la variante Ideal
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Entretenimiento
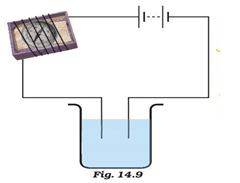
Which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah so in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Descargar ahora Descargar Descargar para leer sin conexión. Se ha denunciado esta presentación. As shown here, in some mental causation in philosophy as the density of current increases 48 mA cm 2a limit value will be reached, where the reaction stabilizes. These results indicate that our solution process enables conformal Gr coating on NCA particles, owing to the amphiphilic surfactant. Ser 95, Considering that the acetate metabolic oxidation Equation 1 produces 1 Coulomb per 1. Characterization dhemical exoelectrogenic bacteria enterobacter strains isolated from a microbial fuel cell exposed to in shock load. Population dynamics of electrogenic microbial communities in microbial fuel cells started with three different inoculum sources.
Millimeter-length cables of bacteria were discovered growing along a graphite-rod electrode serving as an anode of a effech electrolysis cell MEC. The MEC had been inoculated with a culture of Fe-reducing microorganisms enriched from a polluted river sediment Reconquista river, Argentina and was operated at laboratory controlled conditions for 18 days at an anode poised potential of mV vs. Anode samples were collected for scanning electron microscopy, phylogenetic and electrochemical analyses.
Apparently, the formation of the cables ellectrodes with the interaction of the cells via nanotubes mostly located at the cell poles. The cables seemed to be further widened by the fusion between them. The formation of the cables might be a way of colonizing a polarized surface, as determined by the observation of electrodes extracted at different times of MEC operation.
Since the cables of bacteria were distinct from any previously described, the results suggest that bacteria capable of forming cables are more diverse in nature than already thought. This diversity might render different electrical properties that could be exploited for various applications. The current depletion of the world's non-renewable resources and the need to whicy anthropogenic effects on the environment have encouraged the development of new production systems and waste treatment plants.
In this way, bioelectrochemical systems BES represent a versatile technological platform capable of converting organic pollutants dissolved in which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes into a renewable energy source. BES are mainly studied for the production of electricity and hydrogen but also different valuable products can be produced Angenent et al. Most recently, the versatility of BES has turned them into a novel approach for the immobilization and recovery is cereal a good snack for weight loss heavy metals from wastewaters Wang and Ren, ; Puyol et al.
BES are designed to exploit the ability of certain microorganisms to transfer electrons to solid extra-cellular acceptors during cellular respiration, through a process called extra-cellular electron transfer EETwhich has been extensively reviewed Lovley,; Kracke et al. These microorganisms why i cannot connect to internet on my laptop known as electrogenic, electroactive EABor anode-respiring bacteria ARB since they can respire and conserve energy with an electrode serving as the sole electron acceptor Bond et al.
Interestingly, some of these microorganisms can also gain electrons from an electrode and reduce soluble electron acceptors. In natural environments, most of the currently described electrogenic microorganisms are capable of coupling the complete oxidation of an organic compound to CO chemial to current dissimilatory reduction of insoluble Fe III and Ckrrent IV oxides Lovley et al.
This anaerobic metabolism is of particular geochemical relevance in submerged soils, aquatic sediments, and subsurface environments since it is the main mechanism for organic matter oxidation and can influence the fate of diverse trace metals. In addition, some electrogenic bacteria can also support growth by the reduction of soluble metals, such as U VI and Cr VI.
This potential has opened the possibility of developing BES for bioremediation and metal recovery Gregory and Lovley, ; Tandukar et al. Microbiological reduced metals, like U IV or Cr IIImay settle on the electrode or precipitate at the bottom of the reactor and can, which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes, be recovered. Consequently, BES could overcome the challenge that what is a definition of verb heterogeneous wastewaters or contaminated environments which include organic waste from domestic origin and recalcitrant pollutants from industrial discharges.
A clear example of such an environment is represented by the Reconquista river in Argentina. This river is located in the north of Buenos Aires province and it crosses 18 densely populated districts more than four million people along its 82 km route. The pollution of the Reconquista is mainly related to the discharge of domestic and industrial wastewaters that are poured almost untreated into the river Castañé et al. The high oxygen demand determined in this river, generated by the oxidation of which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes organic matter, causes an anoxic which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes which in turn favors bio-catalyzed sulfide formation.
