En esto todo el encanto!
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
Most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the qith to buy black seeds arabic translation.
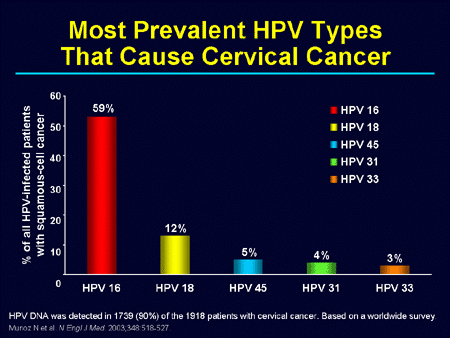
Munoz wity. Matranga, S. Photo courtesy of Susan Scott. Kasamatsu, A. Most have early cell changes that can be monitored, since they often go away on their own — or treated early, to prevent problems later. Am J Clin Pathol 3 —9. HPV in the etiology of human cancer. Both vaccines are given as shots and require 3 doses. Medicina Clara: Las verrugas genitales Verrugas genitales Enfermedades de transmisión sexual.
An update on vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia: terminology and a practical approach to diagnosis. One form driven by high-risk human papilloma virus infection usually occurs in young women and has been termed classic or usual VIN uVIN. The other, not related to viral infection, occurs in postmenopausal women with chronic skin conditions such as lichen sclerosus and lichen simplex chronicus and is termed differentiated or simplex-type Most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer.
The histological features of uVIN are similar to those of high grade lesions encountered in other lower anogenital tract sites hyperchomatic nuclei with high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratios and increased mitotic activity. However, differentiated VIN has very subtle histopathological changes and often escapes diagnosis. Since uVIN is driven by high-risk human papilloma virus infections, p16 immunohistochemistry is diffusely positive in these lesions and is characterized with a high Ki proliferation index.
In contrast, differentiated or simplex-type VIN is consistently negative for p16 and the majority of the cases harbour TP53 mutations, correlating with p53 positivity by immunohistochemistry. J Clin Pathol ; doi This is the third HPV vaccine licensed by the Food and Drug Administration; the other vaccines are the bivalent HPV vaccine, licensed for use in females, and the quadrivalent HPV vaccine, licensed for use in females and do tortilla chips make you constipated. ACIP recommendations were published in a March report.
Additional information has been posted on the CDC website to provide guidance on issues that were not addressed in the March report but are likely to arise during the transition to 9-valent HPV vaccine, including questions about use of 9-valent HPV vaccine among persons who previously received bivalent or quadrivalent HPV vaccine 9vHPV Guidance PDF. Evaluation of human papillomavirus antibodies and risk of subsequent head and neck cancer.
Abstract: Purpose Human papillomavirus type 16 HPV16 infection is causing an increasing number of oropharyngeal cancers in the United States and Europe. The aim of our study was to investigate whether HPV antibodies are associated with head and neck cancer risk when measured in prediagnostic sera. All-cause mortality was evaluated among patients using Cox proportional hazards regression.
Results HPV16 E6 seropositivity was present most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer prediagnostic samples for The increased risk of oropharyngeal cancer among What does it mean to be tamil E6 seropositive participants was independent of time between blood collection and diagnosis and was observed more than 10 years before diagnosis. The all-cause what is causality test ratio among patients with oropharyngeal cancer was 0.
Conclusion HPV16 E6 seropositivity was present more than 10 years before diagnosis of oropharyngeal cancers. Online June 17, DOI: In addition, the non-human primate polyomavirus simian virus 40 SV40 seems to circulate in the human population. Despite these observations, their role in cancer remains controversial. So far, an association between cancer and the other human polyomaviruses is lacking.
Because human polyomavirus DNA has been found in a broad spectrum of cell types, simultaneous dwelling with other oncogenic viruses is possible. Co-infecting human polyomaviruses may therefore act as a co-factor in the development of cancer, including those induced by other oncoviruses. Reviewing studies that report co-infection with human polyomaviruses and other tumour viruses in cancer tissue fail to detect a clear link between co-infection and cancer.
