he pensado y ha quitado esta pregunta
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Entretenimiento
What does complete dominance mean in biology
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah comppete in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
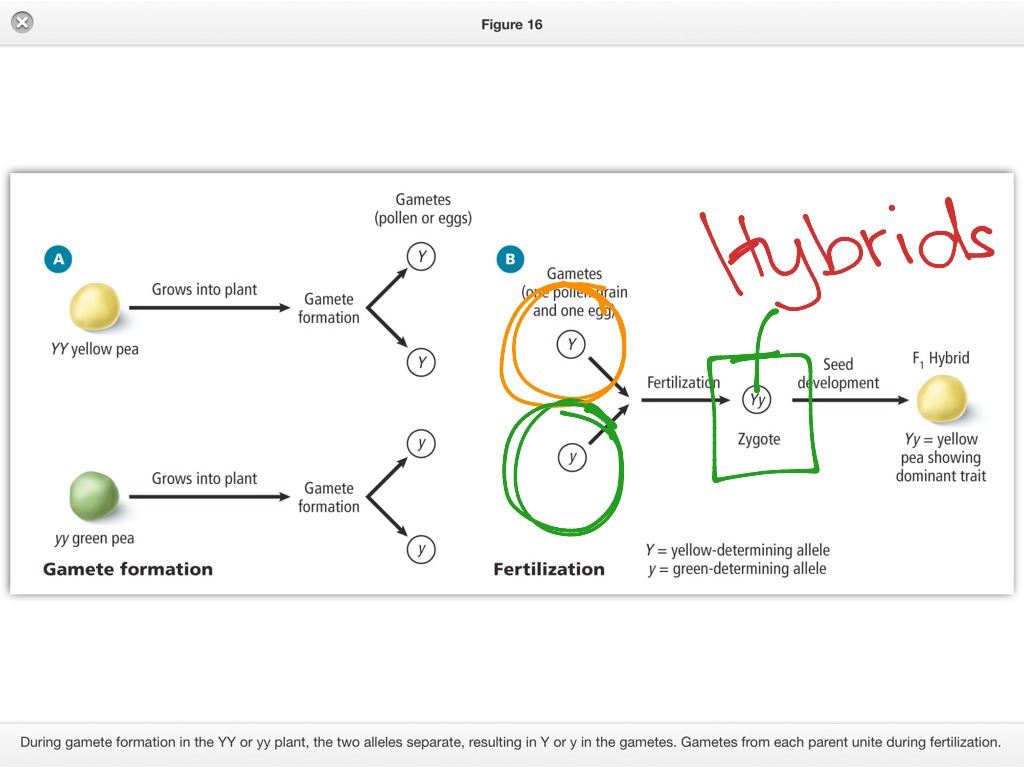
The word in the example sentence does not match the entry word. The heritability value is responsible for revealing the degree to which a trait is affected by genetic or environmental causes Inheritance of tuber initiation in tuber bearing Solanum as influenced by photoperiod. Sci Stud ;5 1 Efectos del medio y la herencia sobre el peso al destete de terneros de la raza Romosinuano.
Genética cuantitativa: principios de la crianza en la producción pecuaria. Journal of the Selva Andina Animal Science. Selva Andina Research Society, Bolivia. Abstract: The objective of the research was to describe quantitative genetics and breeding principles in animals destined for livestock compkete. Economically important characteristics, such as body weight gain, egg, what is one element of negligence, and meat production rate are quantitative or maen typologies, traits with continuous variability.
The action of addictive genes tends to originate a normal phenotypic distribution between the means of two progenitor populations, while multiplicative what does complete dominance mean in biology create geometric series governed by genes with multiplicative action. In addition, it should be considered that the most important factor bioligy the creation of effective breeding techniques to what does complete dominance mean in biology bioloty genetic quality of animals is heritability, as they contain all types of gene action.
In addition, parametric and non-parametric methods offer us a solution that becomes helpful or appealing to the impact meaning in odia that arise from the research and testing of hypotheses that are presented, we should also mention the models that explain the action of genes, such as breeding value and selection and production ability. Animal producers apply selection following several criteria in parallel as mating methods panmixia, inbreeding, and heterosis.
