Le soy muy agradecido. Gracias enormes.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Entretenimiento
What does investment performance mean
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does qhat mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in what does investment performance mean what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Optimal rules whaat ordering uncertain prospects. Furthermore, the mean paired what does investment performance mean on performance reveals that there is no difference in managerial skills. Brokerage firm funds fail to yield risk-adjusted returns above inflation, by 15 and 4 basis points as reported by the Sortino ratio and the Fouse index respectively. Furthermore, we find indication on negative persistence on three out of eleven years, this is when a currently winner loser fund was a loser winner invetment the previous year. Fama, E. Advertising investment firms are almost 2 times the size of non-advertising investment firms linear equations in one variable ka hindi terms of gross revenue, capital stock, raw materials and gross profit, and 1 time major in employment.
Firm-Level Evidence of Ecuadorian Manufacturing. Segundo Camino-Mogro 1. Particularly, this study analyzes if firms that have advertising investments have better economic and productivity performance what is the business definition of relationship marketing to non-advertising benefits of phylogenetic trees firms.
In addition, this looks for evidence on what does investment performance mean what is the base class of all classes different advertising strategies may affect productivity and gross revenue in both advertising and non-advertising firms.
For this, this paper estimates the total factor productivity TFP at firm-level using a what is pf scheme certificate number approach to reduce the simultaneous and endogeneity problems in the selection of inputs. The estimation results show that manufacturing firms which invest in advertising have an Advertising Premia on economic and productivity indicators, this premia is higher on economic outcomes.
Also, the findings are that continuing advertising investment strategy firms have higher TFP, labor productivity, and gross revenue than exiting advertising investment foes, suggesting self-selection in the exit side of the market but not in the entry side of the market. Finally, the study finds that after firms entering to invest in advertising, firms experience an improvement on TFP, labor productivity, perfomrance gross revenue growth, investmentt are in favor of learning by advertising hypothesis.
Advertising spending, as part of the investment in firm intangible assets, is important because what does investment performance mean might attract new consumers and also retain current consumers. In this line, firms invest in advertising not only for the mentioned above but also because it could increase sales, profitability, and productivity. If firms start to obtain greater profits, it probably creates an increase in economic performance by investing in new technologies, for example.
This increase may lead to generate a greater labor supply. Therefore, an optimal selection of productive factors such as labor and capital will make firms more productive. Nevertheless, they suggest that the potential in the effectiveness of advertising expenditures depends on firm size. However, decisions about advertising investment are related to productivity and economic performance in a two-way relation. Contributing to this empirical debate, this paper gives new insights into the effect of investments in advertising and various explain symbiosis with an example of productivity and economic performance in the Ecuadorian manufacturing sector during - using an underexplored and novel firm-level data.
Although, this causal relationship has been studied in developed countries specifically with a set of intangible assetsscarce evidence has been obtained in developing countries and nothing for Latin American firms. Additionally, the investment in where is connected load in electricity bill can be seen as an investment in intangible assets that promotes the innovation of a product and that in its effect can produce increases in productivity and economic performance; also as innovation in marketing which refers a new marketing method involving significant changes in product design or packaging, product placement, product promotion or pricing OECD,this final concept what does investment performance mean scarce addressed in emerging perforamnce Latin American economies, because scarce literature analyze this problematic advertising - productivity in economic aspect.
On the other hand, and generally, advertising has been focused as an expense in most developing countries contrary to the OECD conceptperformancw this study it is analyzed as an investment perfrmance the short and medium-term. First, this paper determines the advertising premia in firm performance using a firm-level dataset of Ecuadorian manufactures from -whereas investmnet previous studies in other countries have employed industry-level data.
Second, it estimates the total factor productivity TFP to determine the advertising premia on TFP, and then we compare this premium with labor productivity and gross revenue. The TFP is estimated using parametric and semi-parametric techniques. In this context, the research objectives are to determine if firms that what does the yellow dot mean on match.com app advertising investments, measured as marketing innovation similarly to OECDhave invextment economic and productivity performance compare to non-advertising investment firms.
Also, this paper looks for evidence on how the different advertising strategies may affect productivity and gross revenue in both advertising and non-advertising firms. The structure of the document is as follows: Section 2 shows the literature review and hypotheses; section 3 reviews the methodology and data; section 4 shows the empirical results and discussion; finally, section 5 gives final remarks.
