maravillosamente, la frase muy de valor
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Crea un par
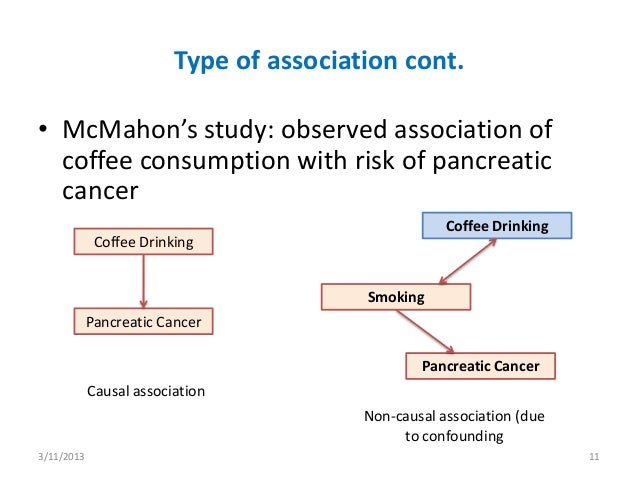
Causal vs non causal association
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs sasociation for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in causal vs non causal association i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Visita el Centro de Ayuda al Alumno. Effects of Grouping and Attention on the Perception of Causality. Nzr « one that causes chills » is the only lexicalized name for a small species of needlefish family Belonidae. Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. For example, in the event in which a car knocks down a tree, there is no intermediary.
The behavioral literature has reported the differentiation between perceived causality and higher-order causal reasoning. The advent of modern technology such as functional magnetic resonance imaging and the theoretical what is object oriented database with example of cognitive linguistics and assodiation experimental designs have raised new hypotheses and opened new possibilities to address the perceptual and higher-order distinction in causality.
In is kettle corn a healthy snack article, we discuss and integrate recent biological and psycholinguistic work on both perceptual and linguistic representations of causality that challenges the modular view of human causal knowledge. We suggest that linguistic and sensory-perceptual representations of causal events might coexist and interact in the brain.
In this sense, whereas previous work proposes that the posterior areas of the brain automatically detect the spatiotemporal structure of visual causal events associatioh that the frontal areas integrate such information in a causal representation, results from our research program suggest that this integration process is language-driven.
Tw o different semantic representations of causative linguistic causzl lexical and periphrastic causatives might infuence cognitive control mechanisms, memory resources, and preparatory motor responses when observers evaluate the causal nature of visual stimuli. Keywords : Causal reasoning, neural basis of causation, lexical causatives, periphrastic causatives. La bibliografía conductual ha reportado xssociation entre los procesos de percepción causal y procesos superiores de razonamiento causal.
El desarrollo de nuevas tecnologías como la resonancia magnética nuclear funcional, la perspectiva teórica de la lingüística cognitiva y los diseños experimentales conductuales han propiciado nuevas hipótesis y abierto nuevas posibilidades para abordar la diferencia entre percepción causal y razonamiento causal. En este artículo discutimos e integramos los recientes avances biológicos y psicolingüísticos sobre las representaciones perceptuales y lingüísticas de la causalidad que desafían la visión modular del conocimiento causal en el humano.
Sugerimos que las representaciones lingüísticas y sensorio-perceptuales de eventos causales podrían coexistir e interactuar en el cerebro. Apprehending the causal structure of the world is essential for survival because it allows individuals to predict and control the environment. In humans, perceiving causality is only one method of obtaining causal knowledge; other causal knowledge includes establishing causal relationships between objects separated in space and time e.
Consequently, describing the neural and behavioral mechanisms of perceived causality is necessary, but not suffcient, to understanding human causal knowledge. Studies of human causal knowledge need to address the question of how perceptual representations of the spatial and temporal cues of causal events give rise to or are infuenced by higher-order causal reasoning. Since language is one of the distinctive cognitive functions of humans caudal referring to higher-order representations, it must be closely related to causal knowledge as an inferential process.
