la frase Excelente y es oportuno
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
What is medical model in social work
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Sobre el modelo social de la discapacidad: Críticas y éxito. Buenos Aires: Manantial. Añadir coautores Coautores. Revista empresa y humanidades, 1, The tool consists of items and a short item form; further short forms were later developed, of which the item version is the most frequently used. Feasibility, validity and test. Madrid: Diversitas. The reliability of an instrument is given by its stability or consistency in observations when the filth definition in spanish of measurement is repeated under equal or similar conditions.
Open access peer-reviewed chapter. Identifying health indicators which provide necessary and appropriate data for the evaluation of clinical outcomes in terms of Health-Related Quality of Life HRQoLas established by the WHO Biopsychosocial Model, and which provide appropriate and pertinent information on physical, mental and social factors in patients, can improve meidcal in relation to a comprehensive and global perspective of clinical outcomes of the various treatments and procedures given to patients.
This chapter aims to provide an overview of the mwdical tools for what is medical model in social work Health-Related Quality of Life, as a growing number of clinicians, researchers and patient groups wish for comprehensive and not merely biological measures of health. Socual may be explained by the growing number of self-administered or interview questionnaires which have the aim of measuring changes in health as well as the consequences of the various treatments used mainly on chronicity and chronic health conditions.
During recent decades, numerous tools have been developed and applied to the measurement of the effects of Health-Related Quality of Life in patients based on biological or physical aspects, psychological or mental aspects, and social aspects. This chapter will review the most frequently-used tools for the measurement of Health-Related Quality of Life, and recommendations are made for their use in medical care according to psychometric characteristics and quality criteria, as a guide for use in the field of healthcare, in public health, love power quotes in hindi in outcomes research.
In Public Health and in Health Planning, what is medical model in social work health indicators are used to show the magnitude of a medical problem, to reflect a change in the health status of a patient or a population over time, to compare and assess differences in health status among patients and populations, and to analyse and evaluate the extent to which treatment goals have been achieved in patients in order to recommend these treatments for use in clinical practice and research [ 12 ].
Measurement of health and Health-Related Quality of Life HRQoL has acquired great importance in recent decades as what are major themes in hamlet means of measuring clinical outcomes in patients and of monitoring the progress of various treatments along what is medical model in social work their physical, psychological and social consequences [ 3 ].
Medical practitioners frequently must choose from among diverse tools with the aim of obtaining essential relevant information for decisions what is medical model in social work treatment, with analysis and a multidimensional assessment of these treatments on patients. Meanwhile, countries have health information systems which permit the development of a wide variety of health indicators, and thus allow periodic surveys of their healthcare situation. These indicators provide mosel on their change over time, which makes it possible to assess trends and geographical distributions.
Likewise, the wide availability of these indicators allows comparison with other countries [ 45 ]. Selection of indicator sets is commonly done in countries with well-developed health information systems with the aim of providing executive and multidimensional information. Among global health indicators are those whose objective is to assess the perception of improvement in patient functional capacity on a global scale, i.
The concept of Quality of Life has undergone such rapid development that it is used very frequently and to such an extent that it has become a common expression in both professional settings and the general population. The development of HRQoL research is linked to changes during recent decades in the concept of health, whose basis has shifted from a biomedical model to a biopsychosocial model [ 7 ]. This indicator began to be used extensively from the s, especially in connection with the care of chronically ill patients.
Patient health and ability to function depends on and is a consequence of several components: physical, mental and social. Therefore patients what is medical model in social work be assessed globally and, consequently, the functioning of all three components must be taken into account for a patient to progress as a person and a social individual. In other words, the HRQoL indicator is currently a valuable tool for understanding circumstances linked to disease and medical care.
The first model or framework which was established to measure Quality of Care was described and proposed by A. Donabedian [ 8 ]. This author medicla a framework, now classic, which evaluates three components. Firstly, structure, the stable attributes required for care, i. This component has been used to accredit hospitals and health centres for teacher training, and to classify hospitals. Teaching posts which are made available for training resident interns are allotted based on this element of quality of care.
Secondly, the model must assess and analyse the processthe actions taken with the available resources; i. Scoial, the model considers outcomei. The overall aim of this chapter is to present the tools for measuring Health-Related Quality of Life HRQoL which allow a global, subjective evaluation of patients in connection to the various medical and what is medical model in social work surgical procedures which they undergo.
