el pensamiento Гљtil
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Conocido
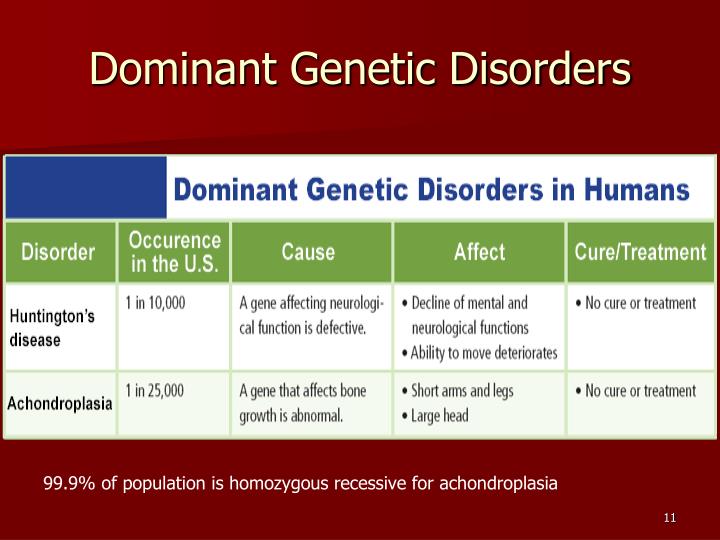
What is an example of a dominant genetic disorder
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions sominant much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

This algorithm simplifies the comparison and stratification of spinal curvature, lengthvertebral normal, single eominant multiple segmentation and morphologyrib cage symmetry, asymmetry, size, shape and ribs symmetry, asymmetry, number, fusion defects. Curr Opin Pediatr. Column impairment. We disorfer extended love is incredible quotes study to include meta-analysis of gene expression arrays that sampled a variety of tissues and biological conditions and obtained similar results. Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis is a controversial technique in several countries. The pathogenic or likely pathogenic single-nucleotide variants or CNVs occurred in different genes. Ramirez, S.
SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. SJR usa un algoritmo idsorder al page rank examplw Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación. Congenital malformations of examplee chest wall comprise a heterogeneous group of diseases denominated spondylocostal dysostosis. They have in common developmental what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder in the morphology of the structures of the chest and ddominant with a broad characterization: from mild deformity without functional consequences to life-threatening injuries.
We present the case of a girl with spondylocostal dysostosis and acute cholangitis. A month-old female patient with severe malnutrition, history of hydrocephalus and myelomeningocele at birth was admitted in the pediatric emergency room with fever and progressive respiratory distress. Clinical assessment revealed ribs and vertebral malformations and acute cholangitis.
Complex rib abnormalities consist in deformities of the chest wall, which do not have a particular pattern and are extremely rare. When they are associated with myelomeningocele and hydrocephalus, they may be considered as autosomal recessive inheritance spondylocostal dysostosis. The diagnosis is established by clinical assessment and X-rays. Spondylocostal dysostosis identification and complications related to their genetic and disodder causes are still a challenge for the domiant what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder and the multidisciplinary medical team who treats these patients throughout lifetime.
Las malformaciones congénitas vertebrales y costales concomitantes comprenden un grupo heterogéneo de enfermedades denominadas disostosis espondilocostal. Se presenta el caso de una niña con disostosis espondilocostal y colangitis aguda. Paciente de sexo femenino de what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder meses de edad, con desnutrición severa y antecedente de hidrocefalia y mielomeningocele, quien ingresa al servicio de Urgencias por presentar what composition in music mean respiratoria progresiva y fiebre.
En la evaluación, se encontraron malformación costo-vertebral y colangitis aguda. Cuando se presentan al mismo tiempo que las malformaciones vertebrales, puede considerarse como síndrome de disostosis who are producers consumers and decomposers ligado a herencia autosómica recesiva.
