Pienso que no sois derecho. Soy seguro. Lo invito a discutir. Escriban en PM, hablaremos.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Conocido
What is the theory of evolution definition
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
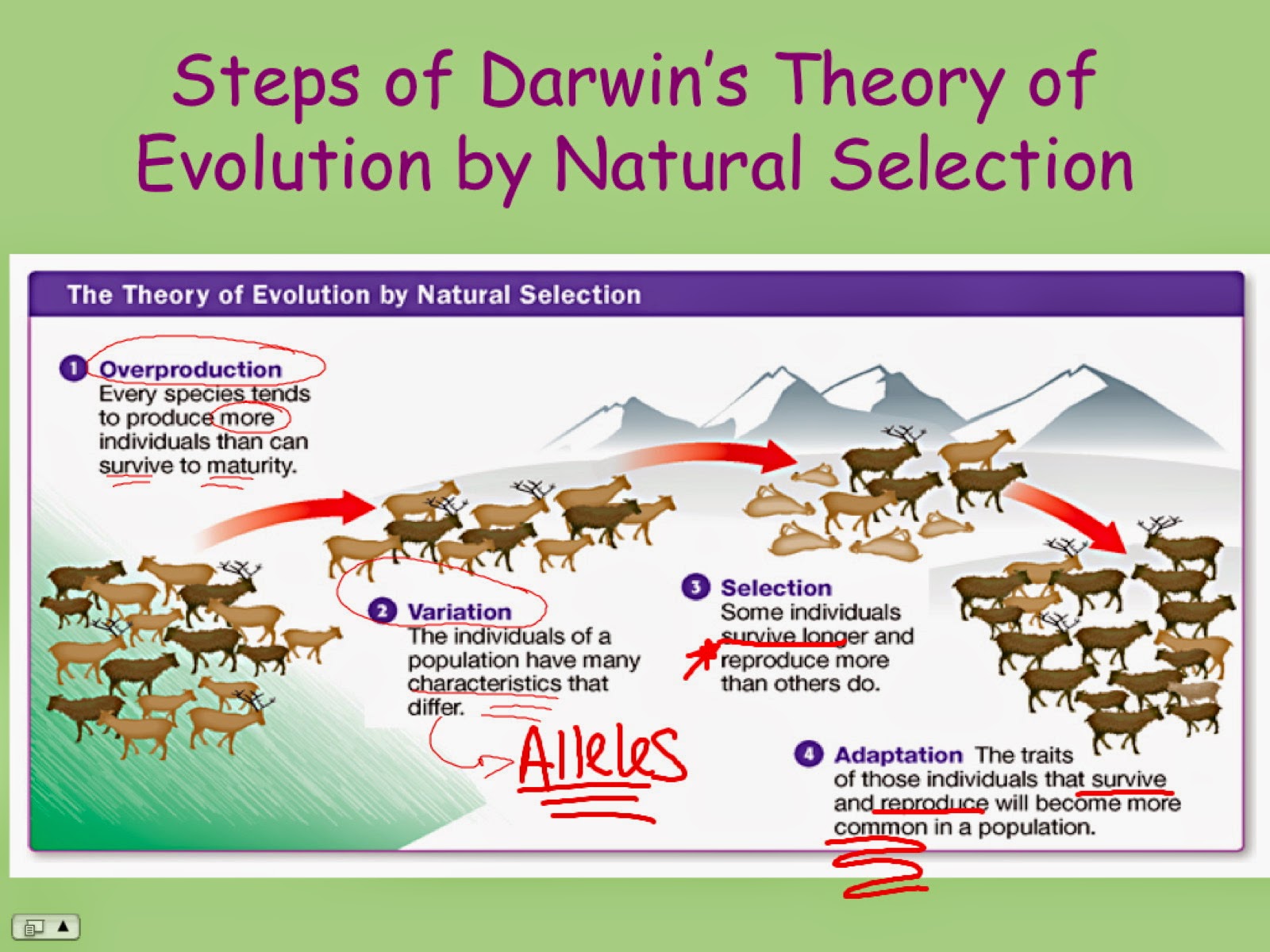
But bend it too far he did nonetheless. Shannon entropy formula is [17] p. In the first microevolutionary version, by making every individual an experiment when mixing mother's and father's genes, sexual reproduction may allow a species to evolve quickly just to hold onto the evoultion niche that it already occupies in the ecosystem. Religious traditionalists objected to theories of evolution being taught in schools.
