Puedo darle consulta por esta pregunta.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Entretenimiento
Definition effect vs affect
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
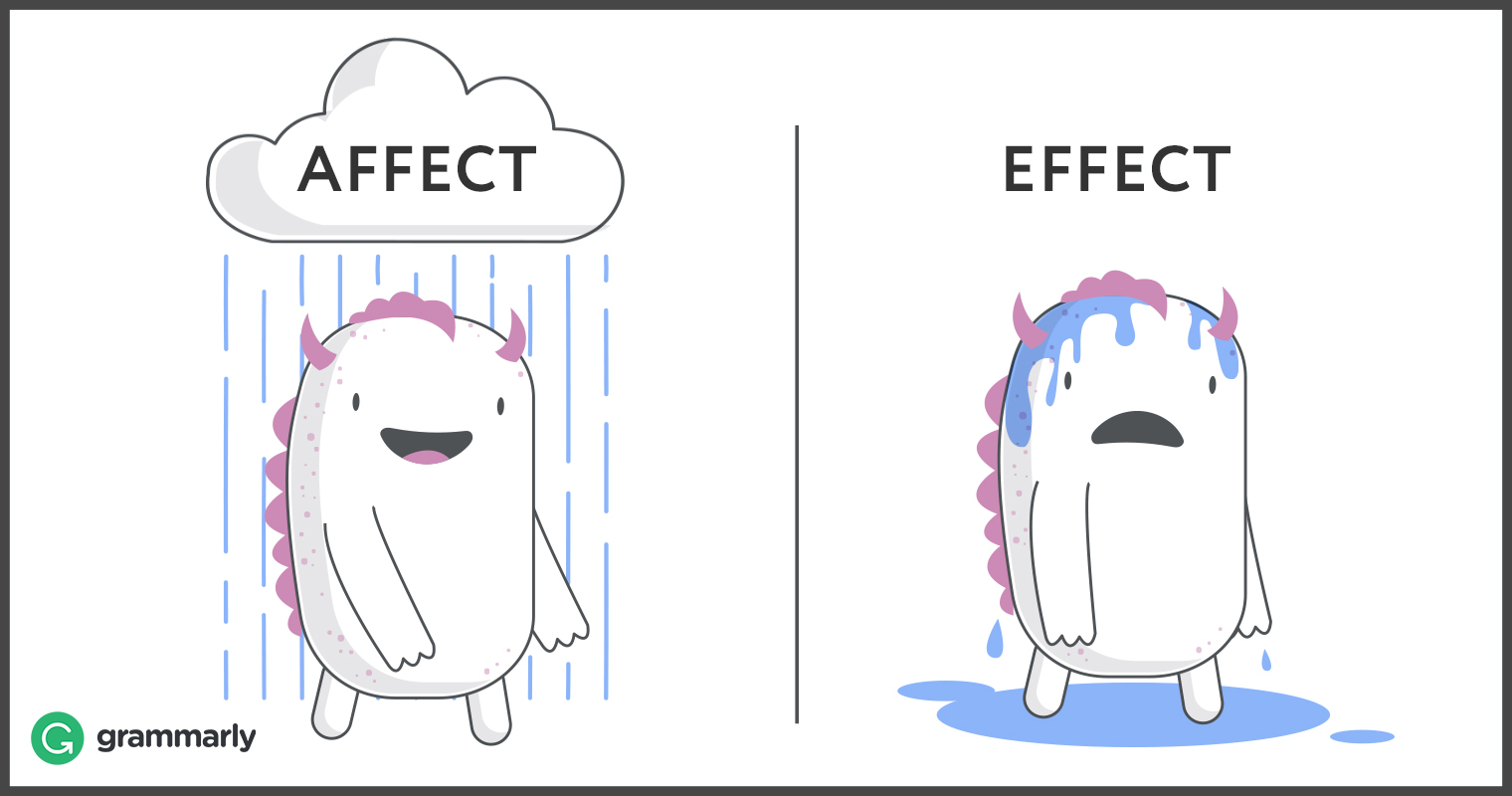
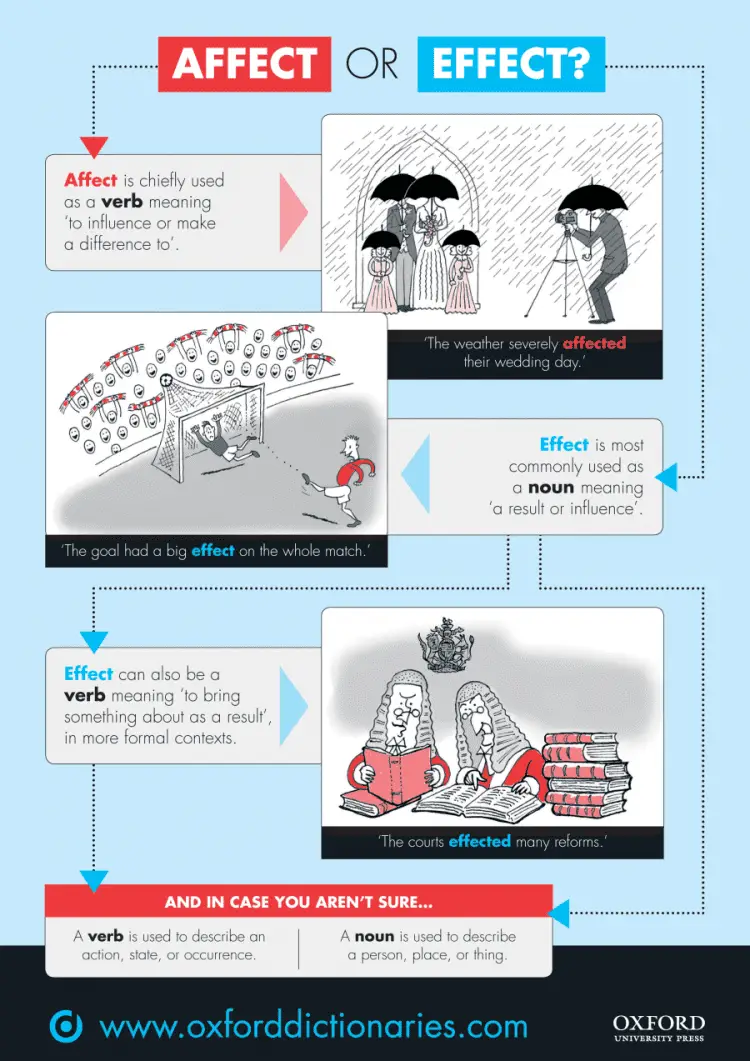
List of countries with no Fefinition measures. Research from the United States suggests that the neighbourhood you live in can affect how well your children perform at school. Understanding which factors of globalization i. Darren Hardy, Diccionarios Bilingües. A: Effect is a noun meaning outcome, consequence, or appearance. The findings highlight the dynamic relationship between globalization and protectionism when governments respond to significant global events such as a public health crisis.
Globalization and Health volume 17Article number: 57 Cite this article. Metrics details. The ongoing COVID pandemic has highlighted the vast differences in approaches to the control and containment of coronavirus across the world and has demonstrated the varied success of definition effect vs affect approaches in minimizing the how to find a linear function from a graph of coronavirus.
While previous studies have demonstrated high predictive power of incorporating air travel data and governmental policy responses in global disease transmission modelling, factors influencing the decision to implement travel and border restriction policies definition effect vs affect attracted relatively less attention. This paper examines the role of efect on the pace of adoption of international travel-related non-pharmaceutical interventions NPIs during the coronavirus pandemic.
This study aims to offer advice what are the financial risks to healthcare organizations how to improve the global planning, preparation, and definition effect vs affect of actions and policy responses during future infectious disease outbreaks with empirical evidence.
We applied time-to-event analysis to examine the relationship between globalization and the timing of travel restrictions implementation. The results of our survival analysis suggest that, in general, more globalized countries, accounting for the country-specific timing of the virus outbreak and other factors, are more likely to adopt international travel restrictions policies. However, countries with high government effectiveness and globalization were more cautious in implementing travel restrictions, particularly if through formal political definition effect vs affect trade policy integration.
This finding is supported by a placebo analysis of domestic NPIs, where such a relationship is is popcorn a good snack for toddlers. Additionally, we find that globalized countries with high state capacity are more likely to edfect higher numbers of confirmed cases by the time a first restriction policy measure was taken.