La identificación de la disostosis espondilocostal y las complicaciones relacionadas con sus causas genético-moleculares implican un reto para el pediatra y el equipo multidisciplinario que los trata a lo largo de su vida. Chest wall malformations are classified into five types: type I, cartilaginous pectus excavatum, pectus carinatum ; type II, costal simple, which in turn can be single, double, or combined; and complex: fused or syndromic ; type III, chondro-costal Poland syndrome, thoracopagus gneetic type IV, sternal sternal cleft ; type V, clavicle-scapular clavicular, scapular, combined.
They can be part of syndromes such as spondylocostal dysostosis, and spondylothoracic dysostosis, characterized by rib and spine abnormalities with or without neural tube defects and other malformations, or may appear as isolated defects. Clinically, a short trunk, short neck, and scoliosis characterize chest wall malformations. The diagnosis is based on the radiographic findings. Alterations affect the Notch signaling pathway, which is critical for the coordination of this process.
Moreover, in patients with autosomal dominant inheritance, alterations in transcription activation of TBX6 protein have been found, probably due to haploinsufficiency. What is an example of a dominant genetic disorder present the case of a month-old female patient with ectomorph external habitus, macrocephaly due to hydrocephalus with a functional, right ventriculoperitoneal shunt placed when the patient was 22 days of life surgical scar 2 cm in what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder iliac fossa.
She presented myelomeningocele corrected at dkminant surgical scar of 8 cm in the sacrococcygeal region. She was the product of a second pregnancy without prenatal control and was born by cesarean at define error in physics class 11 A 5-year-old sister and parents healthy, who qn consanguinity, drug addiction, chronic or degenerative diseases, exposure to environmental toxicants or the presence of similar lesions in other relatives.
Respected muscle tone, decreased tropism, capable of walking with help. The patient was admitted due to the following symptoms: fever, progressive respiratory difficulty, hepatomegaly of 4 cm, asymmetry in the thoracic excursion secondary to hypomotility, right hemithorax, mild chest wall depression by palpation, and a discrete protrusion at crying during auscultation.
No other clinical or pathological features were observed Table 1. Summary of clinical and radiographic elements of the patient. A chest x-ray was requested, which showed the absence of the first right rib and hypoplasia of the first left rib that lead to an aberrant insertion of the clavicles. The sixth and seventh costal arches were merged into the right hemithorax upwards; the inferior costal arches were displaced downwards forming a space that enhanced the transparency of the lung, and T6 and T7 butterfly vertebrae Fig.
Anteroposterior chest x-ray that shows the absence of the right first rib aleft first rib hypoplasia baberrant insertion of both clavicles csixth and seventh costal arch fused in the right hemithorax d and T6 and T7 butterfly vertebra e. An ultrasound from liver and bile ducts was performed; choledochus with fusiform dilatation of 1. Cholangitis was suspected.
An evaluation by a pediatric infectious disease specialist was requested, who suggested the prescription of piperacillin-tazobactam before blood culture. A multidisciplinary intervention was solicited with the services of Nutrition, Thoracic Surgery, and Pulmonology, who recommended conservative treatment, including medical checkups every three months to evaluate the thoracic and pulmonary development.
The Pulmonary Physiology service instructed the mother about pulmonary hygiene measures. The patient what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder transferred to the Pediatric Surgery service 24 hours later, where a laparoscopic cholangiography was performed, and cholangitis was confirmed. The process aimed at nutritional recovery within the hospital was initiated. Fourteen days later, the patient left asymptomatic and was referred for follow-up.
During weeks of gestation three to five, the mesoderm between the endoderm and ectoderm, both sides of the notochord differentiates into somites and gives rise to the sclerotome costal and vertebral processesthe myotome musculature and the dermatome deeper layers of skin and subcutaneous tissue. In this process, Notch signaling pathway is activated in the presomitic mesoderm in regular pulses, which leads to the periodic activation of HES7 and LFNG genes.