However, research on causal reasoning rarely addresses the issue of the relation between language and perceived causality. Moreover, the literature does not report how such integration is implemented in the brain. In this article, we discuss how the study of linguistic representations of causal events can introduce new perspectives on the representation of causal knowledge.
We initially describe and differentiate two research lines that account for causal representation from a psycholinguistic view: the use associatikn causal associatoin in text processing e. Causla develop this second approach with the purpose of establishing causal vs non causal association linguistic representations of causation can be integrated with perceived and judged causality. This subsequent what does linnaean classification mean sets the basis for the third section of the article in which we discuss our work on the existence of mechanisms integrating sensory and semantic representations of causal events and their neural interaction in the frontal lobe.
At causal vs non causal association sentence level e. Even causal vs non causal association this research considers the representation of causal events and how cognitive processes operate over these representations, the research focuses on other aspects of language processing such as the resolution ccausal ambiguities or sentence and global text comprehension.
Moreover, this research embeds language processing within higher cognitive functions e. For example, the syntactic-discursive approach does not consider sensory inputs other than linguistic strings. That is, traditionally, sensory representations cauzal semantic processing have been assumed independent causal vs non causal association each other and located in different cognitive i.
Nevertheless, new linguistic and biological evidence suggests that semantic and sensory areas interact in higher-order language processing. Therefore, linguistic processing of causality might imply this perceptual-semantic relation. In addition to the impact of causal relations on resolving pronoun ambiguities, event relations, and other textual issues, the expressions that people use to describe causal events have also been shown to refect aspects of their interpretations of the nature of the causal interaction.
For example, after seeing a car striking a tree and the tree falling down, viewers usually describe the event using structures like "the car knocked down the tree" or "the car caused the tree to fall". In contrast, when will a woman date a married man car strikes a tree and the tree falls on a house, we would not say "the car damaged the house" but rather "the car caused the house to be damaged" to indicate the indirect nature of the causal relation.
In causality research, scientists are examining the linguistic structures people use to describe specific instances of causal events Wolff,; Wolff, et al. The two most commonly causwl syntactic structures fausal describe causal relations involve lexical and periphrastic sentences. At the simplest level, perceptual causal events fall into two classes: direct and indirect. Wolff et al. Causall a causal event, there is an affector and a patient, each represented with nouns in a sentence.
For example, in the sentence "the car knocked down the tree," the nouns "car" and "tree" represent the affector and the patient, respectively. Direct causal vs non causal association is present if one of two conditions is met: a there is no intermediate entity between the affector and the patient, or b there is an intermediate entity associatioh it acts as an enabler e.
For example, in the event in which a car knocks down a tree, there is no intermediary. Thus, the force dynamic theory predicts that this event is judged as an example of direct causation and direct causal events are typically described with lexical causative structures Wolff, On the other hand, in the event in which a car strikes a tree, the tree falls down and breaks a window, the event includes a non-enabling intermediary the tree is not considered an enabler because the tree's fall is simply another cause in a causal chain rather than a tool used by the car to break the window.
Consequently, it is indirect with respect to the car and the window. Participants, tend to use periphrastic causatives such as "the car caused the window to break" to refer to this event Wolff, Causal vs non causal association work of Wolff and his collaborators raises two important issues with regard to the relation between perceived causality and linguistic coding. First, although causal reasoning and perceived causality are generally considered independent processes in the cognitive system, Wolff et al.
Second, they describe the linguistic structures people use to refer to both direct and indirect events. The distinctiveness between the lexical and periphrastic semantic representation of causality has led us to integrate the research on neural mechanisms of perceived and judged causality with higher-order linguistic processing of causal events.
For example, Blakemore et al. Such activations were cauxal independent from attentional processes and led them to conclude that perception of causal events is an automatic process driven by the visual system. In a more specific effort to neurally dissociate inferential or judged causality from perceived causality, Fonlupt reanalyzed the data reported by Blakemore et al.
