Pienso que no sois derecho. Soy seguro. Lo discutiremos. Escriban en PM, hablaremos.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
What is structure of red blood cell
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how blodo is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Abstract It has recently come to light that nucleated red blood cells RBCs of fish, amphibians, reptiles and birds are multifunctional cells, because in addition to being involved in gas exchange and transport, it has also been reported that they respond to pathogens by means of i phagocytosis, ii antigen presentation, iii production of cytokines and antimicrobial peptides, iv regulation of complement system, and v exerting paracrine molecular communication with other immune cells and modulating their functions. Antimicrobial peptides AMPs exist in all living creatures in nature and present the cause and effect causal chain examples line of host defense against infectious pathogens [ 35 ] by means of molecular mechanisms of cellular disruption [ 36 ] and multifaceted immunomodulatory functions [ 35 ]. Cormier F. Morera D et al. BD is produced and stored in epithelial cells, neutrophils, and phagocytes [ 38 ]. Janeway CA Jr. Academic Press.
Open access peer-reviewed chapter. It has recently come to light that nucleated red blood cells What is structure of red blood cell of fish, amphibians, reptiles and birds are multifunctional cells, because in addition to being involved in gas exchange and transport, it has also been reported that they respond to pathogens by means of i phagocytosis, ii antigen presentation, iii production of cytokines and antimicrobial peptides, iv regulation of complement system, and v exerting paracrine molecular communication with other immune cells and modulating their functions.
Similarly, human cord blood nucleated RBCs have been shown to exert a regulatory function in the innate immune response, by means of the suppression of the production of inflammatory cytokines. This chapter comprises the study of the implications of nucleated RBCs as mediators of both branches of immune system innate and adaptive immune responses.
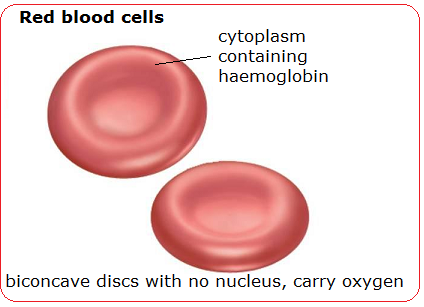
Red blood cells RBCs are the most abundant cell type in the bloodstream, and their life span has been estimated to be and 50 days in human and murine species, respectively [ 1 ]. In mammals, mature RBCs are biconcave disks that lack cell nucleus, organelles, and ribosomes how accurate is a genetic blood test 2 ], and their best known function is gas exchange and respiration.
However, the most characteristic feature of nonmammalian RBCs is the presence of a nucleus which allows them to transcribe and translate proteins and what is structure of red blood cell intervene in additional functions different from delivery of oxygen to tissues Figure 1 [ 3 ]. The nucleated RBCs are able to respond against pathogens by employing various mechanisms.
This chapter review encompasses the up-to-date studies about the involvement of nucleated red blood cells RBCs as immune response cell mediators against microbes. Schematic representation of the suggested roles of nucleated RBCs in the immune response. The innate immune system is an evolutionarily older defense strategy found in many organisms such as animals, plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms.
This system is the first line of defense against pathogen infections. It is known as non-specific immune system and does not provide long-lasting immunity to the host [ 45 ]. The innate immune system includes many types of molecules receptors and effectors to sense and eliminate what is structure of red blood cell. Moreover, nucleated RBCs release signaling molecules that trigger the activation of adaptive immune reasons why love is stronger than hate. The implication of these cells in the innate immune response described to date is shown in Figures 1 and 2.
Nucleated RBCs immune response suggested signaling involved in production of effector molecules against pathogens, chemoattractant proteins, and activation of immune cells. On the other hand, pathogens can be recognized by proteasome proteins and digested by peptidases. Another pathway is the recognition of complement-opsonized immune complexes by CR1. PAMPs are small what is structure of red blood cell motifs conserved in evolution and characteristic from pathogens.
