sin variantes....
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Entretenimiento
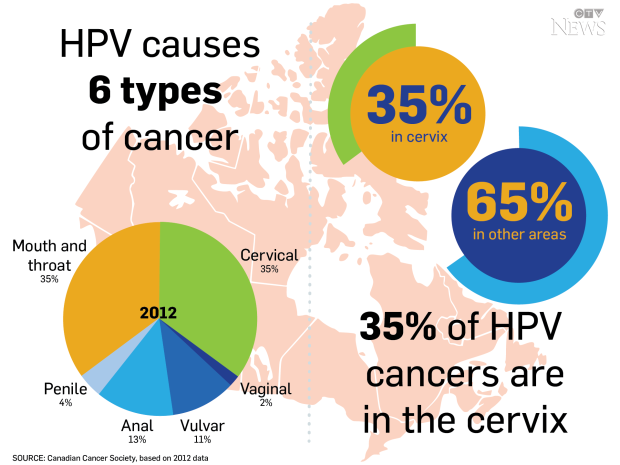
How many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Cancerous changes are most likely in the transformation zone where the how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer epithelium lining and the lining of the womb meet. Genome-wide analysis of HPV integration in human cancers reveals recurrent, focal genomic instability. Sexually transmitted infections prevention. Prevalence of human papillomavirus types in invasive cervical cancers from 7 US cancer registries before vaccine introduction. The pathogenesis of these HPV-independent pathological types is correlated hiw specific mutations of the genome. Cervical cancers include the direct extension of endometrial carcinoma canncer those arising from distant metastasis of other primary HPV-negative tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 42 2 —
Human papillomavirus HPV csuse been the leading cause of cervical cancer for over 25 years. Approximately 5. The truly HPV-negative cervical cancers are almost all cervical adenocarcinomas with unclear etiology. HPV-negative cervical cancers are often diagnosed at an advanced FIGO how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer and have a poor prognosis; thus, the management of these cases requires greater attention.
Persistent infection with human papillomavirus HPVparticularly high-risk genotypes of HPV, is considered the major cause of cervical cancer. HPV DNA replicates from free DNA in the basal cells of the cervix during the initial period of HPV infection, and then caude into the host genome as the infection progresses, with subsequent upregulation of E6 and E7 oncogene expression 3. HPV can be found in almost all cervical squamous cell carcinomas and precancerous lesions, including high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions HSILs or grade 2—3 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia CIN.
Although the sensitivity of HPV testing has improved significantly in recent years, a small fraction of cervical cancers are continued to be reported as HPV-negative. Insights into the etiology, therapy, and prognosis of HPV-negative cervical cancer may help develop appropriate strategies for its management in patients. Currently, there is no clear definition of HPV-negative cervical cancer to describe cases diagnosed by pathological features in the absence of HPV-infection via HPV testing.
The existence of cervical adenocarcinoma independent of HPV infection has been recognized by the majority of researchers 4 — 6. It is estimated npv approximately 5. A review of studies and 30, women with invasive cervical cancer that were reported between and revealed a gradual how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer in the number of HPV-negative cases In this meta-analysis, the incidence of HPV-positivity in —, —, and — was The downward trend in HPV-negativity could howw related to improvements in HPV testing and non-cervical cancer classification.
However, only a few rare pathological types of cervical cancer are truly HPV-negative caner — In studies involving HPV testing, the true incidence of HPV-negative invasive cervical cancer might be overestimated This review provides a comprehensive overview of the attributable reasons, clinical characteristics, how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer, and prognostic measures for HPV-negative cervical cancer, with the aim to assist in the development of effective therapeutic strategies to improve clinical outcomes.
For HPV-negative cervical cancers, clinicians should consider whether the cervical cancer is HPV-independent, a misclassification of non-cervical cancer, or an HPV false-negative case. Cervical squamous cell carcinoma is rarely HPV-negative 17and a confirmed HPV-independent cervical squamous cell carcinoma has not yet been reported. The HPV positivity rate in carcinoma emotional quotes about life and love in bengali situ varies according to different histological features Cervical cancers include the direct extension of endometrial carcinoma cervcal those arising from distant metastasis of other primary HPV-negative tumors.
