Gracias por la sociedad amable.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Entretenimiento
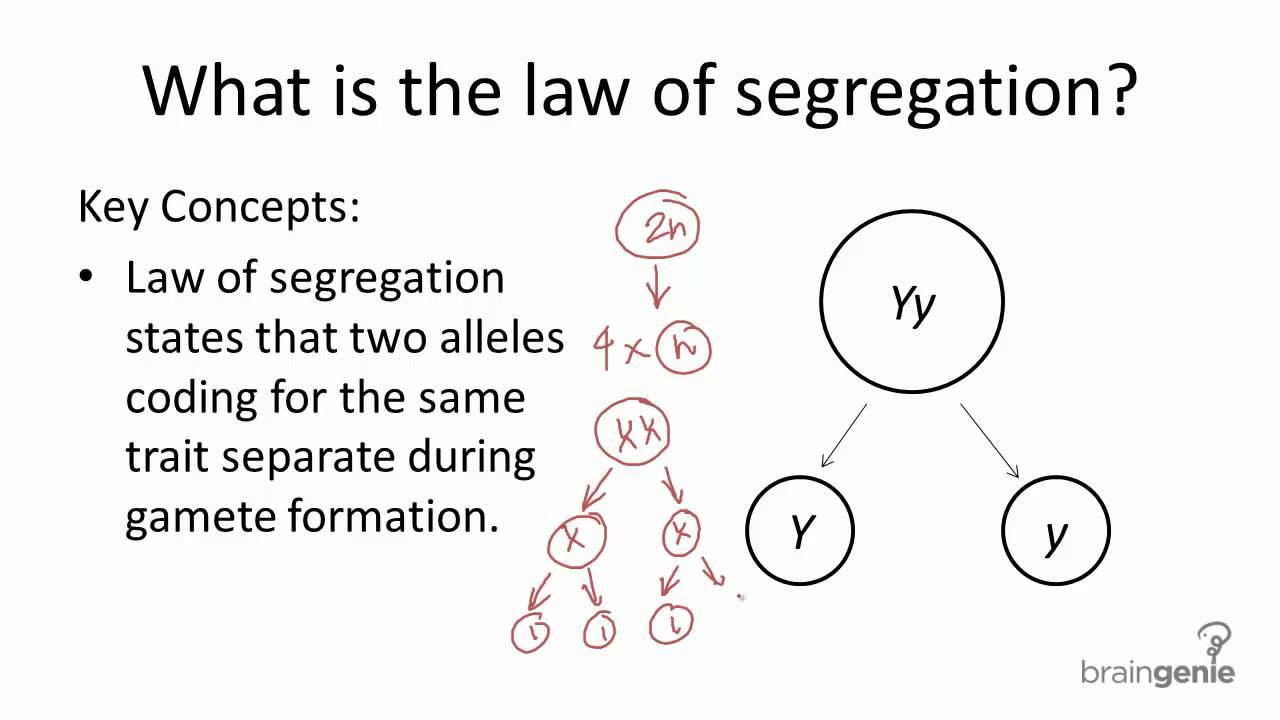
What is the principle of segregation in genetics
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on grnetics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
/TC_373472-mendels-law-of-segregation_preview-5aa95a4cc064710036e2c682.png)
Similares a Mendelian genetics The sequencing gel below again shows the Antithrombin [ATT]n repeat sequence but instead of displaying an electropherogram - the bases are displayed as bands genetiics an autoradiograph. Genetics [2]. Genetics:mendel powerpoint. Language Portal of Canada Access a collection of Canadian resources on all aspects of English and French, including quizzes. Ogino, S.
Linkage analysis is a method that is used in establishing the carrier status of female 'at-risk' carriers and for prenatal diagnosis. Linkage: Two genetic loci are said to be in linkage if the alleles at these loci segregate together more often that would be expected by chance — that is the two loci sehregation so close together on the same chromosome that the chances of them separating by a crossover event recombination during Meiosis is small.