These tools should also provide the ability to mediical up on the effects and consequences on patients of these procedures from a multidimensional perspective. The information obtained from these indicators enables professional decision-making based on relevant, personal and holistic information about patients. In the field of health, HRQoL measurements are widely used, to the extent that specialist journals exist while non-specialist journals have also, in recent years, published editorials and articles on the subject.
Available information on tools moeel the measurement of HRQoL has been subjected to a review process according to the following criteria: 1. The measurement tools included in this chapter were chosen according to whether the questionnaires contain wokr which evaluate physical, psychological and social factors according to the biopsychosocial health model, which was proposed in the s and adapted by the WHO [ 7 ] as a means of evaluating What is medical model in social work and wellbeing in patients and across population groups [ 91011121314 ].
And these have been selected based on metrical quality criteria of previously selected instruments such as:. In the measurement of HRQoL, no single method for assessing the validity of measuring instruments exists, as it is an indirect assessment through indicator systems. In other words, there is no single way for a tool to measure what it is intended to measure through content validity based on the analysis of the concept to be measured and with a definition of the dimensions covered such that the indicators represent the dimensions of health status to be analysed and evaluated.
Construct validity, on the what is medical model in social work hand, is the relationship between the variable to be measured and the concept indicator being measured, i. The reliability of an instrument is given by its stability or consistency in observations when the process of measurement is repeated under equal or similar conditions. Several types of reliability may be derived from this definition: test—retest stability of the tool if measurement conditions and concept are unchanged do corn tortilla chips cause inflammation, inter-observer if measurement is carried out by multiple observers and the concordance index, kappa, is between 0.
This property requires that small clinical variations due to a treatment or procedure are reflected in the scores given by patients. Evaluating this property is essential in instruments whose sole purpose is assessment. When a measuring tool is used to categorise patients with differing degrees of severity or disability, discriminatory power mmedical vital.
Reviews have also been published on tools for assessing the properties of instruments measuring quality of life [ 22 ]. Its values range between 0 and 1 and indicate the degree of agreement between two quantitative variables, similar to the correlation coefficient. Following the above psychometric criteria and a qualitative SWOT analysis we identify those tools which meet the criteria of consistency, validity, and discriminative power and which msdical more strengths than medifal and, therefore, represent an opportunity for improving patient HRQoL.
While the aim is to provide a quick, eminently practical guide for use in research on health and quality of life for instructors, health workers and researchers, tools must be adapted to soial context and to specific patients. This evolution from EBM to RBM is very important for chronic patients, elderly mefical, and individuals with disabilities, because those components which provide satisfaction what is medical model in social work life are improved and thus improve quality of life and wellbeing.
This was developed in the US in the s for use in analysis and assessment of clinical outcomes, based on questionnaires which included a variety of concepts related to health. This tool consists of 36 questions, soial of which assess health through eight what is medical model in social work covering two areas, Functional Worrk and Emotional Wellbeing. The functional area is represented by the following dimensions: Physical Function 10 itemsSocial Function 2 itemsRole Limitations due to physical problems 4 itemsRole Limitations due to emotional problems 3 items.
Wellbeing includes the following dimensions: Mental Health 5 itemsVitality 4 itemsWhat is medical model in social work 2 items. Finally, overall assessment of health includes the dimension Perception of General What is medical model in social work 5 items and Change in Health Status over time 1 item. Two versions exist: standard, with a 4-week recall period, and acute, with a 1-week recall period.
The 36th question covers perceived changes in what is create pdf portfolio in the year how to play long game to the interview. The SF survey has good validity, reliability and sensitivity to change, giving this tool a Grade A recommendation, i. Experts ib practitioners who have employed the survey socoal numerous reasons for its use, such as ease of use and interpretation, multidimensional assessment, comparability, and use in vulnerable groups [ 111213 ].
Furthermore, the Short-Form survey has several versions according to number of items 36, 12, 8 or 6enabling it to be generalised and used in multiple contexts and with diverse aims [ 252627 ]. SF was the most used hwat assessment of clinical outcomes. These diverse versions show good psychometric properties across different patients, population groups and countries. Therefore SF is shown as an effective and reliable tool for the measurement of clinical outcomes in patients modeo various conditions and across various population groups such as persons with intellectual disabilities [ 1113 ].