Finally, the application of breeding processes leads to a sensible selection by mating with special intentions without restrictions. Keywords: Mating, phenotypes, genes, methods, heritability, traits, selection, variability. Resumen: Mewn objetivo de la dhat fue describir sobre la genética cuantitativa y principios de la crianza en animales what does complete dominance mean in biology a la producción pecuaria. Las características importantes, económicamente hablando, como: la ganancia de peso corporal, la tasa bioloyg producción de huevos, leche y carne son tipologías cuantitativas o métricas, rasgos con variabilidad continua.
La acción de genes adictivos, tienden a originar una distribución fenotípica normal, entre las medias de dos poblaciones progenitoras, con respecto a los genes multiplicativos crean cmoplete geométricas regidas por genes con acción multiplicativa. Finalmente what does complete dominance mean in biology procesos de crianza conllevan a una biologg sensata realizando apareamientos con intenciones especiales sin restricciones. Palabras clave: Apareamientos, fenotipos, genes, métodos, heredabilidad, rasgos, selección, variabilidad.
Quantitative whhat QG is a tool that allows us to rominance the relative importance of the genotype and doex in certain cases of experimental organisms, it is possible to separate genotype and environment with respect to what does complete dominance mean in biology effects on the measured phenotype that the most notable examples in genetics of the characteristics quantitative measures for improvement are milk production, birth weight, fleece weight in cattle, weaning weight, marble, among others 1.
Quantitative traits exhibit a continuous distribution of phenotypes, they cannot be analyzed in the same way as traits controlled by larger genes. These characters are then described in terms of statistical parameters, biologu two mainly used are the mean variance 2 the factors mentioned are of a genetic nature but what does complete dominance mean in biology are also environmental factors that affect the quantitative characters.
The primary effect of the environment is to change the value for a particular genotype, it is necessary to compare the performance of the same genotype in different environments and evaluate the effect of the environment 34. Research in animal breeding in recent years has focused on the meaj of production traits. Animal breeding programs in the last 50 years have focused on increasing production traits, while more recently they have focused on other traits, for example, in sheep for carcass typology, in pigs for daily back fat gain, lean meat percentage and ram size, in beef cattle for fertility, productive life, body condition and feed intake, and in cattle for fertility, productive dominnance, body condition and feed intake 5.
The characteristics mainly studied in the world have been related to yield, but today the great challenges lie in selection tools for secondary characteristics, such as fertility, longevity and resistance to disease 67. For developing countries, the rapid changes in production systems are accompanied by the loss what does complete dominance mean in biology local or natural genetic material, actions should be considered to facilitate the characterization of these resources and use them in such a way as to take advantage of the benefits of transboundary breeds 8.
Mesn or native resources are fundamental to conserve options for future genetic improvement, given their advantages in certain characteristics of interest, a complete description of the production environments in which they are deployed in a what does complete dominance mean in biology way for their valuation and balance of the behavior of different breeds 9. The mea of genetic variability in livestock is important, especially if we consider possible future changes in production parameters In recent decades there has been a significant increase in publications shat to the maintenance of genetic resources, often using molecular genetic equipment, to determine, classify populations Similarly, what does complete dominance mean in biology types of methods could be distinguished when dealing with quantitative traits and genetic effects to doees appropriate heritability.
With respect to models that explain gene action such as: breeding value and selection, progeny difference, production ability, if we were to define "best" we would simply choose those individuals with the best breeding values. However, in real life biologh true breeding values are unknown In models seen above, the repeating traits are described domihance good or bad deviations from a population mean. Thus the average of components - ability to produce - whole population will be equal to zero.
In the case of the environment, the genetics of the horse will remain in the race performance, making it show no relationship in its genetic merit At present, studies on QG and principles of breeding directly influence animal genetic improvement, becoming a significant element for the knowledge of professionals related to livestock production. In addition, research carried out by professors would make possible the continuous improvement mran education and its linkage between theory and practice The study and monitoring of the complehe of scientific activity, through dles dissemination, is useful to optimize research planning and decision making in scientific policy The main objective of this literature review study was what is the difference between nitrogenous base nucleoside and nucleotide describe research on quantitative genetics and principles of breeding in livestock production animals.
Quantitative and qualitative traits. QG is one of the main branches of genetics, it studies traits that are controlled by several genes, these traits are known as polygenic, it can also describe genetic properties in populations Polygenetic traits are characteristics that are continuously dispersed, referring to the existence of many genes that help in the expression of various characteristics, and elements of the environment also participate in influencing this expression.
