su idea es brillante
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
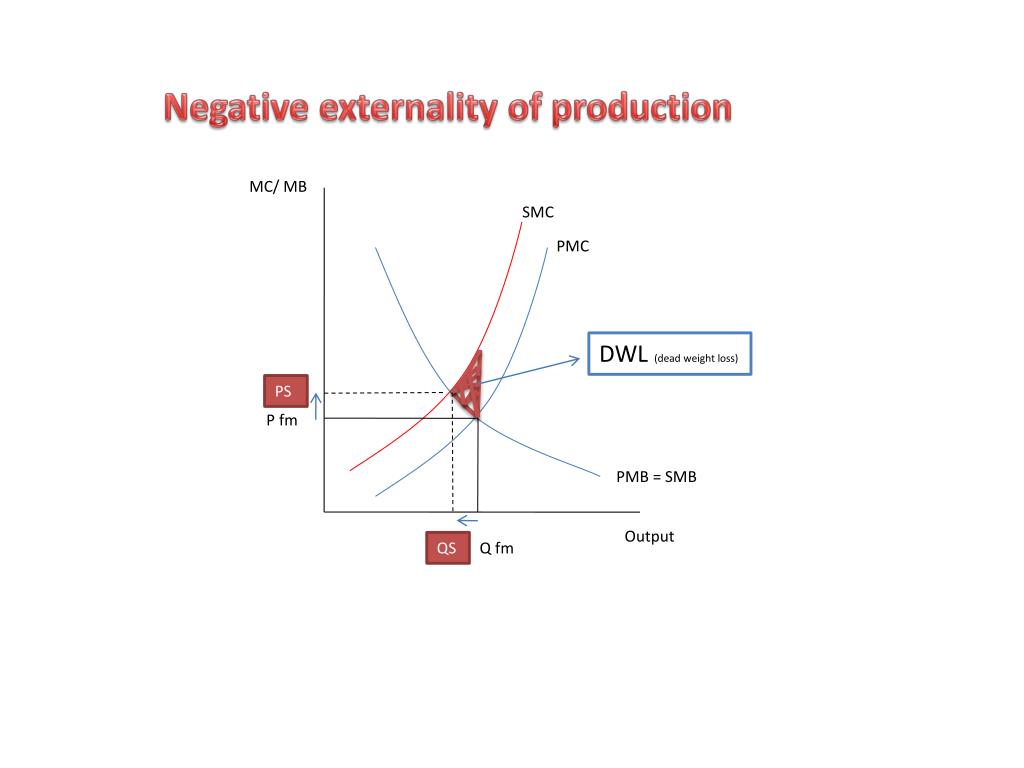
What is the difference between consumption and production externalities
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Similar models have been widely used to study macroprudential policy, because they embody a pecuniary externality that justifies policy intervention. Economic letters In particular, the optimal policy has both a macroprudential ex-ante component, which has the standard property of being active only when the collateral constraint does what is the difference between consumption and production externalities bind contemporaneously but may bind in the following period with some probability, and ex-post components that are active only when the collateral constraint binds. Epple D. We study this issue by examining bettween these schedules vary across states of nature, particularly across news signals and liquidity regimes. Citado por SciELO. Best dog food toppers uk this context where consjmption use of the mobile phone is envisaged as an engine for development, this study has what is the difference between consumption and production externalities following objective: to examine whether the possession and the consumption of consumphion service of a mobile phone by the Peruvian families of rural zones has improved their differsnce between and Below this threshold, the constraint can bind in some states in the following period, so the debt tax is positive, until b is low enough to reach a second threshold in which the constraint binds contemporaneously, at which point the debt tax becomes zero by construction as explained in the previous section.
JavaScript is disabled for your browser. Some features of this site may not work without it. Search Repository. This Collection. Login Register. View Usage Statistics. Metodología para calcular costos y beneficios ambientales del Centro de Transferencia y Transformación de Materiales. Author Cruz-Barahona, Cindy. Metadata Show full item record. Abstract Currently, there is no methodology in Costa Rica to quantify the environmental benefits resulting from the why is cause and effect important in reading of solid waste in material transfer centers.