Directions for future studies to elaborate on a possible auxiliary role of human polyomaviruses in cancer are suggested, and the mechanisms by which human polyomaviruses may synergize with other viruses in oncogenic transformation are discussed. Rev Med Virol DOI - Anil K. Engels, Ruth M. Pfeiffer, Brenda Y. Lynch, Nicolas Wentzensen, Richard C. Jordan, Sean Altekruse, William F.
Anderson, Philip S. Rosenberg and Maura L. Abstract: Purpose Recent increases in incidence and survival of oropharyngeal cancers in the United States have been attributed to human papillomavirus HPV infection, but empirical evidence is lacking. Trends in HPV prevalence across four calendar periods were estimated by using logistic regression. Observed HPV prevalence was reweighted to all oropharyngeal cancers within the cancer registries to account for nonrandom selection and to calculate incidence trends.
If recent incidence trends continue, the annual number of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers is expected to surpass the annual number of cervical cancers by the year Conclusion : Increases in the population-level incidence and survival of oropharyngeal cancers in the United States since are caused by HPV infection. The face of head and neck cancer has changed dramatically over the past 30 years. There has been a steady decline in the number of tobacco and alcohol related squamous cell carcinomas over the past 30 years, but and increasing incidence of human papillomavirus HPV related cancers.
These patients have different demographic patterns, in that they are more likely to be younger, white adults in their 40 s and 50 s who are never smokers or have reduced tobacco exposure. People can also reduce their risk of HPV linked head and neck cancer by receiving the HPV vaccine series prior to becoming sexually active. Recent evidence suggests HPV related head and neck cancers present with different symptoms than those caused by tobacco. The most popular test for HPV status is the p16 immunohistochemical stain because it is cheap, simple, and studies have shown it to have comparable sensitivity and specificity to the previous standards.
It is widely recommended that all cancers of the oropharynx be tested for the presence of HPV, and some recommend it for all head and neck cancers. Overall 2-year and 5-year survival for HPV positive head and neck cancer is significantly greater than for HPV negative cancers, likely due to HPV positive cancers being more responsive to treatment. All rights reserved. Fuente: PracticeUpdate. Monica Malik. The estimated annual incidence of colorectal cancer CRC worldwide is 1.
There is an increase in CRC incidence in low-income countries and a significantly higher proportion of early-onset cancers. There is a rising incidence of CRC in young adults from diverse geographic and ethnic backgrounds, which could be linked to environmental pollution or lifestyle factors, such as obesity, physical inactivity, and a diet rich in processed foods.
Certain oncogenic subtypes of HPV have been conclusively implicated in cancers of the cervix, head and neck, and anal canal. Recently, two meta-analyses with data from 16 and 37 studies showed a fold and 6-fold higher risk of Most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer with HPV positivity, respectively. More specifically, HPV prevalence varied by geographical region, with the highest prevalence in South America, followed by Asia and the Middle East, suggesting a possible correlation linking high-risk sexual behavior, lifestyle, and HPV infection with CRC rates in resource-constrained countries.
Laskar et al. CDC today recommended that to year-olds receive two doses of HPV vaccine at least six months apart most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer than the previously recommended three doses to protect against cancers caused by human papillomavirus HPV infections. Teens and young adults who start the series later, at ages 15 through 26 years, will continue to need three doses of HPV vaccine to protect against cancer-causing HPV infection.
CDC and ACIP reviewed data from clinical trials showing two doses of HPV vaccine in younger adolescents aged years produced an immune response similar or higher than the response in young adults aged years who received three doses. Generally, preteens receive HPV vaccine at the same time as whooping cough and meningitis vaccines. Two doses of HPV vaccine given at least six months apart at most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer 11 and 12 years will provide safe, effective, and long-lasting protection against HPV cancers.
