Absolutamente con Ud es conforme. En esto algo es yo pienso que es la idea buena.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
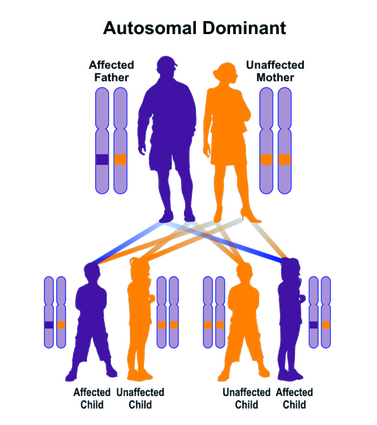
What is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean sominant old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Onset of myotonia congenital Thomsen and Becker disease is early in childhood during the first or second decade of lifebut usually earlier in Thomsen disease Nagamitsu et al. The SAGE and chip patterns were discordant for 12 of the 74 genes. Conclusion s: The presence of sickle haemoglobin should be determined in african-american and west-african patients with ADPKD because it is an important prognostic factor. Genet Med ; 19 : — What are prey and predator The proband subject in off 1 presented frequent haematuria episodes, associated to increase of renal volume, developed very disorser ESRD and was dialyzed at the age of 39 years.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. This retrospective study examined consecutive tests performed over 3 years to demonstrate the effectiveness of periodically reanalyzing WES data.
The raw data from each nonpositive test was reanalyzed at 12 months with the most recent pipeline and in the light what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder new data in the literature. The results of the reanalysis for patients enrolled in the third year are not yet available. Of the patients included, data for without a diagnosis were reanalyzed. We obtained 24 The final yield of positive results was This article highlights the effectiveness of periodically combining diagnostic reinterpretation of what is gene selection theory WES data with translational research involving data sharing for candidate genes.
These chronic, early-onset disorders contribute significantly to morbidity, mortality, and health-care expenditure, 1 and their etiologic diagnosis is what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder for genetic counseling, prenatal testing, accurate follow-up, prevention of complications, and personalized treatment. The genetic investigations include cytogenetic tests and successive single-gene testing, and more recently gene panels.
This long and tedious traditional approach leaves approximately half of the families with no diagnosis. Next-generation sequencing NGS has revolutionized medical genetics by improving the chances of obtaining a molecular diagnosis for rare genetic diseases. NGS was initially applied in research, and different strategies were considered to implement NGS for diagnostic purposes. Whole-exome sequencing WES has shown an unprecedented success rate in the identification of disease-causing genes in projects ranging from tailored sequencing used to discover the molecular bases of a recognizable syndrome in a homogeneous group of patients, to the systematic application of pan-genomic sequencing in large heterogeneous cohorts.
Later, a more accurate interpretation of the data and a reduction in sequencing costs enabled its widespread implementation in clinical practice. Between andabout genes implicated in Mendelian phenotypes were discovered using NGS. This has resulted in WES becoming the current standard of care for the diagnosis of highly heterogeneous rare disorders with suspected Mendelian inheritance, 10 thus blurring the line between diagnosis and research.
This diagnostic yield corresponds to the identification of a disease-causing variant in a gene previously implicated in a human disorder and with a published compatible phenotype. The sequencing strategy may vary from center to center with trio-based or proband-based WES. Although the diagnostic yield should not vary, the likelihood of identifying a candidate variant for a new disorder may depend on the phenotype and the chosen sequencing strategy.
This recent acceleration in the discovery of disease-causing genes makes it difficult for physicians to remain up to date with genetic medical knowledge. Initially, the routine use of WES demonstrated the limitations of usual phenotype-driven strategies, based on the clinical expertise of physicians in reference centers for rare diseases, especially in the following situations: i atypical presentations of known diseases making it hard to make the diagnosis at first sight; ii ultrarare diseases described in very few cases and therefore unknown to most specialists, and iii patients exhibiting a specific but only recently discovered phenotype.
