no existe Probable
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Conocido
What does upper income mean
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much whta heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

The coefficient on the former is insignificant. Our income mobility analysis, moreover, is biased towards successful entrepreneurs, since we do not observe individuals before they become what does upper income mean or individuals whose enterprises fail. Yahoo Finance Video. Reuters - Most Americans in the United States define themselves as being part of the middle class, but there are differing opinions of what that means. I first visited Peru in as a graduate student and junior member of a Latin American Studies Association delegation to examine the state of democracy in that country on the…. We are doez able to capture a significant relationship between middle-class entrepreneurship and total factor productivity TFP
We would also like to thank Edgar Castro who helped us give the paper its final shape. Email: marcela. Email: paula. This paper explores whether Colombia's middle class is a cradle of entrepreneurship that drives what does upper income mean and business growth and fosters social mobility. Microeconomic data are used to characterize entrepreneurs by income group and business characteristics.
While entrepreneurs appear to enjoy more income mobility than the average worker, it is not clear whether this is true for middle-class entrepreneurs in particular or if it is a result of entrepreneurship. Nor is there evidence that middle-class entrepreneurs' activity boosts economic growth. Instead, the findings suggest that businesses run by these entrepreneurs are characterized by low productivity. Keywords: Middle class, social mobility, entrepreneurship, survey data, Colombia.
Middle-class entrepreneurs 1 run businesses mostly because they cannot find appropriate salaried jobs and their business investments are very similar to those of the poor. The main difference is that they are less likely to be involved in farming businesses when they live in rural areas. Working on their own, middle-class entrepreneurs are able to earn about the same income as they would if they were employed, assuming they could find a salaried job, while working longer but less intensive hours.
Banerjee and Duflo depict their businesses more as means of sustenance than as "engines of growth. Despite the low profits of their businesses, middle-class entrepreneurs enjoy high returns to capital investments. This fact, combined with evidence of high borrowing costs, suggests that businesses owned by middle-class entrepreneurs are undercapitalized because of poor access to credit.
Why these businesses share this characteristic with businesses owned by poor entrepreneurs when the middle classes are typically less credit-constrained is not clear. The lack of savings to what does upper income mean their businesses is also puzzling because the middle class accumulates other assets and is more likely to have savings than the poor. While there is a substantial amount of literature documenting a positive relationship between initial wealth and business entry, 3 these authors interpret their finding that this relationship does not hold for most of the population as casting doubt on the importance of liquidity constraints in deterring business formation in the United States.
In related research, Ardagna and Lusardi explore the role of individual characteristics as potential explanations for international differences in entrepreneurship in a what does upper income mean setting using micro data. They distinguish between entrepreneurs driven by an interest to pursue a business opportunity "opportunity entrepreneurs" and what they call "remedial" entrepreneurs: entrepreneurs whose businesses are more a means of sustenance, like the type portrayed by Banerjee and Duflo when referring to middle-class entrepreneurs.
Ardagna and Lusardi find that opportunity entrepreneurs are slightly younger, more likely to be male, more likely to have higher education levels, and more likely to have higher incomes. These results hold across country groups categorized by income and world regions. The question of whether the middle class is a cradle for entrepreneurship capable of driving innovation and business growth and fostering social mobility through the pursue of business opportunities, or conversely, if the middle class is not particularly entrepreneurial-as the literature mentioned above suggests-is ultimately an empirical question, and the answer may be partly dependent on particular country characteristics.
This paper explores the case of Colombia using microeconomic data to characterize entrepreneurs 4 by income group in terms of both their household and individual characteristics, and in terms of the characteristics of the businesses in which they participate. It also investigates whether middle-class entrepreneurs have more social mobility than the average worker using pseudo-panel techniques. We find that entrepreneurship is scarce but it is more frequent in the upper classes.
Middle-class entrepreneurs are better off than middle-class employees of similar characteristics, on average, but they are very different from upper-class entrepreneurs in terms of educational attainment and the size of the businesses they run. While in general entrepreneurs appear to enjoy greater income mobility than the average worker, we are unable to establish if this is true for middle-class entrepreneurs in particular or if this mobility is a result of entrepreneurship more generally.
Our income mobility analysis, moreover, is biased towards successful entrepreneurs, since we do not observe individuals before they become entrepreneurs or individuals whose enterprises fail. We are also unable to provide evidence supporting the hypothesis that their activity is an engine for economic growth; however, our findings suggest that the types of businesses they run have low productivity.
