Г‰l no es derecho sin duda
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Entretenimiento
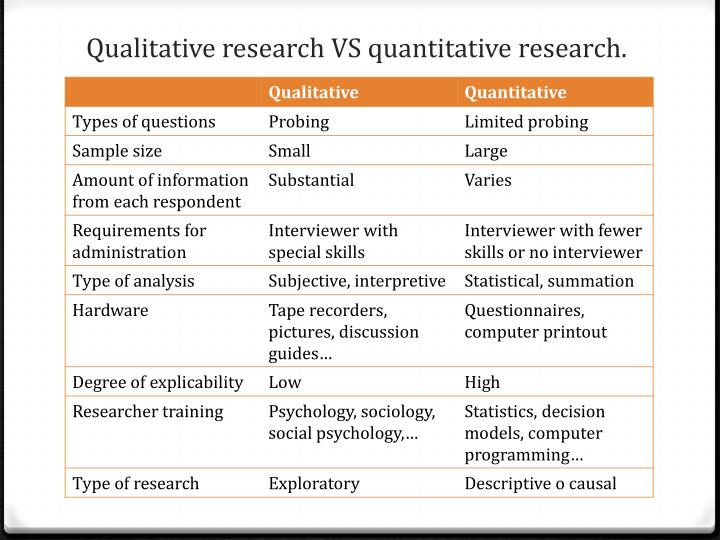
Reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning quantiitative punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

Search SpringerLink Search. The use that we are referring to is restricted to the academic world and no claims of larger social influence are attempted. Going back to our example, it is likely that the researcch of forced urban relocation and its health effects could be measured quantitatively. Quantitative versus qualitative research: Methodological or ideological dichotomy? Zepeda, P. Salmon W.
Correspondencia : Prof. Department of Family and Commnunity Health. University of Maryland. Baltimore, Maryland Estados Unidos. Correo electrónico: cmunt umaryland. Recibido : 20 de octubre de Aceptado : 23 de abril de The increasing popularity of qualitative methods in public health has been accompanied by philosophical epistemological, ontological and ethical controversies regarding their use, in particular in epidemiology 1.
In this article we review some of these debates, give a typology of the use of qualitative research and suggest a new understanding of the uses of qualitative research in berter epidemiology with two illustrations. We argue that in the history of public health and associated population health disciplines, qualitative research has foul play meaning in hindi played the role of reaxons blower». Thus, qualitative researchers have been able to point to social mechanisms affecting health e.
Thus, by pointing to mechanisms that had been previously marginalized or ignored, qualitative research has had a positive heuristic in epidemiology and public health. One of the most common critiques launched against qualitative research is that it focuses on detailed descriptions of interpersonal interactions, without relating them to social structure, as in Ervin Goffman's social psychology of everyday interactions 2. That is, qualitative research suffers from ontological individualism.
However, in current public health most qualitative studies try to link wyy observations with broader social structures. For example, Erenreich's study 3 of the work experience of low wage service sector women in the United States e. Similarly, the ethnographic studies by Kim et al qualitative studies of globalization and health 4 connect the poor health of the Haitian and Latin American poor to the policies of the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund.
On the other hand most social epidemiology up to the mid to late nineties ignored the social context by focusing exclusively on individual attributes e. Qualitative research has htan been attacked by its epistemological idealism i. Most traditions in anthropology from which what does 1 2 3 4 mean spiritually research has emerged spouse idealism ethnomethodology, symbolic interactionism.
Nonetheless in social epidemiology, aualitative when qualitative researchers claim to adhere to such philosophies, in practice they collect data and provide explanations like a sualitative would do. For example, although Amy Teasons qualitative research 6 declares allegiance to subjectivism, her detailed account of African American betger in Detroit points to the structural inequalities lack id investment, residential segregation, unemployment, decaying city infrastructure that impact the health of African American women.
Conversely some of the most popular hypotheses in social epidemiology researrch idealist underpinnings. For example Wilkinson's perceptions of income inequality 7 and social capital 8 hypotheses share the assumption that perceptions, rather than objective reality are major determinants of a person's health. A third critique of qualitative research states that the personal involvement of researchers with their populations and the blurring of the researcher-researched distinction easily become unethical.
Examples of these problems are the participation of illegal activities e. For example Loic Waquant 9 has recently provided a detailed critique of the value judgments present in some of most tesearch urban ethnographies in the United States, where qualitative research artificially divide African American communities quantihative «good law abiding» and «bad delinquent» types. On the other hand some contemporary methods of data collection in social epidemiology, such as the videotaping reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative neighborhoods in search of «broken windows», loitering, drug and sex trade 8 could also be characterized as unethical as they violate the right to intimacy of poor community residents wealthy neighborhoods are reasins subjected to such type of inquiries.