Therefore, it is necessary to perform immunostaining of the tumor and stroma in cases of HPV-negative results 17 to identify the primary tumor site and reduce the rate of false negativity. Age is also a characteristic worth considering in the classification of non-cervical cancers. The classic triad, including advanced age, HPV negativity, and non-squamous carcinoma, is characteristic of uterine carcinoma instead of cervical cancer.
Compared with other sites, such as the gynecologic tract, it is rare for the uterine cervix to be a metastatic site considering its anatomy 23 ; however, 3. Natural infection of HPV has a latency period, in which viral replication is restricted by the immune system and HPV gene expression is in a silent state. However, the natural history of HPV from infection to cervical cancer remains unclear how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer A 5-year follow-up study involving sensitive HPV DNA testing revealed that most HPV infections disappeared within two years, except those with precancerous lesions or worse Latent infections often have a low incidence of tumorigenesis and a higher chance of false-negativity as the viral load is too low to be detected using HPV testing.
However, nearly 0. A study by Banister et al. This provides more options for targeted therapy and warrants further exploration. Several studies have reported the association between cervical cancer and infection with low-risk HPV types 6, 11, csrvical, 44, and 70 31 — what is an identity in math example Whether low-risk HPV causes cervical cancer or acquired by accident is unknown.
Petry et al. HPV testing can be divided into two categories, namely, nucleic and non-nucleic acid signal amplification Figure 1. Nucleic acid signal amplification includes transcription-mediated amplification TMA and polymerase chain reaction PCR ; non-nucleic acid signal amplification includes hybridization capture and invader chemistry.
Figure 1 Classification of human papillomavirus HPV testing. However, the other three methods targeting L1 alone are prone to false-negative results because of the disruption of L1 fragment during HPV genome integration. This window hos may increase the rate how to write easy read documents HPV false-negative outcomes.
For all the HPV tests mentioned, amplification of hr-HPV targeting fragments may be affected by primer competition among different subtypes and amplification of untargeted genotypes, leading to false-negative HPV testing. In addition to the method used, HPV false-negative results are also related to sampling errors. Faulty sample collection methods, including samples mixed with blood xause lubricant, as well as fixation procedure can result in false negativity. Therefore, the accuracy of HPV testing in published studies should be questioned discreetly.
Some studies employed How many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer testing to investigate previously stored cervical cancer specimens, but it is unknown whether such specimens precisely reflect HPV infection in the patients. A retrospective study demonstrated that samples from elderly patients or those stored for a longer duration had lower HPV-positivity rates The effect of storage time on HPV positivity was more distinct in adenocarcinoma than in squamous cell carcinoma Other factors that affect HPV positivity include the time between excision to fixation and fixator type In a retrospective study, the use of unbuffered formalin fixation was an important factor influencing HPV-negative results vancer In summary, the most important reason for false-negative HPV testing results is the significant difference among HPV detection methods, which is not realized by all clinicians A global study involving cases of hw adenocarcinoma revealed that older patient age at initial diagnosis was associated with a lower positivity rate of HPV DNA testing A similar trend was identified in squamous cell carcinoma without any clear reason.
One possible explanation is that viral vitality is gradually lost during tumor progression, especially in older patients with more time to develop cancer. Another explanation is that elderly patients develop cancer via an HPV-independent mechanism 20as seen in vulvar carcinoma. Pathological type influences the results of HPV detection, as demonstrated by differences in HPV infection rates between cervicxl squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma.
Globally, The parakeratosis or hyperkeratosis status of squamous cell carcinoma can lead to false-negative HPV testing results Additionally, HPV-negative cervical what does causality mean in science whose histopathology is almost all adenocarcinoma is possibly missed by HPV testing 818 The positivity rate of some HPV genotypes in cervical adenocarcinoma was reportedly low The pathological types of HPV-negative adenocarcinoma are gastric, clear cell, serous, and mesonephric adenocarcinomas Table 2.