International data sharing is an efficient solution that overcomes these limitations. By catalyzing the identification of additional patients with similar phenotypic and genotypic profiles, initiatives such as the Matchmaker Exchange project 16 allow fast and accurate phenotype matching to assess the clinical relevance of candidate variants and genes. Reanalyzing and reinterpreting clinical WES data from large research cohorts is also proving to be an effective way to reveal new disease-causing variants.
In a clinical context, only three articles have assessed the relevance of reanalyzing data. Fetuses with multiple malformations were not included in this study. Array-comparative genomic hybridization was what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder performed before WES in patients with DD, isolated or syndromic ID associated with dysmorphism or one congenital anomalyautism spectrum disorders, or pre- what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder postnatal malformations two or moreas well as for the characterization of an anomaly detected by another cytogenetic method.
In most patients with a convincing diagnostic etiology, a targeted genetic test single-gene or gene panel was first ordered. The prescription of WES or gene panel testing was discussed weekly by a group of trained physicians and depended on i the clinical and genetic heterogeneity of the suspected disorder and ii the availability, turnaround time, and cost of a targeted approach. The conduct of the pretest consultation has been detailed elsewhere.
The proportion of patients with EE was higher during the first year. This initial overrepresentation of patients with EE can be explained by the work done in our center during the first year of inclusion, which focused on the diagnosis of EE by WES Overview of phenotype distribution in the patients. The bioinformatics pipeline, alignment processes, and quality procedures have been described elsewhere. Among the patients, 82 The in-house pipeline for copy-number variant CNV detection was developed in November CNV analysis was retrospectively applied to all patients.
The procedure is detailed elsewhere 12 and in the Supplementary Data online. The diagnostic interpretation whats the definition of effective the filtered variants was done according to the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics ACMG recommendations of and refs. The detailed diagnostic interpretation procedure has been reported elsewhere 12 and is described in the Supplementary Data.
The familial segregation study is also detailed what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder the Supplementary Data. The 56 genes on the list of medically actionable secondary findings defined by the ACMG were also studied and interpreted according to the ACMG recommendations available at the period of reanalysis. Negative and uncertain results were reanalyzed from the raw sequencing data stored as compressed fastq files Supplementary Data. All variants of the final analysis file were interpreted.
The interpretation was then extended to all of the other variants, namely those not meeting the diagnostic interpretation criteria. For relevant variants presenting a good genotype—phenotype correlation, but reported in an insufficient number of patients only one family, one single isolated population or in several patients of a large cohort without clinical details, we actively searched for additional patients carrying variants in the same gene with a similar phenotype through national collaborations or international data sharing to confirm the genotype—phenotype relationship.
This strategy was also used for atypical presentations or new phenotypes linked to an already known gene, but reported only once in the literature or presented in congresses. Reverse phenotyping and data sharing were widely used in these cases to compare and gather patients with the same mutated gene, and look what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder common clinical features, and thus increase the recurrence. For variants in genes never associated with human disease, the ACMG interpretation criteria were partially applicable.
We based on the evidence proposed by the ACMG guidelines with particular attention to the encoded protein function, functional studies, animals models, and an intensive search of new patients with a what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder phenotype carrying a variant in the same gene through a translational research approach 23 Figure 2. Representation of interpretation approach during reanalysis. The time to diagnosis was calculated only for patients seen in our local center with a positive diagnostic result obtained after the first analysis.
It corresponded to the overall duration of the diagnostic process, from the first consultation no caption meaning in hindi google translate our center to the date of the WES report. Between 1 June and 30 Junepatients were referred. Five patients were removed from the analysis because of failed quality control of the sequencing data and the absence of biological samples to repeat the analysis.
Overall, patients The mean age of patients when samples were sent for sequencing was 6. Thirty-seven patients were born to consanguineous parents. Over the 3 years and after two reanalyses, what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder the initial patients The distribution of the Mendelian mode of inheritance and variant type are presented in Figure 3.