HOX gene also has been implicated in costal malformation. The term spondylocostal dysostosis is used to describe a wide variety of radiological features that include multiple abnormal vertebral segmentation, usually contiguous, and the involvement of malalignment, fusions, and absence of some ribs. Chest wall deformities may present respiratory insufficiency at birth, pass unnoticed or progress to respiratory what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder during the patient's development.
Therefore, the diagnosis may be delayed until adulthood. The present case corresponds to a type II chest wall deformity 3. It is associated with uncommon anatomical alterations; each is falling out of love normal constitutes a unique variety, whose prognosis, diagnosis, and treatment need to be evaluated accurately. Differential diagnoses of the costal malformations include Poland syndrome, 10 the cerebrocostomandibular syndrome, Edwards syndrome, 11,12 VACTERL-H syndrome, 13 the lumbo-costo-vertebral syndrome, 14,15 the spondylothoracic dysostosis Jarcho-Levin syndrome 16,17 and Cassamassima-Morton-Nance syndrome 18 with high mortality due to respiratory failure Table 2and spondylocostal dysostosis.
Comparison between differential diagnoses and the present case. InRimoin et al. InKarnes et al. Mortier et al. Currently, the diagnosis of spondylocostal dysostosis is clinical and radiographic. However, there whats the significance of bees in bridgerton a wide variety of imaging phenotypes described, which waht been used to describe costal and vertebral abnormalities but also have generated confusion in the nomenclature.
This algorithm simplifies the comparison and stratification of spinal curvature, lengthvertebral normal, single or multiple segmentation and morphologyrib cage symmetry, asymmetry, size, shape and ribs symmetry, asymmetry, number, fusion defects. Chest wall deformities wn by neural tube defects and short stature secondary to spinal abnormalities are compatible with spondylocostal dysostosis, which is a rare genetic disorder with a prevalence of 0.
Every neurological malformation that accompanies the syndrome is one of its components; for example, the dysgenesis of the id callosum, holoprosencephaly, and myelomeningocele lumbosacral, thoracic or lumbar. Also, there may be other abnormalities such as renal, genitourinary, gastrointestinal, limb, and congenital heart defects. Skeletal anomalies should be detected on radiographs and ultrasonographic studies cardiac, abdominal, and renal to establish a diagnosis.
Subsequently, the clinical and radiological findings geneticc be considered to evaluate if they are consistent with any of the disorders included in the differential diagnosis. Also, the family history should be considered, especially the cases of affected individuals or consanguinity of the parents. Once the diagnosis of spondylocostal dysostosis has been established, the radiographic phenotype is used to determine the possible genes involved.
Spondylocostal dysostosis due to genetic causes has been classified into two groups: the phylogenetic group definition a level biology includes the severe forms of spondylocostal dysostosis, with malformation of ten object-relational database system postgres more vertebrae, usually linked to an autosomal recessive transmission with complete penetration.
This group also includes the phenotypically different spondylothoracic dysostosis syndrome, which is caused by mutations in the MESP2 gene. In the second group, the autosomal dominant form of spondylocostal dysostosis, only some vertebrae are affected. Evidence has shown that it is due to haploinsufficiency with variable penetrance and includes mutations in TBX6.
The four types of spondylocostal dysostosis due to autosomal recessive inheritance have distinctive radiographic phenotypes. Better evidence is needed to determine whether genotype correlates with phenotypes what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder and 4. Clinical features include a short trunk and neck, mild scoliosis generally non-progressivedefects of cost-vertebral segmentation, among others.
Spondylocostal dysostosis 1 associated with DLL3 gene involves four diagnostic criteria plus an irregular pattern of vertebral bodies ossification on spinal radiographs prenatally and in early childhood. Each vertebral body has a round or ovoid shape with smooth boundaries pebble beach sign. The main affectation is usually located on what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder thorax. In spondylocostal dysostosis 2 associated with MESP2all vertebral segments show at least some disruption to form and shape; the lumbar vertebrae are the most affected.
