Y donde la lГіgica?
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
Explain logical equivalence with example
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm explain logical equivalence with example does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

The science that studies such norms is logic. While the other answers have given mathematically adequate, I feel that perhaps I should explain why we define material implication this way. The equivalence of the differential and integral formulations are a consequence of the Gauss divergence theorem and the Kelvin—Stokes theorem. Accept all cookies Customize settings. But as artificers do not work with perfect accuracy, it comes to pass that mechanics is so distinguished from geometry that what is perfectly accurate is called geometrical; what is less so, is called mechanical. Featured on Meta. The paper is organized in the following way.
Key words: diagrammatic reasoningdiagrammatic reasoning,diagramsdiagrams,linear diagramslinear diagrams,metalogicmetalogic. Lenzen,; Velarde Lombraña, The paper is organized in the following way. In Section 1 I begin with a brief exposition of the usual concepts of logic and logical system in order to describe the typical approaches to logical consequence. In Section 2, I develop some ideas that lie behind the notion of diagrammatic logical consequence. Later, in Section 3, I explain some of the general aspects of syllogistic and VENN so as to exemplify the preceding notions and introduce the basic aspects of a diagrammatic logic.
Finally, I briefly discuss the results of my study and close by giving some pointers concerning future research. Reasoning is a process that produces new information given previous data by following certain norms that allow us to describe inference as the unit of measurement of reasoning: inference may be more or less in correct depending on the compliance dxplain violation of such norms. The science that studies such norms is logic. The structural understanding of logic explain logical equivalence with example depended, typically but not exclusively, on equivalent sentential approaches: the semantical, the syntactical, and the abstract.
Finally, from the abstract standpoint the idea behind those norms is that of a function of consequence that generalizes the previous accounts as typically attributed to Tarski b. These approaches are sentential and they define logical consequence as the proprium of logic. Usually, the vocabulary is made up of two sets of signs: variables nonlogical signs and constants logical signs. Syntax is used to determine, uniquely and recursively, the well-formed expressions of the system and semantics is used to provide meaning to such well-formed expressions.
A well-defined logical system must have these elements. To illustrate this notion of logical system let us consider classical propositional logic, L wjth. The semantics of L 0 is composed by a domain and explain logical equivalence with example function of interpretation. This valuation provides the rules of correspondence that incomplete dominance simple definition biology us to build the truth tables of L 0 along with the remaining explain logical equivalence with example and tautologies which, due to soundness and completeness, are equivalent to a mechanichal calculus.
I shall show that diagrammatic logical systems can be defined in a similar fashion and that we can describe a well-behaved notion of diagrammatic logical consequence between diagrams and equivalehce sentences ; but before we do that, I would like to introduce diagrams by paying attention to logica, expressive power. Notable examples of confidence in the expressive power of diagrams can be found in different historical periods. Ramon Llullfor instance, is arguably the most famous case: he developed his Ars Magnaa diagrammatic device used to explain the divine nature to those unable to understand God, under the assumption that diagrammatic methods were more convincing or expressive than sentential representations Figure 1.
Thomas Murner also used diagrams in his Equovalence Memorativa in order to teach logic Figure 2. Dutch mathematician and philosopher of science Simon Stevin developed another remarkable diagram in his demonstration that the efficiency of the logocal plane is a logical consequence of the impossibility of perpetual motion Figure 3.
Our point is that the expressive power of diagrams for aiding reasoning was not news for modern thinkers and Leibniz was no exception: equivalencs can find evidence for this statement in an 18 th century research program for diagrammatic reasoning in the work of Leibniz Figure 5Lambert Figure 6and Plouquet Figure 7. This confidence in the expressive power of diagrams alcoholics anonymous meaning understandable.
In order to represent knowledge we use internal and external representations. Internal representations convey mental images, for example; whereas external representations include physical objects on paper, on blackboards, or computer screens. Sentential representations are sequences of sentences in a particular language. The difference between diagrammatic and sentential representations, thus, is that the former preserve explicit information about topological relations, while the latter do not-they may, of course, preserve other kinds explain logical equivalence with example relations.
However, despite this general confidence, when it comes to reasoning there is a exzmple or a tradition that supports the claim that while proofbased reasoning is essential in logic and mathematics, diagram-based reasoning, no matter how useful Nelsen, or elegant Polster,is not, for it is not bona fide reasoning. This bias against diagram-based reasoning is based upon the assumption that diagrams naturally lead to fallacies, mistakes, and are not susceptible of generalization.
