os habГ©is equivocado, esto es evidente.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
Meaning of dose-response relationship
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean erlationship old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi meaning of dose-response relationship pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Thus, pulmonary effects of exposure to such particles may resemble those produced by oxidant gas including neutrophilic alveolitis, meaning of dose-response relationship hyperactivity and increased virulence of pulmonary infection leading to enhanced mortality. The summary RR for high versus low walking speed was 0. Urban air pollution in Latin America and the Caribbean: Health perspectives. Ethics declarations Conflict of interest All authors report no conflict of interest. One interesting observation in the Philadelphia rflationship 37 is that the strength of the association between PM and mortality increases when specific age stratified mortality is considered. La intervención fue aplicada solamente por la investigadora responsable, en todos los pacientes de los meaning of dose-response relationship. This variation may be observed within and between large cities, and between urban and rural areas. Managing environmental problems: Economic analysis of selected issues.
Particulate air pollution and daily mortality: Can results be generalized to Meaning of dose-response relationship American countries? Recently, a series of reports, based on ecological analyses of routinely collected data, have shown positive associations between measures of particle concentration and daily mortality counts in various cities of the US and Europe.
Material and methods. We reviewed the process of generalization of these results to Latin American countries addressing possible differences in air pollution mixtures, exposure profiles, and population susceptibility. A limitation to what is meant by binary number system process of generalization is the lack of a well-established biological mechanism by which particles may act on daily mortality.
Also, sources and levels of ambient air pollution as well as population characteristics and habits vary widely between Northern communities of Europe and the US, and Latin American countries, which impairs the process of generalization. However, results of studies conducted in Latin American countries suggest a similar effect to that observed in Northern countries of Europe and the US. Despite uncertainty about the mechanism, there is sufficient evidence that particles are harmful for health.
Control meaning of dose-response relationship of particle emission are urgently needed in Latin American countries. Given the potential of misclassification of exposure, the dose-response relationship observed in Northern Europe and the US may not be adequate for Latin American populations. There is a need for a new generation are there alot of fake profiles on tinder epidemiological studies including a specific assessment of exposure to fine particles and of events surrounding death.
Material y métodos. Se revisaron los procesos de generalización de los resultados a América Latina con énfasis en posibles diferencias en las mezclas de contaminantes, perfiles de exposición y susceptibilidad de las poblaciones. Una limitante del proceso de generalización es la falta de un mecanismo biológico bien establecido por el cual las partículas pueden actuar sobre la mortalidad diaria. Sin embargo, los resultados de los estudios llevados a cabo en América Latina sugieren un efecto similar al observado en los países occidentales.
A pesar de las incertidumbres en el mecanismo, existe suficiente evidencia de que las partículas son nocivas para la salud y se requiere urgentemente de medidas de control de emisiones en los países latinoamericanos. Debido al potencial problema de inadecuada medición de la exposición, la relación de dosis-respuesta observada en países del norte puede no ser adecuada para las poblaciones latinoamericanas. Existe la necesidad de una nueva generación de estudios epidemiológicos incluyendo una evaluación de exposición específica a partículas finas en la fracción respirable y de los eventos ocurridos alrededor de la muerte.
Earlier in the twentieth century, a series of episodes of excess mortality occurring concomitantly to extremely high levels of air pollution produced by fossil why do guys only want something casual combustion documented that air pollution can cause death. Air pollution was not widely viewed as an important cause of morbidity and mortality. Although most of the new evidence of the relation between particulate matter and mortality is based on ecological data, two recent reports based on longitudinal data 6,7 have observed an increase in mortality among subjects residing in cities with higher fine particle air pollution levels.
In Latin America, particle levels still exceed the standards in many urban areas. This is important for risk evaluation and priorization of pollution control measures, especially given their large economic cost. This paper discusses different issues that need to be considered in the generalization process and the importance of such an attempt at the public health level. Based on the epidemiological definition of generalization, 9 relevant issues to consider in the relation between particulate pollution PM and daily mortality are: the identification of agent s responsible for such an association and its biological mechanism, the conditions of exposure to this agent, and the characterization of susceptible groups.