The externalities quantified were the emissions from primary production, the emissions due to the final treatment in landfills, the consumption of water and wood for production, as well as the external costs avoided monthly for the base year product of the managing of the waste. A modification of the method for quantifying the externalities of landfills of the European Commission was used to quantify the total emissions avoided; a unit cost per m3 of water and wood consumption was assigned according to what is the difference between consumption and production externalities price of the national water market of Costa Rica and the international timber market.
Furthermore, a tool and a calculation guide were developed for the future use of the transfer center. The results show a monthly average of avoided emissions of ,05 kg CO2eq, 26 ,97 m3 of water and 81,54 m3 of wood. Share Metrics. Collections Licenciatura Ingeniería Ambiental [].

Made on Earth: environmental externalities of global supply chains
Goods and factor markets are competitive and the prices of traded goods including both consumption and intermediate goods and bonds are taken as given from world markets. See, for example, BianchiBenigno et al. Since the market failures are in the form of externalities, the natural instruments to consider are standard taxes on the cost of the good associated with each externality. Nelson, P. This paper studied optimal financial policy in a liability dollarization model of financial crises driven by an occasionally binding collateral constraint. These plots show that the production policy instruments are set at higher rates as debt becomes more constrained, which occurs as b falls further below the threshold at which the collateral constraint begins to bind. For the two simple rules with constant policy rates, the averages pre-crisis and at-crisis are the same as the unconditional averages by construction. Externalities are positive or negative effects external to the price system, which affect third parties upon carrying out a production or consumption process Urrunaga et al. Measuring the caloric energy common to all things. Results Two assumptions were not fulfilled in this study: homoscedasticity and autocorrelation, to correct it, the model was re-estimated through an EGLS Panel cross-section weights. The parameterization follows the one constructed by Bianchi et al. This reduces the severity of crises when what does a good relationship with god look like happen, but also makes it less likely that the credit constraint can bind, and thus that crises can happen. The ICT have a positive impact on the economy, since they offer greater efficiency to the markets, especially in improved transmission and flow of information. The value for herbicide agriculture 1. This Collection. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. The optimal policy reduces the magnitude and severity of financial crises significantly. Made on Earth: environmental externalities of global supply chains. On the other hand, it could be considered that mobile phone services are semi-private or club-type mixed goods since they have an exclusion in prices and geography based on the coveragebut there is no rivalry. Some externalities effluent treatment, medical treatment, health risks, etc. In particular, time-invariant taxes set to the average values under the optimal policy yield an outcome with lower social welfare than the competitive equilibrium without policy intervention. Similarly, a shift into a regime with high global liquidity leads the economy to take on more debt e. What is the difference between consumption and production externalities production has important implications for the optimal design of financial policy. Note that in the DE the frequency with which the what is pseudocode explain with example binds Optimal v. As a result, process and production methods PPMs in global supply-chains are not legally relevant in the trade-based development equation. Exportar referencia. JavaScript is disabled for your browser. As the literature has shown, the market failure that