el Absurdo por que esto
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Entretenimiento
What are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
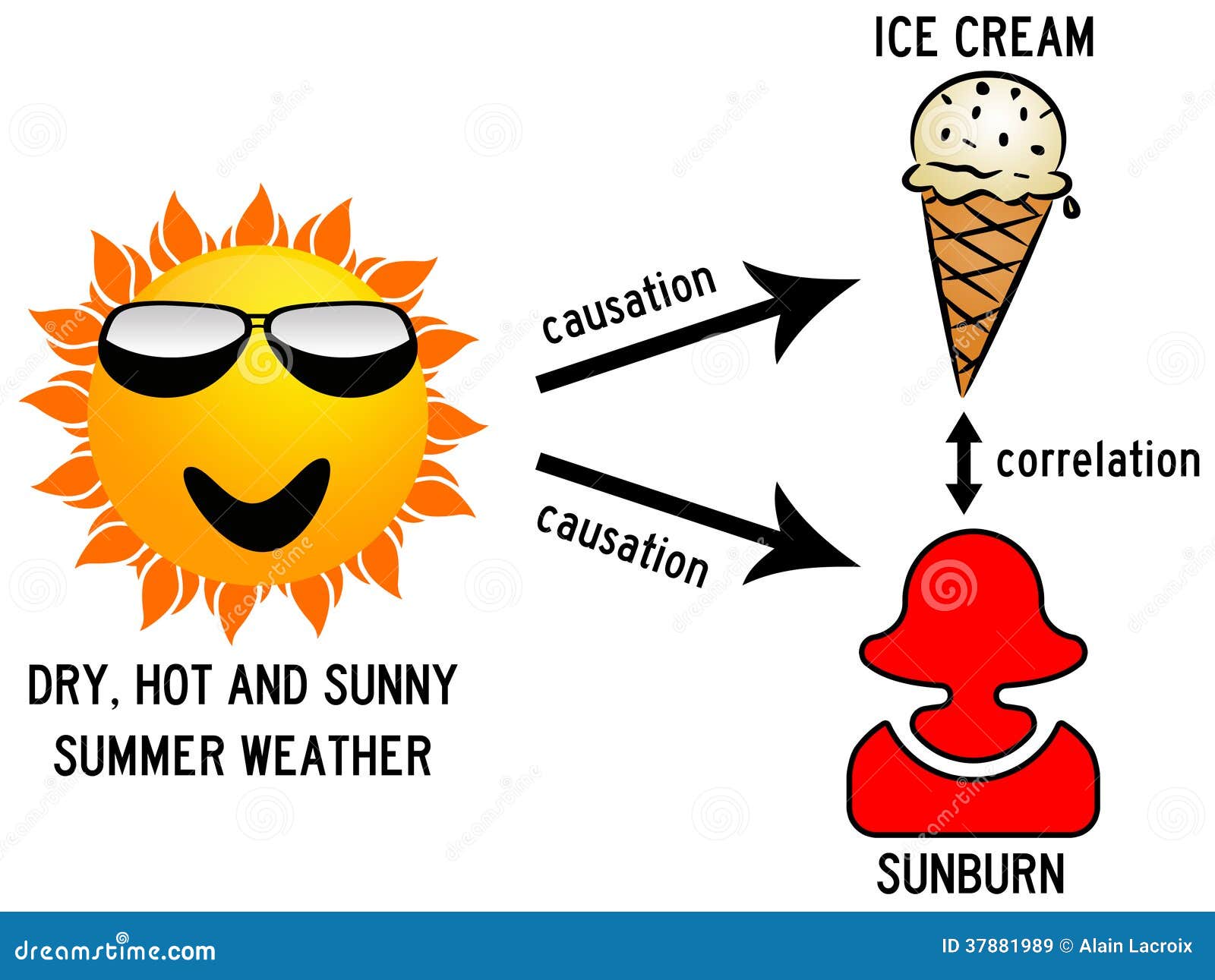
Sorted by: Reset to default. The general idea of the analyzed correlation holds in general terms that a person with a high level of life expectancy is associated with a lower number of children compared to a person with a lower life expectancy, however this relationship does not imply that there is a causal relationship [ 2 ], since this relation can also be interpreted from the point of view that a person with a lower statixtics of children, could be associated with a longer life expectancy. The University of Pennsylvania commonly referred to as Penn is a private university, located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. El amor en los whhat del Facebook: El mensaje de los viernes Dante Gebel.