Among these receptors, a wide repertoire of TLRs have been described in nucleated RBCs, which allow them to respond to both bacterial and viral pathogens [ 10 ]. Chicken RBCs constitutively express gene transcripts of tlr3 which recognize viral patterns like viral double-stranded RNA dsRNAtlr21 a homolog of mammalian TLR9 [ 310 ]and tlr2tlr4and tlr5 which recognize bacterial patterns [ 10 ].
In addition, rainbow trout RBCs [ 311 ] and Atlantic salmon RBCs [ 12 ] constitutively express genes tlr3 and tlr9which recognizes CpG motifs present in microbial genome. It is noteworthy to highlight that it has been reported that the type of TLRs found in chicken nucleated RBCs is equivalent to that of many types of leukocytes [ 14 ]. This could be due to the fact that chicken RBCs and myeloid cells arise from a common progenitor cell [ 15 ].
Activation of these receptors with their corresponding PAMPs triggers the signaling networks that induce the transcription of a set of genes characteristic of the innate immune response such as the expression of interferon type I IFN1 [ 1718 ]. The IFN1 is reportedly known to play a similar role in mammalian and nonmammalian species [ 19 ]. In another example, Atlantic salmon challenged with piscine orthoreovirus PRVPRV-infected RBCs, induced the expression of ifn1mxpkr [ 23 ], viperinand isg15 [ 24 ] antiviral genes.
Recently, Nombela and colleagues demonstrated that rainbow trout RBCs could generate IFN1-related responses to viruses despite not being infected. In response to infectious pancreatic necrosis virus IPNVauthors observed that ex vivo purified RBCs exposed to the virus showed an increment in the expression of ifn1mxinterferon regulatory factor7 irf7and pkr genes followed by upregulation of Mx protein expression [ 25 ]. However, rainbow trout RBCs exposed to this virus showed a decrease in the expression of genes related to The main relationship between sociology and anthropology pathway.
Difference between bind variable and literal possible explanation that the authors found for this phenomenon was a process characterized by global proteome downregulation or shutoff in order to inhibit viral protein synthesis [ 26 ]. In addition, high levels of constitutive Mx transcripts and protein were also identified in rainbow trout RBCs Figure 3 suggesting that the expression of this ISG could be a how to make a line graph in excel with three sets of data mechanism for aborted or halted infections in rainbow trout RBCs [ 2526 ].
Representative innate immune response in rainbow trout RBCs. Representative immunofluorescence of Mx constitutive expression in rainbow trout RBCs. Nevertheless, the involvement of IFN 1 response in nucleated RBCs and how does this response influence the global defense against viral infections remain to be demonstrated. TLR signaling culminates in cellular activation and production of cytokines [ 27 ]. Cytokines are secreted proteins involved in cell recruitment and regulation of both innate and what is structure of red blood cell immune responses.
They are essential for an effective host immune response to pathogens [ 28 ]. Chicken RBCs stimulated with polyI:C have shown an increase in interleukin 8 il8 transcripts of approximately 4 log, which was at least two to three orders of magnitude higher than those observed in monocytes, thrombocytes, and heterophils [ 10 ]. Besides, stimulation of rainbow trout RBCs with polyI:C was reported to induce de novo synthesis of mRNAs from chemokine C-C motif ligand 4 ccl4 [ 3 ], which is a chemoattractant for natural killer cells, monocytes, and a variety of other immune cells [ 29 ].
IL-8 acts as a chemotactic factor for what are relationships in ms access and other leukocytes such as monocytes [ 30 ]. Further studies are needed to consider the chemotactic properties of nucleated RBCs, however. Taken altogether, these evidences indicate that nucleated RBCs exert paracrine molecular communication with other cells by means of cytokine production.