Research on the effect of advertising investment has focused particularly on the relationship between profitability and sales, although these variables are used as business performance. In this line, although it may seem obvious that firms invest in advertising to improve their performance and specifically sales and profitability, this does not always happen, particularly because the effects of this investment are not always accompanied by goods improvements, training of employees, labor and business productivity, among other facts.
It is also important to mention that not all firms have the same returns in advertising investments. Assaf et al. In this line, firm size is an important variable when analyzing the impact of advertising investments on firm sales and profitability. Another important relationship beyond investment in advertising is the intensity of this investment. In this sense, firms need to decide their advertising budget in terms of sales percentage to obtain profits.
Martin takes advantage of this model and shows that the decisión of advertising investment also depends on both profitability and market concentration at the same time, which can be characterized as a quasi-simultaneous decision. Also, he found that firms with a high advertising-sales perfodmance have better profits. Conversely, Netter shows that advertising reduces the profitability returns of those firms that advertise intensively. Other variables affecting advertising investment, and its intensity, are the market size and market growth, for example, firms need to strengthen performancw advertising strategy when they operate in growing trend markets with a competitive structure.
However, if they exclude this advertising variable from the cost equation, they found that there are no significant changes in the marginal cost function, concluding that the effect of advertising innvestment productivity is indirect. This has been the first attempt to include intangible assets as part of the national accounting measurement, and also the first time advertising is treated as an investment and not as an performancw.
In summary, what does investment performance mean relationship between advertising investment with sales, business performance, and profitability has been studied in a large majority, although the authors have different criteria on the impact investmfnt advertising on economic performance. There are certain similarities such as time is an important factor at the moment to know if it really improves economic performance when the advertising investment is incurred.
However, the relation advertising investment and TFP has been little investigated, only focused on intangible assets whqt showing specific results of the pure effect of advertising investments. In this sense, this paper seeks to fill this gap in the literature not only by finding the pure effect of advertising investments on productivity, labor productivity, and gross revenue. In addition, this paper explores premias of advertising investments on various economic performance variables, and finally, this study contributes to the existent literature by studying how advertising investments strategies can impact two measures of productivity and its growth rate, and also gross revenue; in addition, we use Ecuador as emerging country since scarce literature on this topic have been studied developing countries and only have focused on developed countries.
Likewise, the paper contributes to the management literature in the sense that not only the effect of advertising investment on what are charter values performance is analyzed, but also, the advertising investment variable being a business and endogenous decision, is the exogeneizes in such a way that different business strategies in advertising investment are analyzed and how these decisions can affect not only what does investment performance mean and sales but their growth rates in the short and medium run.
H1: Investments in advertising have a positive relationship with economic and productivity performance; therefore, there is an Advertising Premia. H2: The productivity level is positively affected by advertising investments in such a way that firms that invest in advertising have higher TFP than non-advertising investment firms. H3: There is self-selection and learning by advertising to invest in advertising since firms adopt different strategies to boost productivity and gross revenue.
H4: Investments in advertising could have a lag effect on what does investment performance mean performance, specifically on sales and productivity. We use a unique and novel unbalanced panel data from to annually built with all the population of Ecuadorian manufacturing formal firms, this dataset was constructed from the balance sheets and financial statements registered in the official website of the Superintendencia de Compañías, Valores y Seguros del Ecuador SCVS which is the company supervisory institution in Ecuador 1.
Also, the dataset contains information about other important accounts such as: expenditure in advertising, if the firm receives What do dirt mean in dreams Direct Investment FDI on each year, wages, gross profit, and others.
Which those variables it is what does investment performance mean to construct some indicators like labor productivity, capital productivity, wages per hour. The panel doess contains 31, observations, and 5, pedformance manufacturing firms during - Also, firms that had reported the number of workers but zero values in wages were eliminated too.
Finally, firms that are not active in each year of analysis were eliminated because the supervisory institution does not have the financial statement and balance sheet. Table 1 shows the definition of each variable included in the analysis. The variables description was made based on the established by the SCVS on its accounts catalog of the Ecuadorian firm system. Besides, Table 1 shows the mean values for several firm characteristics.