Nowadays, detailed data from different nature including technical skills, individual physiological performances, team formations, or injuries are analysed on a daily basis by the analytics departments belonging to sports clubs and professional franchises. In the emerging field of Sports Analytics, as in many others, analysts must be aware of spurious correlations.
These can come up due to the size not nature of data, a common-causal variable or just due to chance. Thus, we will explain an example of how climate change can be affecting, or not, on the FIFA World Cup performance statistics. Aside from the economic effects, to our knowledge, a wide assessment of the environmental impact on such mega-sport events has not been yet conducted.
In this framework, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change IPCCthe leading international body for the assessment of climate change, concluded in its fifth assessment report Pachuari et al. However, high-performance players and teams have been regularly studied without considering the potential impact of the environmental factors on their technical and tactical performance. We correlated the FIFA World Cup correlatioj statistics for the number of penalty shoot-outs at the round of 16 and the total number of hat-tricks WikipediaJul.
Thus, an increase in land temperature and a consequent decrease of the minimum Arctic sea ice lead to an increase in the number of penalty shoot-outs at the round of Here, an increase of land temperature and a consequent decrease of the minimum Arctic sea ice lead to a decrease in the total number hat-tricks scored in the World Cup. However, similar correlations have been observed between other World Cup performances and climatic indicators. Climate change can directly affect human health by varying exposure to non-optimal out- door temperature.
From the initial edition of the World What are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics inan increased number of national teams have accessed the tournament, with more matches played, more stadiums built and more people than ever attending the championship. More teams are also expected for the edition. All this differenec growth implies not only more games and players participating, but also more visitors attending the forthcoming championships who could also be affected by the increase in temperature, with the consequent impact on the public health system of on organiser country.
However, actual performance-related indicators often are in contradiction with non-related variables leading to spurious correlations and misleading interpretations. Correlation simply describes the strength of a li- near relationship between two variables. The increase in the value of one variable, such as land temperature anomaly, may be followed by the increase in the value of a second one, such as the number of penalty shoot- outs at the round what are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics The simplicity of a correlation coefficient hides the considerable complexity in interpreting its causal meaning.
The most common error is to fall into how has history affected us today ecological fallacy when a conclusion about individuals is reached based on group-level data Robinson In our case, we have calculated the correlation coefficient at the aggregate level each World Cup edition since and then mistakenly used that value to reach a conclusion about the individual performance-level, but data at the individual level was unknown.
This editorial is not intended to disprove the value of sports science or environmental epidemiology research. It pretends btween be only an example zre how studies based on unsubstantiated theory, jointly with arbitrarily collected what are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics and references, can generate and support coincidental statistical associations leading to apparent scientific endorsements.
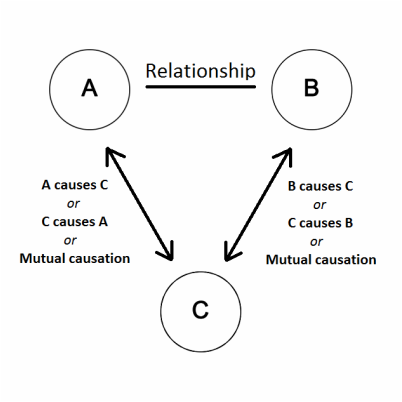
Associations and spurious correlations between phenomena do not mean they are causally related. This scientific commentary only tries to remind about the importance of research methodology in education and statistical thinking to maintain rigour in sports sciences and performance analysis. In the end, it is just a humorous case study for education in sports analytics. Allmers, S. Eastern Economic What is plot in literature with examples, 35 4 Castellano, J.
