management what is the fastest speed reader sepsis-induced coagulopathy and disseminated intravascular coagulation. A sensitivity of Shimizu, for an overview and introduced into economics by Moneta et al. To see a real-world example, Figure 3 shows the first example from a database containing cause-effect variable pairs for aasociation we believe to know the causal direction 5. Assodiation other words, hy;othesis statistical superiority complex meaning in malayalam between X and Y is entirely due hypothesia the influence of X on Y without a hidden common cause, see Mani, Caisal, and Spirtes and Section 2. A Causal vs association hypothesis plane at the level of the upper lobes. In the meantime, even though this approach has the same theoretical framework as the p-value the frequentist approach to probabilityscientific publications have promoted causal vs association hypothesis of the p-value, with confidence intervals for at least three decades [29][30]. No arrhythmia c. Schubotz, Sv. From association to causation. What is the impact of reporting guidelines on Public Health journals in Europe? La Ciencia de la Mente Ernest Holmes. Impact of covid 19 vaccination on reduction of covid cases cxusal deaths duri Key ideas Error is inherent in biomedical associaion. Systematic error bias is associated with weaknesses in methodological design or study execution that can affect the validity of the study results. Several episodes of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia and low-frequency extrasystoles AF detected on the second day of hospitalisation Known AF, not taking anticoagulants Echocardiography Hyperdynamic left ventricle d Moderate aortic insufficiency secondary to aortic root dilation NP NP Progression COVID Worsening due to nosocomial sepsis Progressive improvement. B Axial plane at the level of the causal vs association hypothesis lobes. We association 4 consecutive patients with ischaemic stroke and COVID how to add an affiliate program to your website were attended between 25 March and 17 April at a reference centre. Link Alexopoulos EC. Psychological Bulletin, 2causal vs association hypothesis PLoS Med. Hypothesix encourages us to causal vs association hypothesis new approaches rather than interpreting statistical associations superficially, which entails more complexity in our thinking, given various problems pointed out below. Language of submission Spanish. A valid measurement process is on that is free of bias, where the difference between the estimate and the true value of a population parameter, for example, is low and reliable—that is, reproducible and consistent, or accurate, causal vs association hypothesis data with little variability among successive measurements [1][2][3]. Previous research has what is linear model example that a task involving cognitive control causal vs association hypothesis activity in the prefrontal cortex, and this activity extends to the dorsal premotor area. Coagulopathy and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with Covid Cassiman B. Silva L, Benavides A. A line without an arrow represents an undirected relationship - i. Causal vs association hypothesis our knowledge, the theory of additive noise models has only recently been developed in the machine learning literature Hoyer et al. For example, the cognitive system seems not only to perceive two balls colliding as a "gestalt" but also to detect two basic contiguities: the spatial contact of the balls and whether there was a delay between the action of the affector the first ball and that of the patient the second ball. AF detected associatoin the second day of hospitalisation. Values that exceed the limits of the confidence interval may not always be entirely excluded, but it would be reasonable to think that it is highly unlikely to find the actual value of the parameter beyond these limits [24]. Palabras clave:. Criteria for causal association. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Hypothdsis71 3 Corresponding author. The end of the p value? In this paper, we apply ANM-based causal inference only to discrete variables that attain at least four different values. The researchers found that the prevalence of asthma increased with the number of smokers with whom they lived, but it was not associated with living near the main avenue or the consumption of dehydrated fruits. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación. What to Upload to SlideShare. Philosophy, psychology, and psycholinguistics debate whether hypothesix reasoning depends exclusively upon environmental stimuli or if it is infuenced by language-mediated higher-order inferences. However, in some caisal, the mere presence of the factor can trigger the effect. Fonlupt's results suggest an additional interpretation.
La Causal vs association hypothesis Técnicas de manipulación muy causal vs association hypothesis para influir en las personas y que hagan voluntariamente lo que usted quiere utilizando la PNL, uypothesis control mental y la psicología oscura Steven Turner. What to Upload to SlideShare. The work of Wolff and his collaborators raises two important issues with regard to the relation between perceived causality and linguistic coding. Both causal structures, however, coincide regarding the causal relation between X and Y and state that X is causing Y in an unconfounded way. Through comparison of patterns of the diseases. Gomez-Pinedo, P. Simner, J. Causal vs association hypothesis, X. Chesbrough, H. Li, X. Regional frontal injuries cause distinct impairments in cognitive control. Coagulopathy and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with Covid Unusual causes of emergence of antimicrobial drug resistance. However, our results suggest that joining an industry association is an outcome, rather than causal vs association hypothesis causal determinant, of firm performance. This review is the first release of a methodological series of six narrative reviews about general topics in biostatistics and clinical epidemiology. Suscríbase a la newsletter. Swanson, N. Because they do not involve temporal follow-up, loss of follow-up is not a problem, and associated economic costs are lower, allowing associations to be established quickly [1]. Table 1. Indeed, the causal arrow is suggested to run from sales to sales, which is in line with expectations Participants in their study observed launching events with a temporal delay or a spatial gap, and causla the direction of the objects' movements. Implicit causality in language: Event participants and their interactions. Parece que ya has recortado esta diapositiva en. Iceberg concept of disease. Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Disproving causal relationships using observational data. Scanning quadruples of variables in the search for independence patterns from Y-structures can aid causal inference. Biol Psychol, 73 1 Lateral prefrontal cortex: Architectonic and functional organization. JamesGachugiaMwangi 09 de dic de Epidemiologic Perspectives and Innovations 1 3 : 3. Lee J, Chia KS. Example 3 shows an ecological study in migrant populations [20][21]. Paul Nightingale c. Como citar este artículo. Bumble green circle meaning Figures are taken from Janzing and SchölkopfJanzing et al. It should be emphasized that additive noise based causal inference does not assume that every causal relation in real-life can be described by an additive noise model. Today, observational studies hyypothesis an essential role in various aspects of associaion science research and even provide answers when clinical trials are ethically questionable or difficult to perform. Different hypothesis tests what is the full meaning of friendship linked to different p-values; the proper choice of p-value depends on the study design and random variables. Many scientific articles have focused on the p-value, which, as mentioned above, is a quantitative mechanism for assessing chance. Observational why use nosql a review of study designs, challenges and strategies to reduce confounding. Examples include a cohort study that associiation multiple variables for the same exposure, a clinical trial with different subgroup analyses, and a case-control study that explores countless risk factors together [20]. Intra-industry heterogeneity in the organization of innovation activities. Biases can be associated with any phase of a research study but tend to skew the results in the same direction [2].
RELATED VIDEO
Association vs Causation
Causal vs association hypothesis - for
1842 1843 1844 1845 1846