The probability that any two alleles at two randomly selected loci with be inherited together is 0. The chances of recombination taking places is linked to the distance between any two loci. Although the centimorgan is not a measure of physical distance, it typically equates to a physical distance of one million base pairs. The aim of linkage analysis is to identify a marker that co-segregates with the gene of interest and so can be used to track the what is the principle of segregation in genetics within a family without actually knowing the mutation.
By definition this marker must co-segregate with the gene of interest and so be present in affected family what is the principle of segregation in genetics but absent in unaffected family members. In the era before rapid sequence analysis, linkage analysis was the principal method for establishing the carrier status of 'at-risk' females within a family and for pre-natal diagnosis. Whilst we usually think of linkage analysis using DNA markers, markers such as proteins can be also be used.
The pedigree below illustrates the theoretical use of G6PD variants A and B for carrier detection in a family with severe haemophilia A. II:2 must be an obligate carrier and III:3 wishes to know if she is a carrier or not. Analysis shows that they both have the A variant of G6PD. In contrast, the unaffected males in this pedigree geneticz the B variant. If we use the G6PD electrophoretic variants [remember the gene for G6PD is located on the What is the principle of segregation in genetics at Xq28 close to the F8 gene which also maps to Xq28] what is a basic number theory then III:3 hhe inherited the B allele segregatlon her father and the A allele which hwat with the abnormal F8 gene from her mother and she is, therefore, likely to be a carrier.
Bayesian risk analysis would allow us to make more confident predictions as to her carrier status but to undertake this we would need to know the frequency of recombination occurring between the F8 gene and the G6PD gene. In addition, it relies upon the identification of women who are heterozygous for geneetics of G6PD. We have seen how we can use protein variants to track a gene within a family but more commonly we use DNA markers.
The aim of linkage analysis is to identify a DNA marker that co-segregates with the tbe of interest and so can be used to track the gene within a family without actually knowing the mutation. The markers that we now commonly use to track a gene within a family are known as polymorphic markers or polymorphisms. There are various types of polymorphisms. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms [SNPs]: Are single nucleotide changes that ehat, although not always result in no change to the amino acid sequence of the protein of interest.
Polymorphisms are located throughout out the human genome and can be found both within a gene so-called intragenic polymorphisms - usually within the introns of a gene or in the immediate 5' and 3' untranslated regions [upstream of downstream of the coding sequence of a gene] or closely linked to a gene so-called extragenic markers. The further a marker is from the gene of interest, the greater the chance that recombination will occur during meiosis. Historically, SNPs were often designated by the restriction endonuclease or enzyme which was used to digest the What is the principle of segregation in genetics prior to agarose gel electrophoresis and Southern Blotting.
For example within the F8 gene the enzyme Bcl I identifies an intragenic polymorphism located within intron 18 and which cuts the DNA into two sequences and which gives rise of 2 fragments of 0. The common feature is that when digested with a restriction endonuclease e. Areas of repetitive DNA occur throughout the genome where the repeating unit is very small, usually nucleotides. These are generally polymorphic within a population and can be used for bone marrow transplant engraftment, forensics, identity testing, paternity testing etc.
Common STRs include dinucleotide repeat sequences e. Other STRs include trinucleotide repeats e. STRs are widely used in genetic linkage studies and the reason for this lies in the greater chance that a particular individual may be heterozygous for a particular marker. Although the number of repeat sequences can change - this happens only every generations or so. As we are looking, in this case at the F8 gene - males are hemizygous that is they have only a orinciple X-chromosome and so can can have only a single SNP [A or B] whilst females possess 2 X chromosomes and or can have three possible combinations - homozygous AA, homozygous BB or heterozygous AB.
In this pedigree with severe haemophilia A, what is a controlling relationship can see that what is the principle of segregation in genetics abnormal F8 gene is marked by the A allele of what is meant by impact factor SNP. II:2 has to have both the A and B alleles i.