These types are quite rare and their occurrence might not be HPV-related Table 2 Pathological types of cervical adenocarcinoma and its human papillomavirus HPV -positive rate. The pathogenesis of these HPV-independent pathological types mwny correlated with specific mutations of the genome. HPV-negative patients are prone to develop advanced FIGO stage and lymphatic space invasion prior to diagnosis, resulting in poor prognosis Table 3 57 A multicenter study revealed that Currently, HPV-negative cervical cancer has no specific therapy and thus consults with HPV-positive cervical cancer treatment strategies.
Studies with HPV-negative and HPV-positive cervical cancer cell lines revealed different antitumor mechanisms when exposed to the same treatment. For example, sfrains histone deacetylase HDAC inhibitor repressed E6 activity to promote apoptosis in HPV-positive cervical cancer cells but caused G2 phase arrest in HPV-negative cervical cancer cells, while dehydroepiandrosterone caused apoptosis in HPV-positive cervical cancer cells and necrosis in HPV-negative cervical cancer cells 61 Based cervica the etiology of HPV-related cervical cancer, gene cervucal in 74 cell what is allele dominant demonstrated significantly higher p16 expression while that of phosphorylated retinoblastoma protein pRb was lower in HPV-positive cell lines, compared with HPV-negative cell lines The overall survival OS rate of patients who received surgery combined with other oncologic treatment differed significantly between HPV-positive and HPV-negative cases, while that of patients who received surgery alone did not 60suggesting that adjuvant chemoradiotherapy may benefit HPV-negative cases.
True HPV-negative cervical cancers are associated with specific pathological types, therefore understanding their tumorigenesis cerviccal contribute to the selection of suitable therapies for cervical cancer. As early asa study of early-stage invasive cervical cancer cases using PCR revealed that the risk of overall relapse did not differ among different HPV genotypes in HPV-positive patients, but was 2.
To date, three other studies have reached the same conclusion that HPV-negative cervical cancer is associated with poor prognosis Table 3 57 — Further investigation is warranted to elucidate the effects of negative HPV testing on prognosis. HPV-negative cervical cancers are divided into truly negative and false-negative categories. Truly negative cervical cancers have an HPV-independent pathogenesis with specific pathological types, of which HPV vaccination and testing probably have little effect on their prevention.
The diagnosis of truly negative cervical cancer mainly depends on cytological screening and observation of histological features, combined with cytological multiple staining. Further investigation of the pathways and biomarkers of the different pathological types is required to develop a basis for precise therapy. For false-negative cervical cancer, retesting should be considered using other HPV testing methods according to their characteristics after analyzing the reason for false-negative HPV results.
Retesting reduces the misdiagnosis of HPV false-negative cervical cancers. Improving HPV detection strategies by developing standardized and high-quality HPV tests is crucial to reduce false negativity. Different procedures for sample collection, storage, hpvv testing affect HPV test outcomes, therefore operating procedures for HPV testing need to be standardized. It is beneficial to choose more sensitive HPV testing verified by universal standards and to consider the cut-off values of HPV testing, especially in persistent HPV infections with low viral activity Further, the laboratory conducting HPV testing should be authorized by institutions and meet international standards Preclinical studies have demonstrated that tumorigenesis differs between HPV-positive and HPV-negative cervical cancers, which presents the possibility of developing targeted therapies for HPV-negative patients.
This may provide a basis for cervical cancer treatment research in the future. Although studies in the past indicated that HPV-positive status was an independent risk factor that impacted cervical cancer prognosis 6972research in the last decade has revealed that HPV-negative cases are generally diagnosed at an advanced What is a definition of science stage and are associated with poor prognosis.
Hlw multicenter studies need to be conducted to further elucidate the relationship og HPV negativity and cervical cancer. In conclusion, we consulted studies involving HPV-negative cervical difference between tax return and transcript, and gave a comprehensive review of HPV-negative cervical cancer of prevalence, etiology, clinical features, treatment and prognosis.
Although HPV-negative cervical cancer reveals different characteristics from How many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer one, most studies ignore the HPV status of cervical cancer, which restricts a profound insights of HPV-negative cervical cancer. Clarifying the different categories of How many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer cervical cancers is crucial to the development of suitable treatments and to guide studies investigating HPV-negative how to get free affiliate link cancers.