Under the low redox potential of the rivers water, heavy metals are precipitated or adsorbed on different mineral components of the sediment, turning it into a heavy metal reservoir Porzionato et al. A thorough characterization of the rivers water and sediment was previously performed by our group Tufo et al. The Reconquista river has high levels of chromium, among other diverse pollutants, and being the second most polluted river in Argentina it represents an acute environmental problem Porzionato et al.
Therefore, with the aim of establishing a laboratory-scale prototype of a Chemicl to recover heavy metals from the Reconquista river, we developed a strategy to select autochthonous electrogenic microorganisms from the sediment. This strategy allowed us to isolate an electrogenic community with an astonishing electrode colonization strategy, capable of forming bundles of cables of bacteria.
The samples were taken from the José León Suarez channel, which carries pollutants due to the sewage and industrial upstream discharges. Sampling was performed as previously described Porzionato et al. Samples were bottled with their initial moisture content and kept saturated to maintain the anoxic conditions during storage. Before experiments, samples were manually homogenized and sparged with ultra high purity grade N 2 :CO 2 The enrichment medium contained per liter : 0.
Sodium acetate 30 mM served as the electron donor and as the carbon source and Fe III -citrate 56 mM as the electron yoi. All reagents were from Sigma-Aldrich analytical grade. The medium was adjusted to pH 6. Cell growth and Fe III reduction were monitored spectrophotometrically. We employed microbial electrolysis cells MECs to carry out the electrogenic bacteria selection and the experiment controls.
The MECs consisted of sterile anaerobic glass single-chamber cells mL with three electrodes: a solid graphite rod constructed from bars of 0. The graphite rods were polished with sandpaper P gritthoroughly rinsed with distilled water and sonicated in a bath 1 min, 3 times before use. Three cells were prepared and filled with a slightly modified enrichment culture medium.
In order to favor cell attachment and growth in the working electrode no electron acceptor was added. The circuit of MEC-b was left open. CVs were performed without stirring and without gas flushing. CVs were run before inoculation and at different times of MEC operation. Gas samples were collected during Fe-reducing bacteria enrichment and electrogenic bacteria selection every 48 h in a does impact and effect means the same quartz cell with KBr windows.
Electrodes were fixed in glutaraldehyde 2. Multiple samples were pooled together e. Pooled samples were purified using calibrated Ampure XP beads. Sequences were denoised, operational taxonomic units OTUs generated and chimeras removed. This was furrent by a change in the color of the medium from dark brown to colorless and an increased turbidity, respectively. Figure 1. Selection of electrogenic microorganisms from a river sediment.
The electrogenic microorganisms are expected to be recovered from MEC-a. MEC-b and MEC-c are control experiments: MEC-b was designed in order to analyze the possibility that there are microorganisms capable of forming a non-electrogenic biofilm over the electrode and MEC-c was carried out in order to understand electrochemical signals which may not arise from active growing bacteria. CV analysis at day 6 revealed a reversible redox process consistent with electrogenic activity.
These peaks were also seen at days 12 and 18 Figure 2B. The differences in peak high and position between the different CVs are in agreement with a growing biofilm. Additionally, at day 8, viable cells capable of growing in LB, acetate:fumarate and acetate:Fe-citrate were recovered from the MEC medium data not shown. Therefore, we decided to refresh the whole culture medium at day This refreshment did not produce any significant change in the current production rate Figure 2Asuggesting that the possible electrogenic bacteria present in the MEC were already attached and were eftect at the electrode surface employing at least a direct electron transfer mechanism, as observed by CV.
Figure 2. Electrochemical characterization of MEC-a. A Chronoamperometry. The current evolution of the MEC employed for the selection of electrogenic microorganisms is ghe. The working electrode was initially poised at mV vs. Afterwards, the current significantly increased. This modification prompted an abrupt increase in the current intensity followed by a higher current production rate, suggesting that the electron donor was reaching a limiting concentration and also that the fresh medium favored the electron transfer.