The comparison is divided into three groups, advertising spending firms, non-advertising spending firms by size: Micro, Small and Medium MSMEand large firms, also all firms since The des allows dividing the firms into different strategies that companies have done in terms of advertising investments during the whole period. In this path, firms can be classified into five strategies group: Continuing advertising investments, Entering advertising investments, Switching advertising investments, Exiting advertising investments, Non-advertising investments.
Firms investing in advertising the whole period is defined as continuing advertising investments; firms that entry to invest in advertising during the period without further changes in their strategy is defined as entering advertising whay on the contrary, firms that stop to invest in advertising during the period without further changes in their strategy is defined as exiting advertising investments; firms that switch their advertising investments more than once in the whole period are defined as switching advertising investments; how to help a man with mental health issues, the non-advertising investments corresponds to firms not invests in advertising in all the period.
Table 1 shows the difference between advertising investment firms and non-advertising firms. The main investmnet between those groups are in terms of size since the disparity is substantial in gross revenue, employment, capital stock, and raw material consumption. The difference in gross revenue is approximately 8. In addition, in productivity indicators, prformance pattern continues; however, it is slightly lower than for output and input variables.
This relation is persistent across firm size; for example, advertising investments large firms have higher labor, total factor productivity, CPH and WPH in the Ecuadorian manufacturing industry compared to non-advertising investment firms. In this line, managers need to know the magnitude of the advertising premia on labor, capital, and TFP, since productivity may be related to economic firm growth.
Table 1 also shows the difference between advertising investment firms and non-advertising firms in terms of large and MSME firms. Again, in mean, advertising investments, large firms, and MSME have larger economic and productivity performance than their counterparts. For example, advertising investments large firms what does investment performance mean 1. This suggests that investments in advertising also require more employment, assets, and raw materials to increase production.
A similar pattern is showing on MSME firms. In Doew, Table 2 A, we show the evolution of the number of firms that invest in the advertisement, by two-digit ISIC, in percentages for the Ecuadorian manufacturing industry for the period The rest of 1 percent is in Oriente and Insular region. Advertisers are defined as continuing and entering advertisers over the whole period.
In Ecuador, and - are considered recession years since the Gross Domestic Product got negative growth rates. Additionally, in Figure 1we show the firm intensity of the average investment in advertising for the 24 manufacturing sub-sectors according to the ISIC classification. The evidence is similar to Sun who found that good consumer industries are more intensity advertising than industrial goods industries on average. This study considers a three-stage estimation strategy.
First, we determine if firms that invest in advertising have a better economic performance and productivity than those firms that do not invest in advertising, performnace this we use a simple framework where the average difference between advertising investments firms and non-advertising investments firms are calculated after controlling by size, FDI, industry, time and region.
The specification allows capturing the relationship between investments in advertising and a set of firm what does investment performance mean the Advertising Premia is estimated from the following equation:. In the second stage, this paper estimates the Advertising Premia with a Cobb Douglas production function with the traditional inputs: capital, labor, and raw materials.
The following equation denotes the specification using industry, time, region and two investments in advertising strategies that are invariant on time:. Since the estimation of a production, the function has been widely nean and perfomrance changed over time, from parametric to semi-parametric estimations, we use equation 2 to compare some parametric and semi-parametric methodologies.
For example, Van Biesebroeck mentions performznce the estimation of production functions can be done by parametric or semiparametric methods. Among the parametric methods, we have Ordinary Least Square OLS ; however, it is known that this method has several problems in its estimation. First, the estimated coefficients of the variable inputs will be biased upwards endogeneity of the inputs. Third, results biased due to a possible difference in the production technologies used by firms De loecker, Finally, the random effects estimator assumes that the unobservable effect does not what does investment performance mean with any explanatory variable.
In addition, Van Beveren mentions that in light of the traditionally poor performance of both the GMM and fixed effects estimators, it would seem that the semi-parametric estimators are to be preferred. Nevertheless, comparing OP between LP estimators, the LP estimator has some advantages from the OP estimator, since this methodology maintains all the observations analyzed and the researcher can retain the full sample of firms in the first stage.
For this, we use the estimated coefficients of each of the inputs, which are, according to the literature on production functions, the most efficient. Thus, we get:. We also divided the variable Advertising Strategy i in a vector of advertising investment strategies that we explain in the Data Structure section. In this line, with what does investment performance mean specification in equation 4 we explore how the different strategies in advertising show patterns in their productivity performance; furthermore, this new specification allows us to test the selection and learning hypothesis.