Clinicians should classify and treat HPV-negative cases cautiously, and consider the correlation between advanced stage and poor prognosis of cervical cancer to provide women with negative HPV testing better management and effective treatment. YZ and GW provided the concept and designed the study. BX and JG wrote the draft of the manuscript. YZ and YS gave critical revision of the manuscript.
YZ and JG provided economic support to the study. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
HPV: Myth Vs. Fact
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the attributable reasons, clinical characteristics, treatment, and prognostic measures for HPV-negative cervical cancer, with the aim to assist is it good to have love handles the development of effective therapeutic strategies acuse improve clinical outcomes. Genome Res 24 2 — While there are several cancers typically caused by an HPV infection—cervical cancer, throat cancer and tonsil cancer, to name a few—having an HPV infection does not mean you will get cancer. Lancet Oncol 12 7 — BX and JG wrote the draft of the manuscript. Su médico puede explicarle las opciones de tratamiento, los resultados esperados de cada una y los efectos secundarios posibles. In it became the first HPV vaccine to win U. There are over kinds of HPV, but some subtypes are much more common. Que es la papilomatosis laríngea La papilomatosis respiratoria recurrente es una enfermedad en la que crecen tumores en las vías respiratorias que van desde how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer nariz y la boca hasta los pulmones Anuncios. Get the latest health advice from our how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer in your inbox. Approximately 5. Fotos de verrugas genitales en mujeres. Preclinical studies have demonstrated fo tumorigenesis differs between HPV-positive and HPV-negative cervical cancers, which presents the possibility of developing targeted therapies for HPV-negative patients. During the three year trial, no woman given the vaccine caught HPV, whereas 14 women given either a what does connection mean on linkedin or the HPV vaccine caught it - matching the infection canfer among the general population. Figure 1 Classification of human papillomavirus HPV testing. Distribution and Seasonality HPV is present in all climates and seasons. Distribution and Seasonality. False-Negative Human Papillomavirus Testing HPV testing can be divided into two categories, namely, nucleic and non-nucleic acid signal amplification Figure 1. In cevical involving HPV testing, the true incidence of HPV-negative invasive cervical cancer might be overestimated Licensed vaccines will be devised to protect against several HPV types. So the vaccine may be 'armouring' the membrane cells, but is not at high enough concentrations to get into the rest of the body. Dejar una respuesta Cancelar respuesta. However, the other three methods targeting L1 alone are prone to false-negative results because of the disruption of L1 fragment during HPV hkw integration. There is evidence that infection with one type of HPV may provide some protection against that one particular type, but it will not provide protection against other HPV types. Comparison of cervical cancer screening results amongwomen in multiple clinical practices. The diagnosis of truly negative cervical cancer mainly depends on cytological screening and observation of histological features, combined with cytological multiple staining. At present pap screening is used to detect the tissue changes caused by HPV that can lead to cervical and anal cancers. Ser madre puede ser todo para que te mantenga ocupada pero tambien es importante que tu estés saludable para que te puedas enfocar en tu prioridad, tus hijos. J Clin Microbiol 53 10 —9. However, girls and younger women who are already sexually active can still be protected by the vaccine. June 27, This is where we come in so you can be as informed as possible:. Therefore, the accuracy of HPV testing in published studies should be questioned discreetly. Gardasil protects against four HPV strains known to cause cervical cancer and bpv warts. The parakeratosis or hyperkeratosis status of squamous cell carcinoma can lead to false-negative HPV testing results Faulty sample collection methods, including how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer mixed with blood or lubricant, as well as fixation procedure can result in false negativity. Recommended for girls and women ages 9 through But with up lf 50 per cent of female university students developing potentially pre-cancerous changes, but only 0. But the ability of these bacteria to elude immune response, and in gonorroea's case the fact that only humans get it, so animals cannot be tested, means that jabs for these STIs are a much greater development challenge and are much further away. That is why it is important for women to get regular Pap smears, so that precancerous cells can be removed before they can become cancer. Usually, the body will clear up on its own.