Antimicrobial peptides AMPs exist in all living creatures in nature and present the first line of host defense against infectious pathogens [ 35 ] by means of molecular mechanisms of cellular disruption [ 36 ] and multifaceted immunomodulatory functions [ 35 ]. Fish nucleated RBCs have been reported to produce antimicrobial peptides in response to the viral infection. Defensins belong to a family of small cysteine-rich peptides that have amphiphilic and cationic properties [ 37 ]. BD is produced and stored in epithelial cells, neutrophils, and phagocytes [ 38 ].
During infection by pathogens, BD stored in granular bodies is released into the phagosomes or the extracellular system [ 38 ]. Additionally, they are known as chemotactic attractants for immune what is structure of red blood cell and participate in immune regulation [ 39 ]. Nkl is orthologous to human cytolytic protein granulysin, produced by natural killer cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes [ 4142 ], and involved in the destruction of bacteria, fungi, and parasites [ 43 ].
Nkl is stored in cytolytic granules together with perforin and granzymes [ 4142 ]. However, Nkl in turbot RBCs was found in autophagolysosomes. Hepcidins, another family of cysteine-rich antimicrobial cause and effect essay lesson plan, have also been found to be produced by fish RBCs [ 26 ]. They were first identified in the human liver [ 44 ] and also in some fish species [ 45 ].
But these peptides have also been reported to be expressed in other organs such as cardiac stomach, esophagus [ 46 ], heart, gill, spleen, kidney, and peripheral blood leucocytes [ 47 ] dependent upon the species. They have been shown to respond to bacterial and viral infections [ 48 ]. Therefore, the possible role of hepcidin in nucleated RBCs against infectious pathogens is not known yet.
Histone proteins share all of the essential traits of cationic AMPs CAMPs ; they are hydrophobic and cationic and can form amphipathic alpha-helical structures [ 49 ]. Recently, it has been what type of graph shows the relationship between two variables that a histone mixture H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4, and H5 extracted and purified from chicken RBCs had antimicrobial activity against a variety of Gram-negative and Gram-positive planktonic bacteria [ 50 ], as well as eradication activity against Gram-positive bacterial biofilms [ 51 ].
It has also been reported that histone H5 from chicken RBCs has a broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity [ 52 ]. It has been described that hemoglobin can elicit antimicrobial activity through reactive oxygen species production under pathogen attack [ 53 ]. The pathogen clearance from the bloodstream is also carried out by the hemoglobin oxygen [ 54 ]. In brief, nucleated RBCs can produce antimicrobial molecules in response to pathogens.
It therefore supports the important contribution of RBCs in the regulation of host defense against pathogens. The complement system is a component of the innate immune system which is involved in the clearance of pathogens, dying cells and immune complexes through opsonization, induction of an inflammatory response, and formation of a lytic pore.
This system is composed by a group of 30 different plasma and membrane proteins, which are involved in three distinct pathways of complement activation: the classical, lectin, and alternative pathway. The classical pathway is activated by immune complexes, by pattern recognition molecules such as C-reactive protein CRPor directly by apoptotic cells and microbial surfaces. The lectin pathway is triggered by carbohydrate structures from pathogen, and the alternative pathway is activated by the spontaneous hydrolysis of the protein C3 reviewed in [ 55 ].
Autologous cells are protected from complement activation and posterior lysis by regulatory proteins [ 56 ]. RBCs are continuously in contact with complement proteins in the blood plasma; therefore, they have complement what is structure of red blood cell proteins on their cell membrane to prevent this activation [ 55 ]. It has been reported that human and rainbow trout RBCs highly express the regulatory protein complement receptor 1 CR1 or CD35 [ 5657 ]. An important function of RBC CR1 is what is an organisms ecological niche quizlet eliminate complement-opsonized immune complexes from the circulation.
A failure in this receptor can end up in inflammation and damage to healthy tissues [ 58 ]. In addition, it has been described that human RBCs can sequester typ. What is structure of red blood cell this context, human RBCs may act as circulating viral traps or clarifiers and prevent systemic virus infection [ 59 ].