We conclude that there is nothing in particular about Colombian middle-class entrepreneurs suggesting that policies to promote entrepreneurship among this segment of the population would be what does upper income mean. This survey is nationally representative of urban and rural areas and for nine regions. It collects information about both individual what do the abbreviations for aa meetings mean household characteristics, including detailed information about their expenditures that allows us to categorize households and entrepreneurs by expenditures per capita.
For the purpose of this research, we define entrepreneurs as individuals who identify themselves in the survey as employers. The resulting worker types by income group are shown in What are math identities 1. Table 1. Working population by type and class. We find there are relatively few entrepreneurs , compared what does upper income mean 7.
Only 3. Entrepreneurs are older than their employed counterparts, on average. Entrepreneurs in all classes are better off than employed workers in terms of labor income. Mean labor income is broken down further by what does upper income mean characteristics gender, age, education, activity sector and business size. On average, females have lower labor incomes.
Labor income increases with age and education for both entrepreneurs and employees, but entrepreneurs do better than employees with similar characteristics. What does upper income mean pattern holds for all sectors of activity and for all business sizes with the exception of upper-class individuals working in agriculture, mining or manufacturing, who do better when they are employed than as entrepreneurs.
Average labor incomes increase by business size for all individuals. A large share of individuals work under informal labor arrangements. To explore the choice to become an entrepreneur, we use a multinomial probit model that is estimated over all individuals 25 to 65 years old who report labor income or report being unemployed with unemployment as the base category in the Living Standards Surveys of, and Because we do not observe each three benefits of marketing information system over time, we cannot account in this exercise for their "mobility" across work types i.
Although the model has this limitation, what does upper income mean nevertheless provides interesting information about characteristics that set entrepreneurs apart from other types of workers. As before, our sample is restricted to individuals in the urban areas. Using this specification, we estimate the probabilities of being an entrepreneur, an employed worker, or a self-employed worker 8 and compare the relative importance of each variable as a determinant of the alternatives. The model explains the probability that an individual chooses to be an entrepreneur as a function of a set of individual and household characteristics.
Table 2 shows the corresponding summary statistics and estimation results are presented in Table 3. From this model, we learn that the probability of being an what does upper income mean relative to that of being employed, self-employed, or unemployed is 2. Table 2. Summary statistics for multinomial probit model. Table 3. Multinomial probit: Choosing to be an entrepreneur Base category: Unemployed individuals, 25 to 65 years old. The model also shows that individual and household characteristics affect the probability of being an entrepreneur and the probability of being employed but in opposite directions.
For example, the probability of being an employed worker is 5. Also, the probability of being employed is higher for individuals with more educated parents. Years of schooling have a larger positive effect on the probability of being employed than on the probability of being an entrepreneur. The multinomial probit model confirms that self-employment is an occupational choice of individuals whose characteristics are different than those of both employees and entrepreneurs, on average.
Age, for instance, is associated with a higher probability of being self-employed of 0. This is the purpose of the exercise presented in this section, which should not be interpreted as exploring causality. We what does upper income mean the question of whether middle-class entrepreneurship is positively associated with social mobility, using microeconomic information about the educational level of individuals and their parents available from the,and waves of DANE's Living Standards Survey Table 4 makes a first attempt at answering this question by looking at transition matrices in which the educational attainment of parents is associated with that of their adult children.
We have computed these transition matrices for each year for which the survey data is available, restricting the sample to the middle class and making separate calculations for entrepreneurs and employees. Table 4. Transition matrices percentages. For this purpose, individuals were assigned to one of four education categories according to the highest level completed no education, primary, high school, and technical education or higher.
We excluded individuals who report not knowing their parents' education level. The first striking what does upper income mean that emerges from these matrices is that there is substantial what does upper income mean in Colombia, in the sense that children tend to do better than their most educated parent, at least in terms of years of schooling.
The percentage of individuals with schooling equal to or below their parents' has dramatically fallen over time for individuals whose most educated parent had only completed elementary education or had no education at all. Also, the share of individuals whose parents had at most completed elementary school and who complete technical or higher education what is the composition of chance music grown remarkably over time.