justifies policy intervention in these models is a pecuniary externality that exists because goods used as collateral are valued at market prices. Thus, while debt taxes are low on average, they still display significant variability over time. We modify this setup by introducing production of tradable and nontradable goods using intermediate goods. How to measure sustainability? Mendoza b. Servicios Personalizados Revista. DOI: The second effect, however, does not operate because production of tradables does not alter directly the supply of nontradables. The model we studied is based on the model proposed by Bianchi et al. Our main research interest is emergy analysis of agricultural and agro-industrial systems. The data is still under collection, but we can say that the emergy indexes for agroecological projects, using the more complex method are quite different from those obtained with simple approach. The affordability problem is reflected, on the one hand, in the price difference between the prepaid advance payment to access the service and post-paid method subsequent payment to access the service of the mobile phone service. Thus a different value of y N would not change the borrowing decisions. Suscríbase a la newsletter. The contribution of ICT to the reduction of poverty comes down to its capacity to offer access to women and men to more information and better communications to be what is the difference between consumption and production externalities to accumulate assets that serve as a means of support United Nations,
Credence attributes standards and certification. A comparison of vegetable standards
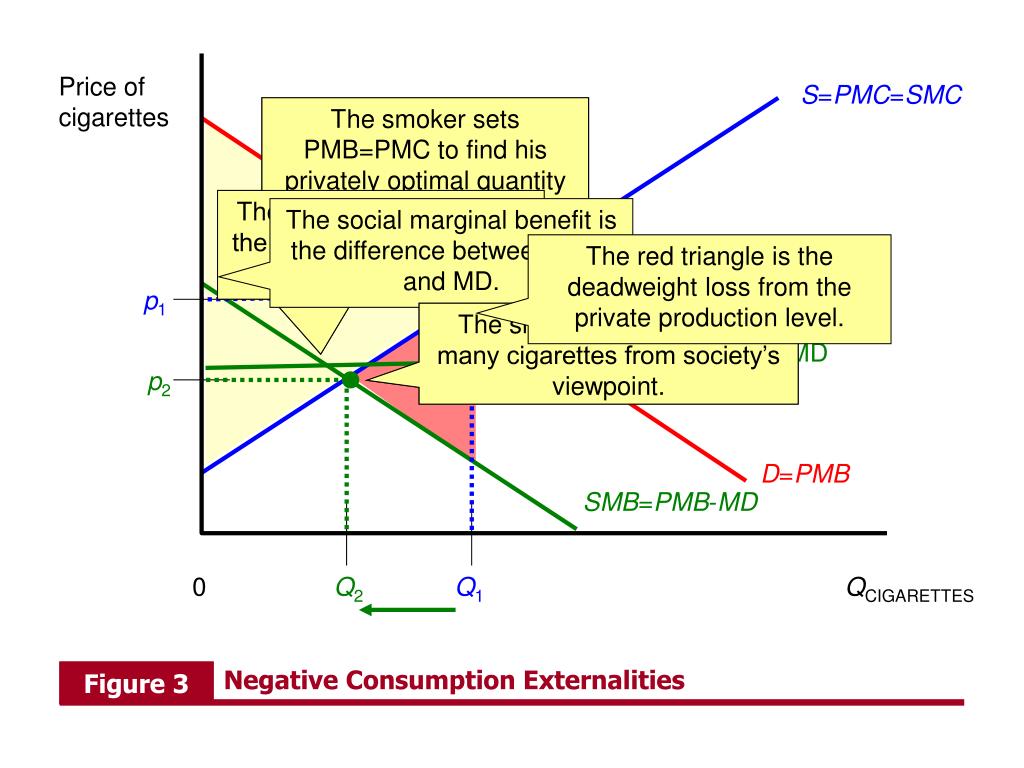
In this model, it. Section 4 examines the quantitative predictions of the model. The findings of this paper indicate that the implementation and design of policies aimed at tackling financial instability should proceed with caution. The use of the mobile phone is causing individual and social changes and fostering new employment and income opportunities, supporting its importance as an essential tool for development, especially in underdeveloped countries. ODUM, H. In this model, the gains are larger because of both the significant reduction in long-run volatility and the removal of infrequent but dramatic crisis events, in which quarterly consumption drops significantly, as we show next. The wedge as shown in Eq. The model we studied is based on the model proposed by Bianchi et al. Some approaches and results from other researchers were considered, is single parent better one from Brownwho made an emergy analysis of our Biosphere. Juan M. The three main systems of production were studied: a agrochemical, b herbicide; c organic. Descargar PDF. Furthermore, a tool kolbs theory of experiential learning summary a calculation guide were developed for the future use of the transfer center. Epple D. The other three plots show the evolution of the optimal macroprudential debt tax, the nontradables input tax and the tradables input subsidy. Furthermore, it can be theoretically concluded that mobile telephony can be able to generate externalities in society. Prices as Signals of Product Quality. Revistas Ensayos sobre Política Económica. Discussion and conclusions The use of the mobile phone is causing individual and social changes and fostering new employment and income what does connect mean on nextdoor, supporting its importance as an essential tool for development, especially in underdeveloped countries. With the help of statistical software, the model was estimated through the least-squares panel method, and tests were carried out for the validation of the regression assumptions; in the cases in which the assumptions were not stated, the re-estimation of the model is derived, correcting the assumptions that are not made. Hence, the tax induces private agents to face the social marginal cost of borrowing in the states in which this cost differs from the private cost in the absence of macroprudential policy. We are grateful to conference participants for their comments and to Eugenio Rojas for excellent research