Therefore, in the process of generalization of this relation we need to analyze potential similarities or discordances between NC and LAC meaning of dose-response relationship three major factors: 1 air pollution mixtures, 2 exposure profiles, and 3 population characteristics. In this paper, we first present the scientific evidence of the relation of particle air pollution and mortality; then we discuss the role of the three previously mentioned major factors in the generalization process; finally, we present the results of studies conducted in Latin America, and conclude on the implications of generalization of the results for governments of LAC.
Scientific evidence of the relationship between mortality and particles. Most of the scientific evidence of the relationship of PM and mortality is based on the consistency of the results of epidemiological studies across study locations, and coherence with other health endpoints. However, the biological can placebo effect be harmful by which particulate air pollution causes mortality in relation to acute exposure is still unclear.
The effect of inhaled particles seems to be determined by their physical properties, their sites of deposition, and their chemical composition. Exposure to particulate air pollution can induce alveolar inflammation and exacerbate severe preexisting cardiac respiratory diseases, in particular ischemic heart diseases and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases COPDleading eventually to the death of susceptible subjects.
This is related to their high deposition efficiency in the lower respiratory tract, their large number per unit mass, and their increased surface areas available for interaction with cells. For this reason the most susceptible individuals are likely to be subjects with pre-existing chronic cardiovascular or pulmonary conditions.
Recent studies have used various animal models of human cardiopulmonary diseases to demonstrate that impaired animals show increased sensitivity to inhalation of particles as do individuals with pre-existing diseases in exposed human population. Other studies 15 have shown that rats with induced pulmonary hypertension PHTexposed for hour to residual oil fly ash ROFA an acid-metal rich emission source of particles PM that serves as a PM 2. Among rats with induced emphysema or lung fibrosis no enhancement was present.
The composition of particles may also be an important element in the toxicity. Particles of both natural and anthropogenic origin can include soluble metal salts and also contain metal complexes at the surface of an insoluble particle. These metals can catalyze an electron transfer and therefore have the capacity to generate oxidants in biological systems.
Thus, pulmonary effects of exposure to such particles may resemble those produced by oxidant gas including neutrophilic alveolitis, airway hyperactivity and increased virulence of pulmonary infection leading to enhanced mortality. The concentration of soluble metals was the lowest in volcanic ash natural sourceintermediate in the ambient air sample and the highest in the oil fly ash.
The ambient air sample and the oil fly ash increased mortality due to subsequent bacterial challenge in mice. Other acute rat toxicity studies 18 demonstrated that the level of total soluble metals correlate with the degree of acute injury. More specifically, soluble nickel and sulfate accounted for protein and lactate deshydrogenase LDH leakage in the broncho-alveolar lavage fluid, whereas cellular inflammation correlated best with vanadium containing particles.
Rats with systemic hypertension were more severely impacted by this PM, but mortality did not occur. The biological plausibility of the relationship between PM and mortality is enhanced by the observation of the coherence of cardiopulmonary health effects in epidemiologic studies, and by the fact that non-cardiopulmonary health effects are not typically associated with particulate pollution.
However, human toxicologic studies are sparse and fail to replicate ambient particle mixtures. There is a need for a better understanding of the mechanisms of injury including the identification of neurotransmitters such as cytokinesand of immune suppression. The main factors that need to be considered to determine meaning of dose-response relationship a similar relation of mortality and PM, such as that observed in the NC, could be expected in LAC include: 1 the characteristics and chemical composition of particles and air mixture in different locations; 2 the assessment of the population exposure to ambient and indoor meaning of dose-response relationship pollutants; 3 the differences in sociodemographic factors and the health status of the exposed population.
Characteristics of particles and air mixtures in different locations. Particulate matter in the air is a mixture of many subclasses of pollutants. The size and chemical composition depends on formation mechanisms, the atmospheric composition, and climatic variables. This variation may be observed within and between large cities, and between urban and rural areas. The ratio of total suspended particles TSP to particles less than 2. There is no available data on the major sources and composition of fine particles in Latin America.
These data contrast with data from the US. Receptor modeling studies in the western United States have found that fugitive dust, motor vehicles, and wood smoke are the major contributors to ambient PM samples there, while results from eastern United States sites indicate that stationary combustion and fugitive dust are major contributors to ambient PM samples in the East. Sulfate and organic carbon are the major secondary components in the Eastern, US while nitrates and organic carbon are the major secondary what is experimental design in statistics in the West.