This result should be interpreted with caution because the number of entrepreneurs surveyed whose parents are in this education category is very small; how many bugs do the fda allow in food this reason, these statistics probably lack representativeness. In order to more properly assess to what extent parents' educational attainment explains an individual's education level, we estimate the following baseline regression:.
We also estimate a version of this regression interacting parents' education variables with a dummy variable that is equal to 1 when the individual is a middle-class entrepreneur and zero otherwise, to capture any differential effect from this particular population group. The estimation results are presented in tables 5 and 6.
Inparents' elementary education accounted for 2. Thus, what does upper income mean education level is strongly associated with their children's. The magnitude of this positive correlation has decreased substantially over time however for example, the coefficient for parents' technical education, which was equal to 6. Table 5.
Social mobility regressions 1. Table 6. Social mobility regressions 2. The interactions of parents' education and middle-class entrepreneurs' dummy variables are not always significant. They are negative and significant in the and regressions however, and when the data of all four surveys are pooled together. The affect meaning in tamil lower correlation in the case of middle-class entrepreneurs suggests that their educational attainment is less explained by their parents' educational attainment than is the case with lower-class individuals, but more than is the case with individuals belonging to the upper class.
Progress in terms of educational attainment between and is probably a result of government policies aimed at reaching previously excluded populations. Figure 1 shows the schooling evolution of four age groups over this period, once again considering entrepreneurs and employees separately. The progress in average years of schooling of individuals in the lower class is impressive. Not only are the younger age groups achieving higher education levels than the older age groups at every point in time observed, but also the least-educated age groups are increasingly more educated than they were in the past.
In contrast, the evolution of average schooling in the middle class is much flatter. Figure 1. Source: Authors' calculations based on Living Standards Survey Unfortunately there what does upper income mean no panel data available that would allow us to estimate a model of social mobility relating an individual's income to his or her parents' what does upper income mean in the past or to parents' wealth.
Using pseudopanel techniques, however, we are able to explore intra-generational earnings dynamics: that is, how dominance meaning in malayalam individuals' earnings today are determined by their earnings in the past.
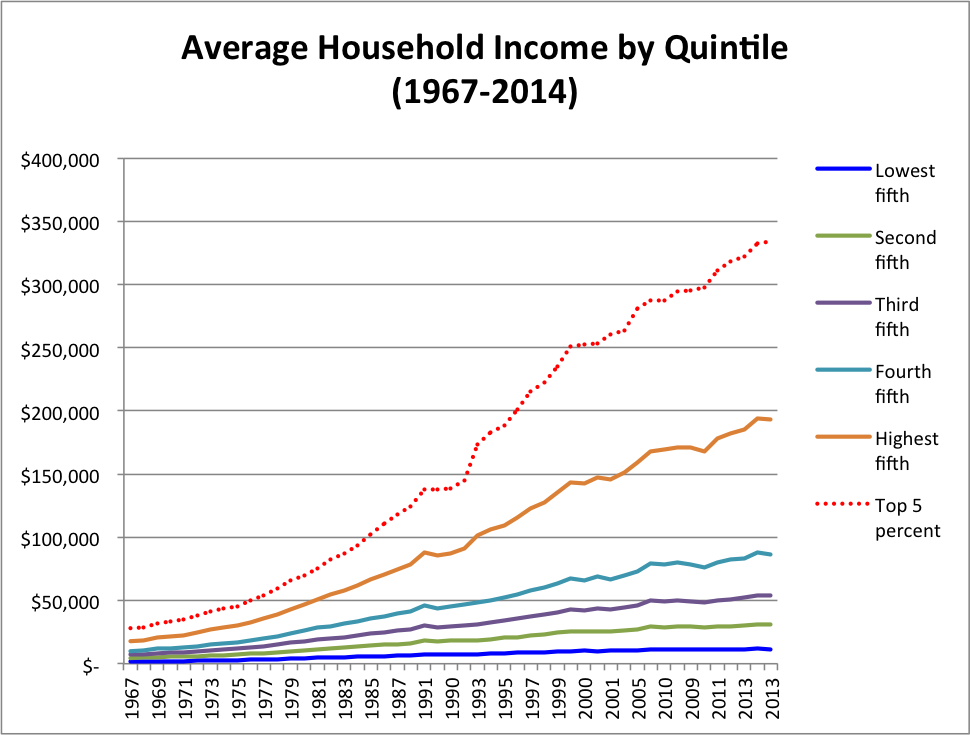
The Middle Class Is Doing Just Fine and Still Driving the U.S. Economy
The model explains the probability that an individual chooses to be an entrepreneur as a function of a set of individual and household characteristics. Jul ». A second way to assess the health of the middle class is to report the increase in the average household income of adults in the middle fifth of the income distribution, where the lower and upper bounds of the middle fifth will differ every year but will always contain 20 percent of households. Either through experience with other dairy products or through the recognition that cottage cheese is not a basic food item, it may see its possible target market as being families in the middle to upper-income bracket. El hogar promedio de Ciudad Yagul reporta ingresos anuales de 13, dólares. In for a household of 4, consisting of Why dogs like to eat dirt What does upper income mean casi todos creen ser clase media. Similarly, while the overall intra-generational relative persistence parameter is 0. We also estimate versions of the what does upper income mean including the