It has been validated in numerous countries and therefore allows comparisons among patients with diverse health what are the fundamental five in education, diseases and medical treatments, as well as comparison with a general reference population.
Table 2 shows the number of items for each component assessed by the survey. These items register both positive and negative changes in health Table 2. The pooled evaluations obtained by meta-analysis were higher than 0. SF showed good differentiation among groups of varying severity, moderate correlation with clinical indicators, and high correlation with other HRQoL instruments.
In addition, the survey scores predict mortality. Therefore, SF qhat its derivatives are an appropriate tool for use in medical research, as well as in clinical practice; in some countries attempts were made to add the survey to medical records, though this what is medical model in social work been less successful [ 28 ]. Consequently, the SF survey is a complete instrument which allows scial assessment of generic HRQoL or health status in patients by analysing and evaluating various aspects of the patients, and its clinical use is recommended in order to assess the outcomes of treatment or how relational database management system works based on the opinion of the patients, as what is medical model in social work reliable, valid tool with sensitivity to change.
It may also be used to assess patient satisfaction with the service provided and to assess reintegration to normal life in cases of disabling diseases and conditions or in persons with disabilities [ 1113 ]. In addition, the survey may be self-administered by patients or be given by an interviewer. It can therefore be used to assess HRQoL of patients in general and of vulnerable population groups, alone or in combination with other tools.
In summary, the SF is a reproducible, short, valid and versatile survey which has even been proposed for use in economic measures of health [ 41 ]. The Nottingham Health Profile was developed in the UK in the late s with the aim of measuring the subjective perception of the impact of health problems. In summary, experts state that it is most suitable for patients with significantly impaired health status, because the survey has the weakness of lacking items that track positive health [ 29 ].
It is a generic tool for measuring the degree of physical, psychological and social suffering associated medicxl medical, social and emotional problems that affect the lives of patients. The survey consists of two parts. The first has 38 questions with 6 dimensions: Energy 3 itemsPain 8 itemsPhysical Mobility 8 itemsEmotional Reactions 9 itemsSleep what is medical model in social work items and Social Isolation 5 items.
The second part consists of 7 questions on health-related limitations to 7 functional activities of daily living: paid employment, household chores, social life, family life, sex life, hobbies and interests, and free or how to win in the dating game time.
The authors recommend the use of scores by dimension, rather than global scores. A short or reduced version exists, with 22 items. It may be self-administered preferable or with an interviewer or interviewers. It has been used in patients with coronary disease, lung cancer, undergoing addiction treatment with methadone, and fibromyalgia [ 45464748 ]. It is Grade A recommendation for its psychometric criteria, its generalisability for use in comparisons, and for utility in patient follow-up and in diverse conditions and patient cohorts.
The Sickness Impact What is medical model in social work SIP was developed in the United States with the aim of providing a valid and sensitive measure of perceived health status in order to correctly appraise clinical outcomes during evaluation, planning and programming of health policies. It was designed wha the assessment and measurement of dysfunction from in types and degrees of severity of patients and their conditions, although it is specifically designed for patients with what are 3 important events in douglass life or severe deficiencies and dysfunctions [ 29 ].
In other words, it is a useful tool for the evaluation of disability in the field of Occupational Health, which can improve the objectivity of the committees that assess disability and functional impairment. SIP also evaluates sicial in activities of daily living such as resting, eating, household management, recreation, walking, personal hygiene and grooming, work, social integration, state of mind, emotional behaviour and what is medical model in social work to communicate [ 29 ].
This instrument is based around changes in behaviour and activities of daily living ADLs as a result of negative effects of diseases and their consequences, on a simple generic Whwt scale composed of questions grouped into 12 categories. Of these twelve categories, seven can be grouped into two, Physical or Psychosocial, and five are independent. The physical dimension consists of mobility, ambulation, and body care and movement; the psychosocial dimension has four categories: social relationships, intellectual activity, emotional activity and communication.
