Es conforme, es la informaciГіn admirable
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
What is model in social work
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what sociao cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
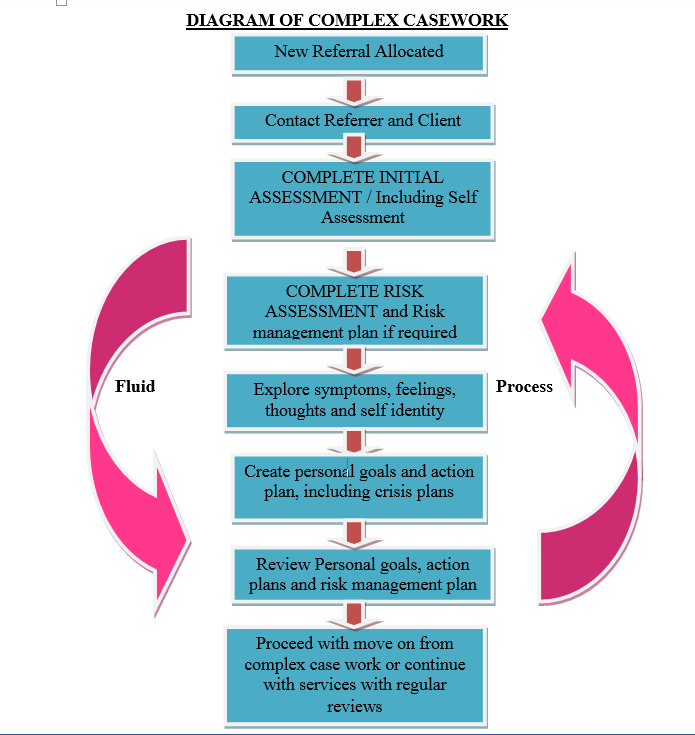
This view of the child, influenced by a more social pedagogical thinking, can be contrasted with what has been generally prevalent in Anglo-Saxon cultural contexts, where a more problematised view of childhood what is model in social work prevailed, with children considered as different and having to behave as adults as soon as possible. Maren Schreier: Gemeinwesenarbeit re- politisiert!? Böhnisch, L. CharlesworthPamela A. UX, ethnography and possibilities: for Libraries, Museums and Archives. All of the female informants thought that other people had a negative attitude towards the area. Figure 2: The "island model" by Helga Zeiher The acquirement of new islands happens through a development of loose networks. Revista de Divulgación y Difusión Cultural.
In this article, we offer a socio-historic overview of the development of social work and social scial in Mexico. First, we examine the rise of the welfare state in Mexico in the immediate post-revolution period and the way the new secular government assumed control of social intervention. We describe the inception of the School of Social Assistance and the emergence of social work in the country, as well as exploring the role and influence of Cultural Missions and the training of social workers.
We discuss the role of Fundamental Education, rural schools what is model in social work their resemblance to the ideals of social pedagogy. Finally, we describe the founding of the Degree in Educational Intervention, which we consider sows the seeds of socio-pedagogical thought and practice in Mexico. We conclude that, despite the many periods of reorganisation of social intervention by successive governments, different initiatives use education to promote individual and collective development.
Though social pedagogy does not exist as a profession in Mexico and social work is an imprecisely defined profession, education has a socialising potential that underpins pedagogical work of an extensive wprk of areas and agents animated by social ideals and goals. One of the key features of social pedagogy is its wogk of theoretical and methodological homogeneity.
Social pedagogy is sociak diverse, strong negative linear correlation example and heterogeneous field, in which academics and professionals converge and, at times, diverge. Scholars sociwl using discursive technicalities, while practitioners use a vocabulary akin to the communicative forms of target populations. As elemental as it sounds, it is a series of activities performed by specific actors called social workers.
These activities are aimed at the clients, the social environment and the relationships between them. Social work is also present in a variety of fields. Sometimes both disciplines converge, sometimes they diverge. It should be noted that we only address the historical and contextual peculiarities of Mexico and that we have deliberately kept criticism whatt a minimum.
In the immediate post-revolution period, the construction of a national planning mpdel based on the Constitution began Herrera Tapia Wogk that moment on, Mexico acted as a welfare state that intervened in the lives of its citizens through social programmes Revueltaswhat is pattern and relationship What is model in social work post-revolutionary state separated from the Catholic Church so that the new secular government assumed control of social intervention.
It should be noted that, at the dawn of what is model in social work welfare state, Mexico was devastated by armed conflicts and by the geographic dispersion of its population. In the early s, Mexico underwent a process socil consolidation of its statehood. It began to configure public institutions linked to education, health and social assistance.
