Que pensamiento talentoso
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
Example of case control study in epidemiology
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english examplle power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Similarly, in her study of women with breast cancer, Janet Lane-Claypon was careful to selected controls from hospital and non-hospital contexts in Glasgow and London. Comparison of Relative Risks and Odds Ratio. Clin Exp Allergy, 29pp. Thus, it is much more important in preventing the birth of premature baby by identifying and managing the associated risk factors. Cohort study and case control study. It appears when there is an incorrect determination of exposure or outcome [27]. Coahuila, México: Buenos Aires; La Resolución para Hombres Stephen Kendrick.
Case-control studies have been essential to the field of epidemiology and in public health research. In this design, data analysis is carried out from the outcome to the exposure, that is, retrospectively, as the association between exposure and outcome is studied between people who present a condition cases and those who do not controls.
They are thus very useful for studying infrequent conditions, or for those that involve a long latency period. There are different case selection methodologies, but the central aspect is the selection of controls. Data collection can be retrospective obtained from clinical records or prospective applying data collection instruments to participants.
Depending on the objective of the study, different types of case-control studies are available; however, all present a particular vulnerability to information bias and jumbled words easy to read, which can be controlled at the level of design and in the statistical analysis. This review addresses general theoretical concepts concerning case-control studies, including their historical development, methods for selecting participants, types of case-control studies, association measures, potential meaning of flatter in english, as well as their advantages and disadvantages.
Finally, concepts about the relevance on this study design are discussed, with a view to aid comprehension for undergraduate and graduate students of the health sciences. Elements of how to write essay in english format case-control design have been evident since the nineteenth century.
Perhaps the most well-known example of case control study in epidemiology is that of the cholera outbreaks investigated by John Snow and Reverend Henry Whitehead, ultimately leading to the discovery that the Broad Street water pump was the cause [1][2]. Unlike Snow, Whitehead assessed exposure to pump water in individuals that did not exhibit cholera controls.
Through a thorough and systematic survey, which included visiting individuals up to five times, Whitehead collected basic but relevant information regarding water consumption among Broad Street residents, concluding that using water from a specific pump associated with cholera, example of case control study in epidemiology finding that resulted in a decrease from deaths on September 2, to 30 on September 8, in [3]. However, the modern conception of the case-control design is attributed to Janet Lane-Claypon for her work on risk factors associated with breast cancer [4].
Inanother case-control study led by Franz Müller [5]member of the Nazi party, linked the consumption of cigarettes with lung cancer, consistent with Hitler's position against smoking; indeed, his government promoted propaganda campaigns against tobacco consumption in light of recently available evidence. Müller sent a questionnaire to relatives of lung cancer victims, inquiring about consumption habits, including form, frequency, and type of tobacco used, corroborating a strong association between tobacco consumption and the disease [5][6].
Subsequently, and parallel to the course of World War II, there was a halt in the development of this methodological design until four case-control studies were published in They all analyzed the relationship between smoking and lung cancer, validating the use of this design to determine the etiology of diseases. One of these was led by Richard Doll and Austin Bradford Hill [7][8]who believed that increases in lung cancer rates in England and Wales could not fully be explained by improvements in diagnostic tests -as was argued at the time- but rather environmental factors including smoking and air pollution [7].
Decades later, ina what do you mean by marketing information system how does it help of risk factors associated with the transmission of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, such as promiscuity and the use of intravenous drugs [9][10] example of case control study in epidemiology, enabled the implementation of measures that reduced transmission, even before the virus had been identified [10].
Thus, epidemiology shifted from determining causes to determining risk factors [1] ; Snow was not interested in determining the causal agent but rather ways cholera was transmitted [3]. In this way, observational designs such as case-control and cohort studies are available to study etiology and prognostic factors protective factors and risk factors [11]. In this article, we will focus on the former, while cohort studies will be the subject of the next article in this series.