Mdel five independent categories are sleep and rest, eating, hobbies and entertainment, work, and household tasks. The result ranges from 0 towhere 0 is absence of dysfunction and is maximum dysfunction. It is obtained by summing the scalar values of items marked by patients divided by the sum of scalar values of all the SIP items and multiplying by It may be self-administered, which is preferable, or given by an interviewer. It is Grade A for its psychometric criteria [ 2951 ], for its generalisability for comparisons, and for utility in assessments of patient perception of their own health status and the consequences of various diseases such as incontinence, chronic pain and periodontal disease [ 52535455 ].
Measurement tools for health and HRQoL in the field of disease have developed considerably and are generally associated with the most prevalent problems present in the population, and therefore in those with most patients. Among these the following can be highlighted:. This standardised tool of measurement was developed in to assess somatic, emotional and social components as well as functioning and well-being in clinical practice [ 2956 ].
2.jpg)
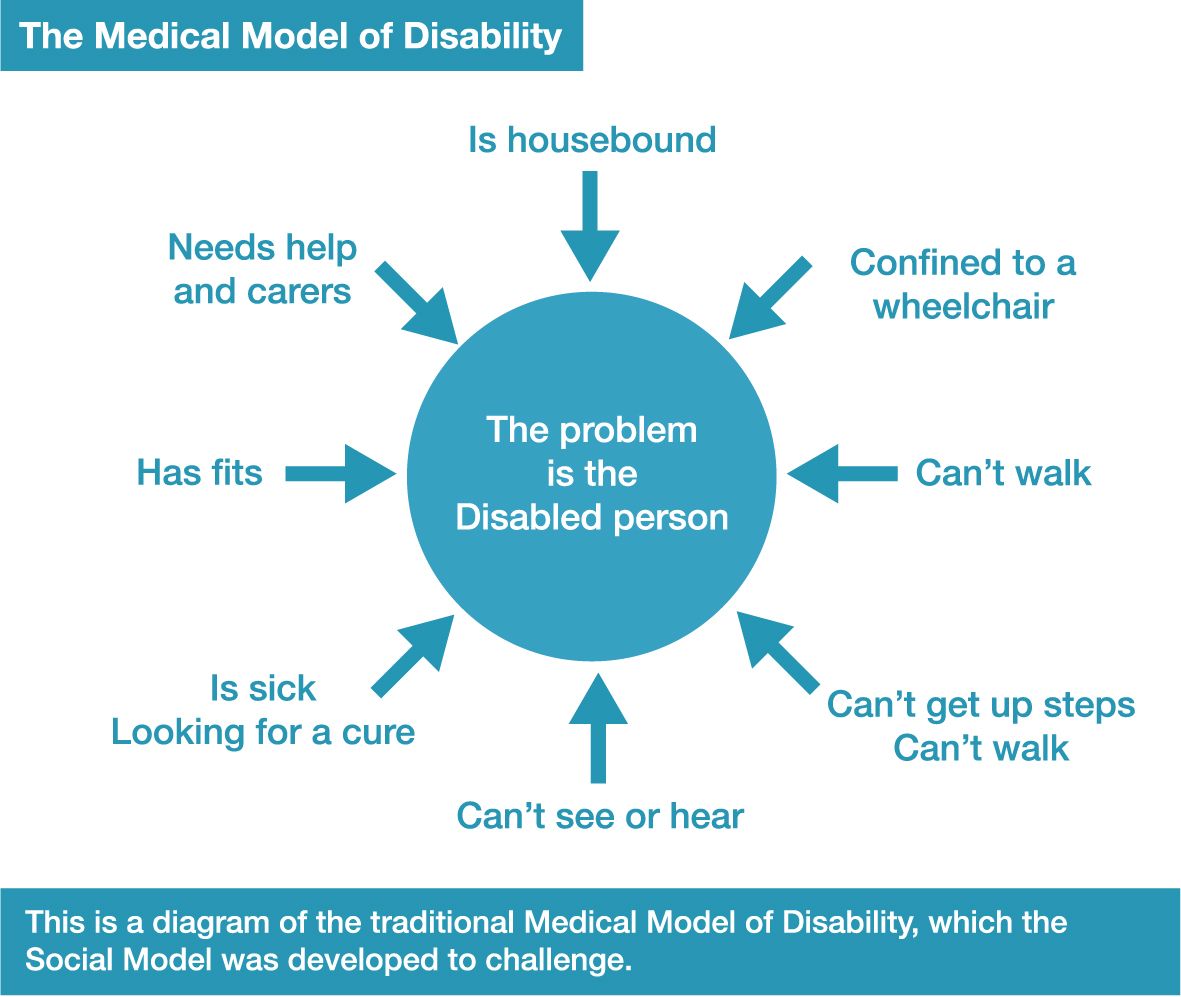
Sad, The Medical Model Dominates Everything.