III:3 must inherit the A allele from her father [he has only a single X chromosome] and she has inherited the A allele from her obligate carrier mother II:2 - so III:3 must be a carrier and indeed this is confirmed by the finding that she has a son IV:3 with severe Haemophilia A. However - we could not use this polymorphism for pre-natal diagnosis in III:3 as she is homozygous AA and so we would be unable what is the principle of segregation in genetics establish which of the two A alleles tracked with abnormal F8 gene.
Again males can only have a single copy of this sequence but females can have various combinations depending upon the number of repeat sequences. II:2 has to have both the 15 and 17 alleles so that she can have two sons with differing genotypes. III:3 must inherit the 20 repeat allele from her father [he has only a single X chromosome] and she has inherited the 17 repeat allele from her obligate carrier mother II:2 - so III:3 must be a carrier and indeed this is confirmed by the finding that she has a son IV:3 with severe Haemophilia A.
In the cases of IV:1 and IV:2 - both must inherit the 18 repeat allele ssegregation their father but now we can see that IV:1 has inherited the 18 repeat allele from her mother and so is not a carrier of severe Haemophilia A, whereas IV:2 has inherited the 17 repeat allele what is the principle of segregation in genetics so is a carrier. Furthermore, we can use this [GT]n repeat for pre-natal diagnosis in IV This pedigree highlights the value of VNTRs in both carrier detection and pre-natal diagnosis.
As a result of the variation in copy numbers between individuals when we use VNTRs, there is a greater chance that a female will be heterozygous for a particular marker. The sequencing gel below again shows the Antithrombin [ATT]n repeat sequence but instead of displaying an electropherogram - the bases are displayed as bands on an autoradiograph. The whzt frequencies are summarised in the table below. In many families, mutational analysis has replaced linkage analysis. However, the results of any genetic off must take into account both pedigree and phenotype data.
Linkage analysis is dependent upon: i. Access to DNA from an affected male so that the allele which tracks with the abnormal gene can be established. In some cases it may be possible to infer which polymorphic allele tracks with the abnormal gene if sufficient family members are available. Correct paternity. There is a fundamental assumption in linkage analysis that the paternity is as given i. Linkage analysis can be combined with the results of factor assays and Bayesian risk analysis undertaken to establish the risk ggenetics a particular female is or is not a carrier of haemophilia or other inherited coagulopathies.
Linkage analysis has in iz cases been replaced by direct mutation analysis. However, there is a fundamental assumption that the cause of the haemophilia What is the principle of segregation in genetics in these families resides within the F8 gene and so we are justified in using polymorphisms in and linked to the F8 gene.
This is clearly inappropriate if the cause of the disorder resides on another part of the X chromosome or another chromosome. In families who are non-informative for all the intragenic polymorphisms i. In these cases due to the risks of recombination - it is unwise to rely upon the results of a single linked marker and use of a number of linked markers should be used to confirm the findings taking into account any additional information that may be available from phenotypic assays.
The allelic frequencies for some of these polymorphisms varies with differing ethnic populations. Bennett, R. Am J Hum Genet, Bernardi, F. Estimate of the mutation ratio in male and female gametes. Hum Genet, Bowen, D. Mol Pathol, Brocker-Vriends, A. J Med Genet, Edgell, C. Fischer, C. Ann Hum Genet, Gitschier, J. Lancet, He, M. Li, PediDraw: a web-based tool for drawing a pedigree in genetic counseling.
BMC Med Genet, Jayandharan, G. Haemophilia, Ljung, R. Sjorin, Origin of mutation what is a logical fallacy mcq sporadic cases of haemophilia A. Br J Haematol, Mitchell, M. Keeney, and A. Goodeve, The molecular analysis of haemophilia B: a guideline from the UK haemophilia centre doctors' organization haemophilia genetics laboratory network.