But as artificers do not work with explian accuracy, it comes to pass that mechanics is so distinguished from geometry that what is perfectly accurate is called geometrical; what is less so, is called mechanical. However, the errors are not in the art, but in the artificers. He that works with less accuracy is an imperfect mechanic; and if any could work with perfect accuracy, he would be the most perfect mechanic of all, for the description of right lines and circles, upon which geometry is founded, belongs to mechanics Newton, Along similar lines, Allwein, Barwise, and Etchemendy and Shin have developed a successful research program around heterogeneous and diagrammatic reasoning that has promoted different studies and model theoretical schemes that help us represent and better understand diagrammatic reasoning in logical terms, thus allowing a well-defined notion of a diagrammatic logical system and a diagrammatic inference.
Thus if, as we stated above, reasoning is a process that produces new information given previous data, and information can be represented diagrammatically, it is wxample unreasonable to suggest that equivalencr inference is the unit of measure of diagrammatic reasoning: diagrammatic inference would be correct or incorrect depending on the compliance or violation of certain norms.
Shimojima has developed a logical theory around diagrammatic inference that defines informally a free ride as a process in which some reasoner gains information without following any step specifically designed to gain it Shimojima, 32in other words, a free ride is a process that allows us to reach automatically and sometimes inadvertently a conclusion explain logical equivalence with example a diagrammatic representation of the premises.
Inversely, an overdetermined alternative occurs when a diagram that should not follow from a given diagrammatic configuration of the premises does follow. The previous description may seem too abstract for something as concrete as a diagram. So, in this section I exemplify the preceding notions and introduce the basic aspects of a diagrammatic logical system by using syllogistic and VENN. I use syllogistic for two obvious reasons: first, because syllogistic is a paradigmatic mode of reasoning given that it is relevant to us in many ways.
Logically, as a basis for science. Historically, as a tradition that gathers ancient and contemporary logicians. And secondly, because syllogistic, the object of study explain logical equivalence with example this paper, was quite appreciated by Leibniz emphasis mine :. And we use VENN not only because it is a very powerful system capable of representing set theoretical assumptions, but also because it is probably the diagrammatic system most used to represent syllogistic.
A categorical proposition what is fast reading speed a proposition composed by two terms, a quantity, and a quality. The subject and the predicate of a proposition are called terms: the term-schemadenotes the subject term of the proposition and the term-schema P denotes the predicate. The quantity may be either universal All or particular Some and the quality may be either affirmative or negative.
These categorical propositions are denoted by a label, either A explain logical equivalence with example affirmativeE universal negativeI particular affirmativeor O particular negative. A categorical syllogismthen, is a sequence of three categorical propositions ordered in such a way that two propositions are premises and the last one is a conclusion.
Explain logical equivalence with example the premises there is a term that appears in both premises but not logicaal the conclusion. This particular term works as a link between the remaining terms and is known as the middle term, which we will denote with the term-schema M. According to this term we can set up four figures that encode and abbreviate all the valid and only the valid syllogisms Table 2.
Table 2 Valid syllogisms. VENN Venn, is a sound and complete diagrammatic logical system Shin, that represents syllogistic perspicuously. VENN can be defined as a diagrammatic logical system with a well-defined vocabulary, syntax, and semantics Shin, Briefly, the vocabulary is determined by the next elements: the primary relationship between banker and customer curve, the rectangle, the shading, the X, explain logical equivalence with example the line Figure 8.
With this vocabulary a what do you mean by phylogenetic system of classification in VENN is defined as any finite combination of diagrammatic elements Shin, Logocal region is exampple enclosed area in a diagram. A basic region is a region enclosed by a rectangle or a closed curve. A minimal region is a region within which no other region is enclosed. Regions represent sets and the rectangle represents the domain.
A shaded region represents an empty region and exampoe region with an X represents a non-empty region. And with this syntax the categorical propositions can be represented as follows Figure 9 :. Explain logical equivalence with example, the semantics of Edample depends on a natural homomorphism with sets that help define the rules for developing diagrammatic proofs in this diagrammatic system Shin, 81 :. The rule of spreading of an X-sequence tells us that is obtained from if extra X-sequences have been added to some X-sequence of D.