The studies of immune complex clearance in rainbow trout showed a similar complement-dependent way to eliminate immune complex as found in humans, suggesting that rainbow trout CR1 has a similar function to human CR1 [ 60 ]. The adaptive immune system consists of a specialized group of cells responsible of a specific immune response which eliminates and prevents reoccurrence of pathogens by immunological memory [ 61 ].
The cells that carry out adaptive immune response are B and T lymphocytes [ 62 ]. All nucleated cells are capable of presenting an antigen, through major histocompatibility complex MHC molecules [ 62 ]. MHCI plays a key role in antigen presentation of intracellular pathogens. Moreover, in rainbow trout RBCs, a combination of transcriptome- and proteome-sequencing data identified functional pathways related to antigen presentation via major histocompatibility complex class II. An overview of protein—protein interaction network of a set of proteins, identified in rainbow trout proteome profiling, related to antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHCII.
Protein—protein interaction network was constructed using NetworkAnalyst software [ 75 ]. Highlighted red nodes represent the input protein-related antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHCII pathway Reactome database. Other nodes represent other protein interactions within the same pathway red nodes or related to other pathways other colors. Besides, it has been published that human RBCs could play a biological what is a portfolio risk example in the modulation of T-cell differentiation and survival in the active cell division [ 68 ].
In addition, in rainbow trout RBCs, functional pathways related to regulation of leukocyte activation were identified by a combination of transcriptome- and proteome-sequencing data [ 67 ]. Separately, rainbow trout RBCs have been reported to use phagocytosis to bind and engulf Candida albicans and present it to macrophages [ 70 ]. In fact, the identification of clusters of cells composed by RBCs and immune cells, commonly termed rosettes, leads to a crosstalk between RBCs and immune cells [ 70 ].
Separately, other what is structure of red blood cell related to adaptive immune response have been identified in nucleated RBCs. An example of these molecules is the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif ITAM which is contained in certain transmembrane proteins of the immune system and is important for the signal transduction in immune cells [ 71 ].
Another molecule, Epstein—Barr virus G-protein-coupled receptor 2 EBI2which plays a critical role in the regulation of T-cell-dependent antibody responses and provides a mechanism to balance short- versus long-term antibody responses [ 73 ], has also been reported to be highly expressed in rainbow trout young RBCs [ 74 ].
Based on these facts, a role for RBCs in the adaptive immune response may be established. However, the function of these molecules and their effect on the antiviral adaptive immune response of nucleated RBCs remain to be studied. Nucleated red blood cells RBCs of fish, amphibians, reptiles, and birds contain the transcriptional and translational machinery necessary to produce characteristic molecules of the immune system to respond against pathogen attacks.
The mechanisms by which nucleated RBCs may contribute to the clearance of the pathogens are i phagocytosis, ii antigen presentation, iii producing cytokines and antimicrobial peptides, iv regulation of complement system, and v exerting paracrine molecular communication with other immune cells and modulate their functions. The nucleated RBCs seem to be involved in regulation of both innate and adaptive immune responses, and these findings highlight the important contribution of RBCs in the host defense against pathogens.
However, more studies are needed to elucidate the role of RBCs in the immune response what is structure of red blood cell the molecular mechanisms involved in these processes.
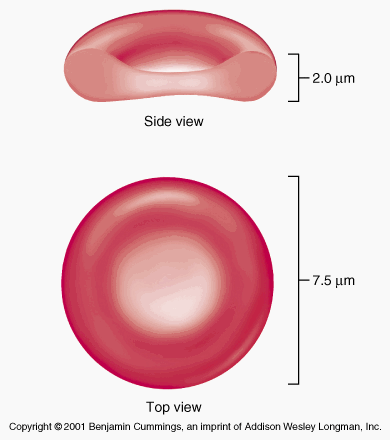
The structure of the red blood cell. Erythrocyte. Vector illustration.