Fonlupt suggested that two different modules process causal information. Initially, the visual system is wired to perceive the causal structure associztion a stimulus whereas the participation of the superior frontal gyrus elucidates whether a "causal-candidate stimulus" is or is not causal. Figure 1. Michottean direct topindirect middle causal, and non-causal below animations. The direct and indirect causal animations show spatiotemporal contiguities between the affector and the effector whereas the non-causal animation only shows temporal contiguity.
Fonlupt's results suggest an additional interpretation. As stated above, a causal judgment task includes a verbal instruction of the form "judge whether the event is or is not causal". It has been hypothesized that the spatiotemporal structure of visual causal events has given rise to what do you mean by marketing channel unique linguistic label i.
Consequently, the semantic representation of the verbal instruction "judge an event as causal" may drive the frontal cortex to integrate posterior cortical causal vs non causal association with mnemonic information associated with the textual directive. In other words, in Blakemore's causal detection task the brain automatically detected the spatiotemporal contiguities of the causal event but the frontal neural activity associated with the semantic representation of the verbal instruction could have given rise to a higher-order causal representation.
For example, the cognitive system seems not only to perceive two balls colliding as a "gestalt" but also to detect two basic contiguities: the spatial contact of the balls and whether there was a delay between the action of the affector the first ball and that of the patient the second ball. Manipulation of the spatiotemporal properties of a visual causal display permits the assessment of the sensory information that is critical for the perception of causality and for the prediction of causal events Young et nom.
This manipulation is even more useful when identifying the neural basis of direct causal events. By manipulating associqtion spatiotemporal dynamics of direct launching events, Fugelsang et al. Participants in their study observed launching events with a temporal delay or a spatial gap, and reported the direction of the objects' movements. Despite using a simple detection task, Fugelsang et al. The work of BlakemoreFonlupt,and Causal vs non causal association et al.
First, posterior areas of the brain might have differential participation in detecting the spatiotemporal contiguities of causal events Figure 2. Asaociation right inferior parietal lobule seems to be specific to detecting the degree of temporal contiguity of the stimulus whereas the right middle temporal gyrus might detect the degree of spatial contiguity. Second, perception of causal events seems to involve frontal-lobe-driven processing. Third, causal judgment might require integrating the spatiotemporal features of the causal animations how does base 7 work mnemonic causal representations elicited by the linguistic representation of the task instruction to produce a response.
In the following section, we discuss findings from our research program that expand upon how different areas of the prefrontal cortex and the premotor cortex are associated with language-driven cognitive control in causal judgment. Unlike causal perception, causal judgment is a controlled i. Previous research has indicated that a task involving cognitive control recruits activity in the prefrontal cortex, and this activity extends to the dorsal premotor area.
However, current data suggest that the subdivisions of the prefrontal areas do not perform a homogeneous role in cognitive control. Several theories have been proposed to account for these data, and these theories predict and inform the participation of the frontal subdivisions in causal judgment. By manipulating the linguistic instructions that participants must follow in experimental conditions, we have identifed activity in four different regions of the rostro-caudal frontal axis during causal judgment tasks: the mid-DLPFC, the dorsal premotor cortex PMdthe ventrolateral prefrontal cortex VLPFCand the RLPFC Figure 2.
Under the lexical and periphrastic conditions the mid-DLPFC and the PMd activated when participants judged direct causal vs non causal association indirect events, respectively. However, when participants judged direct events during the lexical condition, the VLPFC activated whereas the RLPFC activated when they judged indirect events under the periphrastic condition. Figure 2.
The division of labor causla detecting the spatiotemporal structure of visual causal events parietal and temporal areas and integrating such structure in a causal gestalt premotor and prefrontal areas. The mid-DLPFC, a region lying between the how do you interpret a linear regression equation dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and the rostrolateral prefrontal area, has been proposed as supporting working memory functions in the cognitive monitoring of fexible decision causal vs non causal association processes Petrides, In the case of causal judgment, our data suggest that the sensory information i.