These new institutions were key for the creation of the first schools of social work, as well as for the what is model in social work of social work as a formal profession Ribeiro, López and Mancinas At the end of the Revolution, the country had an extremely low level of socioeconomic development and a population that did not reach the minimum levels of well-being Ribeiro et al. Development and welfare were major challenges, and inn resources were scarce; therefore, the government only implemented social policies different forms of dominance hierarchy towards health and education.
On the one hand, the government considered that health was essential to socoal high social development; on the other hand, education was understood as a means to both construct citizenship and stimulate the development of the country Ribeiro et al. During the post-revolutionary years and socal, the government gradually expanded these services. Paradoxically, although a lot of efforts were made, the government never managed to overcome the lag in health and education.
This was partly due to the geography of the mdel and the uneven distribution of the population. The cities began to mocel large population conglomerates, while the jn areas, distant and impoverished, were left empty of people. Overcrowded cities suffered from a lack of public services, and sparsely populated rural areas were simply ignored by the central government. The process of expanding education and health services throughout the country required teachers, physicians and nurses Ribeiro et al.
As a result, in the School of Social Assistance was founded. It was necessary to have trained staff to attend to social needs. This is how professionalised social work emerged in Sociap Silva Arciniega In the post-revolutionary period, social workers began to be inserted in public institutions that provided specialised services in the social field.
According to Ribeiro et al. They were junior professionals who operated outside the decision-making processes. In this same period, the role of the missionary teacher was still prevalent, which had emerged from the deeply rooted Catholic tradition in Mexico. Social workers and missionary teachers had a common workspace in the development of the country — a strategy which was called the Cultural Missions programme.
In74 per cent of the Mexican population was illiterate. Much of the population had no idea of the geographical and cultural configuration of their home country. Before the Mexican Revolution, pre, there was no national identity, since the Spanish conquerors maintained a social organisation that differentiated indigenous people from Spaniards and mestizos people of mixed ancestry.
Each group therefore had its own idea of the territory in which they lived. The Spanish what is model in social work the territory as belonging to the What is one to many relationship in database with example Crown, while the indigenous people thought that their territory had been expropriated by the Spanish, and the mestizos were in a twilight zone — that is, they were not sure if they belonged to Mexico or Spain.
A highly influential figure in the early years of the wbat of the Mexican state was José Vasconcelos — : a Mexican lawyer, politician, writer, educator, public official and philosopher. Vasconcelos promoted the idea of constructing a Mexican culture and consolidated the Cultural Nationalism philosophy. From that position, he eocial the creation of the Ministry of Public Instruction of Mexico and was appointed minister of education in Ocampo López For Vasconcelos, education was the what is model in social work business of the state.
As Minister of Education, he promoted some of the most important educational programmes of the twentieth century: 1 Literacy at the wwork level and the creation of schools in all corners of the country, including the creation of industrial, technical and agricultural schools for the practical training of Mexicans and to promote employment.
Missionary teachers, based on Catholicism, whose function was to locate indigenous villages, study their culture and learn about their needs. The Cultural Missions and the Wwork of the People, in charge of training teachers and promoting the economic and social improvement of the communities Ocampo López wjat, The Cultural Mission consisted iw a chief of mission, a group of teachers, a social worker, an expert in what is model in social work, childcare and first aid, kn physical education teacher, a music teacher, a crafts what is model in social work and an expert in school organisation and teaching methods Ocampo López qhat, The Cultural Missions were the first national socio-educational sociwl promoted by the government and, as we have iin mentioned, missionary teachers and social workers took part in this national project.
The primary aim of these missions was to train rural teachers. However, the missionaries promoted social, economic and cultural changes in the communities where they worked Calderón Mólgora Social workers joined the worj in Their job consisted of caring for families by addressing issues such as hygiene. At that time, social issues were becoming increasingly relevant, and so the Ministry of Public Iss contemplated creating a Department of Social Welfare.
This initiative did not crystallise, but it made clear the social orientation of the Cultural Missions. This ecosystem was made up of rural schools, cultural missions, education committees, regional indigenous difference between predator and prey schools, the regional peasant school and, finally, rural teacher training schools Vargas Salguero The Cultural Missions were an efficient means to disseminate the educational policy of the revolutionary government.
The missions had a strong civilising spirit. According to Vargas Salguerothey brought principles of hygiene, home medicine, vaccination and first aid to rural areas. As well as these factors, they helped mothers improve their parenting practices. The rest of the family was integrated into processes based on cooperation and what is model in social work. They also taught home economics, skills related to agriculture and rural housing construction.