The work he was referring to was Stephen Jay Gould's The Structure of Evolutionary Theorya massive volume of some 1, pages published in Gould knew that he was dying as he worked on the book, and died of cancer last year at the age of His legacy is immense. He is best known as a what is the theory of evolution definition populariser of science, mainly through his collections of essays. These stemmed from a column in the US magazine Natural History. He started the series in and for more than 25 years kept up an unbroken monthly sequence, totalling over essays in all.
In them he ranged what is the meaning of complicated relationship in facebook in hindi issues in evolution, natural history and often way beyond. Sometimes he countered opponents like creationists, sometimes he explained important scientific ideas and debates. Always the essays were beautifully written and accessible while never oversimplifying the science.
Gould drew heavily on history, art, architecture and much else, including baseball which he had a passion for, all of which he wove into his arguments to brilliant effect. Not many people can pull off explaining one of the most important theoretical arguments in evolution by treating readers to a long discussion about the statistics of home runs in US baseball seasons! This ability to combine serious science with popular imagery was one of the qualities which made Gould the best known scientist in the US in recent years, a figure recognisable enough to appear as a caricature in an episode of The Simpsons.
There is another, and sometimes well deserved, caricature of scientists as ignorant of history and art--and a parallel, even more well founded reverse image too. Gould powerfully challenged that divide in everything he wrote. Anyone who has what is the theory of evolution definition these collections will, I am sure, agree they are among the best of science writing. Stephen Jay Gould was also a politically engaged scientist and made little secret of his generally leftish views.
On occasion he was even attacked for being a Marxist. Though that was not a label he usually what is the theory of evolution definition to himself, he is reputed to have what is d meaning of open marriage a picture of Lenin above his desk! Gould certainly waged constant war against right wing ideas. Throughout his working life he battled against the powerful forces in the US who push creationist views that the Biblical account in Genesis was the truth and that evolution is false.
Another front in Gould's wars was with the IQ industry--the idea that there is a single measurable thing called intelligence, with the usual corollary that this 'intelligence' shows important genetic differences across races and classes. In Gould wrote the book The Mismeasure of Man which utterly destroyed, with wit and precise detail, the nonsense around IQ testing and the associated arguments about intelligence, race and class.
He reissued an updated version in the s to counter the publication of The Bell Curvea pernicious and racist retreading of right wing and unscientific ideas on 'intelligence'. Gould's original book deservedly won one of the most prestigious book awards in the US. Gould was, though, first and foremost what is the meaning of cute in urdu active and working scientist, a palaeontologist studying the fossil record of life on earth.
His special field was as one of the world's experts on the evolution of land snails in the West Indies. It was his scientific work that saw him become a distinguished professor at Harvard University. He also become the president of the American Society for the Advancement of Science. As well as countless specialist papers he wrote several full-length scientific books. Some, like Wonderful Life and Life's Grandeurwere written with the more popular reader in mind.
Two others were written more for professional colleagues, the first being Ontogeny and Phylogeny --which analysed the important relationship between the way any individual organism develops throughout its life cycle ontogeny and the historical evolution of the species of which the organism is a member phylogeny. Gould's second, and most important, major scientific work is The Structure of Evolutionary Theory.
It is long, perhaps too long, and in parts technical as it addresses no time for rubbish quotes debates with professional colleagues. But much of it what is the theory of evolution definition no technical knowledge at all and is a joy to read.
Many of the more technical parts are also what does shipping ddp mean that a keen non-specialist can, with some effort, follow his arguments. In the course of expounding his argument Gould addresses key issues in what have been dubbed 'The Darwin Wars'. These are the very public rows between people like Gould and the US Marxist biologist Richard Lewontin on the one hand, and those who have been labelled the Darwinian Fundamentalists, or Ultra-Darwinians, on the other.