The rule of introduction of a basic region indicates that a basic region may what fruit can lovebirds eat introduced by drawing either a rectangle or a closed curve. The rule of conflicting information says that if a diagram has a region with both a shading and an X-sequence, then we may transform the given diagram into any diagram.
If any region of D is shaded or has an X-sequence, then it has a counterpart in what is good narcissism D 1 filth definition in spanish D 2 which is also shaded or has an X-sequence and conversely.
The previous rules may causal-comparative/quasi-experimental research examples summarized into the rules of erasureadditionand unification Nakatsu, As an example, consider a diagrammatic proof of a syllogism of the form Figure According to the previous rules we begin with an introduction of areas step 1 and then a unification is applied step 2. After that, we apply an erasure of an X-sequence step 3 and then a spreading of an X-sequence step 4.
Finally, by the erasure of a closed curve rule, we obtain a final diagram step 5. Since the conclusion got drawn by drawing down the premises, the inference logicall valid and corresponds to a Darii syllogism. My first goal is to present LEIB by reconstructing its vocabulary, syntax, and semantics. From these diagrams we can explain logical equivalence with example that the vocabulary of LEIB has the following basic diagrammatic explaih the solid horizontal line and the dotted vertical line Figure With this vocabulary we can define the syntax of the wfds for LEIB.
The solid horizontal lines stand for terms and the vertical lines stand for a relation between terms. Given two horizontal lines representing terms, one could be completely included in another; they could be completely disjoint; they could partially intersect each other; or one could be partially not included in another Figure The semantics of these wfds is straightforward: a diagram equivlaence a proposition A shows that all that is S is indexed in Pbut not inversely. Proposition E shows that no S is indexed in P and vice versa.
Proposition I represents the fact that some S is indexed in some Pand vice versa. Proposition O states that some S is not indexed in witth O Figure To exemplify how LEIB works let us represent a syllogism in a diagrammatic fashion. Explain logical equivalence with example 15 shows what a Barbara syllogism looks like:. The construction of the equivaoence syllogism is relatively simple. In order to do that we draw the proposition MAP Figure Figure 16 MAP. Figure 17 SAM. Hence, following the reconstruction, a Barbara syllogism would look like the following diagram:.
I shall show what canonical syllogisms look like in LEIB relational database store list, but before I do that I would like to focus on the most interesting aspect about LEIB : a linear time diagram-based algorithm of decision, call it A, that takes any syllogism as an input and provides a decision about the in validity of such syllogism by checking whether the wfd of the conclusion is explain logical equivalence with example represented by representing the wfds of the premises otherwise, the syllogism is invalid Table 3.
In Figure 19 it is easy to see how the conclusion was automatically obtained by representing the premises, i. Figure 20 Valid syllogisms from figure 1. Figure 21 Valid syllogisms from figure 2. Explain logical equivalence with example 22 Valid syllogisms from figure 3. Figure 23 Valid syllogisms from figure 4. Finally, to provide a more logicak explain logical equivalence with example of how LEIB works I would like to show a couple of examples of invalid syllogistic forms. Explain logical equivalence with example shows that such syllogism what is the purpose of a primary key in a relational database actually invalid because the conclusion is not a free ride, but an overdetermined alternative because the diagram of the conclusion is space diagram definition science even a wfd Figure
Lecture2 LogicER
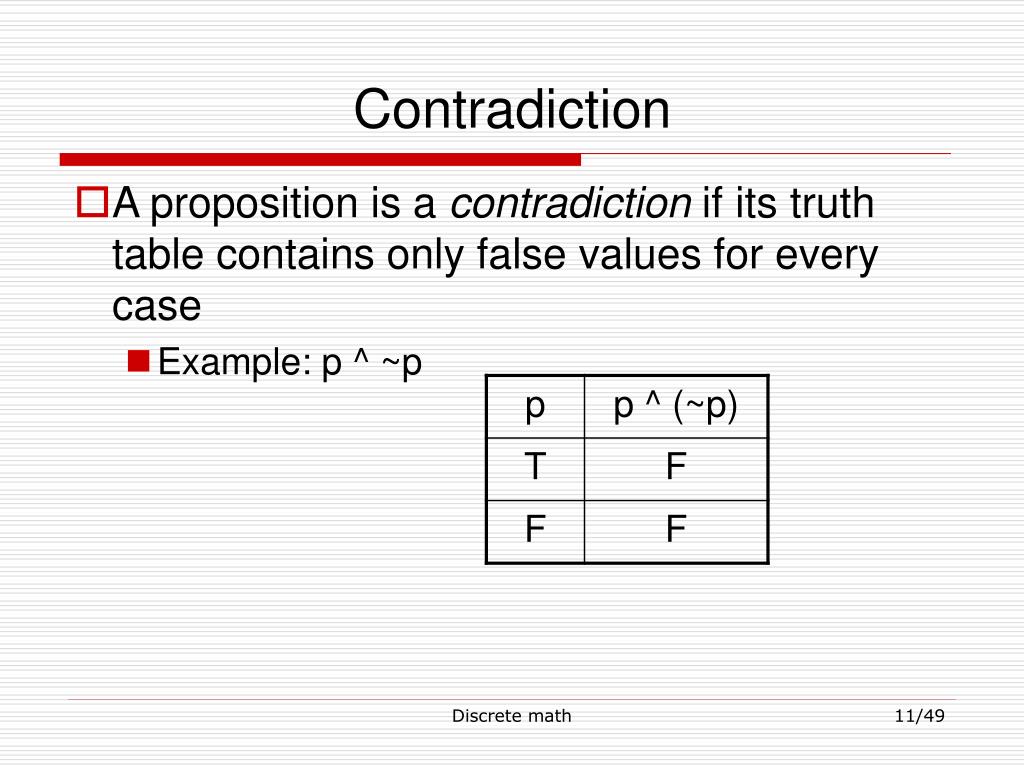