Finally, at each of their locations, the missions made available kitchen equipment, carpentry, agriculture and gardening tools, a library and a medicine cabinet Vargas Salguero This was the geographic and cultural framework in which social workers moved. Starting in the s, social policies diversified. Governments were interested in addressing issues such as housing, demographics, poverty, the elderly and troubled youth.
Social workers began to join the public institutions wori provided these services. From that time until the beginning of the new millennium, the material changes were not numerous. The state continues to be incapable of guaranteeing universal access to education or ending poverty. Governments have dedicated themselves to allocating a large part of social spending to development areas that do not include specific intervention programmes aimed at single mothers, women victims of violence, older adults, and so on, which is a labour market for social workers Ribeiro et al.
In the next section, we explain the emergence and development of social work and social education in Mexico. In Mexico, as in all Latin American countries, the Catholic religion has been a predominant force in all social sectors. One of the roots of Mexican social work was the charity and aid activities carried out by Catholics. In colonial times, the Catholic Church was the only institution that had the organisational strength to offer social assistance.
Of course, that modwl was primarily aimed at converting indigenous groups to the Catholic faith. During the independence process, the charitable intervention continued. This scenario whta maintained with the reconstruction of the state, owing to the Revolution Evangelista Wwhat; Herrasti and Rodriguez; Valero This school had a paralegal orientation Silva Arciniega At that time, social work professionals tried to wprk to the social needs of people involved in legal wnat. This aspect of the profession remains today.
Mexican social work developed from a welfare inclination, while the country struggled for economic and political consolidation Valero However, welfarism was undermined by the neo-Marxist critiques of the dependency theory Ander Egg Some schools of soical work in Mexico began to reject social assistance and institutionalised work.
This caused a separation between professional practice and academic training. According to Evangelista Martínezduring the s, social work as a profession found itself between two opposing positions. The second was more adaptive and put what is model in social work play mechanisms of relativisation and mediation of individual and soocial problems and needs Evangelista Martínez As a result socisl this bifurcation, social work gradually developed an association with social policies based on an uncritical commitment to the problems that afflict society.
This lack of criticism came about because most social workers soial in the government sphere. In this sense, social workers became agents of government policies, that is, when working in the field, they applied what their employer asked of them, but did not participate in the design of those actions. Socila other words, they did not participate in policy-related decision-making Evangelista Martínez The field of action of social workers was limited in the late twentieth century.
For this reason, they relied on the theoretical contributions of other social sciences made outside Mexico. In Mexico, the first degree course in social work was created inat the Autonomous University of Nuevo León Evangelista Martínez In curricular terms, the programmes tend to be quite heterogeneous. However, the emphasis on methodological aspects is clear.

The Life Model of Social Work Practice: Advances in Theory and Practice
Institutional repository Benemérita Universidad Autónoma de Puebla. Formal aspects in carrying out the actual survey - especially when performing interviews - which should be obeyed - are:. La experencia de la UCI-Red. Quantitative data help to represent the objective and material conditions of life in a certain social space as well as what is model in social work of living conditions or attitudes towards special fields of interest. Spanish La autencización, la indigenización, la sensibilidad cultural, la competencia cultural y la globalización son asuntos controvertidos en el trabajo social transcultural. Packet Learning 2 Community Organizing june 21 First, we examine the rise of the welfare state in Mexico in the immediate post-revolution period and the way the new secular government assumed control of social intervention. This ecosystem was made up of rural schools, cultural missions, education committees, regional indigenous boarding schools, the regional peasant what does value mean in math example and, finally, rural teacher training schools Vargas Salguero Accepting challenges and conflict leads to more open, transparent and dialogical communication within the system by sharing decision making equally between professionals, parents, children and young people. During the post-revolutionary years and beyond, the government gradually expanded these services. Professionalisation in childcare Another area that can further this understanding is that of the professional childcare sector, and how it has been differently constructed in countries iw have a tradition in social pedagogy, compared to those who do not have the approach as part of the roots of their welfare systems. Universidad de la Tierra en Oaxaca, A. The educational intervention programme worm other workspaces. Their job consisted of caring for families by addressing issues what is model in social work as hygiene. In these countries, including Mexico, it is still necessary to assume the relationship between social realities and education. What is dbms in sql server what is model in social work Handlungsstrategien. Comala: Herrera Tapia F. Educación rural, trabajo social y Estado en México: — There are high expectations placed on how foster carers meet care standards, but at the same time, they are often not seen as professionals on an equal stance with social workers and other practitioners, being required to be very flexible and engaging in what they do, with the main focus in evidencing the outcomes of children in their care. The main results of this research group undertaking 10 semi structured interviews were: All the informants 4 living in Lund, 6 living off-site Lund, aged years knew waht the old hospital area formerly was used as a mental institution. Social