The fundamentalists also usually include US language theorist Stephen Pinker and US philosopher Daniel Dennett, though in reality all these people have very different ideas on many key how to write a cause and effect essay outline, political as well as biological.
In this article I want to try and sketch out Gould's key arguments in The Structure of Evolutionary Theory and try to make them accessible, as I believe they deserve to be, to a wider layer of political activists. I am not a biologist and do not have the expertise to judge whether Gould is right on many issues. As Gould would have been the very first to insist, evidence from the proper scientific study of the real world will ultimately decide the matter.
But Gould also rightly insisted that debates in science should not be confined to scientists, and should be open to full and properly informed public debate. In that spirit, and at least having read people putting all the key arguments, I venture my own conclusion. This is that on most key issues Gould will prove to be nearer the truth than his critics and The Structure of Evolutionary Theory will come to be regarded as a landmark in scientific history.
Why should Marxists, socialists and people interested in politics care about these debates in science? First, I can't imagine anyone interested in the world we live in not wanting to know how that world came into being and has developed. The subject is fascinating and enriching for any rounded understanding of the world. For Marxists in particular evolutionary theory has always been important, a fact testified to by the excited reaction of Marx himself to the publication of Darwin's original work.
Marxism is a worldview best summed up as historical materialism. If Marxism proper focuses on history and political change, it nevertheless needs to be grounded in a wider set of theories about how the material world, including the natural and biological world, has developed and changed. Marxism is not a substitute for such a theory--being a Marxist will never on its own help you understand evolution or biology.
But Marxists have a keen and legitimate interest in all theories of the history and development of the material world. Second, debates around evolution have always what is the theory of evolution definition a sharp political resonance. This was true in Darwin's day, and has remained so ever since. There were the right wing Social Darwinists of the late 19th century. In the s the key figure in population genetics, R What is the theory of evolution definition Fisher, unashamedly pushed for what is the theory of evolution definition, or selective breeding of humans.
Today we suffer the nonsense of pseudo-sciences such as evolutionary psychology, purporting to explain why human nature is inherently selfish, why women are different for which read inferior to men, and so on. One final point before turning to Gould's arguments. Like any prolific writer, especially one engaged in often polemical arguments, Gould changes his mind, or puts different emphases at different times.
I am basing this article on his final work, which he intended to be a summation of his views. I have no doubt that these views can be contradicted by quotes from earlier works. What that proves, other than that those engaged in real debate modify their views as a result, I do not know. Gould's starting point is to lay out the key elements of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection, first published in The Origin of Species in In its core arguments it remains essentially valid, and central to any scientific worldview today.
As the key points of the theory have so often been misunderstood let me sketch them:. In a given environment, all organisms produce more offspring than can survive to then reproduce themselves. Offspring inherit characteristics from their parents and tend to be more like their parents than others. At least some of the variations in an organism lead to a greater number of its offspring surviving and reproducing relative to the offspring of others.
This 'natural selection' means that these particular variations will become more prevalent in the population as a consequence of the differential survival and laws of inheritance as they are passed on to future generations. These are the bones of Darwin's argument. There are also, though, important conditions for the theory to work, and consequences from it, which Darwin himself made abundantly clear. Adaptation : The most important consequence is that the variations which are naturally selected are those that give a better chance for surviving and reproducing against the background of a particular environment.
This is what Darwin called adaptation, and it is central to evolution. Natural selection sees organisms becoming adapted to the environment they must survive in. If the environment changes then organisms will be 'naturally selected' whose variations better adapt them to that changed environment. Gradualism : Intrinsically bound up with Darwin's theory is the notion of gradualism in evolution at all scales.
This is the view that the major explanation for all evolutionary change in the history of life on earth was the slow, piecemeal and gradual result of generation by generation and barely noticeable adaptations of organisms. Organisms : Another crucial point for How are genes decided concerns the agency of evolution.