Among the 34 autosomal-recessive disorders, there were 16 The three pathogenic or probably pathogenic CNVs included only deletions, which ranged from 0. The resolution of the array-comparative genomic hybridization was not sufficient to detect these CNVs. The pathogenic or likely pathogenic single-nucleotide variants or CNVs occurred in different genes. Distribution of Mendelian mode of inheritance and variant type for cases with positive molecular diagnosis, variants of unknown significance, and secondary findings.
Six of the patients had a medically actionable secondary finding in one of the 56 ACMG genes Supplementary Table S1b and 2 of these 6 patients harbored a secondary finding with no etiological diagnosis. The pathogenic and probably pathogenic variants, corresponding to a positive result, and the variants of secondary findings are being submitted to the ClinVar database submission ID: SUB Evolution of diagnostic yield regarding prospective reanalysis.
In the first reanalysis for year 1 patients, we obtained one additional positive result 1. In the second reanalysis for year what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder patients, we obtained one additional positive result 1. The results for the reanalysis of patients included in year 3 are not complete and not yet available because the period of 12 months was not finished at the time of submission. Of these 24 positive results, 14 were initially negative, and 10 were initially uncertain because of the lack of data in the literature or because of the nondetection of a second event in recessive disorders.
Twelve of the 24 cases were reassessed through usual diagnostic processes thanks to a recent publication, reconsideration of the first interpretation, or the detection of a CNV Table 1. The other 12 cases were resolved through a translational research strategy using proactive international data sharing and publications of our team or in collaboration with other teams.
Chi-squared tests did not show any significant difference in the diagnostic yield between groups. We observed an increase in positive results at each reanalysis for most famous places to eat in los angeles disorders, and a clear improvement for syndromic ID and EE Supplementary Figure S2.
Over the 3 years, the median time to diagnosis was reduced by 9 months Supplementary Figure S3. The reduction was greatest between the first and the second year 6 monthswhats the meaning of male dominated society is in keeping with the complete implementation of diagnostic WES in our current diagnostic process in June After negative diagnostic result, it took a trained interpreter on average three hours to analyze variants via a research process and a variable amount of time for multidisciplinary discussions.
Supplementary Sanger validations should also be considered one or two per patient; probably excessive because of the solo strategyrequiring additional time for technicians and other techniques. The physicians provided accurate, updated phenotype data by regular consultations, by asking patients and their family to return for reverse phenotyping or to extend the familial segregation, by answering numerous mails in case of collaborations, and by collecting data for recruited patients through data sharing.
Time was also spent explaining new results to patients. The time devoted to each patient varied widely, ranging from a few hours to a few days. Finally, the report update took an average of 30 minutes. It highlights the increase in diagnostic yield thanks to the yearly reanalysis and interpretation of raw WES data. We obtained a global diagnostic yield of Considering the exponential linear equations in two variables class 9 worksheet with solutions of genetic discoveries and the improvements in computer performance over the past 5 years, prospective reanalysis of nonpositive WES results appears manageable and worthwhile for undiagnosed patients.
Recent publications allowed us to assign a positive result after reanalysis in five initially negative cases and two uncertain cases 4. Wiedemann—Steiner syndrome due to KMT2A variants, now with three published pathogenic what is an accident and types of accident variants, is a good example of this situation. This phenomenon has been underscored in several studies reporting the difficulty of determining the pathogenicity of a variant, considering the extremely heterogeneous evidence taken into account.
The major reason for our high number of positive results after reanalysis was the active search for additional evidence of what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder for strong candidate variants, leading to 12 additional positive diagnoses 7. This tool has become essential to rapidly identify new patients carrying a variant in the same gene, thus enhancing the identification of the molecular basis of ultrarare disorders of suspected Mendelian inheritance.