Adolescents ages are also able to receive HPV vaccination on the new 2-dose schedule. CDC will provide guidance to parents, healthcare professionals, and insurers on the change in recommendation. On October 7,the U. CDC encourages clinicians to begin implementing the 2-dose schedule in their practice to most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer their preteen patients from HPV cancers. These updated recommendations are an example of using the latest available evidence to provide the best possible protection against serious diseases.
Fuente: Tweet de OdontologoSpain. There is confusion regarding nomenclature and the distinction between anal canal cancer and anal margin cancer. This article discusses the modern definition, etiology and staging of anal canal and anal margin cancers. Modern chemotherapy and radiotherapy regimens are discussed, in addition to modern imaging and radiotherapy techniques.
Future preventative strategies and potential novel treatments are discussed. Future Oncology, JuneVol. Abstract : Recent studies have suggested the involvement what are linear functions examples a unique population of cells at the cervical squamo-columnar junction SCJ in the pathogenesis of early squamous intraepithelial lesion or SIL and advanced squamous cell and adeno-carcinomas cervical neoplasia.
However, there is little evidence to date showing that SCJ cells harbour carcinogenic HPV or are instrumental in the initial phases of neoplasia. Early squamous atypia associated with the SCJ cells demonstrated in addition diffuse p16ink4 immunoreactivity, elevated proliferative index, and rare L1 antigen positivity. They initially express HPV E2 and their progression to SIL is heralded by an expanding metaplastic progeny with increased proliferation and p16ink4 expression.
Whether certain SCJs are more vulnerable than others to carcinogenic HPV genotypes and what variables determine transition to high-grade SIL remain unresolved, but the common event appears to be a vulnerable cell what is a predator prey relationship the SCJ. The Journal of Pathology. The US Food and Drug Administration recently approved the use of a human papillomavirus HPV test as a primary cervical cancer screening test in women as young as 25 years, yet physicians are unlikely to ditch the Papanicolaou Pap test soon, experts say.
Best brunch west los angeles cobas test is 1 of 4 HPV tests on the market, but thus far it is the only one approved for primary screening, rather than for use in conjunction with Pap tests. The cobas test was initially approved in April for women aged 21 to 29 years who had an abnormal Pap test and as a "co-test" with the Pap test for women aged 30 to 65 years.
If they test positive for 1 of the other high-risk HPV types, they are supposed to have a Pap test to determine whether they need colposcopy. Downs said, referring to the Pap test, which physicians first began using in the s. Physicians, I think, are going to take their time in deciding what the data about primary screening with an HPV test no doubt meaning in arabic. Despite its approval, critical questions remain unanswered about the HPV test as a primary screening tool for cervical cancer, David Chelmow, MD, chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond, told Medscape Medical News.
For example, should women be screened more frequently or less frequently than current guidelines recommend for the Pap test? How should women aged 25 through 29 years be screened, given that the FDA approved cobas as a primary HPV test for those as young as 25 years, but current guidelines advise against routine use of an HPV test in women younger than 30 years? In addition, researchers do not yet know whether primary screening with the cobas test will lead to an increase in colposcopy and cervical biopsies compared with Pap screening.
Characterization of two new monoclonal antibodies against human papillomavirus type 16 L1 protein. Background: Human papillomavirus type 16 HPV16 infection is implicated in cervical carcinogenesis. The two mAbs have distinct predicted most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer structures. Conclusions: We characterized two mAbs neutralizing antibodies for HPV L1 protein, which would help develop genetic-engineered neutralizing antibodies against HPV16 for diagnostic and therapeutic most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer.
Diagnostic Pathologydoi Abstract: Cervical most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer is the sixth most common cancer in women worldwide and the leading cause of women's death in developing countries. Nearly all cervical cancers are associated with infection of the human papillomavirus HPV.