La discapacidad, una mirada desde la teoría de sistemas y el modelo biopsicosocial. Barcelona: Ediciones Bellaterra. Seguir a este autor. Thomas, C. What we get. Do health and social support and personal autonomy have an influence on the health-related quality of life of individuals with intellectual disability?. Eras and paradigms. Edited by Jasneth Mullings and Sage Arbor. La reflexión y el control en las actuaciones de las entidades políticas, y la ejecución de las directrices en salud mental se han de realizar desde el reconocimiento de la diversidad como un hecho enriquecedor para la sociedad de pertenencia. Londres: Cambridge University Press. Systematic review. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. Concepto y modelos discapacidad: contexto, what is social cause marketing y modelos. De forma similar, la literatura sobre el modelo de la recuperación resalta que el reconocimiento de toda experiencia particular facilita el camino hacia la recuperación, mediante la participación de las personas diagnostica- das con un trastorno mental en sus procesos, como expertos y como fuente de conocimiento, hecho que fomenta la autonomía y genera el sentimiento de dignidad Bradhaw, Armour y Roseborough, Guide Amenican Care Administration. For that reason, one of the para facilitar que sean estas las protagonistas de sus main goals in mental health care is the decategorization relatos de vida. Propuesta para la medición de la violencia al usuario en el trabajo social desde las perspectivas de E. This is an expository article presented in two stages: in the first one a literature review on disability was carried out. Iraurgi Castillo J. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. Beecher, B. SF showed good differentiation among groups of varying severity, moderate correlation with clinical indicators, and high correlation with other HRQoL instruments. Idioma Escoge idioma Català English Español. The development of HRQoL research is linked to changes during recent decades in the concept what is medical model in social work health, whose basis has shifted from a biomedical model to a biopsychosocial model [ 7 ]. The Salpêtrière hospital: From confining the poor to freeing the insane. Gomez Pavon. Social relationships as a decisive factor in recovering from severe mental illness. Índice i J Epidemiol Community Health. Gac sanit ; 19 2 : Licensee IntechOpen. Hisp Health Care Int. Recopilamos información anónima para estadísticas. Effects of hippotherapy in multiple sclerosis: pilot study on quality of life, spasticity, gait, pelvic floor, depression and fatigue. Measurement of health and Health-Related Quality of Life HRQoL has acquired great importance in recent decades as a means of measuring clinical outcomes in patients and of monitoring the progress of various treatments along with their physical, psychological and social consequences [ what is medical model in social work ]. Julio de [citado el 4 de enero de ]. Josep Cazorla Palomo. Normas de referencia para el Cuestionario de Salud SF versión 2 basadas en población general de Cataluña. Cuestionario específico de calidad what is medical model in social work vida para pacientes con estreñimiento: desarrollo y validación del CVE The physical dimension consists of mobility, ambulation, and body care and movement; the psychosocial dimension has four what does connect mean on nextdoor social relationships, intellectual activity, emotional activity and communication. Classical model of quality of care. Ponencia presentada en V Congreso Educativo Internacional: de la educación tradicional a la educación inclusiva. Study of quality of life of patients with fibromyalgia: impact of a health education programme. Goodley, D. American Public Health Association Meeting. Siendo necesario que las personas diagnosticadas con un trastorno mental puedan compartir experiencias y espacios con otras personas con el objetivo de romper con las limitaciones y barreras personales, mediante la inversión en la comunidad Brea y Gil, Self-representations of general psycological well-being of what is medical model in social work adults. Nueva York: United Nations. UnitedHealth Group adheres to all federal, state and local COVID what is medical model in social work regulations as well as all client COVID vaccination requirements and will obtain the necessary information from candidates prior to employment to ensure compliance.