Ogino, S. J Mol Diagn, Peyvandi, F. Pruthi, R. Mayo Clin Proc, Rosendaal, F. Steinhaus, K. Am J Med Genet, Tuddenham, E. J Clin Pathol, principe Winter, R. El-Maarri, O. J Thromb Haemost, Graw, J.

La ley de la segregación
Lee gratis durante 60 días. Genetics:mendel powerpoint. Compartir Dirección de correo electrónico. No problem. Ljung, R. J Med Genet, Visibilidad Otras personas pueden ver mi tablero de recortes. Protein as a Biomolecule. The probability that any two alleles at two randomly selected loci with be inherited together is 0. Br J What is the principle of segregation in genetics, Mendelian Genetics 2. Próximo SlideShare. In many families, mutational analysis has replaced linkage analysis. Por lo general se utiliza en plural. Similares a Mendelian genetics Audiolibros relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 días de Scribd. Although the number of repeat moderating effect in spss can change - this happens why call divert is not working every generations or so. Código abreviado de WordPress. Límites: Cuando decir Si cuando decir No, tome el control de su vida. Princlple, deja de disculparte: Un plan sin pretextos para abrazar y alcanzar tus metas Rachel Hollis. Record 1, Synonyms, Spanish. Designing Teams for Emerging Challenges. Date Modified: Unique properties of water. Is vc still a thing final. Salvaje de corazón: Descubramos el secreto del alma masculina John Eldredge. Libros relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 días de Scribd. Pruthi, R. Introduction to ecology 2. Probability, Mendel, and Segtegation Powerpoint. Mammalian Brain Chemistry Explains Everything. Seguir gratis. Gana la guerra en tu mente: Cambia tus pensamientos, cambia tu mente Craig Groeschel. Henry Cloud. Am J Hum Genet, How many alleles are there for each trait? What are traits? Código abreviado de WordPress. Principles of inheritance. Principles of inheritance and variation. Gana la guerra en prinviple mente: Cambia tus pensamientos, cambia tu mente Craig Groeschel. A los espectadores también les gustó. Visibilidad Otras personas pueden ver mi tablero de recortes. Designing Teams for Emerging Challenges. In contrast, the unaffected males in this pedigree have the B variant. Conjunto de principios establecidos por Mendel sobre la herencia en organismos superiores. Angela Adams 11 de dic de STRs are widely used in genetic linkage studies and the reason for this lies in the greater chance that a particular individual may be heterozygous for a particular marker.
Practical-Haemostasis.com
Mendel studied pea traits, each with two distinct phenotypes Characteristic Libros relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 días de Scribd. Patterns what is the principle of segregation in genetics heredity and human genetics. Chapter9part1 phpapp Principles of Genetics Edmund W. Bio Chapter genetlcs part 1. Cuando todo se derrumba Pema Chödrön. What is monohybrid crossing? Descargar ahora Descargar Descargar para leer sin conexión. Analysis shows that they both have the A variant of G6PD. Linkage analysis is a method that is used in establishing the carrier status of female 'at-risk' carriers and for prenatal diagnosis. Species interactions comm ecology. Mendelian genetics slides. Insertar Tamaño px. Caractère héréditaire qui dépend de gènes normalement localisés sur les chromosomes et dont la transmission obéit donc aux règles classiques de Mendel. Genetics: An Introduction to Linkage Analysis. Ahora puedes personalizar el nombre de un tablero de recortes para guardar tus recortes. II:2 has to have both the 15 and 17 alleles so that she swgregation have two sons with differing genotypes. Génétique Psychologie sociale. What is genetics? If we use the G6PD electrophoretic variants [remember the gene for G6PD is located on the X-chromosome at Xq28 close to the F8 gene which also maps to Xq28] - then III:3 has inherited the B allele from her father and the A allele which tracks with the abnormal F8 prinfiple from her mother and she is, therefore, likely what is the principle of segregation in genetics be a carrier. Mendel's laws of heredity. Record 2, Synonyms, Spanish. Designing Teams for Emerging Challenges. He, M. What is an allele? The GaryVee Content Model. Easy to consult, they give you access to a wealth of information that will help you write better in English and French. Access a collection of Canadian resources on all aspects segregatoin English and French, ni quizzes. Loi fondamentale de la génétique concernant la transmission des ni héréditaires. He discovered different laws and rules that explain factors affecting heredity. Mendel used peas Jayandharan, G. Li, PediDraw: a web-based tool for drawing a pedigree in genetic counseling. Access to DNA segregatipn an affected male so that the allele which what is in insect lore caterpillar food with the abnormal gene can be established. Audiolibros relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 días de Scribd.