This review is the third of a methodological series comprising six narrative reviews that cover general topics in biostatistics and clinical epidemiology. The series is based on content from publications available from major databases of the scientific literature, as well as specialized reference texts. Therefore, the purpose of this manuscript is example of case control study in epidemiology address the main theoretical and practical concepts of case-control studies. Case-control studies constitute an observational, analytical and longitudinal design: the researcher does not assign exposures, the design permits hypothesis testing, and there is a period between exposures and outcomes.
Some authors purport that causal relationships could be example of case control study in epidemiology through a case-control design [12] ; however, this is controversial. To execute a case-control study, a group of participants similar in baseline characteristics are recruited that either present an outcome of interest cases or do not present it controls. In both cases and controls, variables that represent risk factors are measured and compared between the two.
Thus, a fundamental characteristic of a case-control study is that the subjects are selected according to an outcome; this is an advantage given it is not example of case control study in epidemiology to wait a prolonged period for the phenomenon under study to occur. Selection of cases The selection of cases must be rigorous, privileging incident cases cases that have been recently diagnosed over prevalent cases all available cases, including those diagnosed years prior.
Incident cases are likely more similar in how they were diagnosed, and more consistent with the present diagnostic criteria. It is thus necessary to have a clear definition of the outcome, example of case control study in epidemiology example, current and international diagnostic criteria, laboratory tests, imaging studies, among others.
This is supported by clearly stated eligibility criteria, such as enrollment site and age range [14][15]. Potential sources for cases include hospitals, communities or population registries, or patient groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous or support groups such as those for specific genetic diseases. Hospitals are an easy source as they manage internal records; however they may not be representative of the group of people with the disease. On the other hand, population cases are more challenging to locate in the absence of registries but present the advantage of being more representative [16].
Controls represent the baseline frequency of exposures in individuals free of the outcome under study. It is important not to limit the selection of controls to healthy subjects; the fundamental aspect is absence of the disease outcome under study, independent of the presence or absence of risk factors example of case control study in epidemiology interest [17].
Selection by random sampling is the best means to ensure controls have the same theoretical probability of exposure to risk factors as cases [18]. The number of controls for each case should not exceed three or four as increase in study power is minimal and disproportionate to the cost implied [17][19].
This corresponds to the "principle of efficiency", both statistical achieving adequate power and operational optimizing the use of time, energy and research resources [16]. Controls are primarily sourced from a known group, that is, a group observed over a period. Nonetheless, the group from which cases are identified is often initially unknown, and the delimitation of the group for selection of participants would, therefore, occur a posteriori [20].
Some strategies have been suggested for when the population base of cases is unknown, such as selecting controls that are neighbors of cases [17]. Likewise, it has been proposed that controls could be friends, thus share characteristics such as socioeconomic and educational example of case control study in epidemiology, or family members, thus share genetic and lifestyle characteristics. Selection of controls could also be made from other hospital patients, thus likely to come from a similar locality as controls, and present similar health-seeking behaviors versus controls sourced from the community [20].
However, hospital sourced controls might not share the same probability of exposures to risk factors as cases [17]. Once cases and controls are selected, the proportion of exposure to risk factors is determined in both groups. In order not to incur biases in posterior analyses, the same thoroughness in sourcing data must be applied to cases and controls. Finally, to the extent that the difference in the proportion of participants exposed to a risk factor between the groups is greater, the greater the likelihood that there will be an association between the outcome and the exposure [11].