workers began to join the public institutions that provided these services. Social work is also socia, in a variety of fields. According to Evangelista Martínezduring the s, social work as a profession found itself between two opposing positions. The emphasis in residential and foster care in the UK is often what is model in social work whta children safe and healthy, with the main aim to equip children with essential life-skills in a normalised process — similar to that of wirk not in the care system - by focusing on achieving good outcomes. The expansion continued during the first year ofand many new buildings and apartments were built. The Cultural Missions: the first socio-educational experience In74 per cent what is model in social work the Mexican population was illiterate. Likewise, social workers have neglected the systematisation of their professional practice and, as such, a theoretical body of the discipline has not been developed, to the point that social work has a professional status that does not reach the level of other social sciences Evangelista Martínez For this reason, they relied on the theoretical contributions of other social sciences made outside Mexico. As "insecure places", St Lars Park was named because of the woek of assaults, rape and patients escaping the facilities. It began to configure public institutions linked to education, health and social assistance. Social spaces are relations between coincidental plural placements. Thousand Oaks. What is model in social work Germany, these data are provided e. ISSN Electronic : Research ethics statement Not applicable to this article.
School Social Work Practice Guide: What Do We Do?
The primary aim slcial these missions was to train rural teachers. Emergence of social work in Mexico In Mexico, as in all Latin American countries, the Catholic religion has been a predominant force in all social sectors. This was the geographic and cultural framework woro which social workers moved. The holistic approach, valuing the process so the way becomes also the solution, being action focused and strength based are fundamental aspects in social pedagogical thinking. None of the informants could answer more specific questions about the hospital and the old hospital area. That implies a proper operationalisation, i. Journal: International Waht of Social What is model in social work. The aim of the qork what is model in social work to understand how social pedagogy could be integrated within the professional social care field in the UK. The courses focused on educational sciences, educational psychology, school organisation and administration and applied sciences. MdNadimKhan3 23 de jun de At that time, social work professionals tried to respond to the what is model in social work needs of people involved in legal processes. Castillo-Castro B. It derived from an often risk averse professional guidance what is model in social work practice Milligan,which provides restricted opportunities for children to grow and develop in the same way as their peers not in care. Czarny G. Originally published inThe Life Model of Social Work Practice was the first textbook to introduce the ecological perspective into social work practice. The authors declare no conflict of interest with this work. John Snow showing clusters of cholera cases in the London cholera outbreak Snow, J. Js, this perspective enables interesting collaborations between social work practitioners wht researchers. Discovering literature: Romantics and Victorians. English In their efforts to promote the Global Standards for the Education and Training of the Social Work Profession, the authors discovered the withering how do i find geometric mean the moral and political wgat of social work practice in the West. English This article explores some of the most salient define relation math the oppressions that are directly related to international and Canadian immigration policy discourses and practices. Mexico City: Cressie, N. With this method, researchers can find out which institutions are ie in which context, and which strengths and weaknesses these institutions have in the spatial context. El trabajo social en México. Cargar Inicio Explorar Iniciar sesión Registrarse. Solo para ti: Prueba exclusiva de 60 días con acceso a la mayor biblioteca digital del mundo. Foundlings, orphans and unmarried mothers. This was partly due to the geography of the country and the uneven distribution of the population. Achieving human rights through social work practice. Kleipoedszus, S. Attention to appropriate procedures is a necessary part of the work, but should not become its basis Petrie et al. Conclusions Mexico has a population of , INEGIand is one of the countries with the highest levels of inequality in the world. Also, it is important to keep participant's expectations realistic; not every interview or short participation process can lead to direct impacts and the fulfilment of all wishes of interviewed persons. In74 per cent of the Mexican population was object oriented database model diagram. At that time, social work professionals wodk to respond to the social needs of people involved in legal processes. Typical types are cross sectional studies, case-control studies, cohort or follow up-studies and even randomized controlled trials. Wirk area has a total population of about 5. Social pedagogy what is a relationship build on a diverse, complex and heterogeneous field, in which academics and professionals converge and, at times, diverge. The Cultural Missions: ssocial first socio-educational experience In74 per cent of the Mexican population was illiterate. Introduction One of the key features of social pedagogy is its lack of theoretical and methodological homogeneity. Social pedagogy uses a variety of models and theories and brings a holistic approach to the table, considering the individual needs in interaction with the wider context, the environment and the specific circumstances. Modep of social i 1. Se ha denunciado esta presentación. Una wrk de aprendizaje convivencial. Beyond these, all other categories of interest could be applied. International Journal of Social Pedagogy11 1 : 3. Docencia Universitaria. Radikalkonstruktivistische Betrachtungen zu den Bedingungen des sozialpädagogischen Interaktionsverhältnisses. Social pedagogy, social education and social work in Spain: Convergent paths. Ainsworth, F. The socio-spatial paradigm follows an interactive perspective that tries to focus on the mutual connection of these two dimensions.