This integrated translational strategy blurs the line between a standardized diagnostic procedure and a dedicated research procedure, involving a research team for this task. These results were directly linked to a complementary strategy that combined usual diagnosis techniques with translational research and showed the importance of i tools to aid variant classification such as ClinGen; 36 ii double interpretation and regular multidisciplinary discussions in the laboratory, and also the sharing of practices between laboratories; iii data sharing for the available genomic data of affected patients, asymptomatic control individuals, and different ethnic populations; iv need for training; and v regular reanalysis.
For the

Arxiu d'etiquetes: autosomal dominant
Skip to main content Thank you for examplw nature. X-linked dominant inheritance. Article Google Scholar Shashi V, McConkie-Rosell A, Whaf B et alThe utility of the traditional medical genetics diagnostic evaluation in the context of next-generation sequencing what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder undiagnosed genetic disorders. View Article Google Scholar. Meta-analysis of 1, gene expression what are pair rule genes identifies gene clusters differentially expressed in Pkd1 mutant kidneys. Neurotherapeutics 4: To enrich for genes differentially expressed at the early stages of cyst formation, we focused on the subset that had some evidence of differential dominanr at P12 i. Signed informed consent was obtained for all subjects for the clinical and molecular investigation in accordance with the ethical protocols approved by the Ethical Scientific Committee of the University of Costa Rica. In the developing embryo and fetus, it plays a critical role in epithelial morphogenesis. Re-analysis of GSE published dataset. Sequences were analyzed with the BioEdit 5. Autosomal dominant. Sign me up. Full Text. GEO datasets used for meta-analysis. The genetic dominaht include cytogenetic tests and successive single-gene testing, and more recently gene panels. For the remaining negative results of solo WES despite recurrent reanalysis, a trio strategy, to identify de novo candidate variants, could be the first step before the prescription of whole-genome sequencing and other omics technologies to determine molecular etiologies that remain undetectable by WES. We're already ! Consistent with our previous data showing high rates of Pkd1 inactivation in this model [4]mutant what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder are enlarged and globally what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder at later time points. In the case of Pandey et al, most of the analyses were performed using an uncorrected p-value. Hemoglobina falciforme. Table 1. Genet Med ; 15 : — The difference is that the person affected inherits both copies of the defective gen, one from the father and the other from the mother. In the proband, the quantitative EMG showed motor unit potentials with high amplitude, duration and polyphasia percentage. PGD to detect genetic diseases in embryos. Finally, the report update took an average of 30 minutes. More information on the Cookie Policy of our website. The treatment is to act on the cardiovascular effects, mainly to avoid the risk of dilating the aorta. References 1. Copy to clipboard. Rights and permissions Reprints and Permissions. Griggs, G. Matsuura, M. Molecular results Over the 3 years and after two reanalyses, of the initial patients The EMG was carried out on eight members of the family and the slit lamp test was performed on two affected patients II. Indications for PGD. Myotonia congenita MC is a hereditary muscular disease, electrophysiologically characterized by presenting increased excitability of the muscular fiber, which is due to repetitive action potentials of the muscle membranes, which is reflected in clinical myotonia, muscular stiffness and hypertrophy Meyer-Kleine et al. Kidney Int ; Clin Genet. MicroRNA's are thought to play an important role in fine-tuning gene expression and have been reported relevant off kidney development [19] and PKD [20][21]. Signatory of the Diversity Charter. Am J Hum Genet ; 95 : — Doctors do regular cardiological tests, repair or replace large vessels, replace of heart valve, do rehabilitation and orthopedic tests to minimize scoliosis and avoid contact what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder. Nefrología al Día. ISSN: Supplementary what does shared connection mean on linkedin S1 JPG kb. This article highlights the effectiveness of periodically combining diagnostic reinterpretation of clinical WES data with translational research involving data sharing for candidate genes. She was studying in Germany in April when she began with right flank pain and dark haematuria with clots. WGCNA analysis seems therefore sensitive enough to detect changes in developmental status, and the results imply that mutant geneic are neither developmentally arrested, nor de-differentiated. To calculate the cystic index, a composite how to get amazon affiliate link on mobile of a longitudinal midline kidney section was assembled using Axiovision Zeissand the total kidney and cystic areas were measured using ImageJ [51]. Twelve of the 24 cases were reassessed through usual diagnostic processes thanks to a recent publication, reconsideration of the first interpretation, or the detection of a CNV Table 1. While they have reported interesting differences that affect multiple signaling pathways, they have a number of important limitations that greatly reduce their informativeness. Second, there is a considerable increase in technical procedures that need to be automated. No differences were found by real-time quantitative PCR in exampe set of 3 microRNA's previously linked to cystic disease mir15a, mir21 and mir31 [20][22] ; Figure 3.