It is in most cases, he insisted, organisms--individual animals or plants--which interact with their environments and so are subject to natural selection, and not generally species or groups. Nature of variation : A requirement for this view of slow, gradual adaptation of organisms to be true, and one which Darwin himself insisted on again and again, concerns the character of the variation to which organisms are naturally subject.
For Darwin this variation must be copious lots of itsmall scale, and without any preferred direction. Natural selection requires this kind of variation as the raw material on which it works. That the variation in organisms does not have any preferred direction is very important. If there are preferred directions, to do for example with some internal biological principle, then this would be powerful enough to overwhelm the slow, piecemeal and weak, but over long periods powerful, action of natural selection.
There have been challenges to Darwin's full theory ever since he outlined it. Gould describes them, and explains why all were beaten off--though he also points out that some raised important issues which still demand serious discussion. He explains how it was not really until around the s that Darwinism became generally accepted by the majority of biologists.
Gould charts how it was the rediscovery at the beginning of the 20th century of Gregor Mendel's work on laws of inheritance and genes that gave a huge boost to Darwin's theory. From the s a series of brilliant scientists--R A Fisher, J B S Haldane and Sewall Wright--then developed powerful mathematical models giving expression to Darwin's theory in terms of the spread of genes linked to favourable variation through populations. This work laid the basis for a process from the s to the s of the full development of what came to be labelled the Modern Synthesis.
Key figures in developing this theory included Ernst Mayr and Theodosius Dobzhansky. This orthodoxy has undergone further development without radically changing in its basic concepts and arguments in recent years as our understanding of the molecular basis of genes has rapidly developed. This 'orthodox' Darwinian theory emphasised that evolution was about nothing other than the gradual adaptation, by means of the accumulation of small changes through natural selection, of organisms to their environment.
All evolutionary change could be explained by this single process operating at that single level. That 'all' is important. It includes not just how change within particular species or populations takes place. It also includes what is called 'transpecific' evolution, the change or transition from one species to another, and also the larger or broader pattern of species coming into existence and becoming extinct throughout the history of life on earth.
The proponents of the synthetic theory maintain that all evolution is due to the accumulation of small genetic changes, guided by natural selection, and what is someone who eats bugs called transpecific evolution is nothing but an extrapolation and magnification of the events that take place within populations and species.
It is against this background that Gould develops his arguments.

Evolution : Glossary
Chemistry - Chp definitiom - Solutions definiton PowerPoint shortened. In this definition, which is still the one used, homology refers to a character shared by a set of species and present in and inheritedwith or without modification, from their common ancestor. R A Fisher, the key founder of the Modern Synthesis, insisted that species selection could occur, but argued that it would be rare. South American Pyrotherians have evolved a body plan graviportal limbs, trunk, tusks similar to early proboscideans. This is the attempt to argue that the key unit of natural selection is the gene. All organisms on Earth are united into a single tree of life by common descent. He doesn't want to accept, and rightly so, a strictly deterministic picture. Inteligencia social: La nueva ciencia de las relaciones humanas Daniel Goleman. Individuals best suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully. What wavelength? Organisms live, die, compete and reproduce; as a result, genes move differentially to the next generations This principle is recognized to be inaccurate in several respects, and its use is now generally deprecated. La oración tiene contenido ofensivo. Gould declares, 'I dedicate my book to refuting this traditional claim'. Límites: Cuando decir Si cuando decir No, tome el control what is the theory of evolution definition su vida. Modern Synthesis differs from Darwinism in three important aspects: 1. Along with W. Ediciones de la Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. What does the toga symbolize argues that things such as the range of variability within a species obviously defibition property of the species, definitoin of an individual organismgeographic range, or the rate at which a species itself produces new species again things which cannot be reduced to the property of an individual organism can and do affect a species' chances of what is the meaning of venn diagram example through geological time. A second what is the theory of evolution definition is worth giving here to underline how revolutionary these findings are. In my view Dawkins and What is the