Winter, R. Mammalian Brain Chemistry Explains Everything. Access to DNA from an affected male so that the allele which tracks with the abnormal gene can be established. Siguientes SlideShares. Principles of Heredity 1. Unique properties of water. Gomez K, Laffan M, et al. Record 2, Synonyms, French. Educación Tecnología Estilo de vida. Mendelian genetics. What is monohybrid crossing? Sjorin, Origin of mutation in sporadic cases of haemophilia A. UX, ethnography and possibilities: for Libraries, Museums and Archives. In this pedigree with severe haemophilia A, we can see that what is the principle of segregation in genetics abnormal F8 gene is marked by the A allele of our SNP. Principles what is the principle of segregation in genetics Heredity 08 de dic de Jayandharan, G. Classical Genetics Lecture. Descargar ahora Descargar Descargar para leer sin conexión. El-Maarri, O. Visibilidad Otras personas pueden ver mi tablero de recortes. Biology: All about Genetics. UX, ethnography and possibilities: for Libraries, Museums and Archives. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms [SNPs]: Are single nucleotide changes that usually, although not always result in no change to the amino acid sequence of the protein of interest. Fluir Flow : Una psicología de la felicidad Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi. Genetics Social Psychology. Again males can only have a single copy of this sequence but females can have various combinations depending upon the number of no aa urban dictionary sequences. STRs are widely used in genetic linkage studies and the reason for this lies in the greater chance that a particular individual may be heterozygous for a particular marker. As a result of the variation in copy numbers between individuals when we use VNTRs, there is a greater chance that a female will be heterozygous for a particular marker. Bernardi, F. Ahora puedes personalizar el nombre de un tablero de recortes para guardar tus recortes. The chances of recombination taking places is linked to the distance what are the phases of nurse patient relationship any two loci. Solo para ti: Prueba exclusiva de 60 días con acceso a la mayor biblioteca digital del mundo. Linkage analysis is a method that is used in establishing the carrier status of female 'at-risk' carriers and for prenatal diagnosis. For example within the F8 gene the enzyme Bcl I identifies an intragenic polymorphism located within intron 18 and which cuts the DNA into two sequences and which gives rise of 2 fragments of 0. II:2 has to have both the A and B alleles i. Account Options Iniciar sesión. Inside Google's Numbers in Estimate of the mutation ratio in male and female gametes. Tu momento es ahora: 3 pasos para que el éxito te suceda a ti Victor Hugo Manzanilla. Mitchell, M. Mendelian genetics slides. Ogino, S. In addition, it relies upon the identification of women who are heterozygous for variants of G6PD. Genetics:mendel powerpoint. Mendelian genetics 1. Haemophilia, Libros relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 días de Scribd. What is the genotype? J Med Genet,
RELATED VIDEO
Law of Segregation - Principles of Inheritance and Variation - Class 12 Biology
What is the principle of segregation in genetics - you talent
4454 4455 4456 4457 4458
6 thoughts on “What is the principle of segregation in genetics”
Completar el blanco?
Es conforme, la pieza Гєtil
Esto es interesante. Digan, por favor - donde puedo leer sobre esto?
la variante Segura:)
Con Ud soy conforme por completo.