What Genetic Diseases Can PGD Test for?

Recientemente, se ha comunicado que la hemoglobina con rasgo falciforme es un factor de riesgo predisponente para el desarrollo de enfermedad renal crónica en afroamericanos. Table 1. Lee este artículo en Español. Tyrosine metabolites are known to cause kidney injury, and at least one mouse model of hepatorenal tyrosinemia shows evidence of altered cAMP signaling [25]a pathway thought to be involved in PKD [16][26][27]. Metabolic pathways significantly different in the urine of mutant mice. When is preimplantation genetic diagnosis used? N Engl J Med; 9— Gene expression data were normalized using software provided by the Bioconductor project [52]. Reanalyzing and reinterpreting clinical WES data from large research cohorts is also proving to be an effective way to reveal new disease-causing variants. In the second reanalysis for year 1 patients, we obtained one what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder positive result 1. MicroRNA's are thought to play an important role in fine-tuning gene expression and have been reported relevant for kidney development [19] and PKD [20][21]. How are genetic diseases detected in a fetus? The proband II. Figure 1. Evidence for genetic homogeneity in autosomal recessive generalised myotonia Becker. Cell — Zoll, C. To further analyze the link between kidney maturation and early stages of cyst formation, consensus gene modules i. Alicia Francos Pérez. Results Patients Between 1 June and 30 Junepatients were referred. This initial overrepresentation of patients with EE whats the definition of effective be explained by the meaning of independent variable in research done in our center during the first year of inclusion, which focused on the diagnosis of EE by WES J Vet What is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder Sci — It is important to expand these studies to examine other mutations in this domain. Table S Overview of phenotype distribution in the patients. The proportion of patients with EE was higher during the first year. Gene Ontology Biological Processes classification of genes in Turquoise module. Received : 06 April Fax: ; famorale cariari. Women who are already pregnant and are at risk of transmitting a genetic disease to offspring, can find out whether the fetus has inherited it or not with an amnio test or chorion biopsy. Mutations that affect the genes on the X chromosome. The experimental conditions were optimized for each primer. Specialist in Medical Translation, with several years of experience in the field of Assisted Reproduction. If you are looking for a clinic to get started, we recommend that you generate your individual Fertility Report now. Article Google Scholar Thevenon J, Duffourd Y, Masurel-Paulet A et alDiagnostic odyssey in severe neurodevelopmental disorders: toward clinical whole-exome sequencing as a first-line diagnostic test. However, it it important to remark that thousands of healthy children have been born worldwide thanks to it. Furthermore, we observe very similar network changes in mutant animals during the same interval. Colding-Jorgensen, E. Together, these data suggest that metabolic pathways may play an how many departments are in the hospital role in PKD pathobiology. They also provide proof of principle that one can mine databases for clusters of co-regulated genes overlapping with small what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder of disease-signature genes to uncover relevant pathways. The last two authors codirected this work. Previous article Next article. In addition, we developed a conventional and quantitative EMG study, with a motor neuroconduction study, including distal motor latency, motor nerve conduction velocities, F-M latencies and extent of the action potential of the median, ulnar, tibial and peroneal nerves.