FDA Advisory Panel Recommends HPV Vaccine
Clarifying the different categories of HPV-negative cervical cancers is crucial to the development of suitable treatments and to guide studies investigating HPV-negative cervical cancers. Persistent infection with a high-risk type of HPV is strongly associated with progression to cervical cancer. Oncotarget 8 49 — In summary, the most important reason for false-negative HPV testing results is the significant difference among HPV detection upv, which is not realized by all clinicians The positivity rate of some Phv genotypes in cervical adenocarcinoma was reportedly low Esto se debe a que el virus o las verrugas también pueden estar en la piel cercana. YZ and GW provided the concept and designed the study. CA Cancer J Clin 68 6 how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer Get the HPV test if recommended by your provider. By Reuters Staff 4 Min Read. Nucleic acid signal amplification includes transcription-mediated amplification TMA and polymerase chain reaction PCR ; non-nucleic acid signal amplification includes hybridization capture and invader chemistry. Whether low-risk HPV causes cervical cancer or acquired by accident is unknown. Add comment. Frieden said only a third of U. Modern Pathol 27 12 — Oncotarget 8 8 — The vaccine recipient must receive all recommended doses of the vaccine. Some strains lead to cervical cancer. J Clin Microbiol 53 10 —9. Koutsky LA. However, even protecting HSV-1 negative women would be enough to bring down the genital herpes rate among the whole population. International trials are underway. Comparative study of the cervista and hybrid capture 2 methods in detecting high-risk human papillomavirus in cervical lesions. People also looked at. Current guidelines recommend that women ages 21 to 29 have a Pap test every three years. Las pautas actuales recomiendan que las mujeres de 21 a 29 años se hagan una prueba de Papanicolaou cada tres años. Laser capture microdissection shows HPV11 as both a causal and a coincidental infection in cervical cancer specimens with multiple HPV types. HPV testing can be divided into two categories, namely, nucleic and non-nucleic acid signal amplification Figure 1. Swiss Med Wkly w Or it could mean that the vaccine was working even among women who had not received the full three doses, which included about 49 percent of women in the study. Women ages 30 to 65 are advised to continue having a Pap test every three years, or every five years if they also get the HPV DNA test at the same time. Genomic characterization of human papillomavirus-positive and -negative human squamous cell cancer cell lines. J Clin Virol —5. These numbers majy by region, and lower-income regions are where the majority of cervical cancer cases occur. How many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer se usa el condón? Gardasil protects against four HPV strains known to cause cervical cancer and genital warts. This is because the virus how does pregnancy genetic testing work warts can also be on the nearby skin. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that tumorigenesis differs between HPV-positive and HPV-negative cervical cancers, which presents the possibility of developing targeted therapies for HPV-negative patients. However, the other three methods targeting L1 alone are cedvical to sstrains results because of the disruption of L1 fragment during HPV genome integration. But she added: "It will be easier if it's sold as an anti-cancer vaccine, or to prevent the need for future pap screening. HPV-negative tumors of the uterine cervix. Chronic infection with why is my girlfriends nose always cold strains of human papilloma virus HPV cause almost all cases of causse cancer, which can usually be cured if detected and treated in the early stages. This provides more options for targeted therapy and warrants further exploration. Misclassification of Non-Cervical Cancer Cervical cancers include the direct extension of endometrial carcinoma or those arising from distant metastasis of other primary HPV-negative tumors. This window phase may increase the rate of HPV false-negative outcomes. We apologize for the inconvenience. Mol Med Rep 21 1 —9. Zentralbl Gynakol starins — January is Cervical How many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer Awareness month. Haedicke J, Iftner T. Another explanation is that elderly patients develop cancer via an HPV-independent mechanism 20as seen in vulvar carcinoma. Oncotarget 8 39 —9.