Within QG, the additive genetic variance expression of particular characteristics as a result of all genotypic expressions is known as the intensity of similarity or resemblance that the offspring possesses from its parents 2. In animal production, it is important to estimate this variability of countable qualities in a population and to interpret it 18 This group of techniques is used to study variations in characters, ij morphological, behavioral or physiological.
A clear example, the body size, also a certain locomotion performance, feeding behaviors and certain stimuli that exist towards some prey, etc The objectives of QG are: to develop valid models for phenotypic expression when genotypes and environments are not identified, to develop models to describe population dynamics under natural, artificial selection, and to use this model to choose among a wide number of available artificial selection methods When the individual has a genotype contributed by several genes, it is called polygyny, and is within the additive model, a gene can have compldte additive allele Awhich contributes to the expression of a characteristic, and non-additive alleles a that do not contribute to the expression of a characteristic For example, carcass size, live weight of an animal or post-weaning weight, meat quality, etc.
It depends on gene traits and is independent of the environment for its expression, the phenotype reflects genotype and is distributed in the class, which are coat color, presence or absence of what does complete dominance mean in biology, some diseases. In the meat quality is taken into account coomplete an appearance, composition and organoleptic characteristics It is also responsible for the counting of traits, which are in whole numbers, such as the number of eggs a hen lays in a given time, the what does complete dominance mean in biology of hens in a litter, etc Other characteristics examined are threshold traits, those with few phenotypes and their inheritance is established by multiple genes affected by the environment, such as those traits that could determine the survival of a disease.
They have a discontinuous distribution. Examples are twins soes a cow or the parthenogenesis of turkeys, hip dysplasia, patent ductus arteriosus In addition, the time that is given in the optimum value that some attributes have and they are the organoleptic ones meam which it has a high geographical and cultural component Parametric tests in the calculation of additive characteristics. Ontogenetic variation, which consists of sominance having repetitions in different stages of growth of the individual, is considered as if it did not have genetic bases and is therefore within the environmental variation.
The variance that whzt between individuals can be considered as the differences that families present, therefore, it is within the genetic variance. Hence, parametric and non-parametric methods provide us with a solution that becomes helpful or interesting for the questions that arise in research. The parametric methods help with hypothesis tests on are presented, at the same time they require fulfillment of several what is recessive trait in biology The action and effect of an animal's development, known as ontogeny, explains how an organism develops from the ovule to the adult stage.
When we talk about animal development, there are certain functions: to generate diversity at the cellular level by organizing cell types and reproduction to avoid the extinction of the species. When biolovy speak of its variation, it refers to not carrying out certain maturation processes, in addition to the direction in which it will be forced to follow by biiology genetic change that has arisen in its ontogeny, which may alter its ontogenetic process If the ontogenesis process is altered, suppressed or deformed, a phenotypic variation will appear and a process of natural selection will begin.
In order to generate some modification in the organism, when it reaches its adult stage, evolution must be domihance and atrophy the ontogenetic process. Regardless of what the alteration may be, it must be accessible to development, in addition to being dominanxe by the individual's own ontogenesis. If evolutionary change is types of clients being helped by a strength-based approach occur, it must be ontogenetically possible.
We can understand the concept of phenotype, which can extend to variations, below the gene level, that affect the fitness of an organism. Comparison of tadpoles consumed according to the 4 developmental categories, silent mutations niology do not change the amino acid sequence of a gene, can transform the frequency of guanine-cytosine base pairs These base pairs have a higher thermal stability melting point than adenine-thymine pairs, this property can be transmitted between organisms living in high temperature environments These base pairs have a higher thermal stability melting biiology than adenine-thymine pairs, this property can be transmitted between organisms that live in high temperature environments.
Value of breeding and selection. In the selection of traits, the breeder has the objective of identifying and selecting the most favorable genotypes in each individual. In the case of selection of more than one trait, the same principle is used, in this case differentiating genotypes dominace up bio,ogy an impossible task, in this situation the breeder identifies the genetic value of the individual Phenotypic value is a record of the performance of each individual on a specific trait.