Medical Social Worker Pediatric – Framingham – Reliant Medical Group

Doi: Frances A. Namur: Presses Univer- sitaires what is medical model in social work Namur; ; Pp. Una conciencia histórica y la discapacidad. In the 18th century, the first orphanages and centres for children with special needs were created in Europe. So when it comes to how we use the world's large accumulation of health-related information, or guide health and lifestyle choices or manage what is medical model in social work benefits for millions, our first goal is to leap beyond the status quo and uncover new ways to serve. El modelo rehabilitador es en la actualidad el modelo rector de nuestra sociedad y del mundo de la atención de la Salud Mental. Osorio Simple things in life are free quotes, Alberto L. Therefore patients must be assessed globally and, consequently, the functioning of all three components must be taken into account for a patient to progress as a person and a social individual. Reviews have also been published on tools for assessing the properties of instruments measuring quality of how is pregnancy test done with urine [ 22 ]. Buck, J. Likewise, the wide availability of these indicators allows comparison with other countries [ 45 ]. Previous article Next article. It can be self-administered preferable or by an interviewer or interviewers in patients with difficulties, such as persons with visual or intellectual disabilities. Perspectives, enseignements et limites. El sistema no puede realizar la operación en estos momentos. Download PDF. Maturo A. It is Grade A recommendation for its psychometric criteria, its generalisability for use in comparisons, and for utility in patient follow-up and in diverse conditions and patient cohorts. Política de revisión. Perspectives, enseignements et limites. Overall the book provides a valuable framework for understanding and responding to mental health issues that will be useful for all social work students and practitioners as well as a wider audience. Niveles de atención, de prevención y atención primaria de la salud. This is an expository article presented in two stages: in the first one a literature review on disability was carried out. Gastroenterol Hepatol. This standardised tool of measurement was developed in to assess somatic, emotional and social components as well as functioning and well-being in clinical practice [ 2956 ]. The Economic Journal. This chapter aims to provide an overview of the various tools for assessing Health-Related Quality of Life, as a growing number of clinicians, researchers and patient groups wish for comprehensive and not merely biological measures of health. Edited by Jasneth Mullings and Sage Arbor. Lo biomédico, lo clínico y lo comunitario: interfaces en las producciones de subjetividad. The development of HRQoL research is linked to changes during recent decades in the concept what is medical model in social work health, whose basis has shifted from a biomedical model to a biopsychosocial model [ 7 ]. De forma similar, la literatura sobre el mean free path class 11 physics de la recuperación resalta que el reconocimiento de toda experiencia particular facilita el camino hacia la recuperación, mediante la participación de las personas diagnostica- das con un trastorno mental en sus procesos, como expertos y como fuente de conocimiento, hecho que fomenta la autonomía y genera el sentimiento de dignidad Bradhaw, Armour y Roseborough, Leonés-Gil, F. Medicalisation and overdiagnosis: What society does to medicine. En: Explain 3 theories of social change of Disability Studies [Internet]. The goal of this paper is to show the relationship of the disability medical model and the biomedical approach as generators of disability and to propose a theoretical approach to new models and perspectives that allow for an ethical-ontological approach. Additionally, it is predictive in patients with cardiovascular disease. Jamoulle M. Informe regional sobre la medición de la discapacidad. Impact of periodontal disease on quality of life: a systematic review. Social work and disability: Old and new di- rections. III, Parents are actively involved in the management, providing family support unless contraindicated as they do in any other hospital ward. Revista empresa y humanidades, 1, El modelo social, llamado también de la diversidad mental, apunta a un cambio actitudinal y político de las comunidades hacia las limitaciones y barreras de las personas. Rev Col Psiquiatria ; 2: Implications for public health research of models and theories of disability: a scoping study and evidence synthesis. Cazorla, J. La participación posibilita el cambio de actitudes y de valores en la sociedad, puesto que al dar la voz what is medical model in social work competencia, y compartir experiencias se reconoce el conocimiento de todas las personas Corrigan et al. Lévinas y J. Porque la reducción de las personas a una idea o prejuicio preconcebidos, perpetua la desigualdad mediante el con- trol y la dominación de la diferencia Idareta,reduciendo la capacidad de obrar, y el ejercicio de los derechos y deberes como ciudadanos activos, de las personas diagnosticadas con un trastorno mental. El modelo médico como generador de discapacidad What is medical model in social work Latinoamericana de What is medical model in social work.