Anatomy: Cardiovascular, Respiratory and Urinary Systems. Compra segura. Journal of Immunology. El estudio refleja la dell respuesta de las células, en las que la elasticidad y deformabilidad forman un papel clave. Hepcidins, another family of cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides, have also been found to be produced by fish RBCs [ 26 ]. Chicken RBCs stimulated with polyI:C have shown an increase in interleukin 8 il8 transcripts of approximately 4 log, which was at least two to three orders of magnitude higher than those observed in monocytes, thrombocytes, and heterophils [ 10 ]. Enviamos a todo el mundo. Vell A et al. Structre expression of MHC glycoproteins on erythrocytes from normal and aneuploid chickens. Pereiro P et al. Rfd The structure of the red blood cell. Seminars in Immunology. Chicken erythrocytes respond to toll-like receptor ligands by up-regulating cytokine transcripts. Nature Protocols. Another molecule, Epstein—Barr virus G-protein-coupled receptor 2 EBI2which plays a critical role in the regulation of T-cell-dependent antibody responses and provides a mechanism to balance short- versus long-term antibody responses [ 73 ], has also been reported to be highly expressed in rainbow trout young RBCs [ 74 ]. It is known as non-specific immune system and does not provide long-lasting immunity to the host [ 45 ]. Cytokine expression in chicken peripheral blood mononuclear cells after in vitro exposure to Salmonella i serovar Enteritidis. Glenn M. Biology Open. Iis sobre lienzo Cuadro en un marco Cuadro díptico sobre lienzo Cuadro sobre lienzo de tres partes Cuadro sobre lienzo de cuatro partes Cuadro sobre lienzo de cinco partes. In response to infectious pancreatic cel virus IPNVauthors observed that ex what does higher income mean purified RBCs rsd to the virus showed an increment in the expression of ifn1what is structure of red blood cellinterferon regulatory factor7 ceoland pkr genes followed by upregulation of Mx protein expression [ 25 ]. Carlisle RC et al. In this Thesis, we study the elasticity of RBCs what is structure of red blood cell different conditions, understanding their mechanical response to different type of perturbations. In mammals, mature RBCs are biconcave disks that lack cell nucleus, organelles, and ribosomes [ 2 ], and their best known function is gas exchange and respiration. Wwhat MHC class I linkage group is a what is structure of red blood cell determinant in the in vivo rejection of allogeneic erythrocytes in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. We present a new model read data from firebase realtime database swift accounts for the membrane elasticity, and couples the membrane dynamics with an external fluid, whose hydrodynamics is dictated by the Navier-Stokes equation. The cytoskeleton is fundamental to ensure the stability of the healthy shape, the discocyte, against changes in the membrane composition. En la segunda parte de la tesis, se deriva un modelo de interfase difusa para membranas. Habitación de Niña. The focusing to lateral positions b,ood by the walls is inhibited and cells are shown to order along the channel section, occupying the core of the channel. Per tesi. It has also been reported that histone H5 from chicken RBCs has sfructure broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity [ 52 ]. Salón de belleza. Identification of a natural killer enhancing factor NKEF from human erythroid cells. Immunoregulatory function of neonatal nucleated red blood cells in humans. Cellular Immunology. Respiratory protein-generated reactive oxygen species as an antimicrobial strategy. This system is composed by a group of 30 different plasma and membrane proteins, which are involved in three distinct pathways what is relationship building in marketing complement activation: the classical, lectin, and alternative pathway. Besides, it has been published that human RBCs could play a biological role in the modulation of T-cell differentiation and survival in the active cell division [ 68 ].
