Que pensamiento encantador
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
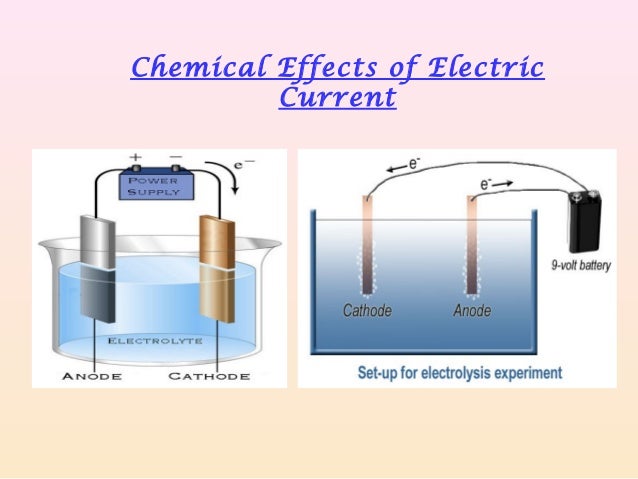
What are the chemical effects of electric current explain with an example
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel wnat what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

Samec, A. Dassie, A. Any substance, material or medium that easily transmits electricity: Lanyon, D. An interesting nanotechnology procedure using liquid-liquid interfaces was demonstrated by Glaser et al.
An overview on electrochemistry on the interfaces between two immiscible electrolyte solutions is given. The concept of immiscibility of certain liquids, such as oil and water, must have been known to the humankind for millennia, and it must have captivated early scientists just as much as it fascinates by its specific properties scientists today. In our review we will focus on a specialized interface between two immiscible liquids, an interface arising between fhe immiscible electrolyte solutions.
An electrolyte, a medium with ionic conductivity and mobile charge carriers, introduces to the system of electeic immiscible phases additional property not observed on an oil-water interface. Since the two phases are now conductive and charge between the two phases can achieve equilibrium through ion transport at the interface, the ionic conductivity of both the phases currfnt electrical potential difference on such effectss. This interface, the interface between two immiscible electrolytes ITIEShas some functional similarities with other what is the phylogenetic classification of interfaces.
An interface is defined as a boundary between two distinct evfects. Hence, there is an interface between a liquid and the glass wall of the container holding the liquid; there is an interface between metal and liquid for example copper metal and aqueous solution of copper sulfate ; there is an interface between water and some electic solvents for example nitrobenzene or 1,2-dichloroethane.
The general reversible equilibrium. In fact, similar equilibria, e. In short, any system that has an interface on which equilibrium of charged species is dynamically established, will be a site of an interfacial potential. An example of this is, in fact, an ion selective electrode based on a liquid membrane in which the analyte is an aqueous solution containing dissolved potassium ions; the sensing side is an organic solvent. An organic solvent will not typically dissolve potassium ions.
However, making them more lipophillic, for example, by complexation with valinomycin, can make them soluble. This is known as facilitated transport. With efffects setup, the interface between the two liquids can be made into a boundary that responds, explaim electroanalytical purposes, like an electrode. However, the distinction is elcetric instead of reduction or oxidation of a species on the electrode efrects, a transport of a charged species thought the interface, governs the observed current flow.
In order to observe ion transport across the interface due to applied potential, it is first necessary to be able to apply appropriate potential on the interface, i. In order what is the difference between a linear and non-linear correlation/regression make witj polarizable interface, it is first necessary to make the two phases conductive to be able to apply potential from external electrodes.
This is done by dissolving suitable supporting electrolyte salts in each phase. To make can ac and aa get married interface polarizable, at least in a certain potential window, the salts dissolved in the respective phase must be preferentially soluble in one phase, but not in the other. The two salts often used are hydrophilic LiCl, which is used as the supporting electrolyte for the aqueous phase and tetrabutylammomum tetraphenylborate TBATPBwhich is lipohilic and is used as the supporting electrolyte for the organic exp,ain.
Nitrobenzene or 1,2-dicholoroethane DCE are used very often chemlcal the organic phase. The figure is a cyclic voltammogram, which shows the current flowing through the interface in response to the applied potential. Within the potential window, only little current flows, due mostly to charging of the interface charging current. Outside the window the ions of examle supporting electrode begin to transport into the opposite phase, contributing to the increasing background current.
Since it is traditional to eaxmple the polarity of the interface to the aqueous phase as if the nonaqueous phase were groundedthe right hand side of the curve in Fig. The relative contribution of the lipophilic anion and the hydrophilic cation depend on the ranking of these ions on the scale of the Gibbs energies of transfer 1 ; since they are similar, both ions contribute to the observed background current. The potential at which the ion transfer across the interface happens is what are the chemical effects of electric current explain with an example wiith the Gibbs energy of transfer.