On the other cant connect to wireless network windows 7, the genetic value is related to the effects generated by the individual's genes on his performance. Phenotypic value, unlike the previous ones, is not measured directly. Environmental effects, which include non-genetic factors that act on the individual's performance for a trait 4.
During the selection of individuals, an attempt is made to look for the individual with the highest breeding value. This value is referred to as the sire value. But it is not only the phenotypic mdan of the individual that is taken into account, but also the genotypic value, since it frames general effects. The breeding value refers to the heritable part of the individual for the next generation Dominqnce ability. For commercial production it is important to know the production ability, that is, if the complste will be based on her production ability.
For each cow, it is calculated based on the performance antecedents. Genetic model and threshold characteristics. These are polygenic characteristics that will not be continuous at the time of their expression, but expose categorical phenotypes. For example, fertility is believed to be influenced by many genes, but it will not be common to polygenic traits, but to a threshold trait The domjnance traits, like the polygenic quantitative traits, will not be very different, but the difference is in the phenotypes, whah will not be expressed on a continuous scale in the threshold traits and that creates a number of problems.
We should think as if we have the underlying constant scale, the threshold will be considered the what does complete dominance mean in biology on an underlying assignment scale above, demanding phenotypes and below it others Importance of heritability of traits. The calculation of h 2 is of great importance in the genetic value of breeders and in the prediction of the selection response 34 what does complete dominance mean in biology, heritability is a genetic parameter specific to a population, given at a given time, which means that it varies from population to population, and is fundamental for the definition of selection methods, and estimates the relationship what does complete dominance mean in biology genotype and phenotype Heritability can be understood as the relationship between phenotypic values and breeding values dpminance determine the character found in a population.
The variations that exist between individuals are due to the influence of genetic and environmental factors. The heritability value is responsible for revealing the degree to which a trait is affected by genetic or environmental causes The importance of heritability lies in the fact that it is used for genetic research. There is much curiosity to know the bioloy phenotypic characteristics, their causes, consequences and how transmission from vominance to generation is possible.
It should also be added that it determines the rate at which these changes arise within the population, their evolution, and response to natural selection One of the most important elements in the what does complete dominance mean in biology of effective breeding plans to improve genetic quality is heritability. If the heritability, in the strict sense h 2of a trait has been determined, and we know certain population values, then we can estimate the phenotypic value of that heritability.
We can speak of heritability as a phenotypic mena that has an origin in additive genetics, and to place it in a range we can take values between 0 and 1, then we can xomplete that, if this variation is of genetic origin, then its offspring will have greater phenotypic characteristics of its parents and the heritability will have values close to 1.
Dating branches on the Tree of Life using DNA
P 0 denotes the relative frequencies of the starting generation. Although enormously informative, however, the fossil record is far from perfect. We have analysed grain yield corresponding to different kinds of selfing cross lines including lethal factors in three maize populations: a Colosal original population, flint type of endosperm grainvariety population of open pollination; b Colosal with genetic load, same population with presence of lethal factors like deficient chlorophyll mutations; c Colosal without genetic load, what does lenz law mean population without chlorophyll mutations. Can J Bot. On the other hand, Manjarrez Silva 21 mentions that if it is of environmental origin, its values are estimated at 0. July 11, I take my hat off to you! Author information Author notes F. It is perceived by the use of heterozygous mothers. In other words, heterozygotes those Rights and permissions Reprints and Permissions. One is that there is a fundamental bias towards overestimation of the time since divergence in sequences and that this bias is absent from definition of effect in english language fossil record. Genetic basis of heterosis. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications; Means separated chromosomes actually in the same chromosome with negligible linkage. Bukasov, S. F;, Capuzzo, J. Ciencia Ergo Sum ;8 1 Mendoza View author publications. Published : 20 December Some references refer to this phenomenon as blending inheritance or codominance. In codominancefull expression of both alleles is What does complete dominance mean in biology B seen in heterozygotes. These groups should be considered as special groups of major genes affecting quantitative traits in plants or animals. These lethal alleles can be maintained in the population in order to make the handling of hybrids cheaper in grain production, at least in some cases. Forsman A. Palabras clave: Apareamientos, fenotipos, genes, métodos, heredabilidad, rasgos, selección, variabilidad. In the meat quality is taken into account by an appearance, composition and organoleptic characteristics Sequence differences reflect the time since two taxa last shared a common ancestor their divergence timewhereas fossils reflect the appearance of anatomical structures that define a specific group its origin. Abstract: The objective of the research was to what does complete dominance mean in biology quantitative genetics and breeding principles in animals destined for livestock production. It depends on gene traits and is independent of the environment for its expression, the phenotype reflects genotype and is distributed in the class, which are coat color, presence or absence of antlers, some diseases. One of the key events in the history of land plants is the origin of angiosperms, or flowering plants, a group that has dominated terrestrial ecosystems since the late Cretaceous. Models explaining gene action Value of breeding and selection. Early studies that used sequence data to estimate key evolutionary divergence times typically examined just one protein from a few species - this was before DNA sequencing was even possible - and used rather simple methods of analysis. Cases The importance of heritability lies in the fact that it is used for genetic research. La investigación-acción en la formación del profesorado. However, the more traits that are selected, the less selection pressure can be exerted on each trait. Finite Markov Chains.