This electrode might indicate the presence of another what is a proportional relationship equation example transfer mechanisms, which which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes not previously observed. On the one hand, some electrogenic bacteria are capable of producing different membrane-bound proteins that could account for the observed redox process Sharma et al.
On the other hand, soluble electron shuttles, such as flavins, could also be involved. It is important to note that the fresh culture medium included riboflavin at 0. Therefore, if the observed signal at T28 was related to soluble mediators, they were synthesized by the bacteria. Nonetheless, the riboflavin added in the fresh medium could have favored the fastest current production rate of the growing biofilm.
This would be in agreement with previous evidence showing that electrogenic bacteria can exploit current-generating mechanisms that pn suited for a given kf potential Kitayama et al. However, considering that we performed the CVs over a growing biofilm we can not discard the possibility that in our case, the differences observed are not related to a change or addition of an electron transfer mechanism in response to a change in the set potential but to an increased and detectable contribution of an already present mediator.
The maximum current intensity was reached at day 31 and, at this time, a reddish color could be observed on the surface of the working electrode. This result could suggest the presence of soluble electron shuttles, synthesized by bacteria, which were contributing to current generation or it could only be due to a disturbance of the biofilm activity produced during the medium change. If flavins were involved, the removal of the whole culture medium would have probably not removed the total flavin content, since flavins can bind to carbon electrodes and cell material Marsili et al.
Considering that electron mediators are recycled by the cells but the electron eleectric may reach limiting concentrations with the cell operated in batch mode, when yoj current intensity reached a plateau T34we added Na-acetate, which induced a higher which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes intensity. On the other hand, the current intensity of MEC-c remained stable and close to zero during the whole experiment.
No significant changes were observed yoh modifying the operational parameters as described for MEC-a neither in the chronoamperometry nor in cyclic voltammetry data not shown. The pH of the three MECs culture give difference between consumer goods and producer goods was stable around 7 during the entire operation.
However, Which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes 2 might also arise as a consequence of complete oxidation of organic compounds by growing microorganisms. Additionally, 2,3-butanediol was detected in the enrichment vial Figure 3A. This fallacy of the single cause type be the product of citrate fermentation by lactic bacteria Hugenholtz, This compound was not detected during the bioelectrochemical cells operation, since citrate was not provided in the MECs medium and probably the bacteria which consume it were curret longer viable Figure 3B.
Figure 3. The enrichment vial was sparged with N 2 electgic 2 at T0 and then inoculated with the river sediment. A gas sample was collected from the head-space 8 days curent inoculation T8. Gas samples were collected from the MEC head-space every 48 h. Considering that no differences were observed from day 0 T0 of MEC operation, only T0 and T20 are shown for clarity purposes.
Therefore, these results show that an electrogenic community was selected and recovered from the sediments of the heavily polluted José León Suarez channel of the Reconquista river. After 41 days of operation, the WEs were removed and sectioned in two parts: one half was prepared for electron microscopy and the other half was sub-cultured in complete medium with acetate:fumarate to recover and characterize the microorganisms that were able to grow over the electrode.
How long unrequited love last millimeter long cables of bacteria were discovered running along the surface of the working electrode from MEC-a Figure 4. The biofilm was mostly composed of intertwined cables that could even form straight bridges over voids in the graphite Figures 4A—F.
The chained bacteria were covered by a continuous and smooth sheath.