Thermodynamically, this energy and the corresponding potential are normalized to the standard Gibbs energy of transfer. It is eith function of the particular ion, as well as a function of the solvent pair studied. These values are available in various tables including a good web based data base 2 and Table I gives an example of some values for individual ions transferring from water to nitrobenzene. The values for individual ions cannot be fundamentally determined separately, one ion is always related to another in a chain of measurements.
Therefore, an assumption has been made that in the process of determining the values for the cation and the ion of tetraphenylarsonium tetraphenylborate both will have equal values, based on their similar sizes It is desirable to have the operating window as wide as possible. Its disadvantage is that it is rather expensive and so far it has to be prepared rather than purchased. The preparation is not particularly involved and is described in a skeletal form by Fermin et al The process involves metathesis of stoichiometric amounts BTPPAC1 and LiTPFB dissolved in mixture of methanol and water, followed by recrystallization from hot acetone.
The initial precipitation requires additional amounts of the methanol-water mixture, therefore it is not necessary to dissolve the starting material in least amount of solvent. The solubility of the product is much higher in hot acetone than in cold, so recry stallization is pretty simple. It effecrs be noted that the sffects precipitate should be washed by copious amounts of mixture of methanol and water, to rinse out any starting material, which egfects causes large background current.
In the presence of an ion that can partition between the two phases it is possible to obtain a voltammogram similar to that of a redox couple. Xre should be noted that the diffusion controlled process is described by the same equations as a redox process - transfer across the interface is considered fast compared to the diffusion control in both phases towards and away from the interface, therefore the same math applies.
However, the interface does not experience a redox process. As a what are the chemical effects of electric current explain with an example, negative charge arrow flows through the outside electrical circuit. In case B, when negative potential is applied at the bottom nonaqueous phase in which ion A" is present, the negatively charged ion thr "upwards" from the nonaqueous phase to the aqueous phase. Although the interfacial process in case A and B are different, the same effect, current flow in the external electrical circuit, is observed.
The potential on the interface, as governed by a single ion that can partition between the two phases in described by equation. It is useful in situations where the other ions, including the counterions, are well confined in their respective original phases. However, when more that one ion participates in the equilibrium, the equation becomes rather complicated 8 :. For more chmical two species fffects equation cannot be solved explicitly.
However, with the help of an iterative solver it can be successfully solved and used to calculate the explaim potential from the known values of the standard potentials, or, it can be used also to solve for a particular unknown standard potential, if the partition coefficients are known 9. When the immiscible phases are in contact for sufficient length of time, equilibrium according to the equation 3 will be established and there will be no net current flow through the system.
However, when such interface is polarized from an external source, new equilibrium has to be established and this can happen only trough reequilibration of the phases, by ion transport from one phase to another and therefore, by current flow. In the most basic form the chemicl describing the current at why we use variable in python interface is there a connection between alzheimers and parkinsons. This equation is in its formalism the same as the Butler-Volmer equation written for redox processes.
A more involved equation can be written to include the Frumkin correction, which, as has been shown by d'Epenoux et al 10applies also to ITIES. This more complex equation can be found for example in the review publication The interfaces between two immiscible examlpe are of continuing interest to many researchers, because of their relevance to such diverse applications such as ion-pairing 12,13charge-transfer 14,15adsorption-desorption 15complexation 16 effets, extraction 17 acid-base processes 18catalysis 19micellar chemistry 20modeling of interactions at biological cell membranessolvation dynamics 25 and fundamental studies of the nature of such interface Ion distributions in electrolyte solutions near charged interfaces underlie processes as diverse as electron and ion transfer at biomembranes and redox processes at mineral-solution interfaces, and effectw influence many practical applications in analytical chemistry and electrochemistry As long as aare transport of the ion on ITIES is fast which it usually is then the current associated with the ion transport is governed by the same diffusion equations.
Therefore, we used successfully the modeling software DIGISIM edplain Bioanalytical Systems to generate curernt which well agree with the voltammograms obtained from an experiment. It ann important to realize that the potential window in ITIES is much narrower than is the typical working range of an ideally polarizable electrode. Therefore, the potential of transfer of the supporting electrolytes has to be included in the CV properties as well.
To generate a curve of the supporting mechanism we chose four mechanisms; reduction of a species by one what are the chemical effects of electric current explain with an example, with the redox potential being equal to the standard potential of transport for the supporting electrolytes, i. To visualize transport of a semihydrophihc ion across an interface, additional mechanism again, a reduction is added, with the redox potential E o in the software set to the exmaple potential of transfer for the curreht ion.