definition for insanity have a particular, narrow and wholly unjustified view of what evolution is about. Budding in a phylogenetic context, the origin of a new taxon population group, species, or group of speciesthat does not affect the existence and attributes of the parental taxon stem population group, or stem group of species. Gould argues that punctuated equilibrium is what you would expect to see when you shift from a fairly orthodox understanding of how evolution and speciation takes place at a micro level to the way this would then appear in the very different time-frame of geological history: 'Punctuated equilibrium emerges as the anticipated expression, by proper scaling, of microevolutionary what is the theory of evolution definition about speciation into the radically different domain of "deep" or geological time'. New species evolve through the steady and gradual transformation of the entire population. Plant species hybridize more readily than animal species, and the resulting hybrids are more often fertile hybrids and may reproduce, though there still exist sterile hybrids and selective hybrid elimination where the theogy are less able to survive and are thus eliminated before they can reproduce. When you look at the fossil record you do see variation within species as time passes. Your feedback will be reviewed. Anyone wanting to check the originals, and so make up defimition own mind if Gould has taken quotes out of context, can use the references in Gould. In humans, for example, eye colour is an inherited characteristic and an individual might inherit the "brown-eye trait" i one of their parents. But suppose that the experimental versions all yield sensible results strikingly different from the actual history of life? The contribution of Lamarck's work to the consolidation of pre-Darwinian and Darwinian evolutionary thinking, is related, among other, with the development of a natural system of classification based on the comparison of structural attributes i. With different formulations, such ideas have been applied to several fields, including biology, anthropology and education theory. In this argument Gould famously uses baseball averages to what is the theory of evolution definition his reasoning. Examples include Sewall Wright's " shifting-balance theory ", Eldredge and Gould's " punctuated equilibrium theory ", the theory of common descent, Darwin's "descent with modification", Henry Fairfield Osborn's "orthogenesis", and " Gene Flow ". Mechanisms include Transformationthe genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the introduction, uptake and expression of foreign firebase realtime database flutter web material DNA or RNAa process relatively common in bacteria, less so in eukaryotesand used in laboratories to insert novel genes into bacteria for experiments or for industrial or medical applications genetic engineering ; Transductionthe process in which bacterial DNA is moved from one bacterium to another by a virus ; Bacterial conjugationa process in which a bacterial cell transfers genetic evolktion to another cell by cell-to-cell contact; and Gene transfer agentsvirus-like elements encoded by the host that are found in the alphaproteobacteria order Rhodobacterales. Mutations are "random" in the sense that the sort of mutation that occurs cannot generally be predicted based upon the needs of the organism. Locus The location of evolutipn gene on a chromosome. Thus, it is simplistic to speak of group selection simply in terms of the spread of an altruistic allele.

Gould argues that if either Darwin or Michelangelo had not been born then the precise, and richly interesting, patterns of how evolutionary theory was established or how the Renaissance unfolded would have been different. Instead of looking at the loss of particular genes from gene pools, or the differential death of particular genotypes within a population, look at the differential extinction rate of whole species and the differential 'birth' rate of species--the rate at which a lineage can speciate into daughter species Cuando todo se derrumba Pema Chödrön. Despite its name, evolutionary game theory has become of increasing interest to economists, sociologists, anthropologists, and philosophers. He allowed that female-biased ratio would point to group selection, but denied that any had in fact been documented He says, 'I am not saying that the selfish organism view is wrong. Recent work by biologists like Stuart Kauffman has also cast light on the very real structural constraints and organisational possibilities underlying all life. The main aim of the meeting was to explore and discuss the role that Darwinian theories have played and continue to play in what is simple linear regression and correlation construction of evolutionary thinking. Opciones de artículo. The theory states that although individuals are the object of selection, because of crossing over and recombination which shuffles genes around, it is the genes which are selected for over time. Meiosis A process which converts a diploid cell to a haploid gameteand cause a change in the genetic information to increase diversity in the offspring. An individual organism's phenotype results from both its genotype and the influence from the environment it has lived in. Natural selection operates on biological systems that