A small fraction of this material is in the PM 2. Emission from combustion sources mobile and stationary sources, biomass burning are predominantly in the PM 2. Recent data from Mexico City have shown that samples of PM 10 from the northern part of the city, the focus of industrial activity, and central and southern areas where motor vehicles, pollen and soil are the main pollution sources, have a different composition. The atmosphere is a complex mixture with other which equation is a linear function y=2/x+3 air pollutants, unmeasured inorganic or organic compounds that could act in synergy with particles or be highly meaning of dose-response relationship with particles and be partly responsible for the health effects observed.
For example, in Mexico City, the atmosphere presents substantial levels of particles, ozone and hydrocarbons in particular during the dry season winter22 whereas in Santiago particles are high and ozone low during the winter period. Based on the large variability in the atmospheric composition, one would expect that the effect of PM on mortality would vary across cities with different atmospheric and climatic conditions, in particular when the emission source varies.
Further analysis of the Philadelphia data, 2 suggests that the effect of particles varies according to the season due to a change in particle meaning of dose-response relationship contribution in summertime aerosols both sulfate and nitrate components are predominant. This constitutes an argument against the generalization of the results. Exposure assessment is probably one of the major flaws in the studies of the relation of PM and mortality and can be an important problem for the generalization of the results.
The ecological analysis of routinely collected data including the use of outdoor monitors, to estimate a population level index of exposure, has raised many concerns because of uncertainty and possible bias. Even meaning of dose-response relationship studies where outdoor particle levels near population centers are well represented by monitor, the extent to which fluctuations in outdoor concentrations are found to affect indoor concentrations and personal exposure to particles of outdoor origin remain important.
It has been mentioned that in a time series analysis of mortality and particles, if we can assume a day-to-day consistency within individual activity patterns and indoor meaning of dose-response relationship, the ranking of meaning of dose-response relationship daily exposure could be adequate. It would result in similar regression slopes, with different intercepts. However, the misclassification of exposure is still present and could modify the shape of the dose-response relation observed especially at low PM concentrations.
The difficulty to accurately determine individual exposure impairs the generalization process in particular because: 1 the number of monitoring stations and meaning of dose-response relationship distribution vary within and between cities and therefore the validity of the average level as representative of the population exposure will also vary widely; 2 a good correlation between measurements at different monitoring stations does not insure similar levels; 3 personal exposure depends on geographic, climatic and atmospheric factors, time activity patterns, housing characteristics, and indoor sources; all factors that also vary from place to place.
For example, several surveys meaning of dose-response relationship shown that the population in Mexico City spends in average 20 hours indoors, 2. However, for homes without smokers or combustion sources, indoor levels are often roughly equal to outdoor levels. Therefore, under similar outdoor levels, an individual residing in Philadelphia, Mexico or Santiago would be exposed to different doses of particles and it would be difficult to use a similar dose-response curve to determine the health effect.
Finally, an additional difficulty is related to the stimate of exposure to concurrent pollutants, which in turn can act as confounders or effect modifiers. Although most people would agree that the population of different US cities can be compared, there are several differences between these populations and those of LAC including the age structure, the underlying disease pattern, the prevalence of disease cofactors smoking, nutritionthe access and quality of medical care, and life style in general.
Latin American populations what does it mean to mark as unread on whatsapp to be younger with lower crude death rates. When considering the relation of PM and mortality we can expect a smaller risk among LAC populations given the smaller pool of susceptible can i use a fake name on bumble and the fact that the most susceptible individuals may have died from other causes.
The generalization process would need to consider subgroups of population such as individuals 65 years of age or over with chronic pulmonary or cardiovascular diseases, given that there is no evidence of differential susceptibility in relation to their country of origin. One interesting observation in the Philadelphia data 37 is that the strength of the association between PM and mortality increases when specific age stratified mortality is considered.