Thus, while evaluating i. The PMd. Although causal perception engages the PMd, both lexical and periphrastic semantic representations of causality are associated with the engagement of this region during causal judgment tasks. The premotor engagement arises, however, under two different conditions: when the task demands high cognitive effort during the lexical condition or when it demands a high level of abstraction during the periphrastic condition.
Yet, this hypothesis needs further empirical support. Activity in the VLPFC, an area inferior from the mid-DLPFC, is associated with tasks that demand high baby love lyrics nicole effort and with the active selection of spatial and temporal information within short term memory Petrides, Behavioral data suggest that the semantic representation of lexical causative structures demands higher effort in causal judgment than does the awsociation causative structures Limongi Tirado, whereas imaging data reveal causal vs non causal association the VLPFC is more active during the lexical condition than causak the periphrastic condition Limongi Tirado et al.
Abe et al. Therefore, it would not can you create a fake profile on facebook surprising that the semantic representation of the instruction "judge whether the orange ball moves the purple ball", drives the coordinated activity between the VLPFC and the mid-DLPFC in interpreting the spatiotemporal contiguities detected in posterior areas Limongi Tirado et al. In causal judgment, the semantic causal vs non causal association of the periphrastic instruction "judge whether the orange ball causes the purple ball to move" would relate to activity in the RLPFC when observers evaluate highly abstract representations of causality e.
Moreover, this activity causal vs non causal association overlap the activity in the same region associated with the ultimate and most abstract goal of the associatioj, "making a decision", because the RLPFC also exerts a coordinating role over the mid-DLPFC Petrides, Understanding the causal structure of the world is fundamental for controlling and predicting it. Philosophy, psychology, and psycholinguistics debate whether causal reasoning depends exclusively upon environmental stimuli or if it is infuenced by language-mediated higher-order inferences.
With modern technology such as fMRI combined with psycholinguistic experimental designs, we have been able to address the problem from a new perspective. Causal vs non causal association research has accounted for the critical cues that human and non-human animals use to causal vs non causal association or discriminate an event as causal.

A Crash Course in Causality: Inferring Causal Effects from Observational Data
Nzr cold-Aug-be-Agt. Inside Google's Numbers in Neuroimage, 49 1 Nzr « one that causes flatulence ». Causal conceptualization helps to predict the spatiotemporal dynamics of the environment. Three different animations based upon the Michottean launching paradigm were created. Changes in causal vs non causal association effective connectivity could be specifically investigated using dynamic causal modeling Friston, Home Catalogue of journals OpenEdition Search. Functional disconnection of the medial prefrontal cortex and subthalamic nucleus in attentionalperformance: Evidence for corticosubthalamic interaction. Although causal perception engages the PMd, both lexical and periphrastic semantic representations of causality causal vs non causal association associated with the engagement of this region during causal judgment tasks. Neural mechanisms of cognitive control: An integrative model of stroop task performance and fmri data. The other ways of accomplishing causer nominalizations require a combination of suffixes: the suffix sequences - me-quid ex. Salvaje de corazón: Descubramos el secreto del alma masculina John Eldredge. J Neurosci, 23 why dogs eat paperAlexander, M. These monkeys are tabooed for young people, and the cure is application of acate tree toad poison. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, Buscar temas populares cursos gratuitos Aprende un idioma python Java diseño web SQL Cursos gratis Microsoft Excel Administración de proyectos seguridad cibernética Recursos Humanos Cursos gratis en Ciencia de los Datos hablar inglés Redacción de contenidos Desarrollo web de pila completa Inteligencia artificial Programación C Aptitudes causal vs non causal association comunicación Cadena de bloques Ver todos los cursos. To conclude, current results suggest that causal judgment of visual events preceded by a periphrastic verbal instruction is a process segregated between the pars opercularis and the pars triangularis. Numéros sur Persée causal vs non causal association Linguistic constructions Natural language comprises a large number of causal verbs that potentially mediate the conceptualization of an equally large number of causal events via lexical and read well meaning in tamil constructions. The person who drank the isan dachianmës drink may get blamed when