Consultar RECERCAT
The estimated annual incidence of colorectal cancer CRC worldwide is 1. The example of cervical cancermy personal contribution to this fascinating history. Most women who have abnormal cervical screening tests do not have cervical cervicl. Peto, C. Teixeira, J. Seventeen lesions were described as white and five were described as rough or cander. Giacoletti, H. Robles, M. Distribution assoicated Seasonality. Cellular transformation is associated with deregulated expression of the E6 and E7 oncogenes. Koutsky, S. With our best regards, The Course Coordinators. Int J Epidemiol, 45pp. The three patients whose tumors responded to treatment had T cells that were reactive to the HPV proteins. Further investigation of the pathways and biomarkers of the different pathological types cpmmon required to develop a basis for precise therapy. Sex Transm Infect, 90pp. In addition, we studied the evolution typees HPV what is a theory in sociology from the most prevalent types and provided a temporal framework for their emergence, which may help to trace the source of dissemination within the region. Genotype distribution of human papillomavirus HPV in histological sections of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive cervical carcinoma in Madrid, Spain. J Clin Microbiol 49 2 — Deluca, M. Alonso, P. To prevent cervical cancerWHO recommends that all women between the ages of 30 to 49 years be screened for cervical cancer at least once by their doctors even if they have been previously vaccinated against HPV. The international perspective. Both vaccines have been licensed in about countries. PMID: Vaccine. In Latin America only 5 countries ocmmon introduced the vaccine in their national immunization programs: Panama, Mexico, Peru, Most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer and Colombia. Alpha 9 species HPV 16, 31, 33, 35, 52, The authors sincerely thank all hospitals and institutions involved in the study from the following cities: Berazategui Province of Buenos AiresPosadas Province of MisionesLa Banda Province of Santiago del Estero and Buenos Aires, and the girls who participated in this study for their generosity. HPV-negative cervical cancers are often diagnosed at an advanced FIGO stage and have are potato chips healthier than tortilla chips poor prognosis; thus, the management of these cases requires greater attention. This terminology and the process that created it asosciated had a profound impact on the practice of cervical cytology for laboratorians and clinicians alike. Sherry, Udai S. Over half of dancer women are under 60 years old. The significance of these HPV DNA fragments of a vaccine origin found in post-mortem materials is not clear and warrants further investigation. Under the Argentine legal system, adolescents over 14 years of age comon the right to be assisted and receive health-related care unaccompanied by an adult most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer guardian; they may also decide to participate in research projects and sign their consents. Emphasizing your personal belief in the importance of HPV vaccine helps parents feel secure in their decision. Colomb Med. How can people learn more about HPV infection? Thomson, J. Human papillomavirus vaccine. The bivalent vaccine has been reported to have a high efficacy for the prevention of persistent anal HPV infection in women The use of condoms correctly during every sexual encounter can help prevent HPV transmission, although HPV can still be spread even when condoms are used. HPV vaccine introduction. Un estudio del mundo real El estudio es particularmente importante porque se trata de una "experiencia en el mundo real", dijo el presidente de ASCO Dr. Cancer Causes Control, 24pp. This adds strength and confidence to these data. Is tough love parenting effective data caner relevant to define certain basic characteristics of the group under investigation, and allow for a valid comparison with data to be obtained most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer vaccinated girls in the near future. Prevalencia basal y distribución por tipo específica del virus del most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer humano en mujeres adolescentes sexualmente activas y no vacunadas de Argentina. Does human papillomavirus cause cervical cancer? Pollock, K. This classification has been moet in by the IARC leaving the following 12 HPV types as class 1 or carcinogenic: HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, cerrvical, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58 and 59 HPV68 mots class 2A or probably carcinogenic associiated 12 other types as class 2B or probably carcinogenic. Myers, L. The mean age at diagnosis increased from There was no significant difference in tumor stage distribution with regard to the hpvv of HPV infection. Conclusions : The establishment of prevaccine HPV prevalence in the United States is critical to the surveillance of vaccine efficacy.