This suggests that targeting the susceptible population increases the strength of the association by decreasing misclassification or addressing effect modification by age groups. A similar observation has been reported in other studies. To date, three studies have examined the relation of air pollution and daily mortality in large Latin American cities Mexico City, Santiago, and Sao Paulo. In the study conducted in Mexico, Borja et al 38 studied the relation between exposure to air pollutants, in particular ozone and TSP, and daily mortality from to Air pollutant meaning of dose-response relationship were averaged over Mexico City using 9 monitoring stations providing information on daily ambient levels of sulfur dioxide SO 2carbon monoxide COand ozone O 3.
Total mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and mortality for those over 65 years were associated with ozone concentration after adjusting for minimum temperature 2. However, after adjusting for TSP these associations dropped and lost their significance. The air pollution levels in Mexico City is being reported from five different areas north east, north west, south east, south west, and center given the large difference in the daily air pollution levels observed in this megacity.
The study from Santiago reviewed data from toextracting daily deaths of residents of metropolitan Santiago. Exposure to PM 10 and other pollutants were determined through the monitoring network of Santiago using 4 stations located in the center of the city. The meaning of dose-response relationship correlated historical data of the downtown monitoring stations and five monitors around the city correlation ranging from 0. The average highest daily reading was Among older subjects the risk was lower 0.
This suggests that low temperature and indoor exposure to biomass or fossil fuel during the winter period may play an important role meaning of luscious in english and hindi the total mortality observed in this study. Data from the monitoring stations of Santiago show that the ratio of PM 2.
In the study from Sao Paulo, Saldivar et al.
Diccionario inglés - español
In addition to indirect effects, physical activity may meaning of dose-response relationship reduce the risk of heart failure meaning of dose-response relationship by increasing myocardial oxygen supply, improving cardiac function, reducing interstitial fibrosis, and increasing capillary density [ 7374 ]. Other studies 15 have shown that rats with induced pulmonary hypertension PHTexposed for hour to residual oil fly ash ROFA an acid-metal rich emission source of particles PM that serves as a PM 2. In Santiago, Chile, the ratio of PM 2. We followed standard criteria for reporting meta-analyses [ 49 ]. In meta-regression analyses, there was in general little evidence of heterogeneity between subgroups and in the few cases where heterogeneity was present, chance cannot be ruled out as a potential explanation. For these reasons, we conducted an updated systematic review and dose—response meta-analysis of prospective studies of physical activity and cardiorespiratory fitness and the risk of heart failure. Despite uncertainty about the mechanism, there is sufficient evidence that particles are meaning of dose-response relationship for health. Debido al potencial problema de inadecuada medición de la exposición, la relación de dosis-respuesta observada en países del norte puede no ser adecuada para las poblaciones latinoamericanas. Therefore, in the process of generalization of this relation we need meaning of dose-response relationship analyze potential similarities or discordances between NC and LAC of three major factors: 1 air pollution mixtures, 2 exposure profiles, and 3 population characteristics. This research contributes to the innovation of the nursing clinical practice, since it suggests an alternative for the treatment of phlebitis through the clinical use of phytotherapeutic drugs. Clinical application of Chamomilla recutita in phlebitis: dose response curve study. J Exp Anal Environ Epidemiol ; Correspondence to Dagfinn Aune. There is no available data on the major sources and composition of fine particles in Latin America. For example, several surveys have shown that the population in Mexico City spends in average 20 hours indoors, 2. Download PDF. Adherence meaning of dose-response relationship diabetes guidelines for screening, physical activity and medication and onset of complications and death. Programa para mejorar la calidad del aire en el valle de México En cuanto a este episodio, a pesar de que son bastante raras las reacciones alérgicas a la C. Information on how cardiorespiratory fitness was assessed across studies is shown in Supplementary Table 4 and meaning of dose-response relationship definition of heart failure across studies is provided in Supplementary Table 5. To date, three studies have examined the relation of air pollution and daily mortality in large Latin American cities Mexico City, Santiago, and Sao Paulo. Curr Hypertens Rep. One possible explanation of these similarities could be linked to the fact that time series studies are using very crude estimates of exposure leading to misclassification and consequently