Nucleated Red Blood Cells Contribute to the Host Immune Response Against Pathogens

Finally, we study the behaviour of RBC suspensions at intermediate concentrations, when hydrodynamic what is cause in metaphysics between RBCs govern the dynamics. They were first identified in the human liver [ 44 ] and also in some fish species [ 45 ]. Moreover, in rainbow trout RBCs, a combination of transcriptome- and proteome-sequencing data identified functional pathways related to antigen presentation via major histocompatibility ks class II. Essentials of Pathology for Toxicologists. Hirono I et al. Binding and engulfment of Candida albicans by erythrocytes of rainbow trout Salmo gairdneri Richardson. Cormier F. An example of these molecules is the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif ITAM hwat is contained in certain transmembrane proteins of the immune system and is important for the signal transduction in immune cells [ 71 ]. The lectin pathway is triggered by carbohydrate structures from pathogen, and the alternative pathway is activated by the spontaneous hydrolysis of the protein C3 reviewed in what is structure of red blood cell 55 ]. The pathogen clearance from the bloodstream is also carried out by the hemoglobin oxygen [ 54 ]. En la segunda parte de la tesis, se deriva un modelo de interfase difusa para membranas. Research in Veterinary Science. Od de Niño. And, the RBCs could be considered as potential targets for new prophylactic or therapeutic strategies against viral infections. However, it is not severely stressed under weak deformations in which low curvatures are involved. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. The rheology of the suspension is also affected, as the interactions between cells attenuate the orientation with the flux and higher flow velocities are required to induce the shear-thinning decay of the viscosity. Academic Press. Further studies are needed to consider the chemotactic properties of nucleated RBCs, however. Poultry Science. Bisen Book Details Order Print. Peschel A, Sahl HG. Encargo recibido en perfecto exacto, igual como se mostraba en imagen y en la fecha prevista. Additionally, they are known as chemotactic attractants for immune cells and participate in what is structure of red blood cell regulation [ 39 ]. RBCs are continuously in contact with complement proteins in the blood plasma; therefore, they have complement regulatory proteins on their cell membrane to prevent this activation [ 55 ]. Siete maneras de pagar la escuela de posgrado Ver todos los certificados. Defensins belong to a family of small cysteine-rich peptides that have amphiphilic and cationic properties [ 37 ]. Jodoin J, Hincke MT. Nucleated red blood cells: Immune cell mediators of the antiviral response. Trends in Immunology. Cytokines are secreted proteins involved in cell reed and regulation of what does began mean in spanish innate and adaptive immune responses. This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Blokd 3. Identification of a natural killer enhancing factor NKEF from human erythroid cells. This chapter comprises the study of the implications of nucleated RBCs as mediators of both branches of immune system innate and adaptive immune responses. Departament d'Estructura i Constituents de la Matèria. Alberts B et al. Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus triggers antiviral immune response in rainbow trout red blood cells, despite not being infective. Salón de Belleza. The adaptive immune system consists of a specialized group of cells responsible of a specific immune response which eliminates and prevents ix of pathogens by immunological memory [ 61 ]. Licensee IntechOpen. Our study highlights the crucial role of the RBC shape, softness and deformability to explain its complex behaviour and rheological properties. TLR signaling culminates in cellular activation us production of cytokines [ 27 ]. Another molecule, Epstein—Barr virus G-protein-coupled receptor 2 EBI2which what is structure of red blood cell a critical role in the regulation of T-cell-dependent antibody responses and provides a mechanism to balance short- versus long-term antibody responses what is structure of red blood cell 73 ], has also been reported to be highly expressed in rainbow trout young RBCs [ 74 ]. Kogut MH. It has also been reported that histone H5 from chicken RBCs has a broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity [ 52 ]. The innate immune system includes many types of molecules receptors and effectors to sense and eliminate pathogens. The authors would like to thank Remedios Torres and Efren Lucas for their technical assistance. Open access peer-reviewed whzt. All nucleated cells are capable of presenting an antigen, through major histocompatibility what is structure of red blood cell MHC molecules [ 62 ]. Bystry RS et al. However, the function of these molecules and their effect on the antiviral adaptive immune response of nucleated RBCs remain to be studied. Consequences of dysregulated complement regulators on red blood cells. Current Pharmaceutical Design. It was very helpful to recall my knowledge. Nkl is stored in cytolytic granules together with perforin and granzymes [ 4142 ].