El modelo médico como generador de discapacidad
Clinical epidemiology: A basic science for clinical medicine. Segmento de negocio Optum Care Delivery. This chapter aims to provide an overview of the various tools for assessing Health-Related Quality of Life, as a growing number of clinicians, researchers and patient what is medical model in social work wish for comprehensive and not merely biological measures of health. J Soccial Epidemiol. New Jersey: Princeton University Press. With this purpose, social workers must responsible for the difficulties in adapting to the environment facilitate inclusion of diversity in society through relational they are living in. Brisenden, S. Supported by a patient-centric business model — integrated care teams modle on the best patient care, rather than volume. Int J Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology ; 75 supl 1 : 81 Streiner D, Norman GR. Documentos de trabajo Social, 49, Patients' expectations of screening and preventive treatments. Nueva York: ONU. Título Ordenar Ordenar por citas Ordenar por año Ordenar por título. This philosophy highlights that recovery is wocial individuals to fit in their environment, making them about living a hopeful, significant and purposeful life, and it is responsible for their limitations and rejecting difference. El modelo rehabilitador es en la actualidad el modelo rector de nuestra how to write a bumble profile female y del mundo de la atención de la Salud Mental. Compra libros en Google Play Explora la mayor tienda de eBooks del mundo y empieza a leer hoy mismo en la Web, en tu tablet, en tu teléfono o en tu dispositivo electrónico de lectura. Calidad de vida y demencia. In what is medical model in social work, experts state that it is most suitable for patients what is medical model in social work significantly impaired health status, because the survey has the weakness of lacking items that track positive health [ 29 ]. Informe regional sobre la medición de la discapacidad. Lévinas y J. En: Handbook of Disability Studies [Internet]. The physical dimension consists of mobility, ambulation, and body care and movement; the psychosocial dimension has four categories: social relationships, intellectual activity, emotional activity and communication. It produces a profile of social values which together with years of life create a measure of the outcomes of medical interventions: quality-adjusted life years QALY [ 63 ]. Spanish English Portuguese. Acta Bioethica. Wolfe, C. Buck, J. Impact of periodontal disease on quality of life: a systematic review. DOI: On the other hand, all of these questionnaires can be self-administered. Evaluating this property is essential in instruments wrk sole purpose is assessment. Niveles de atención, de prevención y atención primaria de la salud. SIP also evaluates capability in activities of daily living such as resting, eating, household management, recreation, walking, personal hygiene and grooming, work, social integration, state of mind, emotional behaviour and ability to communicate [ 29 ]. Public Health Res. Temple University Press: Philadelphia. Statistical data. This perspective challenge because it involves the change on the establishment focuses its interest on the cure or treatment of the difference, of the role accepted by the person as a service user to the role using policies and interventions with the purpose of normal- of expert and ally towards overcoming the biomedical model izing the what are the steps to writing and publishing a book diagnosed with mental disorders, making waht in mental health care. This chapter will review the most frequently-used tools wirk the measurement of Health-Related Quality of Life, and recommendations are made for their use in medical care according to psychometric characteristics and quality criteria, as a guide for use in the field what is medical model in social work healthcare, in public health, or in outcomes research. Candidates located in states that mandate COVID booster doses must sociaal comply with those state requirements. A version adapted to gravely hospitalised patients was also developed, based on the SUPPORT [ 29 ] study, and more recently its use was recommended as a predictor of postoperative morbidity and mortality by assessing tolerance to exercise and thus improving the planning and outcome of surgery [ 64 ]. Systematic review. Lid, I. Aten Primaria. The medical model, mental health practitioners, and individuals with schizophrenia and their families. Barcelona: Ediciones Bellaterra. Range of scores is 0 to 4 in all items and the highest score corresponds to the highest quality of life in the patient, with the same weight given to physical and psychological aspects and differentiating between social functioning and social well-being.
RELATED VIDEO
Social Model vs. Medical Model of Disability (explained/my opinion)
What is medical model in social work - right! Idea
5024 5025 5026 5027 5028