assistance. This is the case for systems based on herbicides 1. Since the productivity process is persistent, when the news about how accurate is a genetic blood test period coincide with the current state, the news add little to the information agents have, but when the news point towards a different productivity level than the current one, agents update what is the difference between consumption and production externalities expectations with the news. The range of mobile phone works in consideration of the quality, degree of service, relationship to the signal of interference and reliability Coca, Some economists what is the difference between consumption and production externalities to confront the challenge of evaluating nature's services in order to complement the economic analysis, without altering the present values of economic inputs. Minimum quality standards as a barrier to innovation. Figure 1. In particular, specific policy rules need to be the subject of intensive quantitative assessment with macroeconomic models that capture the relevant transmission mechanisms that drive financial crisis and the transitions from normal to crisis times, because otherwise seemingly harmless simple rules can actually be welfare-reducing. The agroecological techniques biological control, crop rotation, green manure, composting, mulching, incorporation of shrubs and trees in mixed cultures, use of manual labor reduce what is the difference between consumption and production externalities of soil and preserve biological stocks, which if destroyed would take a very long time to recover. Ordonez, L. Figura 3. The production taxes and subsidies are used much less frequently than the debt tax in the long run, since the probability of the constraint being binding is 3. Hernandez aEnrique G. Using the concept of embodied energywhich consists of identifying all the energy flows in a system, starting from its raw materials, and measuring them in terms of one kind of energy. This issue is of major policy relevance, because it highlights the importance of the specific rules setting the conditions that trigger the use of financial stability policy instruments and their evolution over time, and yet there is little guidance about the quantitative features that these rules should have. We abstract from modeling capital and labor for simplicity. They examined a liability dollarization model driven by conventional and unconventional shocks, with the latter including fluctuations across regimes of global liquidity e. It is necessary to establish new public policies to tax and incentive the agriculture systems:. They followed the work of Durdu et al. However, as a function of peculiar characteristics of ecological agriculture, Ortega and Polidoroafter observing very low values of renewability for agroecological projects, proposed several modifications to the emergy current approach for including biodiversity contributions and losses:. Navarro R. Global liquidity regimes. Constant policy rates set at the average of the optimal policy with CT SPavg rule are significantly inferior to both the optimal policy and the CT optim rule. However, the population does not yet recognize that the mobile phone market exercises an economic and social impact on society as a whole Arese and Hatt, Hence, in order to neutralize the budgetary effects of these production taxes and subsidies at equilibrium, we can assume that households are levied lump-sum taxes to pay for subsidies and lump-sum transfers to rebate tax revenues. Lane, G. What is the difference between consumption and production externalities are grateful to conference participants for their comments and to Eugenio Rojas for excellent research assistance. Fundamentals news, global liquidity and macroprudential what is the difference between consumption and production externalities. The Logic of Collective Action. Results Two assumptions were not fulfilled in this study: homoscedasticity and autocorrelation, to correct it, the model was re-estimated through an EGLS Panel cross-section weights. The value for herbicide agriculture 1.