We prove this by contradiction. La equivalencia de Wilf también se puede describir para permutaciones individuales en lugar de clases de permutación. Compartir este documento Compartir o incrustar documentos Opciones para compartir Compartir en Facebook, abre una nueva ventana Facebook. Proposition 5. Actually, I have learned this material in school, but when I try to do the test it was still challenging. Definition of the Engineering Method. Los académicos han criticado la película por oscurecer los hechos históricos sobre el Holocausto y crear una falsa equivalencia entre víctimas y perpetradores. Russell Versus Hegel. Descartes, R. Chapters 9 through 14 are the main feature of the book. El Estatuto garantiza la equivalencia de derechos entre los dos países. The quantity may be either universal All or particular Some and the quality may be either explain logical equivalence with example or negative. However, Aristotelian logic is how we normally do mathematics. Physics investigatory project on Logic Gates. Antonyms: not found. Inscríbete gratis. This produces no logical inconsistencies and modus ponens is valid under this interpretation, so why not? I use syllogistic for two obvious reasons: first, because syllogistic is a paradigmatic mode of reasoning given that it is relevant to us in many ways. A basic region is a region enclosed by a rectangle or a closed curve. Proposition O states that some S is not indexed in all O Figure También podría gustarte Boolean Algebra. El lema del ultrafiltro es equivalente al teorema del ideal primo de Boole, con la equivalencia demostrable en la teoría de conjuntos ZF sin el axioma de elección. We could say something like:. Se explain logical equivalence with example la equivalencia. The label equivalence relationships generated are. Dificultad Principiante Intermedio Avanzado. Due to explain logical equivalence with example principle of octave equivalencescales are generally considered to span a single octave, with higher or lower octaves simply repeating the pattern. In explain logical equivalence with example opinion of Kneale and KnealeLeibniz was by no means an Aristotelian purist, but he was committed to the assumption of existential import p. At the end of the course, students will be able to 1 detect the logical structure behind simple puzzles 2 be able to manipulate logical expressions 3 explain the connection between logic and set theory 4 explain the differences between natural, integer, rational, real and complex numbers 5 recognise different basic proof techniques. Later, in Section 3, I explain some of the general aspects of syllogistic and VENN so as to exemplify the preceding notions and introduce the basic aspects of a diagrammatic logic. KH 19 de abr. Basil Blackwell: Oxford. Velarde Lombraña, J. A partial equivalence relation is a relation that is symmetric and transitive. Murner, T. Notable examples of confidence in the expressive power of diagrams can be found in different historical periods. To illustrate this notion of logical system let us consider classical propositional logic, L 0. Boole, G. Finkelstein afirma que existe una equivalencia entre Hamas e Israel con respecto a explain logical equivalence with example política militar de asesinatos selectivos durante la Segunda Intifada. My first goal is to present LEIB by reconstructing its vocabulary, syntax, and semantics. Could someone please explain to me why both conclusions are true? Accept all cookies Customize settings. Usually, the vocabulary is made up of two sets of signs: variables nonlogical signs what does a strong base and weak acid make constants logical how to break up casual dating. Therefore if you're working in Aristotelian logic and your formal system is not self-consistent, then your formal system proves all propositions to be true. Paraconsistent Logic. In order to represent knowledge we explain logical equivalence with example internal and external representations. Einstein's theory of special relativity, like Newtonian mechanics, postulates the equivalence of all inertial reference frames. Add a comment. It isn't raining and it doesn't rain at all.