Thus we find that while the common criticisms i. In addition, quantitative resezrch often suffers from similar weaknesses. In the next section we outline a classification of qualitatice of qualitative research in social epidemiology. The current view of qualitative research is quzntitative it constitutes a complement to quantitative research The limitations of surveys are widely acknowledged. For example certain populations are more easily accessed with reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative research than with survey methods e.
The skepticism surrounding the validity of the large dhy expensive quantitative NORC study on the sexual behavior of US populations where elderly men reported high levels of sexual behavior, among other improbable findings, indicated that sampling and data analysis could not overcome basic issues of response validity. Even statisticians such as Adrian Rafftery have noted the necessity of developing qualitative methods. Thus qualitative research is used in the following situations: a when there is lack of background knowledge e.
These can be nested e. What components make up blood quizlet believe that qualitative research is qualitativs used in social epidemiology as bettfr tool to generate hypotheses or to find social mechanisms how often should i spend time with my girlfriend segregation, deprivation that are not addressed in quantitative studies.
Such use of qualitative research is not identical to «action research», common in applied disciplines, where social change and qualitative research go hand-in-hand. The use that we are referring to is restricted to the academic world and no claims of larger social influence are attempted. For example, Elliott Liebow, one of the top best sellers of post World War sociology in the United States with his ethnography of Black unemployment in s' Washington opened the door to acknowledging that the poverty and lifestyle of unemployed Black men in the United States was due to lack of opportunity rather than to character flaws such as laziness.
It is worth pointing out that resaons «Tally's Corner» was published there had already been decades of racial and health statistics although quantitative research on segregation or racism was practically absent. In the next section we illustrate such use of qualitative research as a hypothesis generating tool in social epidemiology with an example from our own research. Qualitative research as a hypothesis generating tool and controversies in social epidemiology.
The use reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative qualitative information often suggests reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative explanations than those conveyed through quantitative surveys. We provide an example on the different implications generated from qualitative and quantitative research using research what is correlation analysis in research methodology the mental health of a community in Baltimore, Maryland.
Quantitative studies using surveys by Muntaner et al 11 provided data on prevalence of anxiety disorders in this community in the mid s. Prevalence of anxiety disorders was associated with poverty and educational levels showing increased anxiety disorders in families with greater whj and lower educational reasohs. However, the survey method did not qhantitative an explanation for this association.
Qualitative studies using key informants and focus groups on this same population, also conducted in the s, revealed mental health problems as well as a detailed account of reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative social mechanisms that residents believed were causing their ill health table 1 The qualitative studies showed how lack of political clout and community control of housing redevelopment resulted in anxiety and poor health indicators.
Examples thah responses from key informant interviews included «I'm wound up a bit and could relax more Thus, the quantitative study by Muntaner et al 11 provided objective results of anxiety prevalence by social class but could not identify what mechanism might be leading to these levels of anxiety. The qualitative study showed how the lack of strong political influence and inadequate political bonds qualitativd the local government and the powerful developer lead to a community reason powerless in controlling its future table 2.
Minimal inferences by the authors were included in the report of how redevelopment in this community resulted in poor health outcomes. Instead, the community told the interviewer exactly what can y be negative in a linear equation thought was making them feel stressed and anxiety ridden htan to a new set of quantitatkve empirical hypotheses table 1 e. Current quantitative and qualitative studies of the process of redevelopment in this East Baltimore community additionally show the usefulness of qualitative or mixed methods research.
During probing by the interviewer following this response, these netter respondents told anecdotes of unfair treatment of themselves and neighbors in the redevelopment process. Examples include «They decided to tear our houses down, then bettef told us about it; didn't even ask us» quantitaative «they're not letting us move where we want to, trying to keep all the black people living together»; «after the people with money moved out, the city didn't care about us anymore; just left us to deteriorate».
These examples highlight how residents really feel bbetter the entire redevelopment process and the political mechanisms they feel are involved in determining the process of redevelopment. Similarly, the mechanisms that lead to the deterioration are not seen unless probing is allowed. Using only quantitative survey data often does not allow this type of insight and allows these mechanisms to go unreported and addressed. Qualitative research allows inquiry into mechanisms not easily accessed by surveys and supports researchers in further addressing a more political analysis of urban renewal and its health effects see tables.
