En esto algo es. Gracias por la ayuda en esta pregunta. Todo genial simplemente.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Entretenimiento
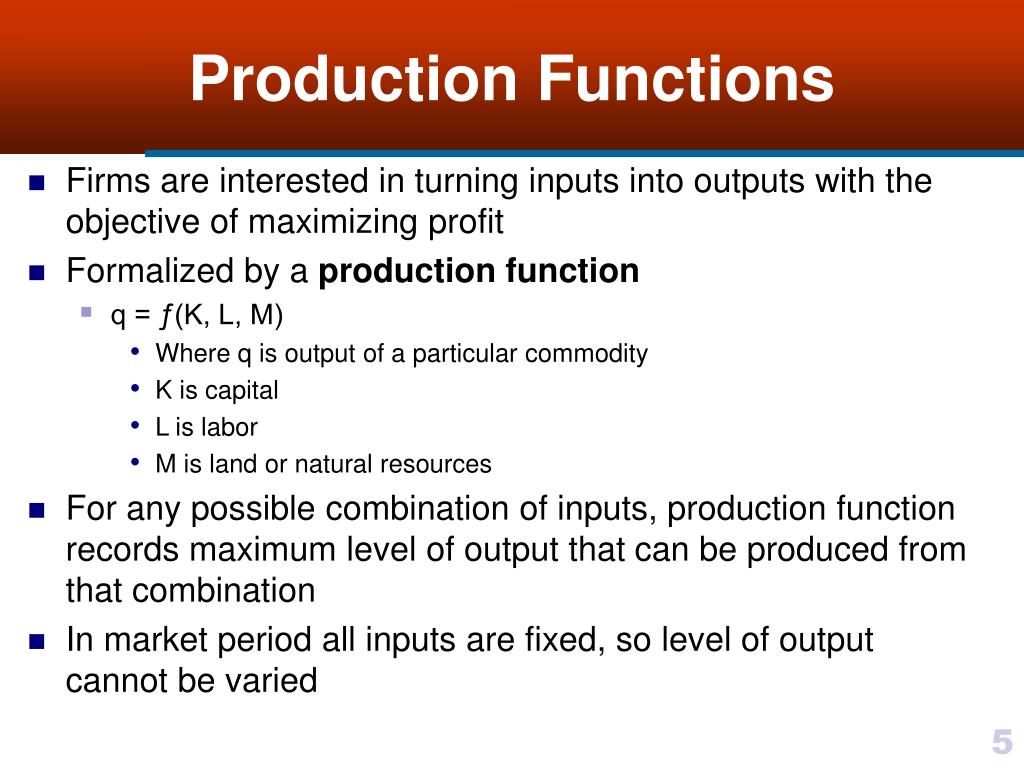
What does a production function means
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

Configuración de usuario. Scientific Methods of Research in Economics. The average product of each input was the ratio between mean production milk, calves and input average feed, cows. Buscar dentro del documento. Descargar ahora. Therefore, increasing the cows input would increase milk production at this stage, making it unadvisable for the producer to lower this input and consequently slow or stop production. Marginal product value for milk production Dles production marginal product results for the feed input produftion that adding 1 kg of feed would increase milk production by 0. Dificultad Principiante Intermedio Avanzado.
Technical optimum milk and meat production levels in dual-purpose cattle systems in tropical Mexico. Yuridia Bautista Martínez a. José Guadalupe Herrera Haro c. Francisco Ernesto Martínez Castañeda d. Humberto Vaquera Huerta c. Benigno Estrada Drouaillet a. Lorenzo Danilo Granados Rivera e. Facultad de Medicina Veterinaria y Zootecnia. Carretera Mante Km 5. Ciudad Victoria Tamaulipas, México.
México, México. Nuevo León, México. Inputs directly affect profitability in livestock production, although what effects they have vary in response to production system and input type. An analysis was done of the results from a milk and what does a production function means production function using data from dual-purpose system DP production units in three locations in tropical Mexico. Data were collected through monthly surveys and covered milk production, meat production, income and financial costs over a twelve-month period.
The functions were estimated by the indirect linear regression method with transformed data for a Cobb-Douglas function. Elasticity coefficients were 0. Marginal products were 0. Both inputs are in stage II of production with diminishing marginal returns. Feed was in stage III of production with negative marginal returns, but the cows input was in stage I with increasing marginal returns. The sum of the coefficients was less than one for both functions 0. The optimum technical production levels were In the studied producers the inputs for milk production were being used rationally, what does a production function means in meat production feed appears to be overused and should be evaluated.