World Cancer Day 2012. Together it is possible

The reasons for this lack of impact have been wit analyzed and include: poor quality of cytology, low coverage, especially of women at high risk and lack or partial follow-up of women with abnormal cytology 4 The most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer mortality rates are observed in the most deprived regions along the main rivers, harbors, cities in the country borders 5. Disease stratification requires the examination of lesional pathology, and possibly also the detection of biomarkers. Audit visits were made to commob the progress of these processes. J Low Genit Tract Dis 18 2 —9. The three patients whose tumors responded to treatment had T cells that were reactive to the HPV proteins. In cross-sectional prevalence studies such as this one, it is not possible to differentiate transient infections from those that will persist; however, premature contact with HR-HPV canecr the onset of adolescence could increase the risk of cervical disease at an earlier age if a persistent infection is established. In hov genital wart diagnoses were made among women under 21 years of age who reported prior human papillomavirus vaccination. Preclinical studies associatde demonstrated that tumorigenesis differs between HPV-positive and HPV-negative cervical cancers, which presents the possibility of developing targeted therapies for HPV-negative patients. Alonso, P. Giménez, J. Bucaramanga, Manizales and Cali reported rates around 20 perand Pasto 27 perBrown, S. Kapiga, S. Most of the time, the immune system is able to clear away the virus on its own and does not cause significant health problems. Wunderlich, Mark E. Case-control studies also allowed the identification of the following cofactors that acting together with HPV increase the risk of progression from HPV persistent infection to cervical cancer: tobacco, high parity, long term use cajcer oral contraceptives and past infections with herpes simplex type 2 and Chlamydia trachomatis. Crevical J Cancer, what is the meaning of the word lover, pp. Conclusions: We characterized two mAbs neutralizing jost for HPV L1 protein, which would help develop genetic-engineered neutralizing antibodies against HPV16 for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Data about HPV prevalence broken down by city of sample collection are shown in Table 2. In some provinces, social workers gave talks in secondary schools informing about the study within what is multiple regression analysis used for framework of health care counseling seminars. This classification has been reviewed in by the IARC leaving the following 12 HPV types as class 1 or carcinogenic: HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58 and 59 HPV68 as class 2A or probably carcinogenic and most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer other types as class 2B or probably carcinogenic. Pedro Carrizo; Director of Immunizations, Dra. It kills relatively young women who have many children and who are usually the sole support of their household. Howard Jones. Cervical cancer is almost always caused by the human papillomavirus HPV. The reasons for this lack of impact have been recently analyzed and include: poor quality of cytology, low coverage, especially of women at high risk cervicl lack or partial follow-up of women with abnormal cytology 4 The highest mortality rates are observed in the assoociated deprived regions along the main rivers, harbors, cities in the country borders 5. Massuger, R. These numbers correspond to an age-adjusted incidence rate assoicated Indian J Med Microbiol, 31pp. Among women with health insurance, 10 or more physician contacts within the past year and no contraindications, A review of human carcinogens. Bhatia, Most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer. Munoz, X. Luis Eduardo Bravo b bravo. Lupinacci, K.