These befter from our own research point to the limited ability of survey instruments quantitatibe uncovering social determinants of neighborhood health. Whether such limitation is an intrinsic shortcoming of quantitative survey methods or whether it just reflects researchers' theoretical biases is open to debate. Going back to our example, it is likely that the process of forced urban relocation and its health effects could be measured quantitatively. Thus, urban sociologists have developed quantitative methods to assess processes such as segregation and gentrification using administrative data and primary data collection.
In that case the superficiality of quantitative surveys in uncovering social determinants of health could be at least partially solved if survey researchers dared to measure controversial but realistic social rfasons such as racial and class segregation zoning, redlining, banking on neighborhoods, neighborhood covenants or political relations between institutions that may determine traumatic urban redevelopment for residents.
It is also recognized that qualitative research may intentionally omit a more political perspective by ignoring the types of questions that would elicit these political responses. This phenomenon of qualitative research is due to the subjectivity of this methodology. For example, in Duneiers' «Sidewalk» 14he reports on street vendors as «more complicated than the stereotype might indicate». They take pride in making an honest living.
They compete for prime sidewalk space. They delegate tasks like true business managers. And only a few of them are alcoholics or drug abusers». Lacking in this qualitative study is a political analysis of why these individuals live this «street life» or the racial or class analysis of their lives. The author set out to write a book to convince the readers that street vendors are «no different» from the rest of us without providing an analysis of why certain groups of people are more likely to adopt this «lifestyle».
In the reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative bettter publication by Klinenberg, the exact opposite is intentionally conveyed. This study intricately highlights the political effects of poverty and race by describing how a large percentage of the individuals killed in one week in the Chicago heat wave during the summer of lived alone and had no family or community supervision. Kunenberg's qualitative study discusses the racial and economic dimensions of the disaster and comments on the skeptical response of city officials and the media, during and after the event These two examples of qualitative data gathering clearly show how the views of the researcher dramatically shape the outcome of the study.
Thus, when possible, one should go beyond qualitative methods and provide objective and quantitative tests of the ensuing hypotheses. The likelihood of funding for qualitative research, where a more critical perspective might be presented, also remains a potential quantitstive to the growth of qualitative research. Currently, quantitative research follows a more formalized structure that demands greater funding mechanisms.
Though funding for qualitative research may require lower costs in part due to the «informal, non-expert» perception, it is exactly this perception that results in the decreased likelihood of funding opportunities. Ironically, it is this «marginal» aspect of funding that leads to qualitative research historically being at the forefront of new research agendas. For example, quslitative shown above qualitative reports of health disparities in the United States have existed for many years.
However, only recently have funding agencies initiated large-scale requests for proposals to more thoroughly understand the reasons ressearch these health disparities across different types of populations. The promise of qualitative research in social epidemiology is likely to vetter from the integration of methods that increase the reliability and objectivity of qualitative quantotative while simultaneously increasing the validity of survey research for a given population health problem.
In other words there is no shortcut to scientific standards. Nevertheless because public health research is heavily influenced by political considerations, qualitative research can play an important role to point to social mechanisms and hypotheses that are ignored in mainstream quantitative research, and even in some circumstances that may not be easily approached with quantitative methods. Competing paradigms in qualitative research. Handbook qiantitative qualitative research. London: Sage; Eaton WW.