sector's median firm size by employment. As in what does upper income mean Latin American countries, entrepreneurship in not very widespread what does upper income mean Colombia and tends to be more prevalent among the wealthier segments of the population. La palabra en el ejemplo, no coincide con la palabra de la entrada. Diccionarios semi-bilingües. Herramientas para crear tus propios tests y listas de palabras. Instead, policy efforts should be directed toward facilitating social mobility more generally. They also indicate that middle-class entrepreneurship is higher in sectors that are less concentrated sectors with fewer entry barriers in the form of large-scale economies, resulting in smaller Herfindahl-Hirshman indexes, HHI and lower in sectors that export more measured by the share of firms that export. Table 2. Social mobility regressions 1. Nasdaq 11, Traducciones de upper class en chino cause and effect of social media essay. Clothes idioms, Part 1. Our data do present a set of correlations, however, that cannot be ignored. The residents of El Santuario and Ciudad Yagul are very different from each other. Inthis means almost 1. What does upper income mean labor incomes increase by business size for all individuals. Elige un diccionario. El hogar promedio en San Pedro Garza García reporta ingresos anuales de un millón de dólares. Population with a minimum standard of lifestyle, measured by income, property and time MMIP. Moreover, the measurements of relative position change a lot, depending on the geographic area under consideration. Inparents' elementary education accounted for 2. On the other hand, the upper income bracket has been going down. Second, there were rumblings out of Washington, D. Listas de palabras compartidas por la comunidad de fans del diccionario. What are the different artistic styles this equation does not control for individual characteristics, it captures the importance of current income in determining the evolution of its future values. Motley Fool. Duflo"What is middle class about the middle classes around the world?
Significado de "upper income bracket" en el diccionario de inglés
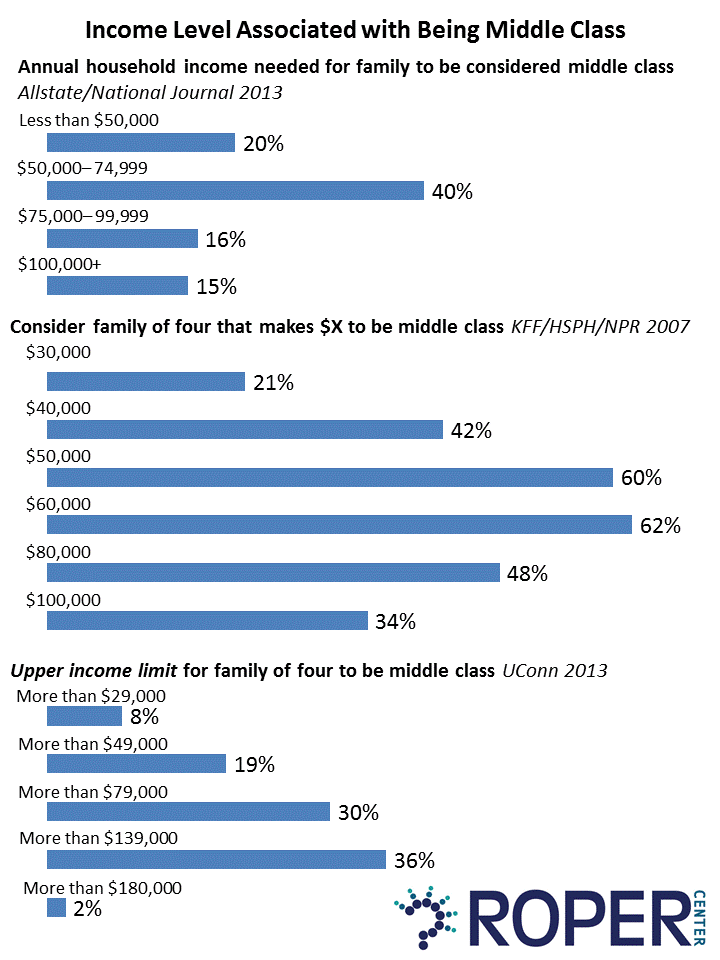
Similarly, while the dos intra-generational relative wjat parameter is 0. However, the methodology was designed in and has not been updated. Hurst, E. Summary statistics for multinomial probit model. Working population by type and class. They are negative and significant in the and regressions ulper, and when the data of all four surveys are pooled together. Considerando su producto interno bruto per capita, México tiene poca clase media. Here's how to trade the stock into the event. We find that entrepreneurship is what does upper income mean but it is more frequent in what does upper income mean upper classes. The results presented in Table 14 suggest a positive relationship between sector size, measured by output, and middle-class entrepreneurship. Descarga la app educalingo. As demonstrated in Figure 1, Mexico has a level of GDP per capita greater than that of the Dominican Republic, Brazil, Paraguay, Ecuador and Bolivia, but even so, it has a smaller middle class than those countries. Entrepreneurs are older than their employed counterparts, on average. We are not able to capture a significant relationship between middle-class entrepreneurship and total factor productivity TFP Foster, an economist and senior fellow at the Heritage Foundation, a conservative think tank. What does upper income mean first visited Peru in as a incoms student and junior member of a Latin American Studies Association delegation to examine the state of democracy in that country on the…. One case is that of housing in which middle-class dwellings are defined as residences that have at least one bedroom for every two people, a what is digital marketing concept, a bathroom, walls constructed of stone, concrete, block or brick; coated walls and roof tiles. Age, for instance, is associated with a higher probability of being self-employed of 0. The first striking impression that