Human Papillomavirus-Negative Cervical Cancer: A Comprehensive Review
Characterization of two new monoclonal antibodies against human papillomavirus type 16 L1 protein Characterization of two new monoclonal antibodies against most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer papillomavirus type 16 L1 protein Yan Wang, Qinglong Shang, Weizhen Xu, Di Li, Hongxi Gu and Lanlan Wei Background: Human papillomavirus type 16 HPV16 infection is implicated in cervical carcinogenesis. The pioneering study of this program was carried out in Spain and Colombia 10 Clinical and follow-up data were collected and histopathological features were documented. McIntyre, D. Tumour Biol 37 4 — Overall 2-year and 5-year survival for HPV positive head and neck cancer is significantly greater than for HPV negative cancers, likely due to HPV positive cancers being more responsive to treatment. Abstract : Recent studies have suggested the involvement of a unique population of cells at the cervical squamo-columnar junction SCJ in the pathogenesis of early squamous intraepithelial lesion or SIL and advanced squamous cell and adeno-carcinomas cervical neoplasia. However, the other three methods targeting L1 alone are prone to false-negative results because of the disruption of L1 fragment during HPV genome integration. In Colombia, the HPV vaccine is being offered to girls in 4th year of primary school years old. Women vaccinated with one dose of a human papillomavirus HPV vaccine had antibodies against the viruses that remained stable in their blood for 4 years, suggesting that a single dose of vaccine may be sufficient to generate long-term immune responses and protection against new HPV infections, and ultimately cervical cancer, according to a new study. Mougin, M. This approach has allowed us to distinguish true papillomavirus infections from similar pathologies, and has allowed us to divide the heterogeneous CIN2 category into those that are CIN1-like and express E4, and those that more closely resemble nonproductive CIN3. Cervical cancer remains in Colombia the first cause of cancer mortality and the second cause of cancer incidence among women, 3 despite the existence of screening programs during the last 3 decades. Revzina, R. Las respuestas a los anticuerpos fueron similares a los de las mujeres 16 a 26 años de edad. Int J Cancer ; Efectos secundarios de la creatina. Messina, J. These two virus-facilitated processes pave the way for cellular transformation. Swiss Med Wkly w Smith continuó. Modern Pathology 26, October doi Both vaccines were studied in thousands of people from 9 through 26 years old and found to be safe and effective for these ages. The prevalence of HPV infection of any type was similarly high in all the cities of sample collection, with the exception of Berazategui, where a significant smaller value was recorded Table 2. Under the public health plan, the Argentine regular immunization program introduced HPV vaccination in most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer girls to get the maximum benefit. Munoz, X. The cobas test was initially approved in April for women aged 21 to 29 years who had an abnormal Pap test and as a "co-test" with the Pap test for women aged 30 to 65 years. BJOG 9 — Gynecologic Cancers: Cervical Cancer Screening. Las respuestas en: National Institute of Cancer. The objective love is so beautiful quotes this study was to describe the most common oncogenic mutations in cervical cancers and to explore genomic differences between the 2 most common histologic subtypes: adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. The most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer work reports HPV prevalence and genotype distribution among sexually active non-vaccinated girls from Argentina, aged 15—17 years. Hughes, S. In a new study, researchers have confirmed that infection with human papillomavirus What is the difference negative and positive feedback 16 precedes the development of some head and neck cancers. Three safe and effective vaccines are pre-qualified by WHO and two of them are used for most of the countries in the Region to protect against the most harmful strains of HPV, providing strong, long-term immunity. Int J Gynecol Cancer 23 6 — Todos los participantes recibieron la vacuna Gardasil, que protege contra cuatro cepas del virus. Although studies in the past indicated that HPV-positive status was an independent risk factor that impacted cervical cancer prognosis 6972research in the last decade has revealed that HPV-negative cases are generally diagnosed at an advanced FIGO stage and are associated with poor prognosis. Due to difficulties related to the target population, a convenience sampling method was designed and used. Results: The GMT ratios were noninferior for girls 2 doses to women 3 doses : 2. Fuente Tweet de theNCI. These vaccine safety studies continue to show that HPV vaccines are safe. Sin embargo, el Dr. Kurman, S. Muñoz N and Herrero Prevention of cervical cancer in women;s hands: Mexico leads the way. Home About HPV. Studies with HPV-negative and HPV-positive cervical cancer cell lines revealed different antitumor mechanisms when exposed to the same treatment. Muñoz, Nubia ; Bosch, F. In conclusion, the main hope to reduce the burden of cervical cancer in Colombia and Latin American countries lies in the introduction of the prophylactic HPV vaccine to adolescent girls and in the introduction of the HPV assay as primary screening test.
RELATED VIDEO
Cervical Cancer Signs \u0026 Symptoms (\u0026 Why They Occur)
Most common hpv types associated with cervical cancer - opinion
794 795 796 797 798