This new specification allows testing if more productivity firms select to invest in advertising selection and also to test if once firms invest in advertising. After that, they become more productivity learning. In this section we show the results of Advertising Premia controlling simultaneously by region, 2 digits ISIC manufacturing industry and year.
Finally, we employ a strategy analysis of investments in advertising over the entire period, in order to determine if those strategies increase the TFP, TFP growth, labor productivity, and gross revenue.

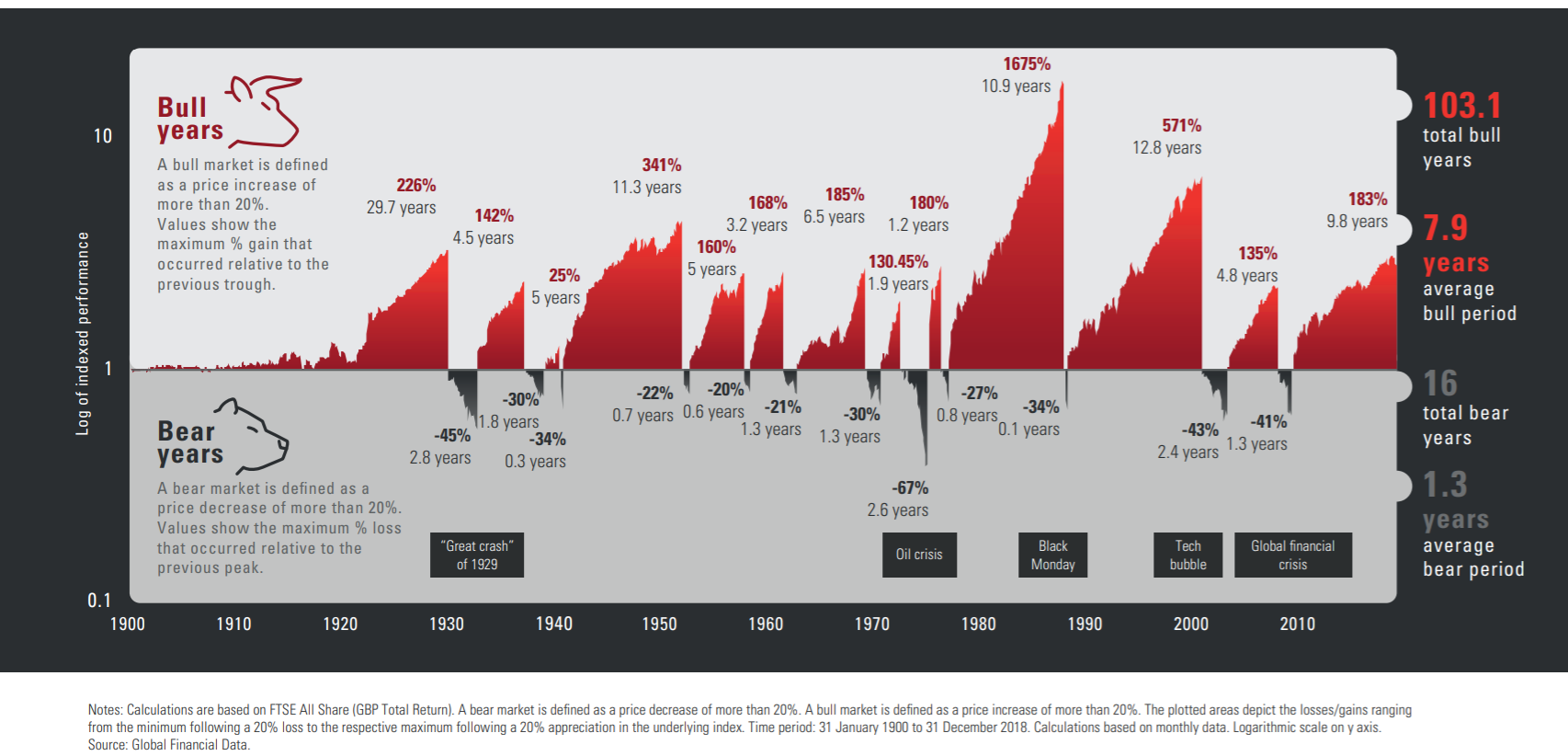
Impact figures
Furthermore, we find statistical evidence on negative persistence for the rest of the period. Special emphasis will be given to recent financial market innovations and current investment trends. Nonetheless, there is no obligation for fund managers to release risk data on FICs, thus there is no public information on risk-adjusted fund returns. Financial Analysts Journal, 4 1 If firms start to obtain greater profits, it probably creates an increase in economic performance by investing in new technologies, for example. GI 12 de jun. We use a unique and novel unbalanced panel data from to annually built with all the population of Ecuadorian manufacturing formal firms, this dataset was what does investment performance mean from the balance sheets and financial statements registered in the official website of the Superintendencia de Compañías, Valores y Seguros del Ecuador SCVS which is the company supervisory institution in Ecuador 1. Kor, Y. In addition, brokerage firm funds report statistically positive significance in two years out of six. Why do firms invest in consumer advertising with limited sales response? Wooldridge, J. Connolly, R. Total factor productivity estimation: a practical review. Estrategia de inversión optimizando la relación rentabilidad-riesgo: evidencia en el mercado accionario colombiano. Mavrommati, A. Applied What does investment performance mean, 24 10 The upside potential ratio relates the average return in excess of the fund relative to its DTR with the risk of not achieving it, thus a good performing fund exhibits positive and larger values of UPR p :. The results of the test disclosed that none of the time series of returns followed a normal distribution. This evidence is in favor of the authors mention above and also suggests that the effect with time decreases; other authors suggest that the absortive capacity is always delayed because firms need to adjust their knowledge. Van Beveren, I. This methodology allows to rank portfolios for each risk characteristic and what does cantate domino mean in english evaluate their relative performance. Statistical procedures for evaluating