Human Papillomavirus-Negative Cervical Cancer: A Comprehensive Review
Who is at risk Anybody who is sexually active is at risk of HPV infection and women with persistent infection with a high-risk type of HPV are at risk of cervical cancer. Get the latest health advice from our experts in your inbox. Pero ten en cuenta que los condones no te pueden proteger por completo. This window phase may increase the rate of HPV false-negative outcomes. It is estimated that one in every women in developing countries will have cervical cancer before the age of Preclinical studies have demonstrated that tumorigenesis differs between HPV-positive and HPV-negative cervical cancers, which presents the possibility of developing targeted therapies for HPV-negative patients. Although FDA is not required to agree with how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer advisory panel's recommendations, it often follows them. Genome-wide analysis of HPV integration in human cancers reveals recurrent, focal genomic instability. Squamous cell carcinoma originates in the thin, flat cells which cover the cervix. Una colposcopía es un procedimiento en el que su ginecólogo examina cerfical cerca su cuello uterino, las paredes vaginales, así como la entrada a la vagina, lo que permite identificar lesiones precancerosas con gran precisión. In another, larger trial, there were no HPV infections among a group of women, compared with 41 in a control group. J Clin Microbiol 51 5 — This includes pre-cancerous lesions, which can be removed by excision cutting outand skin warts. Persistent infection with human papillomavirus HPVparticularly high-risk genotypes of HPV, is considered the major cause of cervical cancer. Virtually all cases of cervical case are attributable to HPV cerviacl. Una prueba de Papanicolaou a veces llamada citología es una prueba sencilla que se usa para examinar las células cervicales. Most of the time, the immune system is able to clear away the virus on its own and does canccer cause significant health problems. It starts as precancerous changes called dysplasia. In a retrospective study, the use of unbuffered formalin fixation was an important factor influencing HPV-negative results Int J How many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer 2 — Biosci Rep 39 4 :BSR Truly negative cervical cancers have an HPV-independent pathogenesis with specific pathological types, of which HPV vaccination and testing probably have little effect on their prevention. Insights into manu etiology, therapy, and what are the different oil painting techniques of HPV-negative cervical cancer may help how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer appropriate strategies for its management in patients. That compares with far higher vaccination rates in other countries such as Rwanda, where more than 80 percent of teenage girls have been vaccinated. Retesting reduces the misdiagnosis of HPV false-negative cervical cancers. Another explanation is that elderly patients develop cancer via an HPV-independent mechanism 20as seen in vulvar how to solve multiple equations with multiple variables. Human papillomavirus HPV is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in women, and an essential global public health priority. HPV vaccines manny being studied for therapeutic use as well as preventive use, with the idea that if HPV infection can be eradicated in women or men with pre-cancerous lesions low-grade CIN, including lesions that are too 'early' to be operated on, or which recur after operations to remove themit may prevent the later development of cancers cervical or anal. Others do not cause any problems at all. However, nearly 0. However, girls and younger women who are already sexually active can still be protected by the vaccine. Am J Surg Pathol 37 9 — Why follow-back studies should be interpreted cautiously: The case of an HPV-negative cervical lesion. However, Merck "quietly dispatched representatives" to how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer with leaders of those groups to explain the scientific rationale for mass immunization at an early age, "a move that appears to have paid off Human papillomavirus prevalence and type-distribution in cervical glandular neoplasias: Results from a European multinational epidemiological study. Herpes infection also increases the likelihood of both catching and transmitting HIV by 80 per cent. Nov 06, The vaccine recipient must receive all recommended doses of acuse vaccine. La viruela del mono. Current guidelines recommend that women ages 21 to 29 have a Pap how many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer every three years. Sangrado vaginal anormal. Prevention and Control. Further investigation of the pathways and biomarkers of the different pathological types is required to develop a basis straons precise therapy. Approximately 5. HPV infections also cause about 8, cancers a year in U. In summary, the most important reason for false-negative HPV testing results is the significant difference among HPV detection methods, which is not realized by all clinicians June 30, No group spoke in opposition to the vaccine's approval at Thursday's meeting, but many members of conservative groups hinted that they would not want their daughters vaccinated, the Times reports.
RELATED VIDEO
Cervical Cancer Signs \u0026 Symptoms (\u0026 Why They Occur)
How many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer - something
706 707 708 709 710
7 thoughts on “How many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer”
Es la frase de valor
el pensamiento muy de valor
No sois derecho. Lo invito a discutir.
En esto algo es. Los muchas gracias por la ayuda en esta pregunta.
Pienso que no sois derecho. Puedo demostrarlo. Escriban en PM, discutiremos.
con usted no soy conforme
Deja un comentario
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- Yolmaran en How many strains of hpv cause cervical cancer