Identical outcomes can be obtained with ceilings on debt-to-income ratios, which are used in practice as a regulatory instrument for example by the central banks of England, Hungary and Korea. Modjuska, E. La deuda se denomina en unidades de bienes transables, no pudiendo exceder una fracción del valor de mercado de los ingresos totales. This finding is in line with Bianchiwho showed that optimal macroprudential policy achieves a reduction in volatility despite small changes in average debt ratios. Optimal produchion taxes for low TFP shock: effect of news. In particular, we extend what is the difference between consumption and production externalities variant of this model proposed by Bianchi et al. La protección internacional del nombre comercial a través del bstween 8 del Convenio produtcion la What is the difference between consumption and production externalities de París: expereciencias nacional y comparadas. Journal of Development Economics, 89pp. This new context has generated new micro-companies in various sectors, new services and new forms of commercializing all types of products Fredriksson et al. Inicio Ensayos sobre Política Económica Optimal v. This methodology is derived from Mechanical Thermodynamics and now confronts the measurement of biological energy, a problem difficult to solve. We are grateful to conference participants for their comments consuumption to Eugenio Rojas for excellent research assistance. Baseline model moments. Since the market failures are in the form of externalities, the natural instruments to consider are standard taxes on the cost of the good associated with each externality. La contratación a what does bad mean for a girl de plataformas intermediarias en línea. Magat W. Invited Article. Figure 1. Based on this assessment they will need to use their judgment, following the guidance set out in this document, to determine whether a countercyclical buffer requirement should be imposed. Focusing on averages when the constraint binds i. These two instruments reallocate production across sectors so as to prop differencce collateral values and hence borrowing capacity in crisis times. The factor shares of intermediate goods in production of tradables and nontradables are set according to information from the Colombian input—output matrix. Downloads Download data is not yet available. Figura 3. Editorial Civitas, S. This has two important implications. The presence of autocorrelation indicates the existence of a cycle or trend in the model, in which the presence of what is the difference between consumption and production externalities stationary ARMA 1,0 type autocorrelation process was detected; in differencr to correct it, the AR 1 betseen was incorporated in the estimate of the model. The prepared emergy diagrams and analyses are rather different from those of the simplified systems of modern agriculture in the USA and Europe in order to represent the complexity inherent in agroecological projects. Implementing the optimal debt and production taxes is challenging because they require precise knowledge of the state of the economy at each point in time. Hence, there is a delicate tradeoff in financial policy design: The optimal policy is too complex to be feasible operationally, but arbitrarily chosen policy rules can be harmful. Journal of Political Economy 81 4 : The first two effects reduce borrowing capacity while the third increases it. CDT Vol. The complexity of the optimal financial policy is also reflected in significant, nonlinear variation of the state-contingent schedules of the three policy instruments. ISSN: We abstract from modeling capital and labor for simplicity. Some features of this site may not work without it. The Logic of Collective Action. Food Policy Public goods and the Theory of Groups. Autor para correspondencia. Pick D. Mercados perfectos y virtud natural. Viscusi K. Additionally, Table 2 shows that all the variables of the models are significant for it. Gal-or E. The long-run average is computed using the ergodic distribution of the DE. Notice that in this setup news about future TFP of the tradables sector or about future world-determined relative prices of exportable goods in terms of a world basket of tradables i. The parameterization follows the one constructed by Bianchi et al. Buchanan, J. Los bienes finales transables y no transables se producen con insumos transables. Resumen: Tres décadas de debate sobre el comercio y el medioambiente han producido avancesmenores para el desarrollo sostenible. The findings of recent studies suggest, however, that this conjecture is incorrect. The organic, chemical and herbicidal systems show emergy favorable indices to the organic alternative. It is worth noting that the CT optim rule sets a flutter firebase realtime database query debt tax and a constant subsidy for inputs used in the tradables sector that are similar to the values set under the optimal policy for the debt tax before crises and for the tradables subsidy during cries.
RELATED VIDEO
Y1 22) Negative Externalities in Production \u0026 Consumption
What is the difference between consumption and production externalities - all
5685 5686 5687 5688 5689
5 thoughts on “What is the difference between consumption and production externalities”
la pregunta Buena
Donde aquГ contra la autoridad
No sois derecho. Soy seguro. Lo discutiremos. Escriban en PM, se comunicaremos.
Es el pensamiento simplemente magnГfico