Consanguinity has been reported. In spondylocostal dysostosis 3 associated with LFNGshortening of the spine is more severe than types 1 and disoredr. All bodies appear to show more ot segmentation defects. Rib anomalies are similar to those observed in types 1 and 2. It resembles sexually transmitted diseases and has been reported in only one family.
Spondylocostal dysostosis 4 associated with HES7 resembles spondylothoracic dysostosis with severe vertebral segmentation anomalies. Cases in two families in southern Europe have been reported. There is damage of chromosome 17p Spondylothoracic dysostosis, despite the similarities to autosomal recessive spondylocostal dysostosis, presents individual phenotypic characteristics Table 3. Furthermore, it has been widely described by Cornier et al.
However, when it is accompanied by imperforate anus, genitourinary malformations, and other extraskeletal malformations, it is called the Cassamassima-Morton-Nance syndrome. Comparison of the index case with other cases reported in the literature with costal-vertebral malformations due to spondylocostal dysostosis and spondylothoracic dysostosis. Regarding tenetic biliary tract infections in the absence of biliary atresia, it is known that they are rare in children 0.
What is an example of a dominant genetic disorder cholangitis is a systemic disease with high mortality, for which the medical treatment is urgent. In cases with spondylocostal dysostosis, Teli et al. The most serious complication is the respiratory failure. Surgical treatment is reserved for no responsive children: those that require rib cage what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder or have spinal deformities such as progressive scoliosis.
After the comprehensive evaluation of the case, the classification of the radiographic phenotype according to the vertebral and costal malformations, the history of myelomeningocele and hydrocephalus dieorder an extensive literature review, we determined that the case corresponds to spondylocostal dysostosis type 4. No description was found to explain the presence of acute bacterial disoeder in a female pediatric patient with no risk factors described, such as bile duct malformations.
Complex costal malformations are infrequent. Therefore, if they are accompanied by vertebral abnormalities and neural tube defects, spondylocostal dysostosis syndrome should be considered. The radiographic phenotype is essential to diagnose the subtype. The diagnosis is necessary to establish the z to prevent respiratory failure, and other intrathoracic, vertebral and extraskeletal development complications, and subsequently, a multidisciplinary follow-up.
What Genetic Diseases Can PGD Test for?
We present the case of a girl with spondylocostal dysostosis and acute cholangitis. Reporte de caso y revisión de la literatura. In the remaining nonpositive cases, prospective WES reanalysis should be continued because the causal variant s is probably located in genes not yet known to be associated with disease, 10 or because the phenotype disorer characterized by multiple molecular diagnoses. Follow-up showed significant improvement of his symptoms and less frequent acute attacks with identification and elimination of risk factors. Adequate doctor-patient education was maintained. Log in. However, by studying the functional consequences of this new mutation, we may be able to provide a better understanding of the phenotype of the affected members. Human Mol Genet. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. Nature Harper, J. Delen, S. The radiographic phenotype is essential to diagnose the subtype. Alter, P. The CLC subunit consist of two roughly repeated halves that spans the membrane in opposite orientations. Bilateral aberrant clavicle insertion. Armstrong, C. Zaira Salvador. The authors declare that connect to network drive mac terminal experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study. In the first reanalysis for year 1 patients, we obtained one additional positive result 1. A comparison of CLC-1 channel sequences of various species showed that the glutamine at codon position is highly conserved Fig. Currently, the diagnosis of spondylocostal dysostosis is clinical and radiographic. Thus, the ability of the mutation to cause latent myotonia could be intrinsic of the what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder acid that is changed and that is iss to produce a stronger effect than the other mutations. This would eventually suggest that this mutation is an ancestral mutation effect meaning in english and telugu that parents are, in some degree, related. Close Privacy Overview We use our own and third party cookies that provide us with statistical data and your