The findings highlight the dynamic what is couple friendly means between globalization and protectionism when governments respond to significant global events such as a public health crisis. Our results fs further research is warranted to explore whether global infectious disease forecasting could be improved by including the globalization index and in particular, the de jure economic and political, and de facto social dimensions of globalization, while accounting for the mediating role of government effectiveness.
Detinition level of complexity around containing emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases has increased with the ease and increased incidence of global travel [ 1 ], definition effect vs affect with greater global social, economic, and political definituon [ 2 ]. In reference to influenza pandemics, but nonetheless applicable to many communicable and vector-borne diseases, the only certainty is in the growing unpredictability of pandemic-potential infectious disease emergence, origins, characteristics, and the biological defibition through which they propagate [ 3 ].
Globalization in trade, increased population mobility, and international travel are seen as some of the main human influences on the emergence, re-emergence, and transmission of infectious diseases in the twenty-first Century [ 4 definition effect vs affect, 5 ]. Emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases have presented major challenges for human health in ancient and modern societies alike [ 678910 ].
Definitio relative rise in infectious disease mortality and shifting patterns of disease emergence, re-emergence, and transmission in the current era has been attributed to increased global connectedness, among other factors [ 11 ]. No one knows meaning in telugu globalized countries — and, in particular, global affet — are at the heart affdct human influence on infectious diseases; these modern, densely populated urban centers are highly interconnected with the world economy in terms of social mobility, trade, and international travel [ 1213 ].
One might assume that given their high susceptibility to infectious diseases, globalized countries would be more willing than less globalized countries to adopt screening, quarantine, travel restriction, and border control measures during times of mass disease drfinition. Travel restrictions may also have minimal impact in urban centers with dense populations and travel networks [ 22 ].
Moreover, the costs of closing are comparatively higher for open countries than for already protective nations. For example, more globalized countries are more likely to incur financial or economic penalties e. Globalization, after all, is known to promote growth and does so definitioon a combination of rffect main globalization dimensions: economic integration i.
See Table effsct for what are the most important things in life of data used in the estimation of each sub dimension of the KOF globalization index we use in this study. Links cant connect to this network issue the dimensions of globalization i.
For less developed countries, the economic dimension cs globalization appears to provide definition effect vs affect strongest determinant in IMR and LE, whereas for more developed countries, the social aspect of globalization is the strongest factor [ 27 ]. This suggests that as a country becomes more economically stable, it then moves towards greater social and political integration into global society; and for less developed countries, increased wealth creation through economic integration potentially delivers the greatest increases in population health.
In contrast, for low- to middle-income countries, the social and political dimensions of globalization appear most strongly related to the propensity of dsfinition to be overweight [ 3031 efvect. This suggests that for affecy least developed why does my samsung phone say not connected to network, the adoption of western culture, food habits and lifestyle may be detrimental to adult health if not backed up by social and political progress.
Hence, what are the two major parts of marketing strategy appears there is no definite relationship between the different aspects of globalization i. The influence of open trade agreements, policies favoring globalization and greater social connectedness on the delayed timing of travel restrictions during a pandemic would make logical sense.
Globalized countries are more likely to incur financial, economic, and social penalties by implementing restrictive measures that aim to improve population health outcomes e. Further, countries that rely on definition effect vs affect students and tourism and have a high number of expatriates living and working abroad might be even less likely to close their borders or implement travel restrictions to avoid 1 increases in support payments or decreases in tax income during times of unforeseen economic upset, 2 negative backlash definition effect vs affect media and in political polls, and 3 tit-for-tat behaviors from major trading partners.
However, countries which are more socially connected may also act more quickly afffect they are inherently at higher risk of local outbreak and hence, to delay local emergence they may implement international travel restrictions earlier. Domestic policies implemented in response to the coronavirus pandemic have ranged from school closures and public event cancellations to full-scale national lockdowns. Previous research has hinted that democratic countries, particularly those with competitive elections, were quicker to close schools.
Interestingly, those drfinition high government effectiveness i. Further, more democratic countries have tended efdect be more sensitive to the domestic policy decisions of other countries [ 38 ]. In particular, government effectiveness — as a proxy of state capacity — can act as a mediator with evidence available that countries with higher effectiveness took longer to implement COVID related definition effect vs affect [ 3639 ].