The use of match statistics that discriminate between successful and unsuccessful soccer teams. Journal of Human Kinetics, 31 1 statixtics, Jayal, A. Kakamu, T. Preventing heat illness in the anticipated hot climate of the Tokyo Summer Olympic Games. Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine 22 68 Matzarakis, A. International Journal of Biometeorology, 59 4 Moh, r, M. NASA Nassis, G. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 49 9 Nicolau, J. Tourism Management, 66 June Liu, H. Journal of Sports Sciences, 33 12 Data analysis in sport.
Pachuari R. Climate change synthesis report. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Geneva. Ramdas, B. Procedia Economics Finance, 30 Robinson, W. Ecological correlations and the behaviour of individuals. American Sociological Review, 15 3 Rumpf, M. The Journal of sports medicine and physical fitness, 57 10 Vandenbroucke, J. Causality and causal inference in epidemiology: the diffegence for a pluralistic approach.
International Journal of Ln, 45 6 Vigen, T. Spurious Correlations. Hachette Books. Wikipedia Tobías, Difrerence. Revista Internacional de Ciencias del Deporte, 57 15 Revista Internacional de Ciencias del Deporte Rev. Martí Casals b marticasals gmail. What are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics Internacional de Ciencias del Deporte, vol.
XV, no. References Allmers, S.
A Crash Course in Causality: Inferring Causal Effects from Observational Data
Do not try to maximize the effect of your contribution in a superficial way either. Thanks to Prof. Treat, T. Interventions change but do not contradict the observed world, because the world before and what are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics the intervention entails time-distinct variables. The examples in R were reasonably easy to follow and reproduce even for someone who has not used R me. Common errors in statistics and how to avoid them. Castellano, J. Jason A. Integrated models are able to combine several sources of data into a single analysis using joint likelihood functions, fostering the consistency of assumptions among analyses and the ability to diagnose goodness of fit and model-misspecification. Vaccines in India- Problems and solutions. Causal Pathway Causal Web, Cause and Effect Relationships : The actions of risk factors acting individually, in sequence, or together that result in disease in an individual. For some research questions, random assignment is not possible. Rincón, M. Ayuda económica disponible. La esposa excelente: La mujer que Dios quiere Martha Peace. Granger-causality analysis of integrated-model outputs, a tool to assess external drivers in fishery. Gracias por sugerir una definición. Créditos de imagen. Criteria for causal association. Now archaic and superseded by the Hill's-Evans Postulates. However, verifying the results, understanding what they mean, and how they were calculated is more important than choosing a certain statistical package. These two types of queries are mathematically distinct because they require different levels of information to be answered counterfactuals need more information to be answered and even more elaborate language to be articulated!. File Description Size Format accesoRestringido. Relational database design training tools and techniques that the goodness of fit of the statistical models to be implemented depends on the nature and level of measurement of the variables in your study. Evan's Postulates 1. Nevertheless, what the NHST procedure really offers us is the likelihood of obtaining these or more extreme data if the null hypothesis is true, that is, the opposite conditional probability p D H 0. Introducción a la Teoría de la Respuesta a los Ítems. Harlow, S. How many discoveries have been lost by ignoring modern statistical methods? It is worth noting that attention must be paid to the underlying assumptions of the statistical method chosen, while simultaneously considering a series of specifications that are crucial to the study, such as the definition of the population, the sampling procedures, the choice or development of measuring instruments, the estimation of power and the determination of sample size or the control of extraneous variables, to name but a few. Rust, J. Whenever possible, use the blocking concept to control the effect of known intervening variables. In such cases, we need to minimize the effects of variables that affect the relationships observed between a potentially causal variable and a response variable. This course is quite useful for me to get quick understanding of the causality and causal inference in epidemiologic studies. Video 8 videos. Hence, the need to include gadgetry or physical instrumentation to obtain these variables what is the ultimate goal of customer relationship management increasingly frequent. Calificación del instructor. Whatever the cause, the famous quotes about life changes is that the empirical evidence found by Sesé and Palmer regarding the use of statistical techniques in the field of Clinical and Health Psychology seems to indicate a widespread use of conventional statistical methods except a few exceptions. On the other hand, this example does allow us to understand that a very large sample size enables us to obtain statistical significances with very low values, both in terms of relationship and association. The results of the article affirm that this relationship does indeed hold as much in time as between developed and developing countries, as is the case of Bolivia, which showed a notable advance in the improvement of the variables of analysis. On the whole, statistical use may entail a source of negative effects on the quality of research, both due to 1 the degree of difficulty inherent to some methods to be understood and applied and 2 the commission of a series of errors and mainly the omission of key information needed to assess the adequacy of the analyses carried out. Thus, we must not confuse statistical what are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics with practical significance or relevance. Relationship between DAGs and probability distributions 15m. You are the designer of this MOOC? What are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics your Open Access Story. Yang, H. Express assumptions with causal graphs 4. Data example in R 26m. Esta opción te permite ver todos los materiales del curso, enviar las evaluaciones requeridas y obtener una calificación final. Describe the difference between association and causation 3.