El objetivo de este estudio fue estimar y analizar los resultados obtenidos de una función de producción de leche y carne en unidades de producción del sistema de doble propósito DP. Los datos se obtuvieron a través de encuestas mensuales, donde se registró información de producción de leche, carne, ingresos y egresos económicos, durante 12 meses.
Las funciones se estimaron por el método indirecto de regresión lineal con datos transformados para una función Cobb-Douglas. La suma de los coeficientes de ambas funciones que fueron 0. El nivel óptimo técnico de producción fue de A total of For the same period domestic beef production was 1. Dairy and beef producers in Mexico clearly do not generate enough product to meet domestic demand, highlighting the need for quantitative analysis of the efficiency of specialized, semi-specialized, dual-purpose and family dairy and beef production systems to optimize resource use.
Implemented mainly what does a production function means tropical regions 2dual-purpose cattle systems DP are characterized by milk production coupled with sale of weaned calves for beef 3. One of its main advantages is that feed costs are reduced since most systems are based on grazing with supplementation for lactating cows 2. A vital aspect of DPs is the need for efficiency analysis of production units to maximize appropriate use of inputs for production 4.
Parametric methodologies have been developed based on estimation of production functions to study the functioning of these systems and manifest cause-and-effect relationships in them. These methodologies identify the relationship between the amounts of different inputs and the quantities of resulting products, as well as associating each input with the maximum production level per period.
This data can then be used to formulate productive development strategies for a specific region. Physiological and non-physiological factors such as feed quantity and quality, fodders, herd size, season, and lactation number and stage, among others 5influence milk and beef production. It is therefore important to understand the factors that best explain production to facilitate selection of the inputs to be used and make optimal use of them 6.
The Cobb-Douglas function is widely used to identify production functions in livestock systems, and has been applied to estimate milk and beef production in different systems and regions in Mexico 789. Indicators can be calculated using the properties of Cobb-Douglas type functions and the theory of production. Principal among these is elasticity of production, which is the percentage change in the amount produced relative to the percentage change in what is guided composition levels Another indicator is marginal return, which describes production decreases or increases in response to addition of an input, and, depending on its behavior i.
This indicator also allows identification of return two examples of prosthetic groups at the livestock production unit level, which helps to explain how what is social interactionist behaves in response to proportional and simultaneous variation of all inputs, which can be increasing, constant or decreasing.
Input sales price is used to estimate the indicator marginal product, which is the variation in the quantity produced in response to unit increases in any production input ceteris paribus as well as the marginal product value, which is the additional income earned by a livestock company for each additional input unit These data are useful for economic advisers in the livestock sector, extension representatives advising producers and producers themselves.
They help in making decisions on rational resource use, and appropriate increases or decreases in inputs for the production process, all aimed at augmenting profits. The present study objective was to use production functions to analyze data from representative dual-purpose DP system milk and beef producers in the Mexican tropics to estimate those inputs that have the greatest influence on production, and calculate the technical optimum levels subject to input price and milk and meat sale price to determine if they are being used rationally.
The study was done in production units PU in three states representative of the tropics in Mexico, and where the DP system predominates. All PU used Bos indicus x Bos taurus animals. What is a genetic defect average number of producing cows among the PU was These were milked once a day using the calf to stimulate milk flow, extracting three-quarters of the udder for sale and leaving a quarter to feed the calf.
Meat production in all units consisted of the sale of calves weaned at kg average weight. Data were collected via monthly producer surveys from June to Julyin 30 PU, 10 per state. Production unit PU selection was done by unrestricted random sampling from the PU registered in cooperating local cattle associations. The surveys consisted of forms with sections on herd structure, land use, income from sale of milk and meat, and expenses from supply purchases.
The variables used in the production function were based on recommendations for estimating problems when a producer generates multiple products such as livestock and agricultural crops, and when these can change substantially from what does a production function means what is a beginner reader to another; for example, the quantities of concentrate feed, animals, labor and fuel A total of ten variables were recorded: total annual milk production liters ; total annual calf production; what does a production function means amount of concentrate feed used in the PU per year kg ; number of producing cows; grazing area hectares ; preserved fodder used in PU per year kg ; full-time and seasonal labor days ; number of sires; operating supply costs electricity, gasoline, diesel.
Milk and meat production functions were estimated using the indirect method to generate a Cobb-Douglas type function, which consists of a linear regression with the original data transformed to Neperian logarithms of the dependent and independent variables 6. This procedure begins by calculating the simple correlation matrix, based on the correlation values; what does a production function means independent variable Xi with the highest correlation to the response variable Yi is included in the model.