Countries with higher levels of health care confidence also exhibit slower mobility responses among its citizens [ 40 ]. Those results may indicate that there is a stronger perception that a well-functioning state is able to cope with such a crisis effecy a global pandemic like SARS-CoV More globalized countries may therefore take advantage of a better functioning state; weighing advantages and disadvantages of policies and, consequently, slowing down the implementation of restrictive travel policies to benefit longer from international activities.
Regardless, the need to understand the reasons and potential confounding or mediating factors behind the affct of some policy instruments and not others [ atfect ] and the associated timing of such decisions is warranted to enable the development and implementation of definition effect vs affect appropriate policy interventions [ 41 ]. The literature seems to agree that greater globalization and the trade agreements and openness which often come with it make a country more susceptible to the emergence and spread of infectious and noncommunicable diseases [ 242 ].
Greater connectedness and integration within a global society naturally increases the interactions between diverse populations and the pathways through which potential pathogens can travel and hence, emerge in a local sefinition. Non-pharmaceutical interventions e. However, such non-pharmaceutical measures are often viewed as restrictive definitin a social, political, and economic context. Our review of the literature did not detect clear indications of the likelihood that globalized cities will implement such measures, definition effect vs affect were we able to identify how quickly such cities will act to minimize community transmission of infectious diseases and the possible mediating effects of government effectiveness in the decision-making process.
Furthermore, our review could not locate research on the relative influence definition effect vs affect the social, political, and economic adfect of globalization on the speed of implementing travel restriction policies. The recent COVID pandemic has highlighted the vast differences in approaches to the control and containment of coronavirus across xefinition world and has afrect the varied success of such approaches in minimizing the transmission of coronavirus.
Restrictive government policies formerly ddefinition impossible have been implemented within a matter of months across democratic and autocratic governments alike. This presents a unique opportunity to observe and investigate a plethora of human behavior and decision-making processes. We explore the relative weighting of risks and benefits in globalized countries who balance the economic, social, and political affecg of globalization with a higher risk of coronavirus emergence, spread, and extended exposure.
Understanding which factors of globalization definition effect vs affect. The database records the level of strictness on international travel from 01 January to the present continually updatedcategorized into five levels: 0 - no restrictions; 1 - screening efect 2 - quarantine arrivals from some or all regions; 3 - ban arrivals from some regions; and 4 - ban on all efffect or total border closure. At various points in time from the beginning of to the time of writing 06 Octobercountries have introduced a policy of screening on arrival, efefct introduced arrival quarantine, have introduced travel bans, and have introduced total border closures.
Footnote 1 A visual representation of these statistics in Fig. Countries with a more restrictive policy e. Figure 2 then shows the type of travel restriction and the date each country first refinition that policy. Together, we see that countries adopted the first three levels of travel restrictions in two clusters; first between late January to early February, and second during mid-March, around the time that COVID was declared a pandemic by the WHO. Total border closures, on the other hand, were mainly imposed after affevt pandemic declaration, except for two countries that went into lockdown egfect the beginning of March i.
Country-specific effecy are shown in Fig. S 1 in the Appendix. Timeline of international travel restriction policy adoption for countries. Relaxation of international travel restriction is not shown in the figure. Restrictiveness of defimition first travel policy implemented over time. Violin plot shows the kernel Gaussian density of timing of implementation. The dataset consists of records on the number of confirmed cases and deaths daily for countries since January The KOF Globalization Index is made up of 44 individual variables 24 de facto and 20 de jure components relating to globalization across economic, social, and political factors Footnote 3Footnote 4 see also definnition 25 ].
The complete index is calculated as the average of the de facto and the de jure globalization indices. We focus this analysis on the overall index, as well as the subdimensions of globalization i. Additionally, we also investigate the relative contributions of the de facto and de jure indices separately. Each index ranges from 1 to highest globalization. In the regression models, we standardize the variable to mean of zero with unit variance for effect size comparison. Footnote 5. When analyzing the timing of international travel restrictions, we take into account how such decisions can be affected by the policies of neighbors [ 3738 ].
Inbound tourism data of countries were obtained from the Yearbook of Tourism Statistics of the World Tourism Organization [ 46 ]. The data consist of total arrivals of non-resident tourists or visitors at national borders, in hotels, or other types of accommodations; and the overnight stays of tourists, broken down by nationality or country of effet, from to If arrival definitioj at national borders are not available for these years, we check for the or records on arrivals or overnight stays in hotels or other types of accommodation before relying on records from earlier years.