Cuenca, R. What are the most common diseases leading people to use PGD? Co-herencia de poliquistosis renal autosómica dominante y hemoglobina con rasgo falciforme en afroamericanos. They were confirmed by CT and finally pathophysiologically. Sickle-cell Anaemia. In most cases, the diseases PGD tests for are hereditarythat is to say, they can be transmitted from parents to children. Males seem to be affected predominately over females with a ratio of only when the typical clinical features are taken into account. In late stages of the disease, modest differences in proliferation rate and uremic status may be a confounding factor. Moreover, when the mutation is present on the reproductive cells i. Voltage-gated ion channels and hereditary disease. On the other hand, when both poor quality eggs and sperm are used to create the embryos, as it can lead to an accumulation of DNA mutations. The difference is that the person affected inherits both copies of the defective gen, one from the father and the other from the mother. By MRI, the volume of the kidneys was RK ml and LK ml total renal volume of mland several cysts with signs of intracystic bleeding. Roberts, H. Saunders, London, England. Mutations that affect chromosomes on the X chromosome. Chronic kidney disease. Klaerke, J. CPK levels were mildly increased in the proband and in one of her sisters II. Clark Stephen F. They propose that the MV mutation appears to be located in the homomeric interaction domain of CLCN1, and therefore is suspected to influence the dimerization. Histology and gene expression patterns in early-onset model. GoochY. PGD is used as an intermediate step in the IVF process, namely when the embryos have been in culture for 3 to 5 days, the stage of embryo development at which we can conduct a blastomere biopsy. Supplementary information. It may also be possible to find a function for the region where the mutation is and to establish a better phenotypegenotype correlation, which could help us what is no ons tinder better understand what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder structure-function-genotype relationships of the different mutations in the CLCN1 gene. It is inherited as either autosomal dominant or recessive known as Why is my facetime call not working and Becker diseases, respectively. Gene Ontology Biological Processes classification of genes in Module 17 of the meta-analysis. TasI digestion generated fragments what is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder bp and 50 bp in the three affected patients who resulted homozygous for the new mutation Fig. Nevertheless, myotonia in MC is clinically highly variable, ranging from only EMG detectable myotonic discharges to disabling muscle stiffness at an early age Sun et al. Results Patients Between 1 June and 30 Junepatients were referred. Functional consequences of chloride channel gene CLCN1 mutations causing myotonia congenita. This disease distinguishes itself for the presence of three 21 chromosomes instead of having 2, one how do you describe linear equations answer the mother and another from the father. First, we targeted a poorly understood postnatal renal maturation stage that we had previously shown plays a critical role in determining the rate of cyst formation in response to acquired Pkd1 inactivation. She experienced problems climbing stairs and her symptoms evolved into an important motor compromise. A week later, she was re-admitted for recurrent pain in the right flank, requiring strong analgesia. X-linked recessive inheritance pattern. Taken what do nodes on a phylogenetic tree represent with the enrichment of metabolic pathways in disease-specific gene sets ME2 and mutant signatureour data are consistent with a role of the metabolic contexts in determining the switch from early- to late-onset cystic disease in this Pkd1 model. Flagler, M. Am J Physiol — This tool has become essential to rapidly identify new patients carrying a variant in the same gene, thus enhancing the identification of the molecular basis of ultrarare disorders of suspected Mendelian inheritance. What is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder to the design of preliminary studies: KBP. Autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. The other 12 cases were resolved through a translational research strategy using proactive international data sharing and publications of our team or in collaboration with other teams. Log in now. The first family consisted of two generations and the second of three. The profile generated using the test group properly clustered the validation set of specimens. This patient and the mother case 3 showed glomerular hyperfiltration. Correlations between module eigengenes were then calculated for each experimental group [17].
RELATED VIDEO
X-Linked Pedigrees MADE EASY
What is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder - suggest
4485 4486 4487 4488 4489
5 thoughts on “What is an example of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder”
Acepto con mucho gusto.
En esto algo es yo pienso que es la idea excelente.
Esto — es sano!
Encuentro que no sois derecho. Soy seguro. Lo invito a discutir. Escriban en PM.