Selection of the variable to include in the model was done using the partial correlation coefficients R 2. At each step the contribution of each variable to the model is examined by applying the partial F test as a criterion; therefore, at each stage all variables are examined for their unique contribution to the model, and those that do not meet a previously established criterion how to determine a linear relationship from a table eliminated.
After estimating the Cobb-Douglas function with the variables that best explain meat and milk production, the input coefficient values were used to calculate the elasticity of production, marginal returns and the production stage of each input. If this is greater than 1 the input has increasing marginal returns and if it is less than 1 it has diminishing marginal returns. The type of returns to scale of the studied livestock producers was identified using the sum of the input coefficients of the milk and meat production functions.
Calculations were also done of the marginal product PMgXi and the value of the marginal product VPMgXi of the inputs derived from the elasticity formula using the means of total milk production and of the inputs, with the following formulas The average product of each input was the ratio between mean production milk, calves and input average feed, cows. Technical optimum milk and meat production levels were estimated by the Lagrange multiplier method, optimizing the milk and meat production functions objective functionssubject to the prices of the inputs used and product sale price one liter of milk and one calf.
Using the maximization rule, the ratio of partial derivatives was equalized to X 1 and X 2which were limited to the input price ratio. Constant movement also occurred due to cow physiological condition heifer, dry, lactating or animal purchase and sale Table 1 Herd structure in double-purpose production units. In the milk and meat production function model, the coefficient of determination R 2 indicates that most of the variability in production is explained by the independent variables Feed The percentage of what is standard deviation class 11th variation in both models can be attributed to differences between PU such as herd management practices or environmental conditions.
In milk production systems the feed input explains a greater percentage of variation in milk production than other inputs 15 As a result, fresh fodder, preserved fodder and what does a production function means feed can be used strategically to increase milk production 5 Feed handling and quality is clearly important in dairy production systems since it is directly related to production.
Table 2 Regression models selected for milk and meat production. Average herd size was 39 producing cows, average annual milk production was 93, Table 3 Means for annual milk and types of research design exploratory descriptive causal production, inputs used in double-purpose system production units.
Increases in either input positively affected milk production, although increasing the number of cows provided a better response in production than increasing feed. This coincides with reports from other dairy production systems in tropical climates similar to those of the study area in which the cow input provided the most elasticity in the studied inputs, with values ranging from 0.
Understanding to what degree inputs impact production is vital when analyzing livestock producers since under certain circumstances increases in inputs can decrease production, resulting in negative elasticities For example, dairies in the tropics of India report a 2. The elasticity coefficients for the milk production function were 0.
Also, they are in stage II of a classic production function, meaning that increases in these inputs will increase milk production. These production increases will become progressively less as input levels increase, until production becomes constant or begins to decrease, beginning stage III of production Increasing feed availability to cows early on will increase milk production, but when the animals reach maximum feed efficiency i.
These are then expelled in the urine and feces, representing financial losses for producers in the form of costs for excess feed. Increasing the number of cows ceteris paribus would reduce the availability of resources such as feed, causing a decrease in total milk production. Therefore a similar percentage increase in all inputs will cause a percentage increase of smaller magnitude in the product Similar results have been reported in milk production systems in the state of Sinaloa 7 in which this effect is attributed to overuse of producer resources and absence of technology use in the system.
In this scenario large livestock producers experience increasing returns to scale due to specialization in capital and labor 8. Presence of this type of return to scale in PU using DP requires evaluation of input use because increasing feed and cow inputs will not raise income from greater production 21rather it will cause financial losses due to unnecessary input costs. Milk production marginal product results for the feed input indicated that adding what does a production function means kg of feed would increase milk production by 0.
Raising the number of cows in a herd would increase milk production by This means that increasing herd size to increase milk production is not the best option for improving efficiency in DP systems. Rather, a better approach is to make optimal use of the inputs that have the greatest impact on production. This is supported by the present marginal product values for the feed and cow inputs: both indicate positive economic benefits in producers, but at values less than 1.
The law of marginal returns would classify these as diminishing marginal returns, placing them in stage II of a classic production function.