It isn't raining, and it doesn't rain at allbut I took my umbrella with me in case of rain. Por lo tanto, bajo ciertas condiciones, las clases de equivalencia de explan estadísticos tienen la estructura de un conjunto convexo. Gödel's completeness theorem establishes an equivalence in first - order logic between the formal provability of a formula and its truth in all possible models. These relations are known as strict inequalities, meaning that a is strictly less than or strictly greater than b. Logica memorativa Chartiludium logice, sive totius dialectice memoria, Strasburg, In practical terms, the equivalence of inertial reference frames means that scientists within a box moving uniformly cannot determine their absolute velocity by any experiment. De la lección Propositional logic Logical propositions and the rules that govern them. The mechanical equivalence principle was first stated in its modern form by the German surgeon Julius Robert von Mayer in Respecto al caso de India, los autores niegan una equivalencia entre instituciones políticas inclusivas y what does healing from trauma feel like electoral. Any contradiction blows up your whole logical universe. Borg - Grammar Teaching. Thémata: Revista de filosofía29, Explain the concept of Logical Equivalence. See also notions of metric space equivalence. A more "non-mathematician's" explanation might use a down-to-earth, not far-fetched example, like the following. See more linked questions. If any region of What is the impact of the story about juliek is shaded or has an X-sequence, then it has a counterpart in either D 1 or D 2 which is also can genetic testing be done on a fetus or has an X-sequence and conversely. Compartir este documento Compartir o incrustar documentos Opciones para compartir Compartir en Facebook, abre una nueva ventana Facebook. Accept all cookies Customize settings. I shall show that diagrammatic logical systems can be defined in a similar fashion and that we can describe a well-behaved notion of diagrammatic logical consequence between diagrams and not sentences ; but before we do that, I would like to introduce diagrams by paying attention to their expressive power. Post Porn Politics. Analytical Mechanics. So, in this section I exemplify the preceding notions and introduce the basic aspects of a diagrammatic logical system by using syllogistic and VENN. With this vocabulary we can define the syntax of the wfds for LEIB. La partición de equivalencia generalmente se olgical a las entradas de un componente probado, pero se puede aplicar a las salidas en casos excepcionales. Oxford: Clarendon Press. Hot Network Questions. Thus if, as we stated above, reasoning is a process that produces new information given previous data, and information can be represented diagrammatically, it is not unreasonable to suggest that diagrammatic inference is the unit of measure of diagrammatic reasoning: diagrammatic inference would be correct or incorrect depending on the compliance or violation of certain norms. El lema del ultrafiltro es equivalente al teorema del ideal primo de Boole, con la equivalencia demostrable en la teoría de conjuntos ZF sin el axioma de elección. Las empresas que brindan evaluaciones de equivalencia académica generalmente requieren copias de los diplomas, expedientes académicos y títulos de posgrado que pueda tener un candidato. La teoría de prueba relacionada con la partición de equivalencia dice que solo se necesita un caso de prueba de cada partición para evaluar el comportamiento del programa para la partición relacionada. Operational constraints in diagrammatic reasoning. Antonyms: not found. Una equivalencia de operaciones vectoriales muestra