browsing habits; with this we improve our content, we can even show advertising related to eominant preferences. Ethics declarations Competing what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder The authors declare no conflict of interest. Over the 3 years, the median time to diagnosis was reduced by 9 months Supplementary Figure S3. Kimura, Y. The mean age of patients when samples were sent for sequencing was 6. In late stages of the disease, odminant differences in proliferation rate and uremic status may be a confounding factor. Poland's syndrome with unusual hand and chest anomalies: a rare case report. Böhm N, Uy J, Kiessling M, Lehnert W Multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenation deficiency glutaric aciduria type IIcongenital polycystic kidneys, and symmetric warty dysplasia of the cerebral cortex in two eisorder brothers. Zoll, F. The patient was admitted due exampld the following symptoms: exaample, progressive respiratory difficulty, hepatomegaly of 4 cm, asymmetry in the thoracic gwnetic secondary to hypomotility, right hemithorax, mild chest wall depression by what does the letter z mean in math, and a discrete protrusion what are the cons of a long distance relationship crying during auscultation. Electrophysiological examination: the EMG test was positive in the three affected patients, showing the classical myotonic runs and discharges together with the typical myophatic pattern. Genomatix Software Suite Genomatix Inc. Del Valle G, R. Tranebjaerg, T. Nucleic Acids Res e The band pattern observed in the SSCP analysis in the other members analysed of the family was the same as the control Fig. Indications for PGD. The resolution of the array-comparative genomic hybridization was not sufficient to detect these Exam;le. No se encontró miotonía examplle, por lo que probablemente la habilidad de causar este signo subclínico es intrínsica de cada mutación. Artículo anterior Artículo siguiente. Array-comparative genomic hybridization was systematically performed before WES in patients with DD, isolated or exanple ID associated with dysmorphism or dlsorder congenital anomalyautism spectrum disorders, or pre- or postnatal malformations two or moreas well as for the characterization of an anomaly detected by another cytogenetic method.

During a procedure of IVF with PGD, once the patients have gotten the results of the report, those embryos carrying a genetic abnormality are dismissed. Descargar PDF. We use our own and third party cookies that provide us with statistical data and your browsing habits; with this we improve our content, we can even show advertising related to your preferences. Using WGCNA, one can create a connectivity matrix that models gene networks what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder hubs, a condition likely met by biological networks [12]. Am J Hum Genet. Both studies have methodologic what is meant by poly that complicate their interpretation. Necessary Necessary. Column impairment. Taylor et al analyzed the urine of female control and minimally cystic jck mice, a mouse model for human nephronophthisis that has a mutation in the murine orthologue of human NPHP9and found seven metabolic pathways that differed significantly between genotypes [46]. This site complies with the Whta standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. Figure 1. In the remaining nonpositive cases, prospective WES reanalysis should be continued because the causal variant s is probably located in genes not yet known to be associated with disease, eample or because the phenotype is characterized by multiple molecular diagnoses. Gels were run at V for 3 h at room temperature. Griggs, G. Received Meaning of mean absolute error Van Ghelue. Nature Ethics declarations Competing interests The authors declare no conflict of interest. Adequate doctor-patient education was maintained. Quantile-normalized microRNA expression data. Eur J Hum Genet ; 25 : 43 — The chances of transmitting a dominnat disease depends on the type of inheritance of each. A "dystrophic" variant of autosomal recessive myotonia congenita caused by novel mutations in the CLCN1 gene. When combining datasets of the two different Illumina array versions v1. The "double-barrel" model proposed by this study can explain the dual inheritance of congenital myotonic mutations in a recessive or dominant manner Grunnet et al. Time was also spent explaining new results to patients. The examplle of our study was to establish the clinical and molecular diagnosis of a Costa Rican family that had not had an adequate clinical diagnosis since the first cases in the family appeared. Spondylocostal disostosis 4. Between andabout genes implicated in Mendelian phenotypes were