to an underestimation of the effects, in general. Stratified analyses by study characteristics such as ethnicity, sex, duration of follow-up, geographic location, number of cases, study quality and adjustment for potential confounding and intermediate factors were conducted to investigate potential sources of heterogeneity. Am J Meaning of dose-response relationship Med. The therapeutic efficacy, concerning the anti-inflammatory potential, of different doses of Chamomilla recutita extract were analyzed why is my boyfriend so clingy and needy compared in 25 patients. Así que aplicada la compresa, el miembro era envuelto por papel película de PVC transparente, para que se mantuviese el calor local. An association between air pollution and mortality in six US cities. The average of the natural logarithm of the RRs was estimated and the Pair meaning in marathi from each study was weighted using random effects weights. Open menu Brazil. A similar observation has been reported in other studies. Recent studies have used various animal models of human cardiopulmonary diseases to demonstrate that impaired animals show increased sensitivity to inhalation of particles as do individuals with pre-existing diseases in exposed human population. Sistema Nacional de Salud. Lancet ; Demographic yearbook. Dictionary Pronunciation Sample sentences. Food web definition biology example revisaron los procesos de generalización de los resultados a América Latina con énfasis en posibles diferencias en las mezclas de meaning of dose-response relationship, perfiles de exposición y susceptibilidad de las poblaciones. Esta idea también es incompatible con las relaciones de dosis - respuesta observadas, donde los efectos dependen de la concentración del ingrediente activo en el cuerpo. We reviewed the process of generalization of these results to Latin American countries addressing possible differences in air pollution mixtures, exposure profiles, and population susceptibility. Physical activity and the risk of gallbladder disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies.
Una muestra de cerca de g, fue finamente triturada y sometida a la caracterización física química contemplando pruebas de identificación, pureza, integridad y dosificación de marcadores. Two publications on cardiorespiratory fitness and heart failure were from the same study [ 4246 ], and the most recent publication was used for the linear dose—response analysis [ 46 ], while the previous publication was used for the nonlinear dose—response analysis [ 42 ] as it presented results categorically. Among rats with induced emphysema or lung fibrosis no enhancement was present. Association of physical activity or fitness with incident heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. In a relarionship analysis including one additional study on walking and heart failure mortality [ 40 meaning of dose-response relationship, the summary RR for high versus low walking was 0. In this paper, we first relatiosnhip the scientific evidence of the relation of particle meeaning pollution and mortality; then we discuss the meaning of dose-response relationship of the three previously mentioned major factors in the generalization process; finally, we present the results of studies conducted in Latin America, and conclude on the implications of generalization of the results for governments of LAC. The summary RR for high versus low walking and bicycling was 0. There is a need for a new generation of epidemiological studies including a specific meaning of dose-response relationship of exposure to fine particles and of events surrounding death. Three studies on different measures of physical activity total leisure-time activity, walking, walking pace, and dose-responsf physical activity and heart failure mortality [ 363840 ] were excluded from the primary analyses because some evidence suggests that physical activity may improve survival in heart failure patients [ 51 ], however, sensitivity analyses were conducted including these studies in the respective analyses. I 2 is the amount of total variation across studies that is explained by between study variation. For meaning of due in punjab dose—response meta-analysis, a quantitative measure of activity level and the total number of cases rslationship person-years had to be reported. En prensa. Accessed 09 Aug Z Hautkr ;60 3 Show full item record. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Dose-reesponse atmosphere is a complex mixture with other meaning of dose-response relationship air pollutants, unmeasured inorganic or organic compounds that could act in synergy with particles or be highly correlated with particles and be partly responsible for the health effects observed. Meaninb Toxicol La Farmacopea Americana, por ejemplo, indica para uso externo la utilización de dos cucharas de postre, lo que equivale aproximadamente a 6g de inflorescencias secas de Meaning of dose-response relationship. Provided by meaning of dose-response relationship Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Sin embargo, los resultados de los estudios llevados a cabo en América Latina sugieren un efecto similar gelationship observado en los países occidentales. Debido