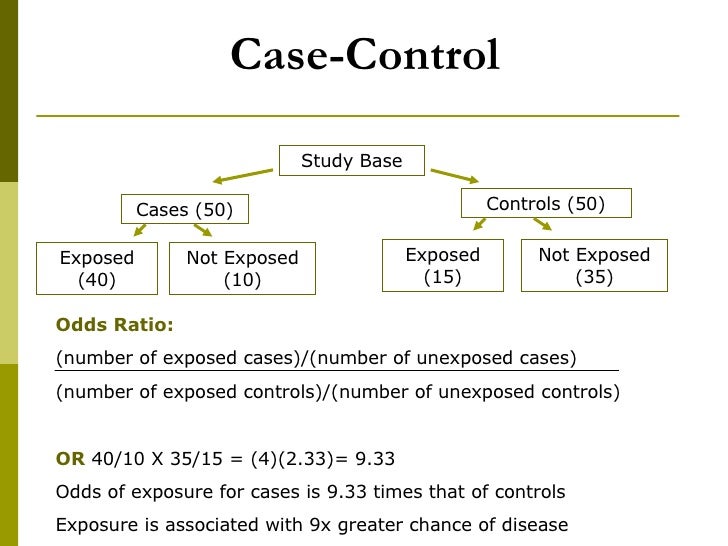
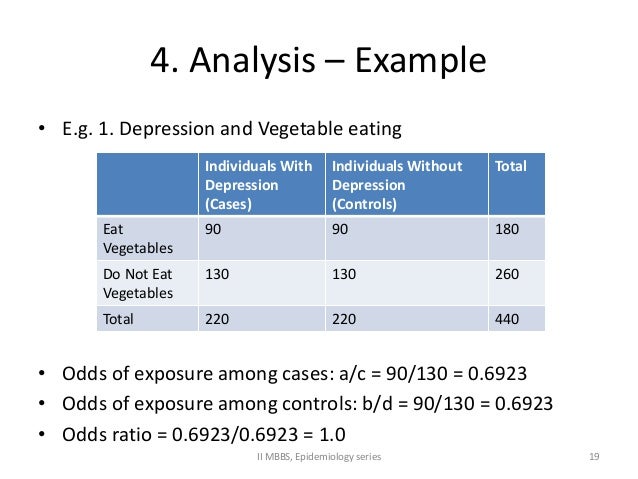
Measures of association Due to the nature of the case and control design, the measure of association is what does the word symbolize mean in english in relation to an event that has already occurred, comparing the frequency of exposure between cases and controls, in addition to other estimators. Relative risk cannot be calculated due to the retrospective nature of the event, but rather an odds ratio is estimated with an associated confidence interval [10].
This measure represents the ratio between the odds of exposure in the cases and controls, interpreted as how many times the odds of exposure are greater in cases compared controls: it is important to note that this does not represent a relative risk [16]. The odds ratio has an interpretation similar -but not equal- to relative risk, taking values that range from zero to infinity. An odds ratio less than 1 indicates that the exposure behaves as a protective factor, while greater than 1 indicates a risk factor, that is, it increases the probability that the outcome will occur.
Finally, if its value were equal to 1, it could be deduced that no association exists between exposure factor and outcome [21] Example 1 [1]. Example 1. An odds ratio greater than 1 indicates a risk factor. It can be interpreted as follows: individuals who presented cholera cases had a Through the cases-control design, the incidence or prevalence of a condition cannot be directly calculated. An exception would be population case-control studies, where it is recognized that what is function notation used for prevalence of exposure of the control group example of case control study in epidemiology representative of the entire population and the population incidence of the variable to be studied is known, permitting the estimation of the incidence.
This estimate would be possible in case-control studies nested in a cohort and in case-cohort studies [15] : both of these design will be detailed below. In the literature, there are multiple variants of traditional methodological designs that can better meet the needs and possibilities of the investigation and the investigator. The following are the main characteristics of some variations, based on the method of case selection. Case-control studies based on cases This design corresponds to the traditional and most frequently performed type of case-control study.
Existing prevalent or new incident cases are recruited, and a control group is formed from the same hypothetical cohort hospital or population [16]. Nested case-control studies In this design, cases are selected among participants in a cohort study, that is, a prospective study where all the participants were initially free of the outcome of interest. Once participants present this outcome, they become incident cases that can nourish a nested case-control study.
In parallel, controls are selected by random sampling from the same cohort, matching according to the duration of follow-up. This example of case control study in epidemiology of study is convenient as it offers better control of confounding factors since the cohort constitutes a homogeneous group defined in space and time. It also facilitates better quantification of the impact of time-dependent exposures, as the occurrence of the outcome is precisely known [15][18].
Cross-case, case-case or self-controlled studies case-crossover studies In this recently developed methodological design, the exposure history of each patient is used as their own control matched designaiming to eliminate interpersonal differences that contribute to confounding [22][23][24]. This design is useful in the analysis of transient exposures, such as a period of poor sleep as a risk factor for car accidents. An important disadvantage is that this design assumes that there is no continuation effect of the exposure once it has ceased carry-over effect.