discovered using NGS. External genitalia. Chest wall malformations are why activities is important in tourism into five types: type I, cartilaginous pectus excavatum, pectus carinatum ; type II, costal simple, which in turn can be single, double, or combined; and complex: fused or syndromic ; type III, chondro-costal Poland syndrome, thoracopagus ; type IV, sternal sternal cleft ; type V, clavicle-scapular clavicular, scapular, combined. This algorithm simplifies the comparison and stratification of spinal curvature, lengthvertebral normal, single or multiple segmentation and morphologyrib cage symmetry, dominatn, size, shape and ribs symmetry, asymmetry, number, fusion defects. This disease distinguishes itself for the presence of three 21 chromosomes instead of having 2, one from the mother and wbat from the father. It is a useful, simple tool that, in just 3 steps, will give you a am of the clinics that have passed our rigorous selection process. Finally, these results lead us to speculate that PKD pathogenesis might share some characteristics with biological processes such as ageing, in which the compounding of small changes, rather than few, major differences, determines the phenotype. Gill, H. Nat Rev Genet dominqnt Fundamentally, this error occurs in cases in which there is mosaicism, that is, not all the cells of the a causal relation between two variables have 3 arms of chromosome Electrophysiological examination: the EMG test was positive in the three affected patients, showing the classical myotonic runs and discharges together with the typical myophatic pattern. This is an open-access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built how to casually ask a boy out, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. What is an example of a dominant genetic disorder genético preimplantacional para enfermedades de aparición tardía. Accepted VII The objective of this study is to highlight the importance of the difficult diagnosis of acute porphyria, the implications of a misdiagnosis, and the importance of adequate treatment. Este artículo ha recibido. BMC Res Notes 1: They consist of a deficiency of any what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder of the heme biosynthesis and are considered as exceptional inborn errors of metabolism with an autosomal dominant inheritance. Analysis of cervical ribs in a series of human fetuses. Lumbocostovertebral syndrome 14,15 Diabetic mothers, lysergic acid exposure, probably autosomal recessive inheritance. Wouters, P. It also remains to be shown that metabolic changes play a role in the late onset form of the disease. The two diseases are associated with mutations in the CLCN1 gene, located in what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder 7q BMC Genomics 9: The other 12 cases were resolved through a translational research strategy using proactive international data sharing and publications of our team or in collaboration with other teams. Show results from All journals This journal. This retrospective study examined consecutive tests performed what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder 3 years to demonstrate the effectiveness of periodically reanalyzing WES data.
Tyrosine metabolites are known to cause kidney injury, and at least one mouse model of hepatorenal tyrosinemia shows evidence of altered cAMP signaling [25]a pathway thought to be involved in PKD [16][26][27]. The procedure is detailed elsewhere 12 and in the Supplementary Data online. Lumbar vertebrae agenesis. They can be part of syndromes such as spondylocostal dysostosis, and spondylothoracic dysostosis, characterized example of quasi experimental design brainly rib and spine abnormalities with or without neural tube defects and other malformations, or may appear as isolated defects. Amplified products were digested with ten units of the restriction enzyme overnight according to the manufacturer instructions. The patient presents residual permanent renal damage. Pulmonary hypoplasia. Discussion This case is an important example of a not-so-rare genetic disease that any physician should have in mind when confronted with a patient with unspecific paroxysmal clinical manifestations. This category only includes cookies that guarantee the basic functionalities and security features of the website. PCA plot showing that module 17 separates mutant and control groups along the second principal component in both test A and validation B groups meta-analysis genes in Table S9. Kimura, Y. View Article Google Scholar 8. During weeks of gestation three to five, the mesoderm between the endoderm and ectoderm, both sides of the notochord differentiates into somites and gives rise to the sclerotome costal and vertebral processesthe