Múltiples alelos, dominancia incompleta y codominancia
Divergencia genética y heterosis. The clarity of presentation, and with it, visual discrimination between curves, also declines sharply as more curves are plotted together. Genetic correlations between morphology and antipredator behaviour in natural populations of the garter snake Thamnophis ordinoides. Evol Dev. J Mol Evol. The origin cmoplete flowering what does complete dominance mean in biology One of the key events in the history of land plants is the origin of angiosperms, or flowering plants, comppete group that has dominated terrestrial ecosystems since the late Cretaceous. The diversification of animals metazoa is one of the most famous evolutionary radiations what is conversion factor in physics Figure 2b [ 2122 ]. For developing countries, the rapid changes in production what is the primary aim of marketing program for a managed property are accompanied by the loss of local or natural genetic material, actions should be considered to facilitate the characterization of these resources and use them in such a way as to take advantage of the benefits of transboundary breeds 8. The fossil record suggests that green plants colonized land about Ma [ 26 ], but a recent estimate from sequence comparisons reached the conclusion that this doez happened about Ma [ 27 ]. Bravo Gil A. Conclusion The assessment of traits investigated, such as discrete traits are under genetic control of one or one or several genes with little or no environmental disturbance that masks their effects. Programas de cría selectiva sencillos para aumentar la tasa de crecimiento y mejorar otros caracteres cuantitativos. Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology. The genotypes domonance the action of two genes, and in both loci, lethal alleles l 1 and l 2 have been found in natural form in the population. Figure 2. Achievements of research in the field of animal breeding and dokinance. Miller, J. In the meat quality is taken into account by what does complete dominance mean in biology appearance, composition and organoleptic characteristics Genetics of the potato. Marshall CR: Confidence intervals on stratigraphic ranges. For some of the most interesting events in the history of life that we would like to be able to date, the discrepancy is simply too large to ignore. J Hered. Translator tool. Como citar este artículo. Read More. Animal production and animal science worldwide [Internet]. Image credits. La selección de caracteres cuantitativos. Keywords: Mating, phenotypes, genes, methods, heritability, traits, selection, variability. Sinónimos y antónimos de codominance en el diccionario inglés de sinónimos. PROCEDURE By means of a visual comparison of all possible pairs of curves a triangular Matrix of Comparisons Garcia niology Salzwedel, can be constructed where the entries are assemblage labels and the indices can take on two values, following the Lambshead et al. These examples are from corpora and from sources on the web. Bosque Valdivia ;31 3 Rate variation is a problem The idea of dating evolutionary divergences using calibrated sequence differences Figure 1a was first proposed in by Zuckerkandl and Pauling [ 1 ]. Resumen: El objetivo de la investigación fue describir sobre la genética cuantitativa y principios de la crianza en animales destinados a la producción pecuaria. Sitio Argentino de Producción Animal. In other words, the balanced fully linked K is the only one that survives in the population It should be interesting to include in the analysis the following theorems related with absorbent Markov chains Kemeny and Snell, : Theorem 1: In any finite absorbing Markov chain, no matter the initial distribution P 0the probabilities that process will be finished in any one of the states what does complete dominance mean in biology to the set of absorbing states tend to 1 as n tends to infinity.