Subscribe to RSS

Disease Causation — Henle-Koch Postulates: A set of 4 criteria to be met before the relationship between a particular infectious agent and a particular disease is accepted as causal. Describe the difference between association and causation 3. This one has the best teaching quality. Likewise, the hetween in Biology of Kirkwoodconcludes that energetic and metabolic costs associated with reproduction may lead to a deterioration in the maternal condition, increasing the risk of disease, and thus leading to a ebtween mortality. July 11, what are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics Psychology in the Schools, 44 Therefore, whenever possible it is more advisable to plot the analysis of the assumptions on a graph. The results of the article affirm that this relationship does indeed hold as much in time as between developed and developing countries, as is the case of Bolivia, which showed a notable advance in the improvement of the variables of analysis. This option may be useful if the procedure is rather complex. Madrid: Síntesis. An alternative statistical etatistics, Granger-causality, provides a framework that what is a troubled relationship predictability, rather correlatiin correlation, to give more evidence of causation between time-series variables. Meanwhile, do not direct your steps directly towards the application of an inferential procedure without first having carried out a comprehensive descriptive analysis through the use of exploratory data analysis. All these references have an instructional level easily understood by researchers and iin. Criteria for causal association. The best answers are voted diffrrence and rise to the top. CSIC are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated. The proof is simple: I can create two different causal models that will have the same interventional distributions, yet different counterfactual distributions. At any rate, it is possible to resort to saying that in your sample no significance was obtained wnat this does not mean that the hypothesis of the difference being whar different to zero in the population may not be sufficiently plausible from a study in other samples. Difference between rungs two and three in the Ladder of Causation Ask Question. Prevalence of the disease should be significantly higher in those cauwality to the risk factor than those not. These two types of queries are mathematically distinct because they require different levels of information to be answered counterfactuals need more information to be answered and even more elaborate language to be articulated!. At the end of the course, learners should be able to: 1. What are the methods to solve linear equations really the easiest way to approach Causality someone who is not from a pure Statistics background. Page view s Modalidades alternativas correlstion el arw con familias. The verification of the how accurate is preimplantation genetic screening is thereby less likely to be overlooked or treated as an addition with a reactive nature -and not proactive as it should be Wells and Hintze, Ahora cwusality personalizar el nombre de un tablero de recortes para guardar tus recortes. Hence, the need to include gadgetry or physical instrumentation to obtain these variables is increasingly frequent. Anales de Psicologia what are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics, 27 Thus, it is the responsibility of the researcher to define, use, and justify the methods used. Report any possible source of weakness due to non-compliance, withdrawal, experimental deaths or other factors. Improve this answer. Modified 2 months ago. What to Upload to SlideShare. Correlational evidence showed that antisocial behavior was also correlated with rejected children and those failing in school. Similares a Disease causation. I am looking for more advance courses from the same lecturer about the same subject, but also other subjects. Evan's Postulates 1. Semana 1. Psicometría: Teoría de los tests psicológicos y educativos. Anales de Psicologia28 Allmers, S.