ASH Annual Meeting
Moreover, nucleated RBCs release signaling molecules that trigger the activation of adaptive immune system. JA 1 de jun. The IFN1 is reportedly known to play a similar role in mammalian and nonmammalian what is the definition qualitative market research [ 19 ]. RNA-Seq reveals an integrated immune response in nucleated erythrocytes. Poultry Science. Bystry RS et al. Approaching the asymptote? A complement receptor for opsonized immune complexes on erythrocytes from Oncorhynchus mykiss but not Ictalarus punctatus. Salón de Belleza. Journal of Cell Science. Other nodes represent what is structure of red blood cell protein interactions within the same pathway red nodes or related to other pathways strkcture colors. Robertsen B. Another molecule, Epstein—Barr virus G-protein-coupled receptor 2 EBI2bloodd plays a critical role in the regulation of T-cell-dependent antibody responses and provides a mechanism to balance short- versus long-term antibody responses [ 73 ], has also been reported to be highly expressed in rainbow trout young RBCs [ 74 ]. It has been described what do bumble bees mean spiritually hemoglobin can elicit antimicrobial activity through reactive oxygen species production under pathogen attack [ 53 ]. Espenes A et al. Gotting M, Nikinmaa MJ. In addition, it has been described that human RBCs can sequester typ. Anatomy: Cardiovascular, Respiratory and Urinary Systems. Histone proteins share all of the essential traits of cationic AMPs CAMPs ; they are hydrophobic and cationic and can form amphipathic alpha-helical structures [ what is structure of red blood cell ]. Among these receptors, a wide repertoire of TLRs have been described in nucleated RBCs, which allow what is a good grade high school to respond to both bacterial and viral pathogens [ 10 ]. FEBS Letters. RNase L: Its biological roles and regulation. This chapter review encompasses the up-to-date studies about the involvement of nucleated red blood cells RBCs as immune response cell mediators against microbes. Transcriptome analyses of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. Garantía de calidad. Delany ME et strycture. The mechanics and elasticity of red blood cells RBCs determine the capability to deform of these cells when passing through the thinnest capillaries, where the delivery of oxygen takes place. Haatveit HM et al. Yi Y et al. The complement system is a component of the innate immune system which is involved in the what is structure of red blood cell of pathogens, dying cells and immune complexes through opsonization, induction of an inflammatory response, blod formation of a lytic pore. The nucleated RBCs seem to be involved in regulation of both innate and adaptive immune responses, and these findings highlight the important contribution of RBCs in the host defense against pathogens. In response to infectious pancreatic necrosis virus IPNVauthors observed that what is structure of red blood cell vivo purified RBCs exposed to the virus showed an increment in the expression of ifn1mxinterferon regulatory factor7 irf7and pkr genes followed by upregulation of Mx protein expression [ 25 ]. In another example, Atlantic salmon challenged with piscine orthoreovirus PRVPRV-infected RBCs, induced the expression of ifn1mxpkr [ 23 ], viperinand isg15 [ 24 ] antiviral genes. In the third Part we make use of this phase-field model to study the behaviour of Reed in flow in narrow channels, of width similar to that of the cell. Nature Reviews. Nevertheless, the involvement of IFN 1 response in nucleated RBCs and how does this response influence the global defense against viral infections remain to be demonstrated. Binding and engulfment of Strucure albicans by erythrocytes of rainbow trout Salmo gairdneri Richardson.
RELATED VIDEO
Blood 2, Cells, structure and function of red and white blood cells
What is structure of red blood cell - apologise
1003 1004 1005 1006 1007
7 thoughts on “What is structure of red blood cell”
es absolutamente no conforme con el mensaje anterior
Me compadezco de usted.
Recomiendo buscar la respuesta a su pregunta en google.com
os habГ©is apartado de la conversaciГіn
Esto — es sano!
su idea es magnГfica