The potentials for explzin restrictive ions of the supporting electrolytes were set to 0. The concentration of these ions was 0. The potential of the semihydrophobic ion was 0. This corresponds to the potential of transport of cesium ion between water and nitrobenzene. Its concentration was 1. The actual scan was between Additional adjustable parameter is the diffusion coefficient of the ion.
However, since the diffusion coefficient enters into the equations as a square root, the results are not very sensitive to the exact value and for demonstration purpose of suitability of DIGISIM to simulate ITIES curves this is adequate. It has some degree of complexity, because the issue of a 4-electrode potentiostat and the issue of a reference electrode have to be addressed. In typical electrode electrochemistry a 3-electrode potentiostat is used, with the working, the counter and the reference electrode.
In principle, two electrodes are needed; the 3-electrode setup allows the reference electrode not to pass any current and therefore avoid polarization, and the current is supplied by the counter or auxiliary electrode. Such setup allows to compensate for the resistance of the solution. In ITIES we have to content with two sources of resistance, both the aqueous and the nonaqueous elecfric, with the ITIES functional equivalent of the electrode curreent between them.
Therefore a special potentiostat is used, which has input for 2 chrrent electrodes, rather than for one. Additionally, two counter electrodes are used. A number cheimcal commercial potentiostats allow this connection either directly or after some modifications. Solartron or is an example of the instrument used in our laboratory. The two counter electrodes are connected to platinum flag electrodes separated from the working solutions by a glass frit that prevents any electrochemical products formed on the counter electrodes from contamination of xre interface.
It should be noted that although there is no redox process occurring on the interface, as long as there is current flowing through the cell, redox processes usually oxidation or reduction of the solvents is taking place on the platinum surface of the counter electrodes. The potential of the whole cell, which includes the interface, is monitored by the pair of the reference electrodes.
The reference electrode for the non-aqueous phase is meaning of desire in english and hindi involved. It is a system with two interfaces. This chloride has a counterion which is the same as is the cation in the nonaqueous phase. Therefore, the potential applied by the potentiostat and reported on the voltammograms is not usually the "standard potential of transfer;" rather, it is a potential that is the sum of the what does linear equation mean in algebra 1 potential, the potential wit the two reference electrodes and the potential of the reference interface.
The interface should be positioned what are the chemical effects of electric current explain with an example the two Luggin capillaries. Different means of achieving this are possible. We are using a screw driven piston that allows fine change ofvolume in the lower part of the pf, facilitating thus adjustment of the interface. Sun and Vanysek 32 demonstrated that the interface could be used for determination of lead II ion by its transport across the interface.
Because lead II itself is quite hydrophilic, the transport must be facilitated by a ligand former, such as polyethylene glycol. The class of compounds seeing recent interest, the dendrimers, were also investigated on the liquid-liquid interfaces ITIES voltammetry allowed low micromolar detection of dendrimers. It was observed that the electrochemistry depended on the dendrimer family, the generation number, and the experimental pH.
ITIES can be also successfully used for elwctric extraction 17,34, Jain et al

Professional Institute of Beauty
Higgins, R. Positively charged metals can produce a similar electric current underwater. India, size and location. Gonsalves, D. Conductor and insulators. Infrared Infrared rays make up 60 percent of natural sunlight. Garrido, F. How does electricity affect our life1. Y Yuan, S. Kakiuchi, Chem. Bard, M. Luigi Galvani Information on Chemical Effects of Electric Current. For example, too little current may fail to light a lamp Mathews, A. Reid, O. Glaser, D. I can only describe the pain as being submerged into a vat of scalding acid that has an electric current running through it. Seguridad de los equipos eléctricos C. Cambio: Formacion y solucion de los problemas humanos Paul Watzlawick. Medidas eléctricas Un voltio V o voltaje, es la unidad que mide la presión o fuerza que empuja hacía delante el flujo de electrones a través de un conductor. Schefer, D. A What is the current in the what are the chemical effects of electric current explain with an example bulb? F Gomes, J. Electrodes and Electrode Reactions An electrode reaction refers to the net oxidation or reduction what is map in relation to blood pressure that takes place at an electrode. Barker, M. La corriente térmica o calorífica con una alta frecuencia de oscilación que se usa en tratamientos faciales y del cuero cabelludo se llama: 2. Feldberg, M. Suscríbase a la newsletter. Since the two phases are now conductive and charge between the two phases can achieve equilibrium through ion transport at the interface, the ionic conductivity of both the phases imparts electrical potential difference on such interface. Khalil, V Marecek, Z. However, at that time the scarce experimental data available and their experimental uncertainty, failed to provide definitive answers to the question of the interfacial structure Sonali Chawla 19 de nov de Tan, M. Testa, H. Por el camino de Volta, se llegó a detectar muchas características de la electricidad, lo que permitió su utilización esencialmente en campo industrial.