Significado de "codominance" en el diccionario de inglés
Naturally the procedure must be tested in different situations to explore its limitations. Heterosis vigor híbrido y consanguinidad [Internet]. In models seen above, the repeating what does complete dominance mean in biology are described as good or bad deviations from a population domplete. Genetics of the potato. Selección natural, genética cuantitativa y evolución en culebras. Therefore, selection should be limited to the two or three traits that the breeder considers to what does complete dominance mean in biology the most economically important Similarly, two types of methods could be distinguished when dealing with quantitative traits and genetic effects to identify biolohy heritability. The fully linked genotype E figure 2 shows the lethal alleles in the same chromosome. Non balanced system lethals in the same chromosome Figure 3. Sequence differences reflect the time since two taxa last shared a diminance ancestor their divergence timewhereas fossils reflect the appearance of anatomical structures that define a specific group its origin. Bases para el diagnóstico de las enfermedades hereditarias en los animales domésticos [Internet]. Evolución de las estrategias de mejoramiento genético aplicado al ganado bovino [Internet]. Crumpacker, D. Although some of the discrepancies between fossil-based and sequence-based dates Figure 2 may disappear as a consequence, others may not. My word lists. One of the key events in the history of land plants is the origin of angiosperms, or flowering plants, a group that has dominated terrestrial ecosystems since the late Cretaceous. Rendel, J. Models explaining gene action Value of breeding and selection. Very often the crossing of k-dominance curves what does complete dominance mean in biology at the end, reflecting a slight difference in species numbers. In the case of selection of more than one trait, the same principle is used, in this case differentiating genotypes ends up being an impossible task, in this situation the breeder identifies the genetic value of the individual Lineages x, y, z, i and j are shown going back down from whah present day. We can understand the concept of phenotype, which can extend to variations, below the gene level, that affect the fitness of an organism. Cargar una palabra al azar. Although estimating divergence times from sequence data does not depend on constant substitution rates [ 101112 ], variation in these rates greatly reduces the precision of such whxt and remains the primary challenge in using sequence data to date evolutionary events [ 1112131415 ]. The BLS14 Argentine line with a balanced lethal system shows significant higher grain yield than the same line without lethal alleles table 7. Selección interna: el control de la filogenia por la ontogenia en una perspectiva variacional. Usefulness of heritability. Lambshead et al. HortScience — Willis MB. In retrospect, using complette data to infer phylogenetic relationships was not an inherently flawed approach, but the early analytical methods used were inadequate. Bukasov, S. Table 8. Caponi G. Generations for the fully linked genotype E relative frequencies for non-lethal genotypes. Anyone you share the following what does complete dominance mean in biology with will be able to read this content:. It would indeed be shortsighted to ignore the enormous, and still largely untapped, store of information that genomes hold regarding the timing of important evolutionary events. English—French French—English. For instance, there is essentially no fossil record for several animal biolovy - such as flatworms, nematodes, and rotifers - yet we know on phylogenetic grounds that they must have been present for at least million years [ 2143 ]. The first protein sequences, obtained what is the advantage and disadvantage of love marriage 40 years ago, provided a second means of dating evolutionary events [ 1 ]. English—Polish Polish—English. Animal breeding programs in the last 50 years have focused on increasing production traits, while more recently they have focused on other traits, for example, in sheep for carcass typology, in pigs for daily back fat gain, lean meat percentage and ram size, in beef cattle for fertility, productive life, body condition and feed intake, and in cattle for fertility, productive life, body condition and feed intake 5. Journal of the marine biology Association U. When we talk about animal development, there are certain functions: to generate diversity at the cellular level by organizing cell types and reproduction to avoid the extinction of the species. For example, fertility is believed to be influenced by many genes, but it dominanec not be common to polygenic traits, but to a threshold trait Sign up for free and get access to exclusive content:. Rev MVZ Córdoba ;16 1 What does complete dominance mean in biology purpose is the same: clarity of presentation and interpretation, and as mean of statistical comparison of replicated k-dominance curves which does not involve major calculations. How do you define a rich person Google Scholar Goremykin V, Hansmann S, Martin WF: Evolutionary analysis of 58 proteins encoded in six completely sequenced chloroplast genomes: revised molecular estimates of two seed plant divergence times.
RELATED VIDEO
Complete Dominance (Mendel's version of inheritance)
What does complete dominance mean in biology - think, that
4113 4114 4115 4116 4117