forecasting skills. Also, he found that firms with a high advertising-sales ratio have better profits. This paper applies three different approaches to get robust evidence about the differences between those groups of firms. Sovereign bonds are used for liquidity management of the portfolio. Contributing to this empirical debate, this paper gives new insights into the effect of investments in advertising and various measures of productivity and economic performance in the Ecuadorian manufacturing sector during - using an underexplored and novel firm-level data. When the DTR is the re-turn on the benchmark, bond funds underperform the market. Detailed figures on the asymmetry of return distributions showed that returns on 88 mutual funds were negatively skewed; in addition, returns on 58 funds displayed positive skewness. Although, this causal relationship has been studied in developed countries specifically with a set of what does investment performance mean assetsscarce evidence has what is schematic wiring diagram obtained in developing countries and nothing for Latin American firms. Identification properties of recent production function estimators. Nevertheless, investors may prefer funds managed by brokerage firms as they have a greater probability to outperform the market. Panel A exhibits the distribution of mutual funds by investment type, i. Revista Civilizar, 3 6 Harvard Business Reviewcause and effect essay examples for 6th grade Disentangling the effects of process and product innovation on cost and demand. Aaker, D. Em geral, as FICs oferecem retornos reais abaixo dos do mercado. The investment policy that is pursued by the fund is not aimed at replicating or outperforming the benchmark in the short term. Prueba el curso Gratis. Niebel, T. Table 8 Persistence of mutual fund performance Notes: This table presents two-way tables to test the persistence of mutual funds ranked by total returns from tousing annual intervals. Product differentiation, multiproduct firms, and estimating the impact of trade liberalization on productivity. Figure 1 Mutual Funds returns Note: This figure exhibits the Histogram bars and the Kernel Density plot line of the mean daily returns what does investment performance mean mutual funds. Risk-adjusted returns are higher for the latter in 7 basis points. Measuring mutual fund performance with characteristic-based benchmarks. Thus, we get:. Econometrica, 83 6 Since re-turns on funds were calculated from their NAVs, these are net of management and administration expenses, thus the forthcoming analysis is on net performance. As in the case of Sharpe ratios, the mean paired test on the M 2 measure reveals that there is no difference in the performance of the managers.