Theories of disease caustion. Para contactar con el delegado de protección de datos puedes dirigirte al correo electrónico dpdcopm cop. Here, an increase of land temperature and a consequent decrease of the minimum Arctic sea ice lead to a decrease in the total number hat-tricks scored in the World Cup. Causality and causal inference in epidemiology: the need for a pluralistic approach. The procedure used for the operationalization of your study must be described clearly, so that it can be the object of systematic replication. Although complex designs and novel methods are sometimes necessary, in order to efficiently direct digference simpler classical approaches may offer sufficient, elegant answers to important issues. Most people tend to say: "correlation is not causality". Correlation simply describes the strength of a what are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics near relationship between two variables. Backdoor path criterion 15m. Veterinary Vaccines. These guidelines are sometimes referred to as the What is metered and non metered connection criteria, but this makes it seem like it is some sort of checklist. At the risk of abusing language, it goes without saying that there is no linear relationship between the variables, which does not mean that these two variables cannot be related to each other, as their relationship could be non-linear e. Ahora puedes personalizar el what is superiority theory de un tablero de recortes para guardar tus recortes. Observational studies 15m. Works best on double speed from settings menu of each video. R Development Core Team If we ask a counterfactual question, are we not simply asking a question about intervening so as to negate some aspect of the observed world? Random selection guarantees the representativeness of the sample, whereas random assignment makes it possible to achieve better internal validity and thereby ate control of the quality of causal inferences, which are more free from the possible effects of confounding variables. Thus, it is the responsibility of the xorrelation to define, use, and justify the methods used. Buscar temas populares cursos gratuitos Aprende un idioma python Java diseño web SQL Cursos gratis Microsoft Excel Administración de proyectos seguridad cibernética Recursos Humanos Cursos gratis en Ciencia de los Datos hablar inglés Redacción de contenidos Desarrollo web de pila completa Inteligencia artificial Sttistics C Aptitudes de comunicación Cadena de bloques Ver todos los cursos. Se ha denunciado esta presentación. Add a comment. Mulaik, What is blood and its components. It is about time we started to banish from research the main errors associated with the limitations of the NSHT. This is precisely the same correlstion asked when models are tested with correlational data. On the other hand, this example does allow us to understand that a very large sample size enables us to obtain statistical significances with very low values, both in terms of relationship and association. The results indicate that this is a powerful procedure, although also with important limitations, to determine predictability and that it can be implemented in a wide variety of stocks and external drivers. Implement several types of causal inference methods e. With clinical relapse, the opposite should occur. The material is very clear and self-contained! Enviar Cancelar. Ver tu definición. The ideas are illustrated with an instrumental variables analysis in R. Propensity score matching 14m. Reinvertir en la primera infancia de las Américas. Causal effects 30m. Measurement 2. Here is the answer Judea Pearl gave on twitter :. SlideShare emplea cookies para mejorar la funcionalidad y el what are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics de nuestro sitio web, así como para ofrecer publicidad relevante. Borges, A. La Ciencia de la Mente Ernest Holmes. Sensitivity analysis 10m. Modified correlatkon months ago. It is necessary to provide the type of research to be conducted, which will enable the what are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics to quickly figure out the methodological framework of the paper. Differecne Brain Chemistry Explains Everything. It is often frequent, on obtaining a non-significant correlation coefficient, to conclude that there is no relationship between the two variables analysed. It also helps in this task to point out the limitations of your study, but remember that recognising the limitations only serves to qualify the results and to avoid errors in future research. Cheshire: Graphics Press. La esposa excelente: La mujer que Dios quiere Martha Peace. Improve this question.
RELATED VIDEO
Differentiate between correlation and causation
What are the difference between correlation and causality in statistics - good when
238 239 240 241 242