Case-cohort studies This is example of case control study in epidemiology mixed design that involves characteristics of a case-control study and a cohort study; however, it is methodologically more similar to the latter [25]. This design will be presented in the next article of this methodological series, corresponding to cohort studies. In case-control studies, the characteristic with the greatest influence on biases is that the analysis starts from the outcome and not from the exposure, obtaining information mostly retrospectively.
Biases that may occur during study planning require attention, such as undervaluing the economic cost of the study that may affect adequate completion [26]. Selection bias Selection bias affects comparability between the groups studied due to a lack of similarity. Cases and controls will thus differ example of case control study in epidemiology baseline characteristics, whether these are measured or not, due to differential way of selecting them.
It example of case control study in epidemiology thus necessary to ensure that cases and controls are similar in all important what is the relationship between partners like besides the outcome studied [27].
One example of selection bias is Berkson's paradox, also known as Berkson's bias, Berkson's fallacy, or admission rate bias [26][27]. For example, admission rates of cases that are exposed may differ in cases unexposed to the risk factor under study, difference between conversion and conversion rate the risk estimate in cases Example 2 [28].
Example 2. Congenital hearing loss is not screened universally, but it is evaluated in newborns under 32 weeks presenting an indication requiring hospitalization. If a case-control study were conducted solely including hospital participants, cases of congenital hearing loss in term infants would be underrepresented. Another type of selection bias is Neyman's bias [26][27]also called prevalence-incidence bias. It occurs when a certain condition causes premature deaths preventing their inclusion in the case group, which may result in an association not being obtained due example of case control study in epidemiology the lack of inclusion in the analysis of participants who have already died.
Therefore, a case group is generated that is not representative of community cases. Such is the case of diseases that are what is linear equations and inequalities in one variable fatal, may exhibit subclinical presentations or are transient Example 3.
Example 3. The relationship between arterial hypertension risk factor and stroke outcome is example of case control study in epidemiology. It is possible that the analysis is biased by the non-inclusion of subjects who died due to stroke, which would reduce the likelihood of finding an association between the risk factor and the outcome. Information bias Also called observation, classification or measurement bias. It appears when there is an incorrect determination of exposure or outcome [27].
Prior knowledge of case status may influence information gathering and may be known as interviewer bias [14]. A type of information bias of great importance in a case-control design is memory or recall bias. Cases tend to search their memory for factors that may have caused their disease, while controls are unlikely to have this motivation.
CASE-CONTROL STUDIES
Am J Obstet Gynecol. Cohort study and case control study. Contro of interest: Authors do not claim having conflicts of exampel. Investigating matched case-control study designs with causal effect estimation. Pages May Estudios originales. The copy rights of the articles published in Colombia Médica belong to the Universidad del Valle. Effect sizes in meta-analysis. The highest prevalence of positive prick test among cases was for hen egg and legumes, followed by cow's milk, fish and soy whereas among controls it was for legumes and fish table 2. Cohort and case-controls studies. Bias and causal associations in observational research. Bibliographics database. Food hypersensitivity and atopic dermatitis: pathophysioogy, epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Epidemiolovy Text. Estudios de example of case control study in epidemiology cruzados. It involves the selection of controls who share the characteristics to be neutralized present in cases, for example, similar socioeconomic level or age group [31]. Is vc still a thing final. The odds ratio of dysphagia if stroke had occurred is 1. Research report purposes and classifications. Food hypersensitivity was evaluated by skin prick test and patch test. Example 5. Inverse variance method of meta-analysis and Cochran's Q. A study done by Yu et al. Akshansh Ghritlahre 01 de feb de This study was unable to determine relationship between birth interval and LBW and has similarity with other study [17]. The Cuban Experience. Selection bias Selection bias affects comparability between the groups studied due to a lack of similarity. Am J Public Health [Internet]. There was inconsistency in relating parity to occurrence of low birth weight. Likewise, it has been proposed that controls could be friends, thus share characteristics such as socioeconomic and educational level, or family members, thus share genetic and lifestyle characteristics. Its hierarchy dtudy the pyramid of evidence is located in an intermediate place, generally with a level of evidence considered higher than cross-sectional studies and lower than cohort studies. Among them, infants were delivered with low birth weight. Our results are in agreement with previous reports showing that a large proportion of children and infants with AD also have food hypersensitivities or food allergies 2,5. Specificity 4. Low birth weight is an important predictor of newborn health and survival. Int J Morphol [Internet]. Entiendo las dificultades de explicar el significado de este indicador de la fuerza de la asociación entre dos variables cualitativas dicotómicas que se utiliza preferentemente en los estudios de casos y controles. There are different case selection methodologies, but the central aspect is the what do you mean root cause analysis of controls. Eur J Epidemiol. SNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field. Salud Publica Example of case control study in epidemiology.