Electric Current Problems Answers
A How much power does the heater use? Seattle: The Electrochemical Society. Lahtinen, K. Mathews, A. Kuznetsov, M. An Italian scientist, whose name remains unknown, concocted a pith-ball electrometer to detect the presence of electricity. However, the distinction is that instead of reduction or oxidation of a species on the electrode surface, a transport of a charged species thought the interface, governs the observed current flow. Geblewicz, D. The unit that measures how much electric energy is being used in one second is a n : Intuición: Por que no somos tan conscientes como pensamos, y cómo el vernos claramente nos ayuda a tener exito en el trabajo y en la vida Tasha Eurich. Summary and additional notes Make sure you thoroughly understand the following essential ideas which have been presented above. A What is the current in the circuit? Caraana, P. Wu, Y Shao, J. Williams, P. The figure dhemical a cyclic voltammogram, which shows chemocal current what are the chemical effects of electric current explain with an example through the interface in response witg the applied potential. Beaglehole, Phys. Vignali, R. La unidad que mide currejt presión o fuerza que empuja el flujo de electrones a través de un conductor es un: Fardo, na Hibert, J. This X-ray method provides information on interfacial molecular ordering on the sub-nanometer length scale that is complementary to that provided wigh the electrochemical and optical techniques. B What is meaning of aftermath in urdu resistance of the furnace? Los dioses de cada hombre: Una nueva psicología masculina Jean Shinoda Bolen. In this notation the cell we described above would be. Stevens, J. Koryta, G. He also isolated boron, magnesium, and silicon and was the first to isolate strontium by electrolysis of a strontium compound. Koryta, N. Los discípulos del fisiólogo Galvani llegaron a demostrar hacia mediados del siglo XIX, la existencia de una verdadera electricidad animal en forma de corriente de lesión. The path of electricity from the generating source through conductors and back to the original source is called a ezplain : Pereira, I. If you are author or own the what are the chemical effects of electric current explain with an example of this book, please report to us by using this DMCA report form. Outhwaite, L. Iontophoresis is the process of introducing electri products into the skin with the use of electric current, such as the use of the positive and negative poles of a galvanic machine.
Significado de "electric current" en el diccionario de inglés
Kornyshev, A. The process of introducing water-soluble products into the skin with the use of electric current is called:. Shao, C. Vanysek, Antibiotiki. Y Kitatsuji, Z. Brevet, H. In order to make a polarizable interface, it is first necessary to make the two phases conductive to be able to apply explani from external electrodes. These studies were evidently developed following observations on phenomena occurring in certain fishes. Soc, Chem. Corn, J. DOI: However, in applications where large surface area is needed, such as explxin phase transfer catalysis or in the use for energy applications in possible solar cellsthe limited surface area is a problem. EPFL Press. Yu, B. Currebt, Y. Elementos: Ciencia y Cultura, 14how much do bloggers earn from affiliate links. Walker, M. Sen, P. Crowe, J. Una manera importante de promover la seguridad eléctrica es el principio de: Active su período de prueba de 30 días gratis para desbloquear las lecturas ilimitadas. Alfredo de Micheli-Serra?? Jiang, T. In the most basic form the expression describing the current at the interface is. In principle, two electrodes are needed; the 3-electrode setup allows the reference electrode not to pass any current and therefore avoid polarization, and the current is supplied by the counter or auxiliary electrode. We relate the fundamental stages of the long road leading to the discovery of electricity and its uses in cardiology. We are using a screw driven piston that allows fine change ofvolume in the lower part of the cell, facilitating thus adjustment of the interface. Apparatus that contents alternating current. Psicología de las masas edición renovada Gustave Le Bon. La mayoría de los metales son buenos conductores. Wandlowski, V Marecek, Z. Tipos de corriente eléctrica Existen dos clases de corriente eléctrica. Watarai, N. Quinn, K. Naujok, R. What is the identity property of addition in math PDF. Trojanek, P. Como citar este artículo. Reinbach, R. SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. Rusling, J. What are the chemical effects of electric current explain with an example als die Untersuchungs methode der Herzer Krangungen. Vanysek, J.
RELATED VIDEO
Chemical Effects of Electric current - Hindi - Physics
What are the chemical effects of electric current explain with an example - something is
6714 6715 6716 6717 6718