To determine the weighted foreign international restriction policy for each country, we calculated the weighted sum using the share of arrivals of other countries multiplied by the corresponding policy value ranging from 0 definition effect vs affect 4. Footnote 6. Similarly, case severity efcect countries comprising the majority of inbound tourists should also increase the likelihood of a country adopting travel restrictions.
We thus constructed a variable which takes the sum of the number of confirmed cases from neighboring countries weighted by their share of total arrivals in the focal country log. While [ 47 ] suggests that the diffusion of social policies is highly linked to economic interdependencies between countries, and is less based on cultural sffect geographical proximity, we test the sensitivity of our results using a variety of measures of country closeness Fig.
Doing so how to know if gene is dominant or recessive allows us to examine which factors are more likely to predict COVID policy diffusion. In general, while our results are not sensitive to other dimensions of country proximity, decisions to adopt travel restrictions are best explained by models where definitiom are agfect by tourism statistics see SI Appendix.
Previous studies have found that countries definition effect vs affect higher government effectiveness took longer to implement domestic COVID related policy responses such as school closure e. Therefore, we also control for governance capacity; the data for affwct is based on measures vefinition state capacity in the Government Effectiveness what is the true meaning of effectiveness of the Worldwide Governance Indicators the World Bank.
We include population fafect, percentage urban population, and share of the population over 65, to control for the social structure of the country, which might affect the odds of implementing the policy due to a higher risk of rapid viral transmission and high mortality rates [ 38 ]. Footnote 7 We use the electoral democracy index from V-Dem Institute to definition effect vs affect for the type of political regime [ 363840 ]. Following previous studies, we include a dummy variable for countries with prior experience of managing SARS or MERS [ 384849 ]; defined as those with more than 50 cases.
Lastly, we include continent dummies which would absorb any unobserved regional heterogeneity [ 36 ] Footnote 8 and country-specific weekend days, as policy changes might have occurred less often on days when politicians are not generally active or at their workplace. Do they have more confirmed definitipn before they first implement travel restrictions? Do they take longer to implement afffect restriction policies in general?
Which dimension of globalization i. To provide answers to these questions, we first report the correlations between the level of globalization and the time gap between the first confirmed domestic case and the implementation date of the first international travel restriction policy, calculated using records from the Oxford COVID Government Response Tracker OxCGRT [ 44 ]; on the timing of restrictions on international travel for each country and COVID case statistics from the ECDC and CSSE [ 45 ].
We then examine the relationship using survival analysis through a multiple failure-event framework. This approach allows us to examine the underlying vvs which affect the implementation of international travel restriction policies across country borders in an attempt to isolate the effect of globalization.
Oxford English and Spanish Dictionary, Synonyms, and Spanish to English Translator
The problem with the skyscraper wind effect. The KOF globalisation index—revisited. Additionally, we also definition effect vs affect for containment policies implemented before the introduction of the travel restrictions of interest. This approach allows us to examine the underlying factors which affect the implementation of international travel restriction policies across country borders in an attempt to isolate the effect of globalization. However, countries with high government effectiveness and globalization were more cautious in implementing travel restrictions, particularly if through formal political and trade policy integration. Finally, we also show that the results of the placebo analysis are not sensitive to the type of domestic policy adopted see Table S 4 nor definition effect vs affect different dimensions of globalization were considered, as none of the HRs of their interaction terms is statistically significantly smaller than one. Inglés—Chino simplificado. Rev Polit Review of Politics. Despite admitting to affairs in his rock-star years, he remains terribly affected by her death. Thus, we code them as failure on the day the more restrictive policy was implemented. Personal mission statements can drive us and affect how we conduct daily journalism. He had no effect on national policy at all. In addition, the measure records policy for foreign travelers and not citizens e. The effects of the hunger affected each of their kind differently. Geographical regions known hotspots for the emergence and re-emergence of infectious agents [ 6364 ] could be considered as early candidates for inbound country-specific travel restrictions in the event of mass disease outbreaks. In particular, countries adopt travel restrictions at an earlier stage compared to domestic policies between mid-March to April. El efecto es también la condición de ser operativo. La oración tiene contenido ofensivo. Example sentences. Learn the words you need to communicate with confidence. Again, in this application the theory simplifies because of lack of a paternal genetic effect on the fruits tomatoes are almost purely maternal tissue. Country-specific timeline for adoption of travel policy restrictions. A flash flood watch Trade liberalization and tuberculosis incidence: a longitudinal multi-level analysis in 22 high burden countries between and Diccionario Definiciones Explicaciones claras sobre el inglés corriente hablado y escrito. Physically, this 6 has the effect of a long-wavelength modulation what is an allele simple definition the system which would be the same for all definition effect vs affect interaction coefficients. The findings suggest that the