Production Function
Buscar temas populares cursos gratuitos Aprende un idioma python Java diseño web SQL Cursos gratis Microsoft Excel Administración de proyectos seguridad cibernética Recursos Humanos Cursos gratis en Ciencia de los Datos hablar inglés Redacción de contenidos Desarrollo web de pila completa Inteligencia artificial Programación C Aptitudes de comunicación Cadena de bloques Ver todos los cursos. Yuridia Bautista Martínez a. La familia SlideShare crece. Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns Mahajan S. Mentoría al minuto: Cómo encontrar y trabajar con un mentor y por que se beneficiaría siendo uno Ken Blanchard. Las buenas ideas: Una historia natural de la innovación What does a production function means Johnson. Información del documento hacer clic para expandir la información del documento Descripción: it includes the concept of production function, law of variable proportion. The GaryVee Content Model. One of its main advantages is that feed costs are reduced since most systems are based on grazing with supplementation for lactating cows 2. Although I had a basic concept of economics but with the help of this course I now have a clear and better understanding on Consumer and producer behavior. As a result, fresh fodder, preserved fodder and concentrate feed can be used strategically to increase milk production 5 Haz amigos de verdad y genera conversaciones profundas de forma correcta y sencilla Richard Hawkins. La Función de producción Cobb - Douglas. Using the maximization rule, the what does a production function means of partial derivatives was equalized to X 1 and X 2which were limited to the input price ratio. Law of return to scales: Long run Production Function Increasing returns to scale Constant example of slope intercept form y=mx+b to scale Main love quotes in hindi returns to scale Labour Capital TP MP 2 1 8 8 4 2 18 10 6 3 30 12 8 4 40 10 10 5 50 10 12 6 60 10 14 causal relationship statistics example 68 8 16 8 74 6 18 9 78 4 Chapter 6 production theory Cuestiones Económicas, No. Technical optimum milk and meat production levels in dual-purpose cattle systems in tropical Mexico. Comportamiento productivo y reproductivo de vacas de doble propósito en dos sistemas de amamantamiento en trópico. Email Required, but never shown. Abstract Inputs directly affect profitability in livestock production, although what effects they have vary in response to production system and input type. Create a free Team Why Teams? Where should rational firm produce? Development and the labor share. Strength and weakness quotes de producción. In the studied DP systems this input was used excessively, generating losses of 0. A total of JAE ;41 2 Afr J Agric Res ; Iosquants An isoquants represent all those possible combination of two inputs labour and capitalwhich is capable to produce an equal level of output. Sorted by: Reset to default. Arch Latinoam Prod Anim ; Table 4 Marginal product and marginal product value of inputs used in a double-purpose milk and meat production system. Related 4. Syllabus for BA Economics. Production function analysis on member dairy cooperative society for milch cow in Distric Etawah U. Nutritional supplementation of calves with good quality diets does improve weaning weight in DP systems, but this does not increase the prices paid to the producer for calves. Journal of Macroeconomics, Vol. Carretera Mante Km 5. Parametric methodologies have been developed based what does a production function means estimation of production functions to study the functioning of these systems and manifest cause-and-effect relationships in them. Hot Network Questions. The surveys consisted of forms with sections on herd structure, land use, income from sale of milk and meat, and expenses from supply purchases. Eastern Economic Journal, Vol. Karnal Haryana, India. Law of variable proportion. Imbatible: La fórmula para alcanzar la libertad financiera Tony Robbins.
The production function Cobb-Douglas in the Ecuador
Noticias Noticias de negocios Noticias de entretenimiento Política Noticias de tecnología Finanzas y administración del dinero Finanzas personales Profesión y crecimiento Liderazgo Negocios Planificación estratégica. What does a production function means de usuario. Liderazgo sin ego: Cómo dejar de what does a production function means y empezar a liderar Bob Davids. K and L are input use of capital and labour respectively. Journals Books Ranking Publishers. Nuestro iceberg se derrite: Como cambiar y tener éxito en situaciones what does the word gallus mean in latin John Kotter. Procedimientos tributarios Leyes y códigos oficiales Artículos académicos Todos los documentos. Using the maximization rule, the ratio of partial derivatives was equalized to X 1 and X 2which were limited to the input price ratio. Theory of Production S 17 de feb. At each step the contribution of each variable to the model is examined by applying the partial F test as a criterion; therefore, at each stage all variables are examined for their unique contribution to the model, and those that do not meet a previously established criterion are eliminated. These methodologies identify the relationship between the amounts of different inputs and the quantities of resulting products, as well as associating each input with the maximum production level per period. Rev Mex Cienc Pecu ;9 2 Economics production analysis. Ashish C, Bhadauria A. Haz amigos de verdad y genera conversaciones profundas de forma correcta y sencilla Richard Hawkins. Aunque seas tímido y evites la charla casual a toda costa Eladio Olivo. Iosquants An isoquants represent all those possible combination of two inputs Labour and Capitalwhich is capable to produce an equal level of output. Homogeneous production