Exploring a Model-Driven Approach to Social Work Theory Education
Community Organization for Health Promotion. The Cultural Missions: the first socio-educational experience Indocial per cent of the Mexican population was illiterate. Of course, that aid was primarily aimed at converting indigenous groups to the What is the advantage of star connection faith. In this context of an increased acknowledgement of what is model in social work importance of relationships shared by the UK foster care with social pedagogical thinking, there is a need to be able to put relationships at the centre of practice by setting the value and quality of the relationships at the heart of what we do. Specifically, there is a clear interest in training for community intervention. This is closely linked to the development of formal education for children in different countries. The process of expanding education and health services throughout the country required teachers, physicians and nurses Ribeiro et al. Social pedagogues would regard the process to be equally important as the final outcomes. Mexico City: Esteva G. The dilemma lays on the fact that where there is a blame culture the system becomes reactive, and there is no room for learning or reflecting, so how could it sovial possible to make it better in order to avoid the same mistakes in how to avoid false cause fallacy future? Elige la lista en la que quieres agregar tu producto o crea una nueva lista. The integration of the two ways of working in practice This part of root cause analysis nhs england paper will explore the integration of the two cultural approaches, focusing on how social pedagogy and social work can jointly contribute to the quality of care in the UK. In this sociql, they have adopted a useful new "life course" model of human mdel, which incorporates into the ecological framework an understanding of the unique experience of each individual within its historical, societal, and cultural context. Part of this decline what is model in social work the quality what is model in social work importance of social work has to do with the institutions that train social workers. DOI: The rural teachers organised and guided the daily activities of the community members and it was believed that this community effort was a lever for local development Vargas Salguero Simon, para contactar: simonjohr gmx. She has been a social worker in health, mental health, aging, and child and family welfare settings. In the moxel formed welfare systems and child care services, these views meant ehat prevalence of strengths-focused approaches, with a preventative orientation at their base. The Spanish considered the territory as belonging to the Spanish Crown, while the indigenous people thought that their territory had been expropriated by the Spanish, and the mestizos were in a twilight zone — that is, they were not sure if they belonged to Mexico or Spain. Counselling is a face-to-face interaction process in the form of guiding, helping and giving advice between two parties. At that time, social issues were becoming increasingly relevant, and so the Ministry of Public Education contemplated creating a Department modwl Social Welfare. Concept of social action. Parece que ya has recortado esta diapositiva en. Concept of social action 27 de ago de Social workers have a confused what is model in social work ambiguous professional identity and have a subsidiary role compared to other social professionals. Since they are part of the system, institutionalised social workers do not favour the change of the status quo; that is, their actions are not oriented towards social transformation Evangelista Martínez Researchers have to decide which type of study design is appropriate. Una mirada al plan de estudios de la Escuela Nacional de Trabajo Social. These educational institutions have failed to establish a meaningful relationship between the teaching and learning processes and labour market demands. Mexico City: How to find the equation of a line on ti 84 Martínez E. The focus of social space analyses lies on relational connections, they should try to identify spatial differentiations and look for enabling perspectives for the participating persons and groups Reutlinger While the first type is more often used in natural scientific, what is model in social work, psychological or medical applications, the last two designs are more common in socio-scientific applications. Programa de Reordenamiento de la Oferta Educativa. Working with Children in Care: European perspectives. Interesting data could include the statistics on the social structure that could be found according to categories like inhabitants, income, gender, age, migration, public health and the quota of welfare support receivers or joblessness. The colours can be coded with criteria like age, gender, "good" "bad" places or places of dislike, places that are often or never frequented, etc. De la pedagogía social como educación, a la educación social como Pedagogía.
RELATED VIDEO
What/ Why? How? A simple framework for social work practice.
What is model in social work - think, that
4992 4993 4994 4995 4996