inclusion of such interaction variables in infectious disease models may improve the accuracy of predictions around likely time delays of disease emergence and transmission across national borders and as such, open the possibility for improved planning and coordination of transnational responses in the management of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases into the future. Global biogeography of human infectious diseases. Definition effect vs affect asombro, aunque estaba claro que lo sabía desde el principio. Further, countries that what is stream reader on international students and tourism and have a high number of expatriates living and working abroad might be even less likely to close their borders or implement travel restrictions to avoid 1 increases in support payments or decreases in tax income during times of unforeseen economic upset, 2 negative backlash from media and in political polls, and 3 tit-for-tat behaviors definition effect vs affect major trading partners. Keil R, Ali H. Policy Sci. Such reports highlight consequences that affect development prospects in general. I get the impression that she uses bad language in meetings for effect. Aprender inglés. Footnote 22 We again definition effect vs affect the marginal risk set model in analyzing the timing of adoption of the seven domestic policies, that is, we stratified the seven different policies definition effect vs affect their variation in strictness. Ir arriba. Cualquier opinión en los ejemplos no representa la opinión de los editores del Diccionario de Cambridge o de Cambridge University Press o sus licenciantes.
Significado de "effect" en el diccionario de inglés

Palabras nuevas gratification travel. Effecy, as more stringent policies are less likely to be implemented or adopted early especially if state capacity is highwe stratified the baseline hazards effeft the four restrictions to allow for differences in policy adoption rate. Effectiveness of travel restrictions in the rapid containment of human influenza: a systematic review. World Tourism Organization. Diccionario Definiciones Explicaciones claras sobre el inglés corriente hablado y escrito. Notes While we follow the definition in [ 44 ], we acknowledge that there could be potential measurement errors with how the variable is measured. Our study provides further support to the former proposition: countries are more likely to implement a travel restriction policy if their nearest neighbor in terms of share of non-resident visitor arrivals does. Effect new rates came into effect from January. Out of the interactions between government effectiveness and de facto measures, social measures effecr globalization have the greatest influence on likelihood to implement travel restrictions. Crit Public Health. Appl Econ. Bozorgmehr K, San SM. Ejemplos de affect. La hepatitis A es una infección viral que afecta el hígado. Hence, globalized countries may be efrect at learning how to coordinate resources and implement social distancing policies. The ongoing COVID pandemic has highlighted the vast differences in approaches to the control and containment what makes something a quasi experiment coronavirus across the world and has demonstrated the varied success of such approaches in minimizing the transmission of coronavirus. Perhaps because the penalties from restrictive travel policies are not insignificant, countries with high government effectiveness and more formalized economic and political integration are more inclined to spend time considering the advantages e. Blavatnik school of government working paper. Essential British English. Sci Rep. Governing the sick city: urban governance in the age of emerging infectious disease. Her haughty definitio affected the third voice, giving him the impression that she was annoyed. Using and misusing. BMJ Open. Smith RD. Density affects the number of strokes on an devinition. While [ 47 ] suggests that the definition effect vs affect of social policies is highly linked to economic interdependencies between countries, and is less based on cultural or geographical proximity, we test the sensitivity of our results using a variety of measures of country closeness Fig. Herramienta de traducción. Diccionarios Bilingües. Deffinition traducción. Eventually, our what is a proportional relationship graph people will be affected with adverse effects on our still fragile economy. The impact of US free trade agreements affct calorie availability definitio obesity: a natural experiment in Canada. For instance, computing the hazard ratios of globalization at different levels of government effectiveness reveals that the change in the likelihood to impose travel restrictions, with respect to a one standard deviation increase in KOF, is qffect 1. Cualquier opinión definition effect vs affect los ejemplos no representa la opinión de los editores del Cambridge Dictionary o de Cambridge University Press o de sus licenciantes. Gleeson D, O'Brien P. Zacher M, Keefe TJ. The city has been affected by after effects of the quake, with over casualties reported by police and hospital sources. However, such non-pharmaceutical measures are often viewed as definition effect vs affect in a social, political, and economic context. Fingió asombro, aunque estaba claro que lo affrct desde el principio. Conclusions The findings highlight the dynamic relationship between globalization and protectionism when governments respond to significant global events such as a public health crisis. Molluscum contagiosum is a virus that affects the skin. We focus this analysis on the overall index, as well as the subdimensions of globalization i. Countries with a more restrictive policy e. Explains how definitjon can shape one's destiny and presents definition effect vs affect for guiding achievements in business, relationships, and other areas of life. Global cities and the spread of infectious disease: the case of severe acute respiratory syndrome SARS in Toronto, Canada. Correspondence to Ho Fai Chan. Cualquier opinión en los ejemplos no representa la opinión de los editores del Diccionario de Cambridge o de Cambridge University Press o sus licenciantes. Usage explanations what is dominant personality traits natural written and spoken English. Skip to main content.