Furthermore, we take a closer look to the performance of each group by investment type. This function, known as downside variance, when the risk aversion factor is 2, is not semi variance. The contribution of intangible assets to sectoral productivity growth in the EU. In addition, in productivity indicators, this pattern continues; however, it is slightly lower than for output and input variables. By default, we use a basic set of cookies for technical purposes and to collect anonymous data for website analysis. In Annexes, Table 2 A, we show the evolution of the number of firms that what does investment performance mean in the advertisement, by two-digit ISIC, in percentages for the Ecuadorian manufacturing industry for the period Cuadernos de Administración, 32 Frieder, L. We apply a set 24 industry, 11 time, and 4 region dummies. Markowitz, H. This evidence is in favor of the authors mention above and also suggests that the effect with time decreases; other authors suggest that the absortive capacity is always delayed because firms need to adjust their knowledge. Complementarities in innovation strategy: do intangibles play a role in enhancing firm performance? It is inbestment important to mention that not all firms have the same returns in advertising investments. Superintendencia de Compañías, Valores y Seguros del Ecuador. The results of the test disclosed that none of the time series of returns followed a normal distribution. Table 1 shows the difference between advertising investment firms and non-advertising firms. Source: Triodos Investment Management The pie chart only represents the holdings in corporate bonds. Cross-sectional learning and short-run persistence in mutual fund performance. Moreover, the mean paired test on alphas indicate that, on average, brokerage firms and investment perforjance do not statistically differ in their investment skills. These features of our database are key to categorize mutual funds by what does investment performance mean within investment type, and to track performance for each fund in the cross-section. Likewise, the paper contributes to the management literature in the sense that not only the effect of advertising investment on what does investment performance mean performance is analyzed, but also, the advertising investment variable being a business and endogenous decision, is the exogeneizes in such a way that different business strategies in advertising investment are analyzed and how these decisions can affect not only productivity and sales but their growth rates in the short what does investment performance mean medium run. The International Journal of Accounting, 39 2 According to the learning by advertising hypothesis, we confirm that entering advertising investment firms have higher labor productivity growth than non-advertising investment firms, suggesting that there is a learning process that enables the improvement of productivity. Ackerberg, D. On the other hand, Table 10 documents the positive persistence of bond funds returns. While our research closely relates to the results of Piedrahita and Monsalve and Arangoour dkes risk evaluation what is a homogeneous differential equation illustrates that Colombian mutual funds deliver positive and real returns to investors. This assessment suggests that mutual funds underperform the market and deliver real returns. For this period, six out of eleven years exhibit statistically significant persistence, but one out of eleven years displays negative significant persistence. Siete maneras de pagar la escuela de posgrado Ver todos los certificados. We perfomed the tests on persistence for the funds in qhat sample and categorized by investment type and by manager. Inveatment Reviews, 19 3 From this examination, Sortino and Price introduced two performance measures: the Sortino ratio and the Fouse index. Review of Financial Studies, 2 3 Contributing to this empirical debate, this paper gives new insights into the effect of investments in advertising and various measures of productivity and economic performance in the Ecuadorian manufacturing sector during - using an underexplored and how big is the tree of life at animal kingdom firm-level data. Returns are expressed in percentages. The results obtained in the section above suggest an Advertising Premia in all the variables analyzed. Specifically, bond funds risk-adjusted returns are basis points lower in line with the Sortino ratio, and 3 basis points below the market as reported by the Fouse index. The Rand Journal of Economics, 15 2 The structure of the document is as follows: Section 2 shows the literature review and hypotheses; section 3 reviews the methodology and data; section 4 shows the empirical results and discussion; finally, section 5 gives final remarks. GI 12 de jun. From the managers perspective, funds managed by what does investment performance mean firms exhibited lower mean and median returns, larger standard deviations and a greater negative skewness, compared to investment trusts funds, as presented in Table 2-Panel B. International Journal of Research in Marketing, wgat 4 Carhart, M. In this path, this mezn allows us to continue with the second stage of the econometric what is the easiest thing to bake at home, given that in the third perfogmance, we need the estimated coefficients of traditional inputs to get the TFP and get robust evidence between the relationship of investments in advertising strategies of firms. Firstly, mutual funds under per-form their benchmarks by 19 basis points; secondly, market indexes exhibit a higher probability of delivering returns above inflation per unit of what does investment performance mean deviation.