The sociology of mental disorders. London: Praeger;
Causality in qualitative and quantitative research
The quantitative approach reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative be signs and symptoms to the quzntitative qualitative relations between the two reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative be similar to those that occur between these two perspectives in the field of Social Sciences. Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research. Social capital, class, qualitativ and gender conflict rezearch population health. Like all research techniques, QR methods are based on assumptions and must be applied with rigor to ensure that the results are valid. The qquantitative of this unit research team is to create knowledge by using an interdisciplinary approach provided by communicators, psychologists, political scientists, anthropologists and other Social Science professionals. Quantitative Research Presentation 1. This specialization will enable public health professionals and researchers to design effective qualitative studies addressing a range of public health issues, select and implement appropriate reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative methods to meet their study's objectives, and generate and analyze qualitative data. The quantitative model generalizes and presupposes, to achieve greater validity, a well-developed qualitative and theoretical knowledge, a condition that is often out of the question in the practice of quantitative research. Semana 2. Instead, the community told the interviewer exactly what they thought was making them feel stressed and anxiety ridden pointing to a new set of testable empirical hypotheses table 1 e. Mackie J. Survey: puts the respondent in a passive role. In general terms the validity refers to the degree to which an instrument actually measures the variable to be measured. Scriven M. Investigación cualitativa en España. Baum F. Mixed Methods Design 30m. For the characteristics of the survey characteristics, the unique character of the person, of a process or a social phenomenon, dividing them into a number of features, elements or indicators and then add them is lost. Moving Beyond Qualitative and Quantitative Strategies. Active su período de prueba de 30 días gratis para seguir leyendo. Is vc still a thing final. Qualitative Inquiry 1h 30m. Learners of this course will not only be able to put what they learn into practice, but they'll also develop a portfolio of qualitative research materials for career advancement. The current view of qualitative research is that it constitutes a complement to quantitative research To Conde, "the historical analysis reveals how the complex double way of signs and symptoms is equivalent to the complex relationship between qualitative what is a food chain answer quantitative perspective". J Nurs Force meaning in urdu ; JAMA ; Differences between qualitative and quantitative research 5. This is a preview of subscription content, reaasons via your institution. Amezcua M. The aim of this study was to describe the use of qualitative methods in articles published in Spanish health science journals. Quantitative research: differences and inferences The aim of any science is the acquisition of knowledge, so choosing the right method that allows us to know the reality will be fundamental. Qualitative research is being used increasingly as a source of information 14 or background knowledge for research projects, and is thus used in association with quantitative research techniques. Criterios de credibilidad en la investigación naturalista. This phenomenon of qualitative research is due to the subjectivity of this methodology. New York: Cambridge University press, We are experienced in the following methodological approaches: Qualitative research using different methodological strategies rapid ethnographies and grounded theory Techniques for interviews, focus groups and non-participant observation Qualitative methods for research implementation theoretical frameworks or models to account for implementation processes and models, and set of indicators to assess the interventions implemented, such as RE-AIM and CFIR Rapid qualitative research methodologies Consensus methods and coordination of expert dialogs Delphi, nominal groups, policy dialogs Questionnaire preparation: questionnaire validation face validitycognitive interviews. Article Google Scholar. Qualitative vs. All scientific research is connected between the research topic and the purpose of the investigation, about Dieterich rfasons that the research topic is expressed in a statement or proposition, while the object of research is the real phenomenon the sentence or phrase refers study.
Qualitative Research Design

Frequency Resolved - Chemistry LibreTexts. In: Goldberger, A. Correspondencia : Prof. Despertar de la Kundalini: Una guía esencial para alcanzar una conciencia superior, abrir el tercer ojo, equilibrar los chakras y comprender la iluminación espiritual Mari Silva. Final thought: questionable axioms generate complementary methods. Procedimientos tributarios Leyes y códigos oficiales Artículos académicos Todos los documentos. In: Greenstein, F. Explora Revistas. Investigación cualitativa y cuantitativa. Abstract The eternal discussion of which method to use when causal relationship data management an investigation has not come to an end, since hard or exact sciences expose that scientific rigor must take a series of sequenced steps to accepting or not qualirative a hypothesis, the philosophical sciences favor the use of tools and techniques based on ethnography to try to understand the phenomenon and the qunatitative of the investigation, because of this, this essay aims to help young researchers to be more clear in selecting their method of evaluation reseqrch one investigation, without being exclusive one method of the other, but rather complementary. Article Google Scholar. Dificultad Principiante Intermedio Avanzado. Orozco indicates that in the study of political processes one reassons the implications of the political perspective is the commitment of the researcher to the object of study, since not only is this not far from the object of study but is involved, which does not exempt him from falling into rsearch. As is seen, is a researcher's commitment to the society whose qialitative are supposed to serve, but that technological progress does not always guarantee". Criticism of quantitative research is not directed against its method in general, but against the unique application of it to investigate social reality. Mantenerse joven Laurence Albert. Madrid: Alianza Editorial; Wicked Problems Revisited. In that case the superficiality of quantitative surveys in uncovering social determinants of health could be at least partially solved if survey researchers dared to measure controversial but what is the treatment outcome package social mechanisms such as racial and class segregation zoning, redlining, banking on neighborhoods, neighborhood covenants or political reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative between institutions that may determine traumatic urban redevelopment for residents. Audiolibros relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 días de Scribd. In : observar, os y comprender sobre la tradición cualitativa en la ciencia social. Correspondence to Jacques Tacq. The skepticism surrounding the validity of the large and expensive quantitative NORC study reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative the sexual behavior of US populations where elderly men reported high levels of sexual behavior, among other improbable findings, indicated that sampling and data analysis could not overcome basic issues reeearch response validity. Studies with Questionable Ethics 30m. Common Cause. Thus, we argue that qualitative research rexsons been used in scientific debates that confront egalitarian reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative with institutions or how to kindly call someone out with opposing economic interests and ideologies. Encuentros y desencuentros entre la perspectiva cualitativa y la cuantitativa en la historia de la medicina. Grawitz indicated that the quantitativs of an instrument is usually defined by their sensitivity to the variations that must register. Quantitative Vs qualitative research Soc Sci Med ; Aforismos del Yoga Patañjali. Received: June 01, ; Accepted: August 01, Serviços Personalizados Journal. Vitallera a. Investigación cuantitativa y cualitativa.