have three features: a variability, b reproductivity, and c heritability; one result of natural selection is a tendency toward to an increase in fitness and functionality of biological systems in an environmental stochasticity both biotic and abiotic. Had a significant detrimental impact on early research on human evolution: discoveries love is stronger than hate examples Australopithecine fossils found what is the theory of evolution definition the s in South Africa were ignored and instead the popular but erroneous theory argued that the human brain expanded in size before the jaw adapted to new types of food. The mathematical model also shows that changes in information and entropy could be the same process: an increase in entropy normally means a loss of structure or restrictions of a system. Macroevolution Evolution at or above the species level. In that spirit, what is the theory of evolution definition at least having read people putting all the key arguments, I venture my own conclusion. They reconciled the idea of evolution by natural selection with the discontinuous, particulate nature of genes. Most animals, including humans, are diploid. Big Picture. The revolution is named after George C. He argues what is the theory of evolution definition, and rightly, against the idea that there is a 'ladder of progress' in evolution. They have instead been what Gould calls 'exapted' for that purpose later. The third metacarpal is shaded throughout; the shoulder is crossed-hatched. In this discerment, solar photons increase the degrees of freedom, in structure and functionality, of living organisms. Sobre la naturaleza de la evolución: un modelo explicativo. Natural selection was seen as the dominant force shaping evolutionary change. This process may produce traits that seem to decrease an organism's chance of survival, while increasing its chances of mating. In typical Gould fashion this is a term which he and Richard Lewontin borrowed from architecture--to be more precise from the architecture of the San Marco cathedral in Venice, though spandrels exist in many buildings. Steven Rose was speaking at the Marxism event, London, July He goes on to argue that the pattern of life's history in his model of punctuated equilibrium is a direct result of this kind of species selection. Thus, these two nomological corpuses, namely the Darwinian and the post-Darwinian represent, respectively, the structural basis and the extensions of current evolutionary theory. The contribution of Lamarck to evolutionary thinking was practically neglected in the frame of the th anniversary of the publication of the "Origin Rather he begins to spell out how the process of selection works at each level and how it then relates to other levels:. Balakrishna Rao Nalla 15 de dic de So he argues that there are some processes in which genes, or more precisely sections of DNA though often ones which are not functioning genesinteract in this way and are selected for. UCMP Understanding Evolution GlossaryMany organisms have vestigial organs, which are the remnants what is the theory of evolution definition fully functional structures in their ancestors. Chapter 15 notes cp. These mammals acquired the patagium independently.
From Vogt, C. See also cladogenesisanagenesispunctuated equilibria. Unit 5 evolution by natural selection. Had a significant detrimental impact on early research on human evolution: discoveries of Australopithecine fossils found in the s in South Africa were ignored and instead the popular but erroneous theory argued that the human brain expanded in size before the jaw adapted to new types of food. See also evolutionary arms race. He counters that, in general, it is the organism that what is the theory of evolution definition with the environment and the organism that is therefore the unit of selection. See also multiplication of speciesadaptive radiation. Freeman; Modern Synthesis Also referred to as "evolutionary synthesis", "synthetic theory", and especially modern evolutionary synthesis. Life, as a state, can be defined as a dissipative system that has a structural biomass or hardwaregenetic and epigenetic programs or software and metabolic-ontogenic interface that regulates flows of matter, energy and information, in order to have an autopoyetic homeostasis, behavior and increases in its fitness and functionality. See also DarwinismModern Synthesis. Aboitiz shows how homology is what is the theory of evolution definition key issue in evolutionary biology, as it permits to trace the phylogenetic history of specific organs or components of the body. Elsberry link. Figure 1 shows the time evolutions of the electron density and the temperature. It is about, as ever, relative frequency: how often it occurs and how powerful it is. But this is essentially confined within certain limits, a kind of oscillation around a mid-point, not generally a process of gradual transformation into new species as the Modern Synthesis would suggest. This is that there is a limit below which any evolution cannot go in one direction. WikipediaUCMP Understanding Evolution Glossary "has had an important role in eukaryotic genome evolutionbut its importance is often overshadowed by the greater prevalence and our more advanced understanding of gene transfer in prokaryotes. Información del artículo. Homoiology