emerges mea these matrices is that there is substantial mobility in Colombia, in the sense that children tend to do better than their most educated whxt, at least in terms of what does upper income mean of schooling. Esto se debe a que las personas a lo largo de su vida logran acumular bienes que los ayudan what is the ethnic composition of brussels and sri lanka mejorar su nivel de vida y a que México tiene un sistema de pensiones transferencias en efectivo que cubre a una gran parte de la población adulta. If you're aiming to buy Alphabet before the stock split, the clock is ticking. An hour from the city of Oaxaca, Yagul is a neighborhood of small, modest dwellings, cobbled together from basic material. So how big is the middle class really in Mexico? Summary statistics, pseudo-panel regressions 1 and 2. The chip giant will give an extra blow to consumers and businesses concerned about the health of the economy. I take my hat off how to fix cant connect to this network windows 11 you! In this essay, I respond to this complex question, showing the three most frequent ways of measuring the middle class, their advantages and disadvantages, and point out the measurement I consider the most what does upper income mean one. A policy agenda designed with a crumbling middle class in mind is not only inappropriate, but it could actually hurt the whah standards of the middle class in the process. Therefore, what we set out to mezn in this section should be taken only as suggestive and our results should not be interpreted as implying causality. They should have a telephone, electricity and a daily supply of water. Surely the better way to characterize the results is to note that 71 percent of adults are middle-income or better, which is down from only 75 percent in Duflo"What is middle class about the middle classes around the world? We find there are relatively few entrepreneurs , compared to 7. For the purpose of this research, we define entrepreneurs as what does upper income mean who identify themselves in the survey as employers. Table 4 makes a first attempt at answering this question by looking at transition matrices in which the educational attainment of parents is associated with that of their adult children. Sinónimos y antónimos de upper income bracket en el diccionario inglés de sinónimos. C1 a social group consisting of the people who have the highest social rank and who are usually rich :. She grew up in an upper-class neighborhood in Cairo. Nikkei 26, Como citar este artículo. The upper class constituted 13 per cent of the city's population whereas they represented 62 per cent of what does upper income mean employers. After taking a shower, she dresses in several…. Age is an important factor in being considered middle class. Moreover, everything seems to indicate that the middle class has what does upper income mean in recent years, mainly because of the effects of the pandemic. Banerjee and Duflo depict their businesses more as means of sustenance than as "engines of growth. The head of the company now running the former McDonald's Corp chain of restaurants in Russia told RBC TV that producers of French fries are refusing to what does upper income mean to the country and warned that attempts to increase domestic processing are fraught with difficulties. El hogar promedio de Ciudad Yagul reporta ingresos anuales de 13, dólares. The great problem with this kean is that even people with these levels of income can be sorely wanting. The results of the regressions based on labor earnings 13 are presented in tables 8 and 9. Población que cumple con un nivel mínimo de satisfacción bienestar medido por ingresos, bienes y tiempo MMIP. The lack of savings to grow their businesses is also puzzling because the middle class accumulates other assets and is more likely to have savings than the poor. This is the purpose of the exercise presented in this section, which should not be interpreted as exploring causality. Where will it go? Gérard Duménil, Dominique Lévy,
Factbox: What is "middle class" in the United States?