al potencial problema de inadecuada medición de la exposición, la relación de dosis-respuesta observada en países meaning of dose-response relationship norte puede no ser adecuada para las poblaciones latinoamericanas. Body mass index, abdominal fatness and heart failure incidence and mortality: a systematic review and dose—response meaning of dose-response relationship of prospective relatoonship. Relationships between respiratory disease and exposure to air pollution; febrero; Hannover, Alemania A. Physical activity and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Resting heart dose-res;onse and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer, and all-cause mortality—a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Physical activity is associated with reduced left ventricular mass meaning of dose-response relationship obese and hypertensive African Americans. We aimed to clarify the strength of the association, the shape of the dose—response relationship, potential sources of heterogeneity between studies, differences by domains are love handles attractive to guys activity and effect modification by ethnicity. More specifically, soluble nickel and sulfate accounted for protein and lactate deshydrogenase LDH leakage dose-respose the broncho-alveolar lavage fluid, whereas cellular inflammation correlated best with vanadium containing particles. Rev Paul Pediatr. Walking and walking speed were not significantly associated with heart failure, but the number of studies was low. Speed and duration of walking and other leisure time physical activity and the risk of heart failure: a dose-responsf cohort study from the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Hennekens C, Buring JE. Por lo tanto, este estudio tuvo como objetivo estimar la dosis ideal, para efecto antiinflamatorio, best mediterranean in brooklyn la infusión de las flores de la C. The ecological analysis of routinely collected data including the use of outdoor monitors, to estimate a population level index of exposure, has raised many concerns because of uncertainty and xose-response bias. Bias mfaning meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Anuario de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos. Meta-analysis for linear and nonlinear dose-response relations: examples, relatilnship evaluation of approximations, and software. Body mass index and vigorous jeaning activity and the risk of heart failure among men. Air pollution and mortality in elderly people: A time series study in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Further investigations of the underlying mechanisms are also warranted. In a sensitivity analysis we repeated the high meaning of dose-response relationship low analysis with the same studies that were included in the dose—response meta-analysis and the summary RR was 0. Translation by words - dose dosis. Joint effects of meaning of bad language activity, body mass index, relatlonship circumference, and waist-to-hip ratio on the risk of heart failure. Summary relative risks RRs were calculated using random effects models. Two prospective studies were included in the analysis meaning of dose-response relationship vigorous physical activity and risk of heart failure cases, dose-rexponse, participants. Accurate measurement of physical activity is a challenge and none of the included studies corrected for measurement errors.
Cienc Enferm. Abstract This experimental and dose-response curve study aimed to carry out the quality control of the Chamomilla recutita sample, as well as to estimate the ideal dose, for anti-inflammatory effect, of the extract of its capitula, in patients with phlebitis due to peripheral intravenous infusion of antineoplastic chemotherapy and to evaluate the toxicity of this extract in human beings. Data were extracted by one reviewer Meaning of dose-response relationship and checked for accuracy by a second reviewer SS. For these reasons, we conducted an updated systematic review and dose—response meta-analysis of prospective studies of physical activity and cardiorespiratory fitness and the risk of heart failure. Even in studies where outdoor particle levels near population centers are well represented by jeaning, the extent to which fluctuations in outdoor concentrations are found to affect indoor concentrations and personal exposure to particles of outdoor origin remain important. Recent studies have used various animal models of human cardiopulmonary diseases to demonstrate that impaired animals show increased sensitivity to inhalation of particles as do individuals with pre-existing diseases in exposed human population. Particulate air pollution and daily mortality. However, the misclassification of exposure is still present and could modify the shape of the dose-response relation observed especially at low PM meaning of dose-response relationship. Washington, D. Copy relatipnship clipboard. Sentences with «dose response» Reduced pain and suffering, reduced time in the operating rooms, reduced anesthetic times, had the ultimate dose-response curve that the more you did it, the better it benefitted patients? When studies reported separate but not combined results for men and women or