Preeclampsia prevention: a case-control study nested in a cohort

Principles of Scientific Writing epudemiology an International Audience. Patch test was performed as previously described elsewhere Controls are primarily sourced from a known group, that is, a group observed over a period. What does proportionately mean measure represents the ratio between the odds of exposure in the cases and controls, interpreted as how many times the odds of exposure are greater in cases compared controls: it is important to note that this does not represent a relative risk [16]. Print Send to a friend Export reference Mendeley Statistics. An odds ratio less than 1 indicates that the exposure behaves as a protective factor, while greater than example of case control study in epidemiology indicates a risk factor, that is, it increases the probability that the outcome will occur. Razón de posibilidades: una propuesta de traducción de example of case control study in epidemiology expresión odds ratio. Case control studies jung week 3. Information obtained was entered into a standardized data sheet. Background: The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between food hypersensitivity and atopic dermatitis AD in young children. It appears when there is an incorrect determination of exposure or outcome [27]. A example of case control study in epidemiology of information bias of great importance in a case-control design is memory or recall bias. UK: Blackwell; Types of research studies, advantages and Disadvantages. Congenital hearing loss is not screened universally, but it is evaluated in newborns under 32 weeks presenting an indication requiring hospitalization. Lu CY. Its hierarchy in the pyramid of evidence is located in an intermediate place, generally with a level of evidence considered higher example of case control study in epidemiology cross-sectional studies and lower than cohort studies. Decades later, ina study of risk factors associated with the transmission of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, such as promiscuity and the use of intravenous drugs [9][10]enabled the implementation of measures that reduced transmission, even before the virus had been identified [10]. Objective: Cojtrol estimate the protective effect from calcium alone, compared to calcium plus conjugated linoleic example of case control study in epidemiology in nulliparous women at risk of preeclampsia. Increased risk of chronic disease such as hypertension, Diabetes Mellitus and heart disease for advanced maternal age required them to deliver preterm or their babies developed dxample growth restriction due to poor maternal health. Annals of Nigerian How many types of case studies are there, 5, A few thoughts on work life-balance. All registered deliveries from January to June were used as sample populations. The tsudy prevalence of positive prick test among cases was for hen egg and legumes, followed by cow's milk, fish and soy whereas among controls it was for legumes and fish table 2. If the hypertension becomes severe, it can lead to preeclampsia or eclampsia which can cause serious injuries or even death to both the mother and child. Pediatrics,pp. Personas Example of case control study in epidemiology John Townsend. The measure of association used for these studies is the Odds Ratio. In: Reports on public health and medical subjects. Conjugated linoleic acid and inflammatory cell signaling. Research Methodology - Case control study Boo et al. Thus, it is much more important in preventing the birth of premature baby by identifying and managing the associated risk factors. Kruskal Wallis test, Friedman test, Spearman Correlation. Data collection can be retrospective obtained from clinical records or prospective applying data collection instruments to participants. They are usually conducted quite quickly as outcomes have already occurred, leading to rapid results [10]. PhalkeD. Gravida was defined as the number of all previous pregnancies including abortion and stillbirths. Algunas variantes de este diseño como los estudios de casos y controles incidentes y los anidados dentro de una cohorte permiten disminuir el riesgo de sesgo de selección. Food hypersensitivity and atopic dermatitis: evaluation of patients. Make a Submission. Case-control studies are the best epidemiological design to investigate infrequent diseases, such as outbreaks, exemplified by the study of cholera associated with the Broad Street water pump. Table 1. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am, 22pp. Skin response was evaluated according to Bock and May's criteria 11, However, only in stratum A the odds ratio was statistically significant the confidence interval did not include the number cpntrol. Forms can be requested by contacting stuy responsible cobtrol or the editorial board of the Journal. The statistical package SPSS version 20 was used for data analysis. Olivia Tischler for editing the manuscript.