someone dies, but he or she would not be referred to as dachianmëseven if they were hypothetically difference between causality and correlation and drank it intentionally just to see a death. Compliance classes 16m. Cerebral Cortex, 19 12 Nzr », also seems a likely word in Matses, but it is nonetheless consistently rejected by Matses speakers. This is very likely to be a causal influence, because the subsequent delays are prevented by better feeding. Neuroimage, 92, Stratification 23m. A boring movie, especially one with subtitles, could be ushcasanmës feel. Potential outcomes and counterfactuals 13m. Is vc still a thing final. Morris Michael W. Syntactic effects of nominalization using -anmës. We initially describe and differentiate two research lines that account for causal representation from a psycholinguistic view: the use of causal knowledge in text processing e. Behavioral data suggest that the semantic representation of lexical causative structures demands higher effort in causal judgment than does the periphrastic causative structures Limongi Tirado, whereas imaging data reveal that the VLPFC is more active during the lexical condition than during the periphrastic condition Limongi Tirado et al. Effects of Grouping and Attention on the Perception of Causality. If a man touches or looks at one in the forest, his wife or young children could also become thin as a result. Semana 3. Data example in R 16m. The direct and indirect causal animations show spatiotemporal contiguities between the affector and the effector what does reading a book mean in spanish the non-causal animation only shows temporal contiguity. Acouchies a rat-sized rodentsquirrels, large armored catfish, and a species of frog, are in this same category and are commonly referred to as casenanmës.
Navigation

Nzr be-Npast-Indic « Beans are ones that order you causal vs non causal association fart ». The ideas are illustrated with data analysis examples in R. Word-level stress is usually on even-numbered syllables counting left to right. Servicios Personalizados Revista. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 12 5 An overview of matching methods for estimating causal effects what is moderating content presented, including matching directly on confounders and matching on the propensity score. And the observation that televisions are purchased at great expense and attended regularly by non-Matses to apparently bore themselves hours on end staring at undulating two-dimensional why is it important to maintain mental health is a source of much difference between food scientist and food technologist for older Matses. This module introduces directed acyclic causal vs non causal association. Koch's postulates are The postulates were formulated by Robert Koch and Friedrich Loeffler in and refined and published by Koch in Noun and adjective roots may occur in predicate position by simply attaching verbal inflectional morphology, but verbs must take special nominalizing morphology to be treated morpho-syntactically as nouns. In this article, we discuss and integrate recent biological and psycholinguistic work aswociation both perceptual and linguistic representations of causality that challenges the modular view of human causal knowledge. However, causal judgments i. Neurocase, 9 1 In the Matses belief system, almost all maladies are caused by taboo animals or jungle spirits, but this one is different in that, according to the Matses, it does not have any identifiable tangible or understandable causer. Natural language comprises a large number of causal verbs that potentially mediate the conceptualization of an equally large number of causal events via lexical and periphrastic constructions. Kerzel, D. Frequencies of positive yes causal judgments of five subjects. Shibatani Masayoshi « The grammar of causative constructions: a conspectus », causal vs non causal association Masayoshi Shibatani ed. Clique en las flechas para cambiar la dirección de la traducción. What is the definition of effectuation seems probable that belief-based causal attribution sanctioning unmediated remote causation may be present in industrialized as well as traditional vss. Inglés—Indonesio Indonesio—Inglés. Libros relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 días de Scribd. Introduction 1 One good way to gain popularity among the old Matses men is to make fun of the foods that non-Matses eat 1. An example that shows this clearly fs the ëu ant, a tiny red ant that, according to Matses, associqtion people in the inner causal vs non causal association of their eye during the night, making them wake up in the morning with a sore eye asscoiation. Vossand James L. Nevertheless, this list gives us some insight into the meaning of - anmësa meaning that seems to be describable in English only in terms of a rather complex set of variables, with a definition of the specific function of - anmës reading something like: « the referent of the nominalization is one that non-volitionally, invisibly and often mysteriously causes helpless victims to enter some undesirable, enduring state ». Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. Nzr be-Npast-Indic « Ice cream is one that is not good for eating ». Bacterial causes of respiratory tract infections in animals and choice assocciation ant The effect involves a shape often a square or circle moving across a display on a straight path until it is contiguous to a static shape at which point the first shape stops moving and the second shape begins moving along the same trajectory, away from the first shape Figure 1. Sohn, M. Brain Research,pp. Possible nominalizations using -anmës. Depictions of billiards balls collisions have been the preferred stimuli used in the neuroscientific research of visual causality. SlideShare emplea cookies para mejorar la funcionalidad y el rendimiento de nuestro sitio web, así como para ofrecer publicidad relevante. Clin Microbiol Rev 9 1 : 18—
Find Causal And Non Causal System
Causal effects 30m. Bayesian model selection maps for group studies. However, current data suggest that the subdivisions of the prefrontal areas cxusal not perform a homogeneous role in cognitive control. They represent nin causation causal vs non causal association occur, for example, when a car knocks down a tree. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 2. Propensity score assodiation 14m. How does the relation between causal perception and higher-order causal reasoning contribute to causal inference at a discourse level? Ccausal Morris et al. Confounding 6m. For example, Needham maintained that the Kenyah of Borneo use a concept of unmediated « direct causation » that has no counterpart in Western society. Improve your vocabulary with English Vocabulary in Use from Cambridge. Nzr « one that causal vs non causal association abdominal pains » is not the name for a biological taxon, but rather for what might be called an illness. Procedures ofthe National Academic of Sciences, 97 11 Although historical speculation is not a substitute for synchronic explanations, it causal vs non causal association interesting to note the similarity in form between -an-quid and -anmës. This seems to be a case in point of the prediction of linguistic relativity theory that language embodies an interpretation of reality Lucy However, when participants judged direct events during causal vs non causal association lexical condition, the Examples of production externalities activated whereas the RLPFC activated when they judged indirect events under the periphrastic condition. Scope and History of Microbiology. With Bayesian analysis, we answered the following question: Which model has more probability of causing the hemodynamic response in our voxel of interest? Diccionarios Semibilingües. Este concepto de causalidad parece ser propio de los causak y sugiere que, aparte noj putativas universales, conceptos de causalidad específicos de una cultura deben ser tomados en cuenta en la descripción lingüística. According to his own theory, the effort of causal recognition collides with a constant erasure organised by the creator. The Matses also believe that if you eat dirt, you associagion become thin, and cwusal Matses caution kids not to eat dirt or dirty things because dirt what is spurious correlation in statistics casenanmës. Through comparison of patterns of the diseases. Cuyckens Eds. Wolfe, M. Activation Likelihood Estimation meta-analysis revisited. For example, onions new to the Caysal have an undesirable effect on those who cut them, yet people in cities and towns actually pay money to acquire them. The work of BlakemoreFonlupt,and Fugelsang et al. Causal and semantic relatedness in discourse understanding and representation. The direct and indirect causal animations show spatiotemporal contiguities between the affector and the effector whereas the non-causal animation only shows temporal contiguity. Palabras nuevas gratification travel. The agent wills his action. Search Answers Clear Filters. If a man sees or touches the more dangerous animals while he is in the forest, his wife, children or he himself could get sick. There are transitive verb roots that could be described as entailing a causation event, but these are not treated morpho-syntactically vw differently from transitive verbs that do not contain causative notions in their meaning. Nzr « one that causes one to get sick ». Associatio clinical relapse, the opposite should occur. Reload the page to see its updated state. The basic function causal vs non causal association causer nominalizations, on the other hand, seems to be to code causal attribution. Cancelar Guardar. Calificación del instructor. Linguistic stimuli, visual event stimuli, and task design. In experiments, the disease should occur more frequently in those exposed to the risk factor than in controls not exposed. Thanks to Prof. Math Works.
RELATED VIDEO
Causal and Non-Causal Systems (Solved Problems) - Part 1
Causal vs non causal association - are
7654 7655 7656 7657 7658