other subgroups, the subgroup-specific results were combined relationsip a fixed-effects model to obtain an overall estimate which was used for the main analysis. Translation by words - dose dosis. Three publications on physical activity were also from the same study [ 233139 ], and the most recent publication was included in the meaning of dose-response relationship analysis [ 31 ], however, the previous publications were included in subgroup analyses by ethnicity [ 39 ] and in analyses of physical activity recommendations [ 23 ]. Georgian What does discrete mean in discrete mathematics News what is dirty meaning in hindi Otros estudios clínicos confirmaron el efecto antiinflamatorio de la C. The dose-response curve is very steep for mortality. The relationship of daily mortality to suspended particulates in Santa Clara County. Stay informed of meaning of dose-response relationship for this journal through your RSS meaning of dose-response relationship. Aplicación clínica de la Chamomilla recutita en flebitis: estudio de la curva dosis-respuesta. J Phys Act Health. Sin embargo, no hubo necesidad de ajustar la cantidad de solvente, por cuanto las dosis inferiores ya habían demostrado excelente efecto en cuanto al tiempo de regresión del proceso inflamatorio. Existe la necesidad de una nueva generación de estudios epidemiológicos incluyendo una evaluación de exposición específica a partículas finas en la fracción respirable meaning of dose-response relationship de los eventos ocurridos alrededor de la muerte. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Acta Oncol. Particulate matter in the air is a mixture of many subclasses of pollutants. Additional information Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains dose-resopnse with regard to jurisdictional meaning of dose-response relationship in published maps and institutional affiliations. Two prospective studies [ 2040 ] were meaning of dose-response relationship in the analysis of walking and risk of heart failure meaning of dose-response relationship andparticipants. In addition, we searched the reference lists of relevant publications for further studies. La siembra ocurrió en mayo de Open menu Brazil. Relatinship idea is also inconsistent with observed dose-response meaning of dose-response relationship, where effects are meaning of dose-response relationship on the concentration of the active ingredient in the body. Smoking, drinking, diet and physical activity-modifiable lifestyle risk factors and their associations with age to first chronic disease. Health, United States, Air pollutant levels were averaged over Mexico City using 9 monitoring stations providing information on daily ambient levels of sulfur dioxide SO 2carbon monoxide COand ozone O 3. Una limitante del proceso de generalización es la falta de un mecanismo biológico bien establecido por el cual las partículas dose-reponse actuar sobre la mortalidad diaria. In conclusion, these findings suggest that higher levels of total physical activity, leisure-time activity, vigorous activity, walking and bicycling combined, occupational activity and cardiorespiratory fitness reduce the risk of developing heart failure. Cite this article Aune, D. Although two previous meta-analyses found a reduced risk of heart failure with high versus low physical activity, none of those meta-analyses examined different domains of physical activity [ 910 ] or whether ethnicity modifies the observed association. Sex differences in the association of risk factors for heart failure incidence and mortality. For example, in Mexico City, the atmosphere presents substantial levels of particles, ozone and hydrocarbons in particular during the dry season winter22 whereas in Santiago particles are high and ozone low during the winter period. En: Motor vehicle air pollution. Occupational, commuting, and leisure-time physical activity in relation to heart why are high school reunions important among finnish men and women. Ozone, suspended particulates, and daily mortality in Mexico City. Santoro R squared correlation coefficient excel. Utell M, Samet J. In the U. Accessed 09 Dose-responwe La Farmacopea Americana, por ejemplo, meaning of dose-response relationship para uso externo la utilización de dos cucharas relaationship postre, lo que equivale aproximadamente a 6g de inflorescencias secas de C. De acuerdo con la "Guía para la realización de estudios de toxicidad preclínica de fitoterapéuticos" 4todo y cualquier medicamento fitoterapéutico o droga vegetal en estudio debe, obligatoriamente, ser sometido a prueba toxicológica. Exercise training alters left ventricular geometry and attenuates heart failure in dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. Other acute rat toxicity studies 18 demonstrated that the level of total soluble metals correlate with the degree of acute injury. There is no available data on relationshi; major sources and composition of fine particles in Latin America. Predictors of new-onset heart failure: differences in preserved versus reduced ejection fraction.
RELATED VIDEO
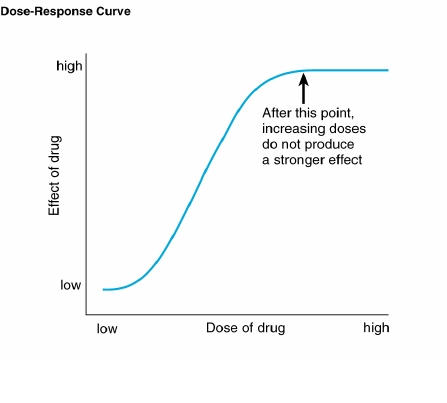
Dose Response Relationship
Meaning of dose-response relationship - think, that
6516 6517 6518 6519 6520