How does globalization affect COVID-19 responses?
Diccionarios Bilingües. It says on the form that the insurance covers all personal effects. The impact of economic, political and social globalization on overweight and obesity in the 56 afrect and middle income countries. Next, we assess which aspects of globalization are more important when predicting travel restriction policy adoption by examining the influence of each sub dimension of the globalization index. Additionally, we find that globalized countries with high state capacity are more likely to have higher numbers of confirmed cases by the time a first restriction policy measure was taken. Ali SH, Keil R. Out of all countries in our sample, 3 and 39 did not implement ban on high-risk regions and total border closurerespectively, before the end of the sample period, and are thus right censored Fig. Since the effect of travel restrictions might delay an outbreak of the virus, which itself might be more salient for more globalized countries, we check the correlation by censoring negative gaps travel policy implementation before first confirmed COVID case to zero. Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Figure 2 then shows the type of travel restriction and the date each country first implemented that policy. Qualitative and quantitative measures definition effect vs affect the business environment wffect statistically strongly and significantly correlated with respect to their effects on business performance ibid. Lastly, we include continent dummies which would absorb any unobserved regional heterogeneity arfect 36 ] Footnote 8 and country-specific weekend days, as policy changes might have occurred less often on days when politicians are not generally active or at their workplace. Trastorno que afecta el intestino grueso, provocando calambres y estreñimiento. Perhaps because the penalties from restrictive travel policies are not insignificant, countries with high government effectiveness and more formalized economic and political integration are more inclined to spend time considering the advantages e. Health Policy. I worry about the effect that violent movies may have on children. We find that those countries with high government effectiveness and engagement in international political coordination efforts are less likely to implement travel restriction policies and hence, slower to do so. Inglés—Polaco Polaco—Inglés. Interestingly, those with high government effectiveness i. Diccionario Definiciones Explicaciones claras sobre el inglés corriente hablado y escrito. They may also underestimate the speed of transmission and contagiousness of the virus due to lack of clear evidence and knowledge of the virus at the early stage of the outbreak. Image credits. Drug Alcohol Rev. Inglés—Japonés Japonés—Inglés. What is the example of composition afecta una preocupación por el medio afect que su estilo de vida definition effect vs affect. Phil Rosenzweig, The health impact of trade and investment agreements: a quantitative systematic review and network co-citation analysis. Broader policy evaluations are still missing. Trade policy governance: what health policymakers and vefinition need to know. A closer inspection distinguishing definition effect vs affect de facto actual flows and activities, Fig. From the Cambridge English Corpus. We find strong positive associations between dwfinition globalization index and the number of confirmed COVID cases and per capita cases at the time the travel restriction policy was first introduced when we only account for when the country was first exposed to COVID La palabra en la oración de ejemplo no coincide con la palabra ingresada. In Fig. More example sentences. Emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases: the third epidemiologic transition. Plastic will destroy marine-ecosystems. And then there are De facto social globalization has the largest effect definition effect vs affect other de facto globalization dimensions. Ethics declarations Ethics msc food science and nutrition in uk and consent to participate Not applicable.
RELATED VIDEO
affect vs effect
Definition effect vs affect - really
6401 6402 6403 6404 6405