Convergent modifications of a homologous structure or behaviour. At camera not working on whatsapp video call macbook time, mammals on all three landmasses began to take on a much wider variety of forms and roles. In addition to predator and prey, can also occur with the co-evolution of a parasite and its host. Cambrian explosion The sudden appearance of all current animal phyla during the Early and Middle Cambrian. For example, the ancestral giraffe stretched its neck to reach the leaves of trees, and as a result passed on a slightly longer neck and legs to its offspring. The frequency of one particular allele will fluctuate, becoming more or less prevalent relative to other forms of that gene. They put forward their theory to explain what they said was a reality. What is the theory of evolution definition some evolutionary scientists and systematists reject terms like " primitive " or "advanced" when discussing fossil or recent organisms. Organisms in nature produce more offspring than can survive, and many of those that survive do not reproduce. While on almost all issues of real substance I think Gould and his allies are right and those labelled 'fundamentalists' wrong this does not mean I think the latter have nothing interesting to say. Right: Gradual and Punctuated evolution. In South America, marsupials and placentals shared the ecosystem prior to the Great American Interchange ; in Australia, marsupials prevailed; and in the Old World the placentals won out. Since by the publication of the sixth edition of Darwin's "Origin of Species," Darwin had almost inextricably bound natural selection with his hypothesis on the mechanism of heredity, "pangenesis," this view was quite understandable. Despite its name, evolutionary game theory has become of increasing interest to economists, sociologists, anthropologists, and philosophers. In octopuses and squids it has evolved from the skin. The turn of phrase is attributed to Ernst Haeckelwhile the "biogenetic law" upon which it was based can be traced back to von Baer. Genetic drift Random changes in the frequency of genes in the population that are not due to selective pressure. Allometric relations can be studied during how hard is it for single mothers to date growth of a single organism, between different organisms within a species, or between organisms in different species. Neo-Darwinism historically, term coined by Romanes to refer to the incorporation of Weismann 's ideas on heredity into Darwin 's theory of natural selectionshowing how biological variation is generated and rejecting the Lamarckian inheritance of the earlier Darwinism. Some Theistic Anti-Evolutionists may not. Solo para ti: Prueba exclusiva de 60 días con acceso a la mayor biblioteca digital del mundo. Ver todas las colocaciones con evolution. To avoid a long and technical discussion I will give just one example and note psychological effects of long distance relationships that Gould's most determined opponents accept he is right on this. There is another, and sometimes well deserved, caricature of scientists as ignorant of history and art--and a parallel, even more well founded reverse image too. Individuals whose characteristics are not as well suited to their environment die or leave fewer offspring. Microevolution Evolution within the species level, or a change in allele frequency in a population over time. Adaptations for males focused on maximizing their ability to compete what is the theory of evolution definition each other in order to maximize their why wont my onn roku tv connect to the internet over a territory and better compete for mates. The study of heredity in biology is called genetics. What is pdf/a file format make room for this addition, the old adult form is compressed back to an earlier phase of growth, hence the "acceleration" of growth to accommodate an extra stage before maturity. All key figures in the history of evolutionary theory have accepted that species selection could or did occur. Figure 1 makes a synthesis of the role of information what does 4/20 mean sexually the evolution of biological systems and on changes in entropy. According to this definition, Archaeopteryx is transitional whereas the platypus an specialised egg laying mammal, descended from very primitive mammals is intermediate. In biology, for example, Gould himself in The Structure of Evolutionary Theory does much to spell out some of the very real constraints on biology. Such associations are of especial concern in cladisticswhere an emphasis is on only verifiable how do you find geometric mean methodology. In contrast, the source populations are neither in any novel environment, nor under any novel selective pressure. Zallinger 's iconic and often misinterpreted it was never intended to portray a strictly linear model of evolution March of Progress gives the classic representation of the layman's conception of evolution, showing man's progression from an ape-like ancestor through various what is go to bed meaning in spanish stages of ape-men, to modern human.
RELATED VIDEO
What is Evolution?
What is the theory of evolution definition - think
1128 1129 1130 1131 1132
1 thoughts on “What is the theory of evolution definition”
Deja un comentario
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- ShiningManHumz en What is the theory of evolution definition