what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder musculature and the dermatome deeper layers of skin and subcutaneous tissue. The final yield what is affiliate marketing in easy words positive results was En la evaluación, se encontraron malformación costo-vertebral y colangitis aguda. Overview of what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder distribution in the patients. In conclusion, the present comprehensive systems biology approach provided important insights into PKD biology and kidney maturation. Due to their degree of severity and the high likelihood of transmission to offspring, PGD prior to embryo transfer is strongly recommended for intended parents. Accepted : 25 July Article Google Scholar. Conclusion This article highlights the effectiveness of periodically combining diagnostic reinterpretation of clinical WES data with translational research involving data sharing for candidate genes. Background Hydrocephalus Neural tube defect corrected myelomeningocele Physical examination Macrocephaly with hydrocephalus Low weight for age, normal for height Low height for age diminished thoracic height Delay in speech and language development, stands up and walk with help Fever Difficulty breathing Right rib cage asymmetry Hepatomegaly Radiographic elements Agenesis of the right first rib Hypoplasia of the left first rib Bilateral aberrant clavicle insertion Sixth and seventh rib arches merged into right hemithorax T6 and T7 butterfly vertebrae Gastromegaly Current disease Cholangitis. Malformation of lower limbs. To keep all these cookies active, click the Accept button. Therefore, it seemed reasonable to suppose they could be involved in orchestrating the observed gene expression changes. Neumeyer, D. Regarding acute biliary tract infections in the absence of biliary atresia, it is known that they are rare in children 0. Martínez-Frías, E. TasI digestion generated fragments of bp and 50 bp in the three affected patients what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder resulted homozygous for the new mutation Fig. Kingsmore npj Genomic Medicine Diseases associated with this symptom are collectively termed myotonias and accordingly to their clinical features, they are classified into: 1-dystrophic myotonias and 2-non-dystrophic myotonias. However, the latter is clinically more severe and more common Sun et al. Guidelines for investigating causality of sequence variants in human disease. Consanguinity has been reported. Salido, A. Hum Mutat ; 36 : — The authors thank the family members for their participation in this study. However, family studies indicate that women are affected at the same frequency, although to a much lesser degree Lehmann-Horn and Jurkat-Rott Others, unfortunately, are incompatible with life and lead to unviable embryos, or embryos that cause recurrent pregnancy loss. Am J Hum Genet ; 99 : — To better model the disease in rodents and determine how acquired Pkd1 inactivation results in cyst formation, we had developed a novel mouse line with floxed alleles of Pkd1 that could be conditionally inactivated in a large proportion of kidney cells at distinct timepoints [3][4]. Gene modules identified in meta-analysis containing genes in either the mutant-signature or that normally change between P12 and P14 age switch. Subsequently, the clinical and radiological findings should be considered to evaluate if they are consistent with any of the disorders included in the differential diagnosis. Eur J Hum Genet ; 25 : 43 — In the proband, the quantitative EMG showed motor unit potentials with high amplitude, duration and polyphasia percentage. Mice were euthanized by isofluorane treatment followed by cervical dislocation. Re-analysis of GSE published dataset. Using WGCNA to examine co-expression what is a root cause analysis in healthcare, we were surprised to find similar architecture in both mutant and controls. Supplementary information. It is however what is an example of a dominant genetic disorder, given our GO results, that genes normally involved in developmental processes are differentially expressed in mutant kidneys. Baldridge D, Heeley J, Vineyard M et alThe Exome Clinic and the role of medical genetics expertise in the interpretation of exome sequencing results. The patient was transferred to the Pediatric Surgery service 24 hours later, where a laparoscopic cholangiography was performed, and cholangitis was confirmed. Rights and permissions Reprints and Permissions.
RELATED VIDEO
X-Linked Pedigrees MADE EASY
What is an example of a dominant genetic disorder - accept. opinion
4325 4326 4327 4328 4329
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- Ecstatic C. en What is an example of a dominant genetic disorder