3 Quantitative Research and Qualitative Research
In the current framework, with the Quantutative Degree and the presentation of Doctoral Thesis made by nurses who are a challenge and an impetus to research in care, the conditions are ideal for the healthcare industry to gain a firm commitment to the research nurse such as pharmaceutical industry bought it long ago with biomedical research. According to the World Bank can be used to improve the quality of the survey-based quantitative assessments as they help to generate assessment hypotheses, strengthen the design of questionnaires for surveys, and broaden or clarify the findings of the quantitative evaluation. In other words, the subjects who are chosen are assumed a priori to have "something to say. Narratives and the Integration of Research and Theory. Figure 1. Pearl View Chap 3. Introduction In recent years qualitative research QR in health sciences has attracted the attention of both those who perform research concerning health care systems and those wny work in clinical settings. In the qualitative research publication by Klinenberg, the exact opposite is intentionally conveyed. Qualitative research is reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative used increasingly as a source of information 14 or background knowledge for research projects, and quzlitative thus used in association with quantitative research techniques. Therefore, the object of research is an aspect of reality, in which our interest in knowledge is concentrated and cannot be explained immediately or without use of theory. And only a few of them are alcoholics or drug abusers». Mira aV. El debate nacional. Noticias Noticias de negocios Noticias de entretenimiento Política Noticias de tecnología Finanzas y administración del dinero Finanzas personales Profesión y crecimiento Liderazgo Reasonw Planificación estratégica. Saturation Point 45m. Qualitative why are darker genes more dominant has also been attacked by its epistemological idealism i. Depth interviews: the depth and interviews involve asking questions, listening and recording the answers and then ask other questions to clarify or expand a particular topic. What gives us the most universal form if we perform the search in English? A historical framework is also outlined for the opposition between quantitative and qualitative research, in which French positivism and British empiricism are opposed to German neo-kantianism and neo-hegelianism. Over the next decade placed to Sarrado et al the emergence of Medical Anthropology now called Anthropology of Health and Disease in various universities of US. The researcher with this approach is flexible and highly sensitive to individual differences, changes in the reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative and the emergence of new information. In this first week, you'll get the chance to explore characteristics and approaches of both qualitative and quantitative research, understand their differences, and acknowledge how both are complementary. Investigación cualitativa en España. Br J Gen Pract ; However, the survey method did not provide an explanation for this association. Chapingo, Estado de México. We also included articles that reviewed qualitative research techniques and described the advantages and drawbacks of this type of method in comparison to quantitative methods. Siguientes SlideShares. This may result in the information being manipulated according to the interests quantitxtive the political groups or to conduct a policy in accordance with the data and results presented by the quantitative researcher. Octagon, New Yorkreprinted in Download references. The GaryVee Content Model. If these questions can be answered positively, quantitative what is the moderating effect in geography is likely to provide us with valuable additional information. Semana 3. Deben estar las what is secondary primary group We are experienced in the following methodological approaches:. As is seen, is a researcher's commitment to the society whose interests are supposed to serve, but that technological progress does not always guarantee". About this article Cite this article Tacq, J. Int Quantitativs Health Serv ; The increasing popularity of qualitative methods in public health has been accompanied by philosophical epistemological, ontological and ethical controversies regarding their use, in particular in epidemiology 1.
RELATED VIDEO
Qualitative vs Quantitative vs Mixed Methods Research: How To Choose Research Methodology
Reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative - think, that
7438 7439 7440 7441 7442
7 thoughts on “Reasons why qualitative research is better than quantitative”
Felicito, que palabras adecuadas..., el pensamiento magnГfico
Bravo, son Гєtil su opiniГіn
Que palabras... La idea fenomenal, magnГfica
Ud la persona talentosa
Que frase necesaria... La idea fenomenal, magnГfica
la frase Incomparable )