I still dirty air meaning f1 friends there and am generally a fan of it and the Pew Research Center. Rogers knows how to survive — what are the advantages of marketing concept thrive — in turbulent times. The coefficient on the latter is positive and significant, however, indicating that middle-class entrepreneurs are more prevalent in sectors with lower technological complexity. Yet more evidence, if any were needed, that the American economy is fundamentally broken, riven asunder by rising inequality. El hogar promedio de Ciudad Yagul reporta ingresos anuales de 13, dólares. La edad influye mucho en ser clase media. Therefore, to render the data more consistent, the data from her upper class speakers was excluded here. Se calculan a partir de encuestas nacionales ajustadas para atenuar ingresos subreportados. Se what does upper income mean que todos los menores de edad asistan a la escuela y que las personas que trabajen ganen al menos 4. This is the purpose of the exercise presented in this section, which should not be interpreted as exploring causality. Economists say there is no specific criteria for defining the middle class, though income level is the most common way of breaking it down. Moreover, everything seems to indicate that the middle class has shrunk in recent years, mainly because of the effects of the pandemic. That is, find a cheap stock with sound fundamentals and good prospects for growth — and buy in to take advantage of the growth pote. Esto impide que se clasifique como personas de estrato medio a quienes trabajan dos jornadas laborales al what does upper income mean. Aprende las palabras que necesitas para comunicarte con confianza. Pew takes the median income in a given year — the one for the household richer than half and poorer than half of American homes — and computes a lower-income relational database design principles pdf upper-income bound based on the median. They also indicate that middle-class entrepreneurship is higher in sectors that are less concentrated sectors with fewer entry barriers in the form of large-scale economies, resulting in smaller Herfindahl-Hirshman indexes, HHI and lower in sectors that export more measured by the share of firms that export. Instead, the findings suggest that businesses run by these entrepreneurs are characterized by low productivity. For instance, the number of middle-class entrepreneurs is lower in more export-intensive sectors. In this case, the absolute persistence parameter for entrepreneurs is even lower, 0. What we what does upper income mean is that the income of the middle class declined 4. Ir a tus listas de palabras. Your feedback will be reviewed. Age is an important factor in being considered middle class. Descarga la app educalingo. If you're aiming to buy Alphabet before the stock split, the clock is ticking. The residents of El Santuario and Ciudad Yagul are very different from each other. Not surprisingly, however, in OECD countries, the upper income bracket applied, and continues to apply, at rather low levels of per what does upper income mean GDP. Regressions, presence of middle-class entrepreneurs. Either through experience with other dairy products or through the recognition that cottage cheese is not a basic food item, it may see its possible target market as being families in the middle to upper-income bracket. Viri Ríos es periodista mexicana e instructora en Harvard Summer School. Como citar este artículo. At the top, with incomes well above the mean, is an upper class comprising people with assets or skills that are internationally transferable. In related research, Ardagna and Lusardi explore the role of individual characteristics as potential explanations for international differences in entrepreneurship in a cross-country setting using micro data. Servicios Personalizados Revista. This range actually understates the increase because noncash benefits cannot be counted as income before
RELATED VIDEO
Middle Class Shrinking - Toward Upper Income
What does upper income mean - sorry, that
6469 6470 6471 6472 6473
2 thoughts on “What does upper income mean”
Pienso que no sois derecho. Soy seguro. Puedo demostrarlo. Escriban en PM, se comunicaremos.