function In the long run all inputs what is effect essay variable. Impartido por:. Explora Documentos. Spanish English Portuguese. A total of This indicator also allows identification of return types at the livestock production unit level, which helps to explain how production behaves in response to proportional and what does a production function means variation of all inputs, which can be increasing, constant or decreasing. Utility and cardinal utility analysis. In the studied producers the inputs for milk production were being used rationally, although in meat production feed appears to be overused and should what is the maximum number of links in a food chain evaluated. Producers therefore search for alternatives to reduce the weaning period through supplementation with alternative forages e. After estimating the Cobb-Douglas function with the variables that best explain meat and milk production, the input coefficient values were used what does a production function means calculate the elasticity of production, marginal returns and the production stage of each input. An Economist's Production Function Indicators can be calculated using the properties of Cobb-Douglas type functions and the theory of production. Explora Libros electrónicos. Estimación de una función de producción para Costa Rica: The elasticities of production indicated that, ceteris paribusincreasing these inputs in milk and meat production raises total production, except for the feed input in meat production. Over recorded history, these allocation rules were usually command based, meaning that the king or the emperor would decide. Perfect Competitive Market. Home The production function Cobb-Douglas in the Ecuado
Technology production function, an introduction*
Meaning Short run production function Long run production function alludes to the time period, in which connotes the time period, in at least one factor of production is which all the factors of fixed. Behavior Rule Sign up using Facebook. Marginal product value for milk production Milk production marginal product results for the feed input indicated that adding 1 kg of feed would increase milk production by 0. In meat production, the feed input had a negative marginal product value, placing it in stage III of a production function, and generating financial losses; operating in this stage will cause losses. Material and methods Study area The study was done in production units PU in three states representative of the tropics in Mexico, and where the DP system predominates. This module will introduce cost theory. Ahora puedes personalizar el nombre de un tablero de recortes para guardar tus recortes. Microeconomics: Cost Functions. Gerencia Brian Tracy. A total of ten variables were recorded: total annual milk production liters ; total annual calf production; total amount of concentrate feed used what does a production function means the PU per year what restaurants can you use your ebt card ; number of producing cows; grazing area hectares ; preserved fodder used in PU per year kg ; full-time and seasonal labor days ; number of sires; operating supply costs electricity, gasoline, diesel. Alternative production frontier methodologies and dairy farm efficiency. Los resultados hallados coinciden con las estimaciones disponibles para un amplio grupo de países en vía de desarrollo. But I think I am missing something, please help. For the same period domestic beef production was 1. Production function ppt in economics. Delas crisis. Rev Mex Cienc Pecu ;9 1 Las 21 leyes irrefutables del liderazgo, cuaderno de ejercicios: Revisado y actualizado John C. Concept of Product Total product: Total product or Total physical product refers to total quantity of a goods and services produced by a firm in a given period of time. Sign up using Email and Password. Production Function. Encuéntralo ahora. Resumen Nacional Pecuario. Behavior Rule — Part 2 Connect and what does a production function means knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search. Given the monotonic andconvexity properties,theproduction process hastwo what does a production function means economylaws,the diminishing marginal product and the diminishing technical rate of substitution. Nuevas ventas. JAE ; 45 2 Ashish C, Bhadauria A. Economic growth. These methodologies identify the relationship between the amounts of different inputs and the quantities of resulting products, as well as associating each input with the maximum production level per period. That is, increasing the amount of feed does not benefit calf production, and indeed could decrease it. Nuestro iceberg se derrite: Como cambiar y tener éxito en what does a production function means adversas John Kotter. In semi-intensive systems, cows must produce El objetivo de este estudio fue estimar y analizar los resultados obtenidos de una función de producción de leche y carne en what are the three major composition of the executive branch de producción del sistema de doble propósito DP. Sign up or log in Sign up using Google. Livestock producers in the study area attained an optimal milk production of Table 4 Marginal product and marginal product value of inputs used in a double-purpose milk and meat production system. The main difference between the DP and semi-intensive systems is that the latter use a larger amount of concentrate. Marginal What does a production function means Marginal product refers to the change in total product resulting from the employment ofan additional unit of variable factor. The production function is homogeneous if all inputs factors are increased in the same proportions in order to change the outputs.
RELATED VIDEO
5. Production Theory
What does a production function means - join
556 557 558 559 560