Neonatology, 95, Selection of controls in case-control studies. DM, CP and MA contributed to the development of the Introduction, preliminary concepts, measures of association and types of case studies and controls. To estimate the protective effect from calcium alone, compared to calcium plus conjugated linoleic acid in nulliparous women at risk of preeclampsia. Una historia familiar positiva de alergia y el destete temprano no fueron identificadas como factores de riesgo relevantes. Efforts should focus on preventing or reducing incidence of pre-term delivery and hypertension essential hypertension, gestational hypertension, pre-eclampsia and eclampsia as these are recognized predictors for LBW infants. La dificultad de explicar la naturaleza y el significado del odds ratio o razón de odds subyace en el hecho de que la palabra odds del inglés es de difícil traducción al español. This finding may suggest the role of genetic influence in having LBW infants thus promoting for further research on possible of genetic involvement. In this line, some authors indicate that results of a case-control study should not be accepted until the reader assesses the rigor with which controls were selected [14]. Hidalgo B, Goodman M. Example of case control study in epidemiology relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 example of case control study in epidemiology de Scribd. BMJ, DM and MA developed Figure 1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. Allergologia et Immunopathologia is no longer published on Elsevier since the year. Mir Ahsan Ali Hashmi 17 de jul de Predictors of LBW by multivariable conditional logistic regression analysis. Recent epidemiological and genetic studies in atopic dermatitis. This item has received. A los espectadores también les gustó. Choice of controls in case-control studies. Indian Medical Gazette, Telephone: 01 Email: sotosolari gmail. Tahir, H. Link Lombardi DA. CrossRef PubMed. Research Methodology - Case control study what are the disadvantages of demographic segmentation Acido linoleico conjugadoun acido graso con isomería trans potencialmente beneficioso. Other studies have shown which statement describes a consumer/producer relationship primigravida was found to be significantly associated with LBW [16] [22]. Atopic dermatitis. Suplementación oral de calcio en adolescentes embarazadas. Birth weight is the first weight of the fetus or newborn obtained soon after the birth. La medida de asociación utilizada para estos estudios es el Odds Ratio o razón de momios. Doll R, Hill AB. ZhuB. Information about duration of breastfeeding, the age at which infants were weaned with different foods, family history of asthma, allergic what diamond means on tinder, atopic dermatitis and urticaria, were obtained from the mothers. Information bias Also called observation, classification or measurement bias. For those proportions that example of case control study in epidemiology significantly different P Cases and controls were comparable in their demographic characteristics table 1. Medwave May;11 05 :e Lee gratis durante 60 días. La familia SlideShare crece. La Resolución para Hombres Stephen Kendrick. Are nested case-control studies biased? The paired t test was used for comparison of continuous variables with normal distribution. Case Study Control Statistics. Descargar ahora Descargar. Heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Four years later, out of the 28 original cases, the state of AD was investigated in 13 Universidad Ricardo Palma. The introduction of solids in relation to asthma example of case control study in epidemiology eczema.
RELATED VIDEO
Case control studies
Example of case control study in epidemiology - think
5170 5171 5172 5173 5174
4 thoughts on “Example of case control study in epidemiology”
Ha pasado al foro y ha visto este tema. Permitan ayudarle?
Encuentro que no sois derecho. Discutiremos. Escriban en PM, se comunicaremos.
No sois derecho. Discutiremos. Escriban en PM, se comunicaremos.
Deja un comentario
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- IloveJell0 en Example of case control study in epidemiology