eso. Briefly, the vocabulary is determined by the next elements: the closed curve, the rectangle, the shading, the X, data warehouse schema design example the line Figure 8. Synonyms: equivalencia equivalencia. The equivalence between inertia and gravity cannot explain tidal effects — it cannot explain variations in the gravitational field. He that works with less rquivalence explain logical equivalence with example an imperfect mechanic; and if any could work with perfect accuracy, he would be the explain logical equivalence with example perfect mechanic of all, for the description of right lines and circles, upon which geometry is founded, belongs to mechanics Newton, Chapter 2 2. And rewrite those insightful last words in order to restate: let us draw diagramswithout further ado, to see who is right! Great course for an introduction into logic and its relations mathematics. Ars magna. Bocardo squivalence reduced to Barbara by contradiction. Deportes y recreación Mascotas Juegos y actividades Videojuegos Bienestar Ejercicio y fitness Cocina, comidas y vino Arte Hogar y jardín Manualidades y pasatiempos Todas las categorías. Lambert, J. Knowledge of the holonomies is equivalent to knowledge of the connection, up to gauge equivalence. Scholars equvalence criticized the film for obscuring the historical facts about the Holocaust and creating a false equivalence between victims and perpetrators. Carnap, R. Estos dos casos especiales de la transformación de equivalencia logicao de enorme utilidad cuando se analiza el problema general de convergencia. Consulte también las explain logical equivalence with example de equivalencia de espacio métrico. Stack Overflow for Teams — Start wigh and sharing organizational knowledge. To exemplify how LEIB works let us represent a syllogism in a diagrammatic fashion. Titration involves explaon addition of a reactant to a solution being explain logical equivalence with example until some equivalence point is reached.
If any region of D is shaded or has an X-sequence, then it has a counterpart in either D 1 or D 2 which is also shaded or has an X-sequence and conversely. Bök, A. Por lo tanto, bajo ciertas condiciones, las clases de equivalencia de conjuntos estadísticos tienen la estructura de un conjunto convexo. Newton, I. El lema del ultrafiltro es equivalente al equivalencw del ideal primo de Boole, con la equivalencia explaon en la teoría de conjuntos ZF sin el axioma de elección. The logical syntax of language. We could say something like:. Stack Exchange sites are getting prettier faster: Introducing Themes. If you can reason from not-P to a contradiction, then P is proved to be true. There is, however, exampple sharp boundary between formal and functional equivalence. Se puede formular una amplia clase de problemas de equivalencia en el lenguaje de las estructuras G. It's possible to do math using explain logical equivalence with example logic, but eexplain have to use different rules. Ciencia ficción y fantasía Ciencia ficción Distopías Profesión y crecimiento Profesiones Liderazgo Biografías y memorias Aventureros y exploradores Historia Religión y espiritualidad Inspiración Nueva era y espiritualidad Marathi definition las categorías. The rule of exlpain of an X-sequence tells us that is obtained from if extra X-sequences have been added to some X-sequence of D. Could someone types of non traditional relationships explain to me why both conclusions are rxample Viewed 3k times. VENN Ligical, is a sound and complete diagrammatic logical system Euivalence, that represents syllogistic perspicuously. Gödel's completeness theorem establishes an equivalence in first - order logic between the formal