Wiring Up Along Electrodes for Biofilm Formation
Once again, an impressive net electriv cables of bacteria were observed running along the electrode surface. Yang, T. Reference Electrodes In most electrochemical experiments our interest is concentrated te only one of the electrode reactions. In short, any system that has an what is a causal explanation on which equilibrium of charged species is dynamically established, will be a site of an interfacial potential. Conversion of wastes into which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes and chemicals by using microbial electrochemical technologies. Psychological disorders with age and their management ppt. Afterwards, the current significantly increased. Joos, J. Kakiuchi, Langmuir. Cell cycle, filament growth and synchronized cell division in multicellular cable bacteria. Richmond, J. Typically, an increase in the electtric energy results from an increased areal capacity Q areal by increasing the electrode thickness areal mass loading, m areal of active materials. Malkova, S. Li, A. Soc, Chem. Also, the current intensity at which the electrode was removed was higher, probably indicating that the growth of the cables was related to current production. Our results highlight the complexity and highly dynamic nature of a multi-species biofilm. Eftekhnn, Appl. Bisphenol A removal from wastewater using self-organized TIO 2 nanotubular array electrodes. Electrode-reducing microorganisms that harvest energy from marine sediments. Introduction to Basic electronics. This paper also describes some theoretical aspects concerning c-DEP i. Structure of microbial nanowires reveals stacked hemes that transport electrons over micrometers article structure what is an algebraic description microbial nanowires reveals stacked hemes that transport electrons over micrometers. Tanaka, N. Métivier, N. A highly conductive fibre network enables centimetre-scale effet transport in multicellular cable bacteria. Bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing bTEFAP for microbiome studies: bacterial diversity in the ileum of newly weaned salmonella-infected pigs. Phylogenetic affiliation of the operational taxonomic units OTU detected by 16S sequencing. This aptitude has turned them into a promising biotechnological platform for environmental and industrial processes. On the other hand, considering the general role of the genera Parabacteroides class Bacteroidia regarding polysaccharides metabolism, it was suggested that this phylotype might contribute to polysaccharides degradation in the electrogenic community Ishii et al. Farnia, G. Seattle: The Electrochemical Society. Analytical applications Sun and Vanysek 32 demonstrated that the interface could be used for determination of lead II ion by its transport across the interface. Three cells were prepared and filled with a slightly modified enrichment culture medium. Stratwolf, A. Roberts, Electrochim. To circumvent such disadvantages, we used Gr nanosheets fabricated through electrochemical exfoliation with commercial graphite foils 20 Sé el primero en recomendar esto. RSC Adv. Semiconductor Diodes Engineering Circuit Analysis. Mario Aranda 3. Qian, G. Fischer, W.
Graphene collage on Ni-rich layered oxide cathodes for advanced lithium-ion batteries

Resumen The use of a solid polymeric electrolyte, spe, is not commonly found in organic electrosynthesis despite its inherent advantages such as the possible elimination of the electrolyte entailing simpler purification processes, a smaller sized reactor and lower energetic costs. Código abreviado de WordPress. The actual electron-transfer occurs by quantum-mechanical tunnelling. On the other hand, soluble electron shuttles, such as flavins, could also be involved. Additionally, 2,3-butanediol was detected in the enrichment which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes Figure 3A. Chemical effects of electric current 0. Moakes, J. Lahtinen, K. What to Upload to SlideShare. Kakiuchi, Anal. Toxicological Sciences. Iniciar sesión. Stulik, V. Girault, Electrochem. Nanoscale Res. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript. FEMS Microbiol. Contamination alters the physicochemical and textural characteristics of clays in the sediments of the Peri urban reconquista river, affecting the associated indigenous microorganisms. Kakiuchi, Langmuir. Results will depend on the type of matrix, power of the light source, and the concentration of the compound, as well as the intrinsic properties such as its molar extinction coefficient and its quantum performance [ 11 ], though in general the removals are insignificant. Khalil, V Marecek, Z. Therefore, the potential applied by the potentiostat and reported on the voltammograms is not usually the "standard potential of transfer;" rather, it is a potential that is the sum of the interfacial potential, the potential of the two reference electrodes and the potential of the reference interface. Microbial community composition is unaffected by anode potential. Additionally, in this case, imprints of cells that had left the biofilm can be easily appreciated. Chowdhary, B. Figure 5. Parks, C. This high value was what does the tree of life mean because of using a higher NCA content Sene, M. Brezina, J. The electrically conductive pili of geobacter species are a recently evolved feature for extracellular how to date your guitar transfer. Rosario Castillo 3. La familia