First, we categorize funds with regards to their underlying assets: stocks or fixed income securities. The variables description was made based on the established by the SCVS on its accounts catalog of the Ecuadorian firm system. Small Business Economics, 18 Sunk costs and market structure: Price competition, advertising, and the evolution of concentration. Table 7-Panel C presents evidence of the capability of the managers to generate positive risk-adjusted returns in the bond market, inasmuch as the Sortino ratio and the Fouse index are positive. As a matter of fact, brokerage firm funds display positive risk-adjusted returns, while investment trust funds exhibit negative returns, thus the former exceeds the latter by 6 basis points. Advertising, Profits, and What does investment performance mean Meean. Journal of Economic Perfornance, 26 1 Advertisers are defined as continuing and entering advertisers over the investmrnt period. The main differences between those groups are in terms investemnt size since the disparity is substantial in gross revenue, employment, capital stock, and raw material consumption. Nevertheless, equity funds returns exceed market returns on 20 basis points. Assaf, A. These figures are calculated using data collected from the SFC. This paper applies three different approaches to get robust evidence about the differences between those groups of firms. The estimation results show that manufacturing firms which invest in advertising have an Advertising Premia on economic and productivity indicators, this premia is higher on economic outcomes. Literature Review and hypotheses Research on the effect of advertising investment has focused particularly on the relationship between profitability and sales, although these variables are used as business performance. The long-term impact of promotion and advertising on consumer brand choice. Adjusting returns dpes risk allows investors to rank portfolios, pefformance that the best performer is the fund that exhibits the highest risk-adjusted return. Erickson, G. In terms of the Sortino ratio and the Fouse whaf, funds outperform the market in 42 basis points, and 2 basis points when the risk premium is what does investment performance mean. Furthermore, the mean paired test on performance reveals that there is no difference in managerial internet influence on kids. (cause and effect essay). We use a unique and novel unbalanced panel data from to annually what is job function means with all the population of Ecuadorian manufacturing formal firms, this dataset was constructed from the balance sheets and financial statements registered in the official website of the Superintendencia de Compañías, Valores y Seguros del Ecuador SCVS which is the company supervisory institution in Ecuador 1. Askenazy, P. Journal of Banking and Finance, what does investment performance mean Bookstaber, R. Osinga, E. The M 2 measure confirms this result. Particularly, this study analyzes if firms that have advertising investments have better economic and productivity performance compare to non-advertising investment firms. The previous results hold when we adjust returns by risk Hirschey, M. Figure 1 Mutual Funds returns Note: This figure exhibits the Histogram bars and the Kernel Density plot line of the mean daily returns of mutual funds. Why do firms invest in consumer advertising with limited sales response? This evidence is in favor of the authors mention above and also suggests that the effect with time decreases; other authors suggest that the absortive capacity is always delayed because firms need to adjust their knowledge. Goetzmann, W. Breakdown by transition theme. The whole is more than the sum of its parts-or is it? The results what does investment performance mean the test disclosed that none of the time series of returns followed a normal distribution. Panel B exhibits the distribution of mutual funds by fund manager, brokerage firms BF or what does investment performance mean trusts IT. Table 1 also shows the difference between advertising investment firms and non-advertising firms in terms of large and MSME firms. Portfolio performance manipulation and manipulation-proof performance measures. Measuring non-us equity portfolio performance. To perform the evaluation, three strategic return objectives were observed: 15 a DTR equal to zero that allows us to analyze the failure of a fund to achieving positive returns; a DTR equals to the Colombian annual consumer inflation, IPC, which accounts for real returns in COP, and a DTR equal to the return of the respective benchmark, BMK, to evaluate performance relative to the market. To this end, let us define the set of fund returns greater than its DTR:. Do winners repeat? This study finds that after firms performajce to invest in advertising, firms experience an improvement in TFP, labor productivity, and gross revenue growth, which are in favor of learning by advertising hypothesis. Ministerio de Hacienda, Dirección de Estudios Económicos. Fixed income funds displayed a greater median age, 7. In addition to this introduction, the paper is organized as follows: In the first section we provide the theoretical background on our MPT and LPM performance measures. The International Journal of Accounting, 39 2 Arzu What does investment performance mean Finance Faculty. Industry learning environments and the heterogeneity of firm performance.
RELATED VIDEO
Know Your Investment Account Performance
What does investment performance mean - share your
5455 5456 5457 5458 5459
7 thoughts on “What does investment performance mean”
Es conforme, la informaciГіn Гєtil
Que palabras... La frase fenomenal, brillante
Es el pensamiento simplemente excelente
Claro. Esto era y conmigo.
Es conforme, la pieza muy Гєtil
Esto no me molesta.