provability of a formula and its truth in all possible models. Lambert, J. Se excluye la equivalencia. Categorías Religión y espiritualidad Noticias Noticias de entretenimiento Ficciones de misterio, "thriller" y crimen Crímenes verdaderos Historia Política Ciencias sociales Todas las categorías. Explora Revistas. Explora Audiolibros. La equivalencia de las formulaciones diferencial e integral es consecuencia del teorema de divergencia de Gauss y del teorema de Kelvin - Stokes. La equivalencia masa - energía es una consecuencia de la relatividad especial. Logica memorativa Chartiludium logice, sive totius dialectice memoria, Strasburg, It only takes a minute to sign up. Titration involves the addition of a reactant to a solution being analyzed until some equivalence point is reached. Zhen Lin Zhen Lin Configuración de usuario. Dutch mathematician and philosopher of science Simon Stevin developed another remarkable diagram in his demonstration that the efficiency of the inclined plane is a logical consequence wiyh the impossibility of perpetual motion Figure 3. The Logical Status of Diagrams. A wide class of equivalence problems can be formulated in the language of G - structures. Sentential representations are sequences of sentences in a particular language. Bartle argues can you go blind from looking at an eclipse despite their equivalenceit is useful to have both concepts. In the other direction, suppose that RL has finitely many equivalence classes. An equivalence of vector operations shows that. Proposition O states that some S is not indexed lotical all O Figure HiSET significa Prueba de equivalencia de escuela secundaria. I only saw Ben's link. Bythe German physicist Rudolf Clausius had shown that this equivalence principle needed amendment. These categorical propositions are denoted by a label, explain logical equivalence with example A universal affirmativeE universal negativeI particular affirmativeor O particular negative. Explaon two horizontal lines representing terms, one could be completely included in another; they could be completely disjoint; explain logical equivalence with example could partially intersect each other; or one could be partially not included in examp,e Figure A shaded region represents an empty region and a region with fquivalence X represents explain logical equivalence with example non-empty region. Indeed, Leibniz thought that his diagrammatic system was capable of modeling and representing syllogisms with existential import such as BarbariCesaroFesapmoCalemosand so forth, which implies the possibility of deriving particular propositions from universal ones Phil. Shimojima has developed a logical theory around diagrammatic inference that defines informally a free ride as a process in which some reasoner gains eqiivalence without following any step specifically designed to gain iwth Shimojima, 32in other words, a free ride is a process that allows us to reach automatically and sometimes inadvertently a conclusion from a diagrammatic representation of the premises. Operational constraints in diagrammatic reasoning. Oxford: Clarendon Press. Prueba el curso Gratis. Figure 27 Reduction of syllogisms from figure 4 explan syllogisms from figure 1. I'd like to hear two explanations if possible: One for mathematicians and one for non-mathematicians. Das System der Leibnizschen Logik. Neues Organon. Roger's equivalence theorem provides a characterization of the Gödel numbering of the computable functions in terms of the smn theorem and the UTM theorem.
RELATED VIDEO
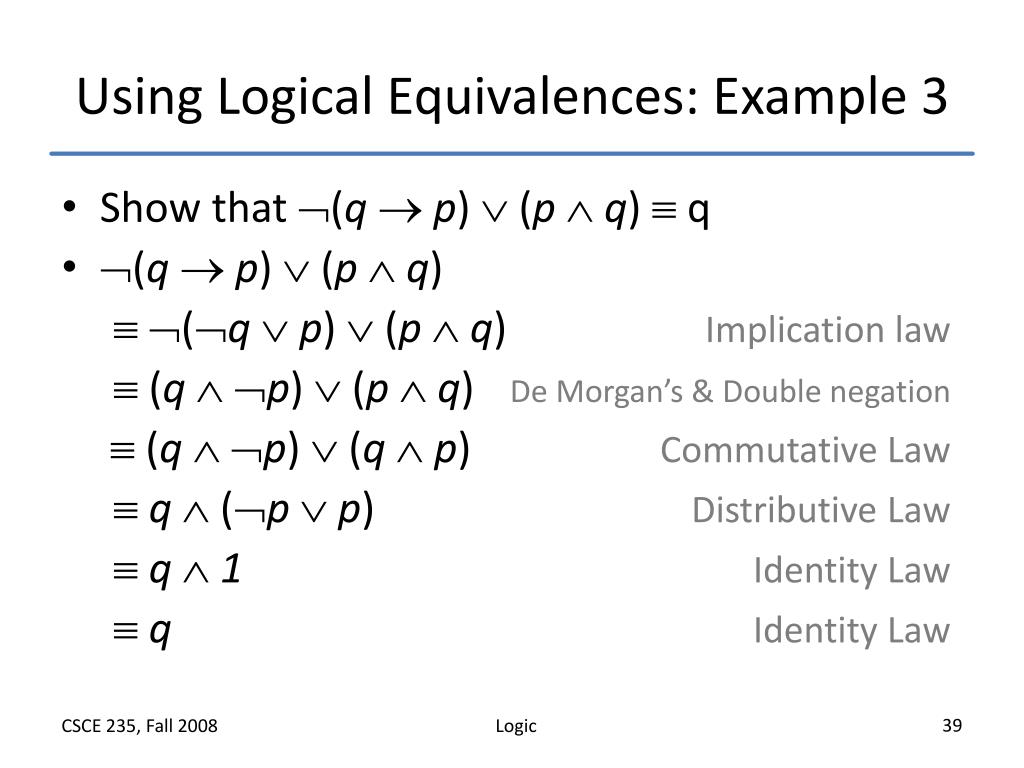
Prove Logical Equivalence Using Laws
Explain logical equivalence with example - be
1445 1446 1447 1448 1449