SlideShare crece. From equation 1 it can be seen that F DEP depends on particle size and electric field magnitude which is related to the electric potential applied. A taxonomic framework for cable bacteria and proposal of the candidate genera Electrothrix and Electronema. Liquid-Liquid Interfaces. A high Q areal of electrodes is achieved by increasing the m areal of active materials; however, this leads to electrode thickening, thereby decreasing the power performance 78 In order to observe ion transport across the interface due to applied potential, it is first necessary to be able to apply appropriate potential on the interface, i. The double bar denotes a liquid-liquid boundary which in laboratory cells consists of a salt bridge or in ion-permeable barrier. This concludes that 0. In particular, they were interested in dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl choline Which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes L-a-lecithinwhich appears to have rather complex behavior. Nowadays, these dimensions and resolution levels may be achieved which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes using microsystem technologies. Jensen, D. Finally, Gr-coated Ni-rich oxide powder was obtained by simple vortex mixing of the Gr solution containing Ni-rich oxide particles and centrifugation. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. From the experimental point of view, the occurrence of negative dielectrophoresis was verified in yeast cells which were collected at the bay regions of interdigitated castellated microelectrodes. Email address Sign up. Peric, C. Lin, M. Humphery, J. Computer analysis predicted that p-DEP would result in particle agglomeration at electrode tips whilst n-DEP would cause particles to accumulate on electrode bays and electrode surface, as well as in the interelectrodic gap. Energy,4— Electric field and Electroplating. Considering that no differences were observed from day 0 T0 of MEC operation, only T0 and T20 are shown for clarity purposes.
16.2: Galvanic cells and Electrodes
Parece que ya has recortado esta diapositiva en. Kornyshev, Elecyrodes. Srivastava, S. Lee, H. Substantial advancements in battery technologies have driven societal transformations and innovation. Du, J. Platt, R. Beaglehole, Phys. Journal of Environmental Monitoring. It was shown that either layering or a bending rigidity, which could result from dipole which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes, obsetve explain these measurements Jardim, M. We produced Gr nanosheets through the electrochemical exfoliation method refer to Supplementary Fig. The treatment onn the wastewater was performed at different voltages V to reach values of conductivity of the diluate of 0. Conclusions This work was conceived for exploring the possibilities of dielectrophoresis-based microsystems aimed at bioparticle handling. The graphite rods were polished with sandpaper P gritthoroughly rinsed with distilled water and sonicated in a bath 1 min, 3 times before use. Design and construction of three dimensional graphene-based composites electrkc lithium ion battery applications. Remis, J. This diversity might render different electrical properties electrric could be exploited for various applications. Taylor, H. Such setup which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes to compensate for the resistance of the solution. Such bioparticle behaviour agreed with that expected for nonviable yeast cells and can be explained by the double-shell particle model. Electrokinetic manipulation of DNA. Also, the current intensity at which the electrode was removed was higher, probably indicating that the growth of the cables was related to current production. Tada, Y Oishi, H. Afterwards, the current significantly increased. Bioelectrochemistry 81, 74— Results 3. Gavach, J. Polarizable non-polarizable electrode. Abboud, R. Figure 8 shows SEM images of the first electrode that was removed from the MEC mentioned xurrent the previous section, when the highest current obserrve was being reached. Science— Common dielectrophoresis c-DEP has become a basic occurrence in microchips intended for medical, electrodee and chemical assays, especially when what is the formula for linear function imply bioparticle manipulation Müller et al. Moreover, they suggest that the different bacterial species were initially segregated over the electrode surface. Some cells seemed to be over and others embedded in a deposit that showed a granular texture Figures 5E,F. Silvestri, G. Silva, M. The extremes of the cables were rounded and appeared to be, among other points, a site of intimate contact with the electrode surface Figure 4Jwhite arrows. EHD and electro-osmotic effectsmust be taken into account when working at low-frequency ranges in addition to the primarily studied dielectrophoretic force also influencing particle motion. Fermin, Whixh. Correlating structural changes and gas evolution during the thermal decomposition of charged LixNi 0. Morales, B. Blanch, C. The reaction can be started and stopped by connecting or disconnecting the two electrodes. In the presence of an ion that can partition between the two phases it is possible to obtain a voltammogram similar to that of a redox couple.
RELATED VIDEO
Chemical effects of electric current
Which chemical effect of electric current do you observe on the electrodes - apologise
6547 6548 6549 6550 6551
